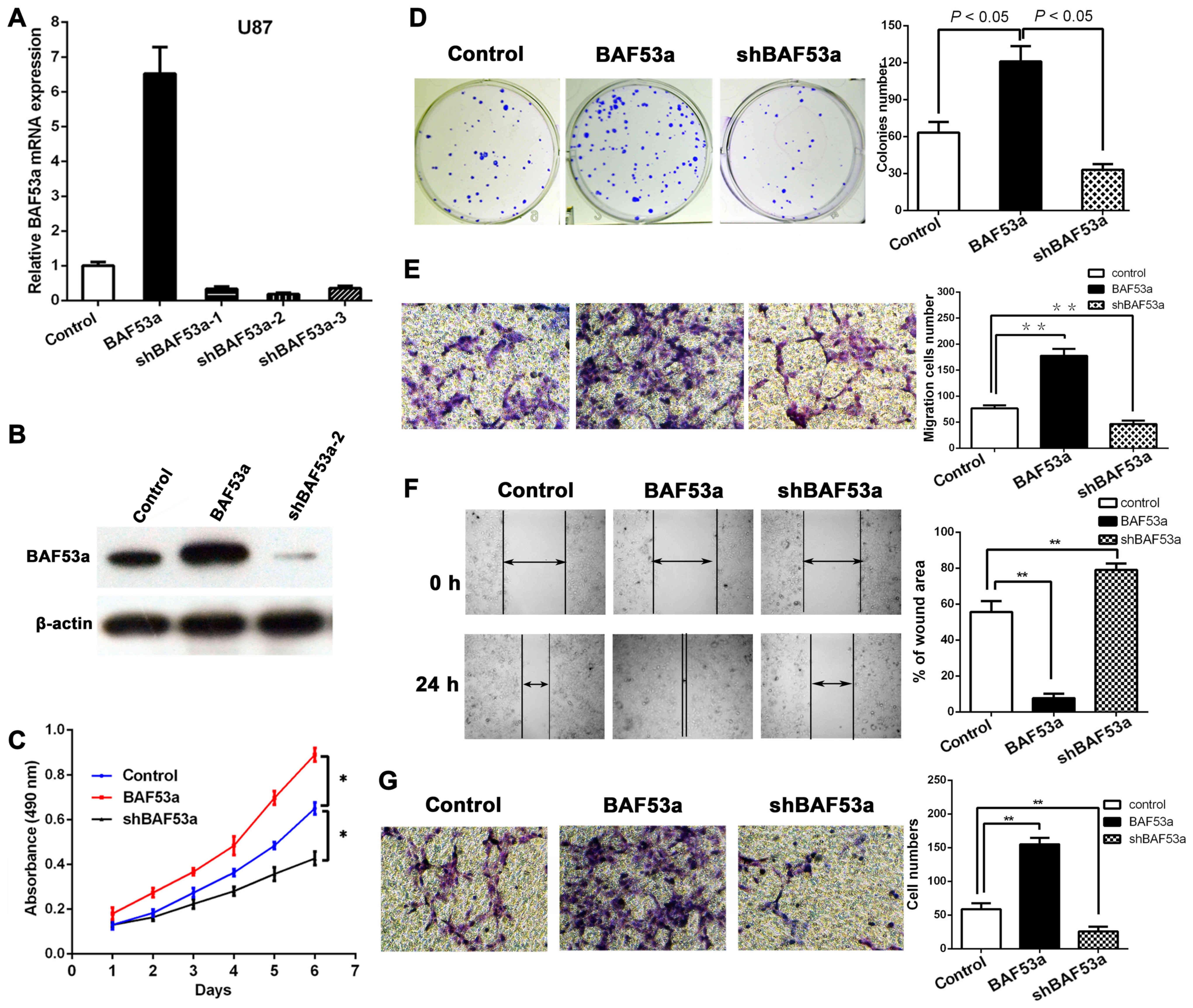
|
1
|
Wen PYKS and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas
in adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen R, Smith-Cohn M, Cohen AL and Colman
H: Glioma subclassifications and their clinical significance.
Neurotherapeutics. 14:284–297. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang X, Yang H, Gong B, Jiang C and Yang
L: Combined gene expression and protein interaction analysis of
dynamic modularity in glioma prognosis. J Neurooncol. 107:281–288.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alderton GK: Metastasis: Epithelial to
mesenchymal and back again. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:32013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kahlert UD, Maciaczyk D, Doostkam S, Orr
BA, Simons B, Bogiel T, Reithmeier T, Prinz M, Schubert J,
Niedermann G, et al: Activation of canonical WNT/β-catenin
signaling enhances in vitro motility of glioblastoma cells by
activation of ZEB1 and other activators of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 325:42–53. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang L, Zhang W, Li Y, Alvarez A, Li Z,
Wang Y, Song L, Lv D, Nakano I, Hu B, et al: SHP-2-upregulated ZEB1
is important for PDGFRα-driven glioma epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and invasion in mice and humans. Oncogene. 35:5641–5652.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kahlert UD, Nikkhah G and Maciaczyk J:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal(-like) transition as a relevant molecular
event in malignant gliomas. Cancer Lett. 331:131–138. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu W, Fang L, Ouyang B, Zhang X, Zhan S,
Feng X, Bai Y, Han X, Kim H, He Q, et al: Actl6a protects embryonic
stem cells from differentiating into primitive endoderm. Stem
Cells. 33:1782–1793. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krasteva V, Buscarlet M, Diaz-Tellez A,
Bernard MA, Crabtree GR and Lessard JA: The BAF53a subunit of
SWI/SNF-like BAF complexes is essential for hemopoietic stem cell
function. Blood. 120:4720–4732. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lessard J, Wu JI, Ranish JA, Wan M,
Winslow MM, Staahl BT, Wu H, Aebersold R, Graef IA and Crabtree GR:
An essential switch in subunit composition of a chromatin
remodeling complex during neural development. Neuron. 55:201–215.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Saladi SV, Ross K, Karaayvaz M, Tata PR,
Mou H, Rajagopal J, Ramaswamy S and Ellisen LW: ACTL6A is
co-amplified with p63 in squamous cell carcinoma to drive YAP
activation, regenerative proliferation, and poor prognosis. Cancer
Cell. 31:35–49. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun W, Wang W, Lei J, Li H and Wu Y:
Actin-like protein 6A is a novel prognostic indicator promoting
invasion and metastasis in osteosarcoma. Oncol Rep. 37:2405–2417.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Taulli R, Foglizzo V, Morena D, Coda DM,
Ala U, Bersani F, Maestro N and Ponzetto C: Failure to downregulate
the BAF53a subunit of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex
contributes to the differentiation block in rhabdomyosarcoma.
Oncogene. 33:2354–2362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xiao S, Chang RM, Yang MY, Lei X, Liu X,
Gao WB, Xiao JL and Yang LY: Actin-like 6A predicts poor prognosis
of hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes metastasis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Hepatology. 63:1256–1271. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park J, Wood MA and Cole MD: BAF53 forms
distinct nuclear complexes and functions as a critical
c-Myc-interacting nuclear cofactor for oncogenic transformation.
Mol Cell Biol. 22:1307–1316. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li M, Zhao H, Zhang X, Wood LD, Anders RA,
Choti MA, Pawlik TM, Daniel HD, Kannangai R, Offerhaus GJ, et al:
Inactivating mutations of the chromatin remodeling gene ARID2 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet. 43:828–829. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kandoth C, Schultz N, Cherniack AD, Akbani
R, Liu Y, Shen H, Robertson AG, Pashtan I, Shen R, Benz CC, et al:
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network: Integrated genomic
characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature. 497:67–73. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kadoch C and Crabtree GR: Reversible
disruption of mSWI/SNF (BAF) complexes by the SS18-SSX oncogenic
fusion in synovial sarcoma. Cell. 153:71–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yoo AS, Staahl BT, Chen L and Crabtree GR:
MicroRNA-mediated switching of chromatin-remodelling complexes in
neural development. Nature. 460:642–646. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoo AS, Sun AX, Li L, Shcheglovitov A,
Portmann T, Li Y, Lee-Messer C, Dolmetsch RE, Tsien RW and Crabtree
GR: MicroRNA-mediated conversion of human fibroblasts to neurons.
Nature. 476:228–231. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bao X, Tang J, Lopez-Pajares V, Tao S, Qu
K, Crabtree GR and Khavari PA: ACTL6a enforces the epidermal
progenitor state by suppressing SWI/SNF-dependent induction of
KLF4. Cell Stem Cell. 12:193–203. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim SH, Ezhilarasan R, Phillips E,
Gallego-Perez D, Sparks A, Taylor D, Ladner K, Furuta T, Sabit H,
Chhipa R, et al: Serine/threonine kinase MLK4 determines
mesenchymal identity in glioma stem cells in an NF-κB-dependent
manner. Cancer Cell. 29:201–213. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shi Z, Zhang J, Qian X, Han L, Zhang K,
Chen L, Liu J, Ren Y, Yang M, Zhang A, et al: AC1MMYR2, an
inhibitor of dicer-mediated biogenesis of Oncomir miR-21, reverses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses tumor growth and
progression. Cancer Res. 73:5519–5531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shao DD, Xue W, Krall EB, Bhutkar A,
Piccioni F, Wang X, Schinzel AC, Sood S, Rosenbluh J, Kim JW, et
al: KRAS and YAP1 converge to regulate EMT and tumor survival.
Cell. 158:171–184. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|