|
1
|
Weissmueller S, Manchado E, Saborowski M,
Morris JP IV, Wagenblast E, Davis CA, Moon SH, Pfister NT,
Tschaharganeh DF, Kitzing T, et al: Mutant p53 drives pancreatic
cancer metastasis through cell-autonomous PDGF receptor β
signaling. Cell. 157:382–394. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R and Abbruzzese JL:
Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 363:1049–1057. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yachida S, Jones S, Bozic I, Antal T,
Leary R, Fu B, Kamiyama M, Hruban RH, Eshleman JR, Nowak MA, et al:
Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of
pancreatic cancer. Nature. 467:1114–1117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Minami K, Shinsato Y, Yamamoto M,
Takahashi H, Zhang S, Nishizawa Y, Tabata S, Ikeda R, Kawahara K,
Tsujikawa K, et al: Ribonucleotide reductase is an effective target
to overcome gemcitabine resistance in gemcitabine-resistant
pancreatic cancer cells with dual resistant factors. J Pharmacol
Sci. 127:319–325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu CP, Xue XJ, Liang N, Xu DG, Liu FJ, Yu
XS and Zhang JD: Effect of chemoradiotherapy and neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy in resectable pancreatic cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 140:549–559.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wennerström AB, Lothe IM, Sandhu V, Kure
EH, Myklebost O and Munthe E: Generation and characterisation of
novel pancreatic adenocarcinoma xenograft models and corresponding
primary cell lines. PLoS One. 9:e1038732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kato M, Shimada Y, Tanaka H, Hosotani R,
Ohshio G, Ishizaki K and Imamura M: Characterization of six cell
lines established from human pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Cancer.
85:832–840. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smith HS: In vitro properties of
epithelial cell lines established from human carcinomas and
nonmalignant tissue. J Natl Cancer Inst. 62:225–230.
1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen WH, Horoszewicz JS, Leong SS, Shimano
T, Penetrante R, Sanders WH, Berjian R, Douglass HO, Martin EW and
Chu TM: Human pancreatic adenocarcinoma: In vitro and in vivo
morphology of a new tumor line established from ascites. In Vitro.
18:24–34. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Koay EJ, Truty MJ, Cristini V, Thomas RM,
Chen R, Chatterjee D, Kang Y, Bhosale PR, Tamm EP, Crane CH, et al:
Transport properties of pancreatic cancer describe gemcitabine
delivery and response. J Clin Invest. 124:1525–1536. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olive KP, Jacobetz MA, Davidson CJ,
Gopinathan A, McIntyre D, Honess D, Madhu B, Goldgraben MA,
Caldwell ME, Allard D, et al: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling
enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic
cancer. Science. 324:1457–1461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moir JA, Mann J and White SA: The role of
pancreatic stellate cells in pancreatic cancer. Surg Oncol.
24:232–238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zagorac S: Identification and functional
characterization of epigenetic determinants of pancreatic CSCs.
2015.PhD dissertation, la Universidad Autónoma de Madrid,
11–16–2015. http://hdl.handle.net/10486/669541
|
|
14
|
Ku JL, Yoon KA, Kim WH, Jang Y, Suh KS,
Kim SW, Park YH and Park JG: Establishment and characterization of
four human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Genetic alterations in
the TGFBR2 gene but not in the MADH4 gene. Cell Tissue Res.
308:205–214. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rückert F, Aust D, Böhme I, Werner K,
Brandt A, Diamandis EP, Krautz C, Hering S, Saeger HD, Grützmann R,
et al: Five primary human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell lines
established by the outgrowth method. J Surg Res. 172:29–39. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Briske-Anderson MJ, Finley JW and Newman
SM: The influence of culture time and passage number on the
morphological and physiological development of Caco-2 cells. Proc
Soc Exp Biol Med. 214:248–257. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang-Liu CM and Woloschak GE: Effect of
passage number on cellular response to DNA-damaging agents: Cell
survival and gene expression. Cancer Lett. 113:77–86. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Esquenet M, Swinnen JV, Heyns W and
Verhoeven G: LNCaP prostatic adenocarcinoma cells derived from low
and high passage numbers display divergent responses not only to
androgens but also to retinoids. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol.
62:391–399. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mohamed A, Blanchard MP, Albertelli M,
Barbieri F, Brue T, Niccoli P, Delpero JR, Monges G, Garcia S,
Ferone D, et al: Pasireotide and octreotide antiproliferative
effects and sst2 trafficking in human pancreatic neuroendocrine
tumor cultures. Endocr Relat Cancer. 21:691–704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murakami S, Ajiki T, Hori Y, Okazaki T,
Fukumoto T and Ku Y: Establishment of a novel cell line from
intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct. Anticancer Res.
34:2203–2209. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kong D, Nishino N, Shibusawa M and Kusano
M: Establishment and characterization of human pancreatic
adenocarcinoma cell line in tissue culture and the nude mouse.
Tissue Cell. 39:217–223. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lawson T, Ouellette M, Kolar C and
Hollingsworth M: Culture and immortalization of pancreatic ductal
epithelial cells. Methods Mol Med. 103:113–122. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
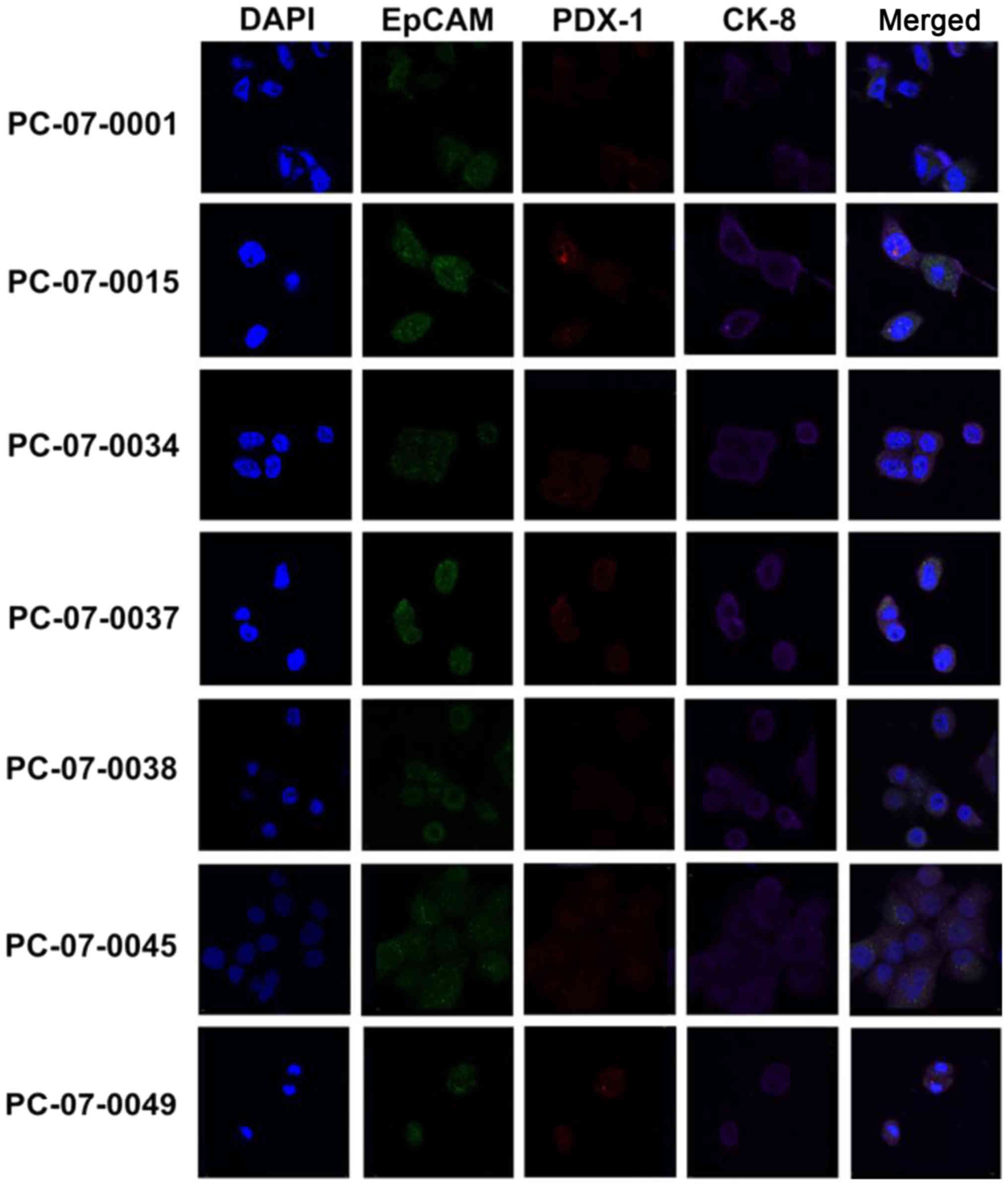
Park JY, Hong SM, Klimstra DS, Goggins MG,
Maitra A and Hruban RH: Pdx1 expression in pancreatic precursor
lesions and neoplasms. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol.
19:444–449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fendrich V and Lauth M: The role of
pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 as a therapeutic target in
pancreatic cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 18:1277–1283. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL, Geiger B
and Krepler R: The catalog of human cytokeratins: Patterns of
expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell.
31:11–24. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Merjava S, Brejchova K, Vernon A, Daniels
JT and Jirsova K: Cytokeratin 8 is expressed in human
corneoconjunctival epithelium, particularly in limbal epithelial
cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:787–794. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu F, Chen Z, Wang J, Shao X, Cui Z, Yang
C, Zhu Z and Xiong D: Overexpression of cell surface cytokeratin 8
in multidrug-resistant MCF-7/MX cells enhances cell adhesion to the
extracellular matrix. Neoplasia. 10:1275–1284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Munz M, Baeuerle PA and Gires O: The
emerging role of EpCAM in cancer and stem cell signaling. Cancer
Res. 69:5627–5629. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Went PT, Lugli A, Meier S, Bundi M,
Mirlacher M, Sauter G and Dirnhofer S: Frequent EpCam protein
expression in human carcinomas. Hum Pathol. 35:122–128. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jones S, Zhang X, Parsons DW, Lin JC,
Leary RJ, Angenendt P, Mankoo P, Carter H, Kamiyama H, Jimeno A, et
al: Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by
global genomic analyses. Science. 321:1801–1806. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Deer EL, González-Hernández J, Coursen JD,
Shea JE, Ngatia J, Scaife CL, Firpo MA and Mulvihill SJ: Phenotype
and genotype of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pancreas. 39:425–435.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Almoguera C, Shibata D, Forrester K,
Martin J, Arnheim N and Perucho M: Most human carcinomas of the
exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell. 53:549–554.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yin X, Su J, Zhou X, Guo J, Wei W and Wang
Z: K-ras-driven engineered mouse models for pancreatic cancer.
Discov Med. 19:15–21. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Moore PS, Sipos B, Orlandini S, Sorio C,
Real FX, Lemoine NR, Gress T, Bassi C, Klöppel G, Kalthoff H, et
al: Genetic profile of 22 pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Analysis
of K-ras, p53, p16 and DPC4/Smad4. Virchows Arch. 439:798–802.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dong M, Nio Y, Yamasawa K, Toga T, Yue L
and Harada T: p53 alteration is not an independent prognostic
indicator, but affects the efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in
human pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol. 82:111–120. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
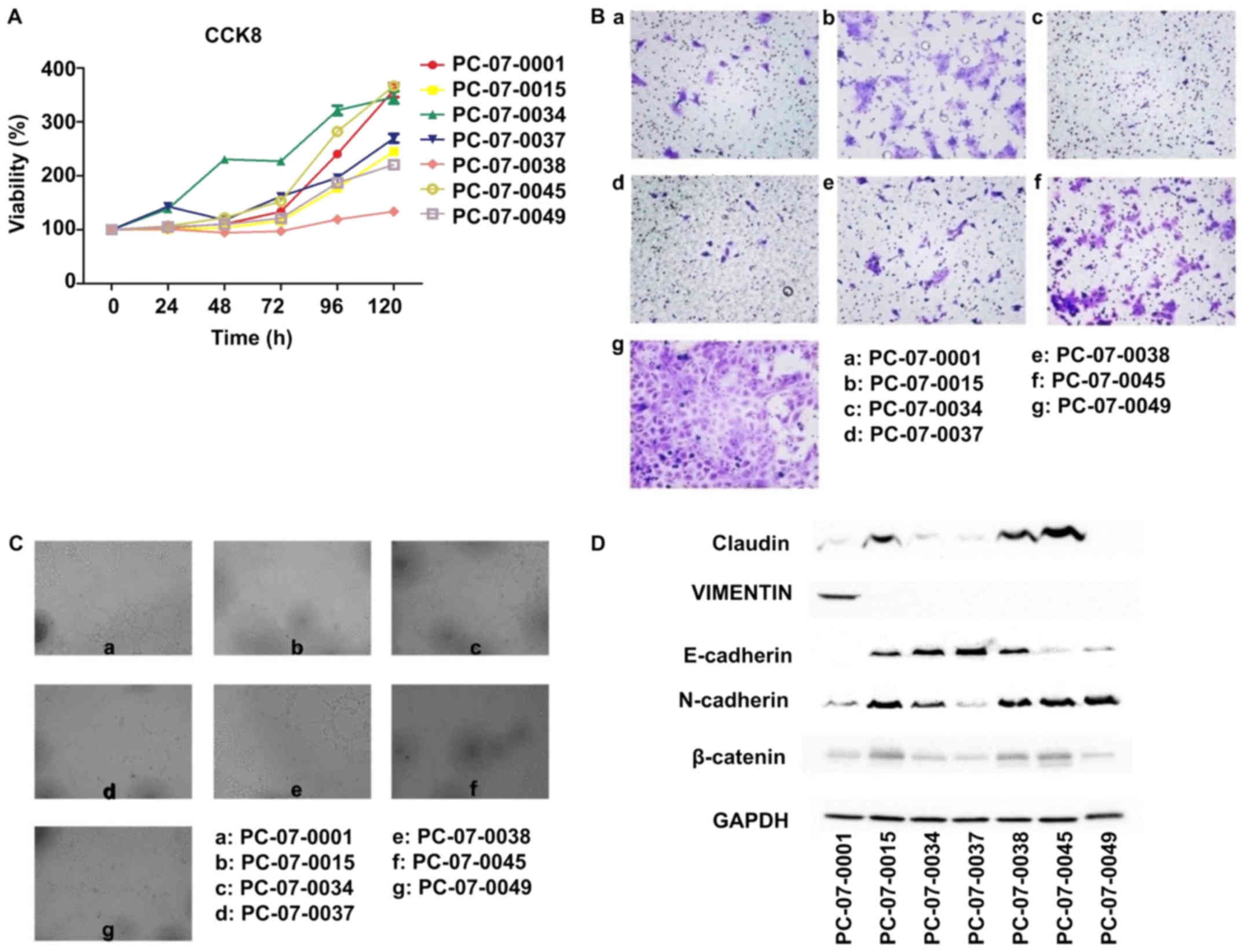
Dave JM and Bayless KJ: Vimentin as an
integral regulator of cell adhesion and endothelial sprouting.
Microcirculation. 21:333–344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Satelli A and Li S: Vimentin in cancer and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 68:3033–3046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hong SM, Li A, Olino K, Wolfgang CL,
Herman JM, Schulick RD, Iacobuzio-Donahue C, Hruban RH and Goggins
M: Loss of E-cadherin expression and outcome among patients with
resectable pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Mod Pathol. 24:1237–1247.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang J, Dokurno P, Tonks NK and Barford D:
Crystal structure of the M-fragment of α-catenin: Implications for
modulation of cell adhesion. EMBO J. 20:3645–3656. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Al-Rawi R: β-Catenin as a biomarker in
diagnosis of tumors with special emphasis on colorectal carcinoma.
Biom J. 3:12017.
|
|
41
|
Overgaard CE, Mitchell LA and Koval M:
Roles for claudins in alveolar epithelial barrier function. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1257:167–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chiurillo MA: Role of the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in gastric cancer: An in-depth literature review. World J
Exp Med. 5:84–102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Van Itallie CM and Anderson JM: Claudin
interactions in and out of the tight junction. Tissue Barriers.
1:e252472013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jamieson C, Sharma M and Henderson BR:
Targeting the β-catenin nuclear transport pathway in cancer. Semin
Cancer Biol. 27:20–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Folkman J: Fighting cancer by attacking
its blood supply. Sci Am. 275:150–154. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xu Z, Pothula SP, Wilson JS and Apte MV:
Pancreatic cancer and its stroma: A conspiracy theory. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:11216–11229. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Snyder JT, Rossman KL, Baumeister MA,
Pruitt WM, Siderovski DP, Der CJ, Lemmon MA and Sondek J:
Quantitative analysis of the effect of phosphoinositide
interactions on the function of Dbl family proteins. J Biol Chem.
276:45868–45875. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fitzpatrick ER, Hu T, Ciccarelli BT and
Whitehead IP: Regulation of vesicle transport and cell motility by
Golgi-localized Dbs. Small GTPases. 5:1–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Liu Z, Adams HC III and Whitehead IP: The
rho-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor Dbs regulates
breast cancer cell migration. J Biol Chem. 284:15771–15780. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Klinger MB, Guilbault B and Kay RJ: The
RhoA- and CDC42-specific exchange factor Dbs promotes expansion of
immature thymocytes and deletion of double-positive and
single-positive thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 34:806–816. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|