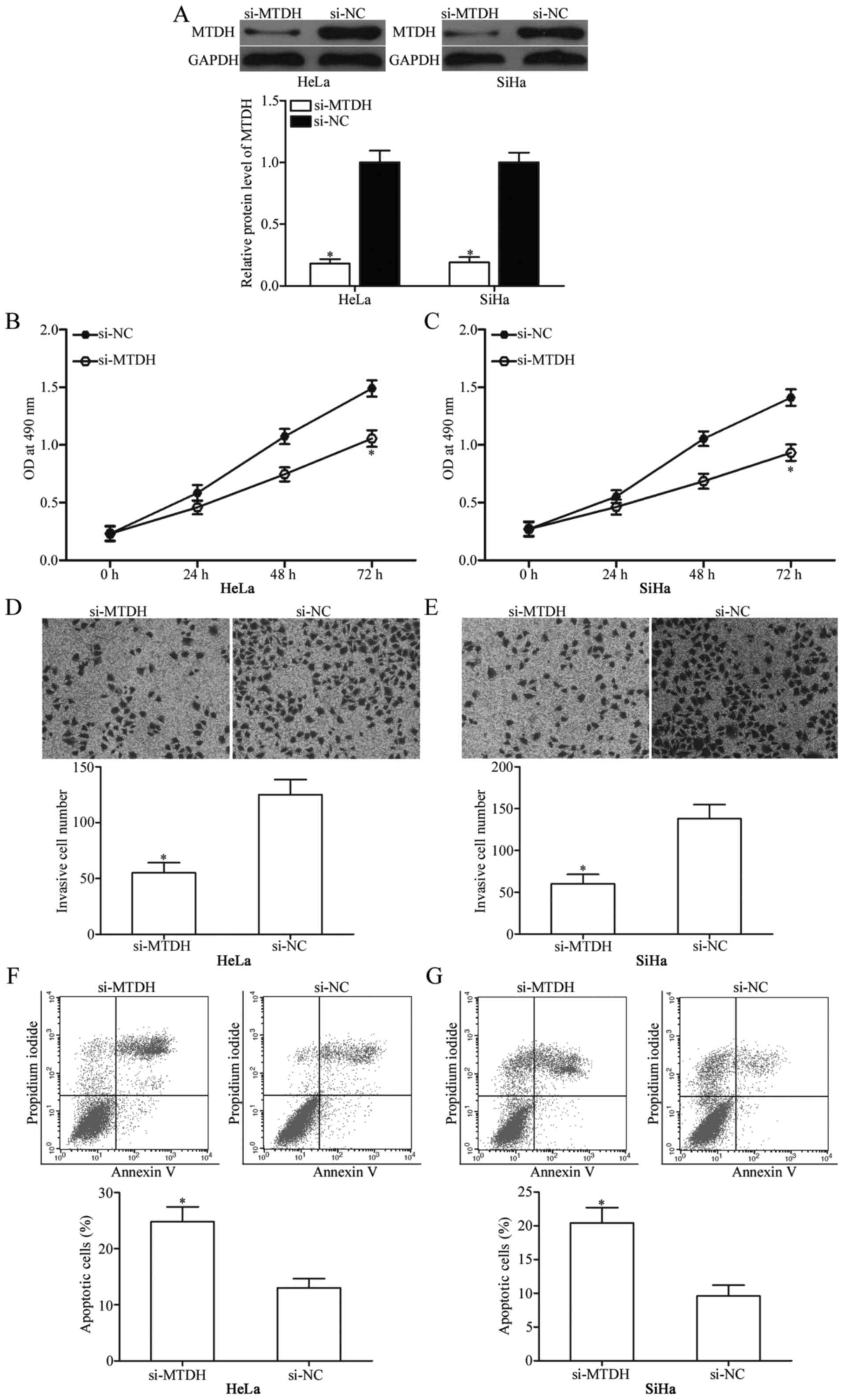
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sankaranarayanan R: Overview of cervical
cancer in the developing world. FIGO 26th Annual Report on the
Results of Treatment in Gynecological Cancer. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 95 Suppl 1:S205–S210. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cuzick J, Bergeron C, von Knebel Doeberitz
M, Gravitt P, Jeronimo J, Lorincz AT, Meijer J L M C,
Sankaranarayanan R, Snijders J F P and Szarewski A: New
technologies and procedures for cervical cancer screening. Vaccine.
30 Suppl 5:F107–F116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crafton SM and Salani R: Beyond
chemotherapy: An overview and review of targeted therapy in
cervical cancer. Clin Ther. 38:449–458. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kokka F, Bryant A, Brockbank E, Powell M
and Oram D: Hysterectomy with radiotherapy or chemotherapy or both
for women with locally advanced cervical cancer. Cochrane Database
Syst Rev. 4:CD0102602015.
|
|
6
|
de Freitas AC, Gomes Leitão MC and Coimbra
EC: Prospects of molecularly-targeted therapies for cervical cancer
treatment. Curr Drug Targets. 16:77–91. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dai S, Lu Y, Long Y, Lai Y, Du P, Ding N
and Yao D: Prognostic value of microRNAs in cervical carcinoma: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 7:35369–35378.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fan JY, Fan YJ, Wang XL, Gao HJ, Zhang Y,
Liu M and Tang H: miR-429 is involved in regulation of NF-κB
activity by targeting IKKβ and suppresses oncogenic activity in
cervical cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 591:118–128. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yan S, Li X, Jin Q and Yuan J:
MicroRNA-145 sensitizes cervical cancer cells to low-dose
irradiation by downregulating OCT4 expression. Exp Ther Med.
12:3130–3136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun P, Shen Y, Gong JM, Zhou LL, Sheng JH
and Duan FJ: A new microRNA expression signature for cervical
cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 27:339–343. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brodersen P and Voinnet O: Revisiting the
principles of microRNA target recognition and mode of action. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:141–148. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Harries LW: Long non-coding RNAs and human
disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 40:902–906. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hong Y, Liang H, Uzair-Ur-Rehman, Wang Y,
Zhang W, Zhou Y, Chen S, Yu M, Cui S, Liu M, et al: miR-96 promotes
cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting PTPN9 in
breast cancer. Sci Rep. 6:374212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Hu X, Xia D and Zhang S:
MicroRNA-181b is downregulated in non-small cell lung cancer and
inhibits cell motility by directly targeting HMGB1. Oncol Lett.
12:4181–4186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bucay N, Sekhon K, Yang T, Majid S,
Shahryari V, Hsieh C, Mitsui Y, Deng G, Tabatabai ZL, Yamamura S,
et al: MicroRNA-383 located in frequently deleted chromosomal locus
8p22 regulates CD44 in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 36:2667–2679.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lai XJ, Cheng XY and Hu LD: microRNA 421
induces apoptosis of c-33a cervical cancer cells via
down-regulation of Bcl-xL. Genet Mol Res. 15:152016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li X, Chen W, Zeng W, Wan C, Duan S and
Jiang S: microRNA-137 promotes apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells
via the regulation of XIAP. Br J Cancer. 116:66–76. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Liu H, Tian L, Wang F, Han L,
Zhang W and Bai YA: miR-15b inhibits the progression of
glioblastoma cells through targeting insulin-like growth factor
receptor 1. Horm Cancer. 8:49–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Jiang W, Hu Y, Da Z, Zeng C, Tu M,
Deng Z and Xiao W: MicroRNA-199a-5p inhibits cisplatin-induced drug
resistance via inhibition of autophagy in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol
Lett. 12:4203–4208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang P, Deng Y and Fu X: MiR-509-5p
suppresses the proliferation, migration, and invasion of non-small
cell lung cancer by targeting YWHAG. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
2016.
|
|
22
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 96
Suppl:R40–R44. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun S, Wang X, Xu X, Di H, Du J, Xu B,
Wang Q and Wang J: MiR-433-3p suppresses cell growth and enhances
chemosensitivity by targeting CREB in human glioma. Oncotarget.
8:5057–5068. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li X, Yang L, Shuai T, Piao T and Wang R:
MiR-433 inhibits retinoblastoma malignancy by suppressing Notch1
and PAX6 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 82:247–255. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liang T, Guo Q, Li L, Cheng Y, Ren C and
Zhang G: MicroRNA-433 inhibits migration and invasion of ovarian
cancer cells via targeting Notch1. Neoplasma. 63:696–704. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Long M, Dong K, Gao P, Wang X, Liu L, Yang
S, Lin F, Wei J and Zhang H: Overexpression of astrocyte-elevated
gene-1 is associated with cervical carcinoma progression and
angiogenesis. Oncol Rep. 30:1414–1422. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang K, Li LA, Meng Y, You Y, Fu X and
Song L: High expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) is
associated with progression of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
and unfavorable prognosis in cervical cancer. World J Surg Oncol.
11:2972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li WF, Dai H, Ou Q, Zuo GQ and Liu CA:
Overexpression of microRNA-30a-5p inhibits liver cancer cell
proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting MTDH/PTEN/AKT
pathway. Tumour Biol. 37:5885–5895. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen X, Si Y, Yang Z, Wang Q, Yuan J and
Zhang X: MicroRNA-542-3p suppresses cell growth of gastric cancer
cells via targeting oncogene astrocyte-elevated gene-1. Med Oncol.
32:3612015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu X, Schwarz JK, Lewis JS Jr, Huettner
PC, Rader JS, Deasy JO, Grigsby PW and Wang X: A microRNA
expression signature for cervical cancer prognosis. Cancer Res.
70:1441–1448. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee JW, Choi CH, Choi JJ, Park YA, Kim SJ,
Hwang SY, Kim WY, Kim TJ, Lee JH, Kim BG, et al: Altered microRNA
expression in cervical carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2535–2542.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo LH, Li H, Wang F, Yu J and He JS: The
tumor suppressor roles of miR-433 and miR-127 in gastric cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:14171–14184. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li J, Mao X, Wang X, Miao G and Li J:
miR-433 reduces cell viability and promotes cell apoptosis by
regulating MACC1 in colorectal cancer. Oncol Lett. 13:81–88. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xue J, Chen LZ, Li ZZ, Hu YY, Yan SP and
Liu LY: MicroRNA-433 inhibits cell proliferation in hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting p21 activated kinase (PAK4). Mol Cell
Biochem. 399:77–86. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang XC, Ma Y, Meng PS, Han JL, Yu HY and
Bi LJ: miR-433 inhibits oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell
growth and metastasis by targeting HDAC6. Oral Oncol. 51:674–682.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang Z, Tsuchiya H, Zhang Y, Hartnett ME
and Wang L: MicroRNA-433 inhibits liver cancer cell migration by
repressing the protein expression and function of cAMP response
element-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 288:28893–28899. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen X, Bo L, Lu W, Zhou G and Chen Q:
MicroRNA-148b targets Rho-associated protein kinase 1 to inhibit
cell proliferation, migration and invasion in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Med Rep. 13:477–482. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Su ZZ, Kang DC, Chen Y, Pekarskaya O, Chao
W, Volsky DJ and Fisher PB: Identification and cloning of human
astrocyte genes displaying elevated expression after infection with
HIV-1 or exposure to HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein by rapid
subtraction hybridization, RaSH. Oncogene. 21:3592–3602. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee SG, Kang DC, DeSalle R, Sarkar D and
Fisher PB: AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC, the beginning: Initial cloning,
structure, expression profile, and regulation of expression. Adv
Cancer Res. 120:1–38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ke ZF, Mao X, Zeng C, He S, Li S and Wang
LT: AEG-1 expression characteristics in human non-small cell lung
cancer and its relationship with apoptosis. Med Oncol. 30:3832013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dong L, Qin S, Li Y, Zhao L, Dong S, Wang
Y, Zhang C and Han S: High expression of astrocyte elevated gene-1
is associated with clinical staging, metastasis, and unfavorable
prognosis in gastric carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:2169–2178. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tokunaga E, Nakashima Y, Yamashita N,
Hisamatsu Y, Okada S, Akiyoshi S, Aishima S, Kitao H, Morita M and
Maehara Y: Overexpression of metadherin/MTDH is associated with an
aggressive phenotype and a poor prognosis in invasive breast
cancer. Breast Cancer. 21:341–349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhou B, Yang J, Shu B, Liu K, Xue L, Su N,
Liu J and Xi T: Overexpression of astrocyte-elevated gene-1 is
associated with ovarian cancer development and progression. Mol Med
Rep. 11:2981–2990. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhou J, Li J, Wang Z, Yin C and Zhang W:
Metadherin is a novel prognostic marker for bladder cancer
progression and overall patient survival. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol.
8:e42–e48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ge X, Lv X, Feng L, Liu X, Gao J, Chen N
and Wang X: Metadherin contributes to the pathogenesis of diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma. PLoS One. 7:e394492012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Liu S, Zhang Q, Wang Y,
Tong L, Chen X, Ji Y, Shang Q, Xu B, et al: Metadherin confers
chemoresistance of cervical cancer cells by inducing autophagy and
activating ERK/NF-κB pathway. Tumour Biol. 34:2433–2440. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hu G, Wei Y and Kang Y: The multifaceted
role of MTDH/AEG-1 in cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5615–5620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|