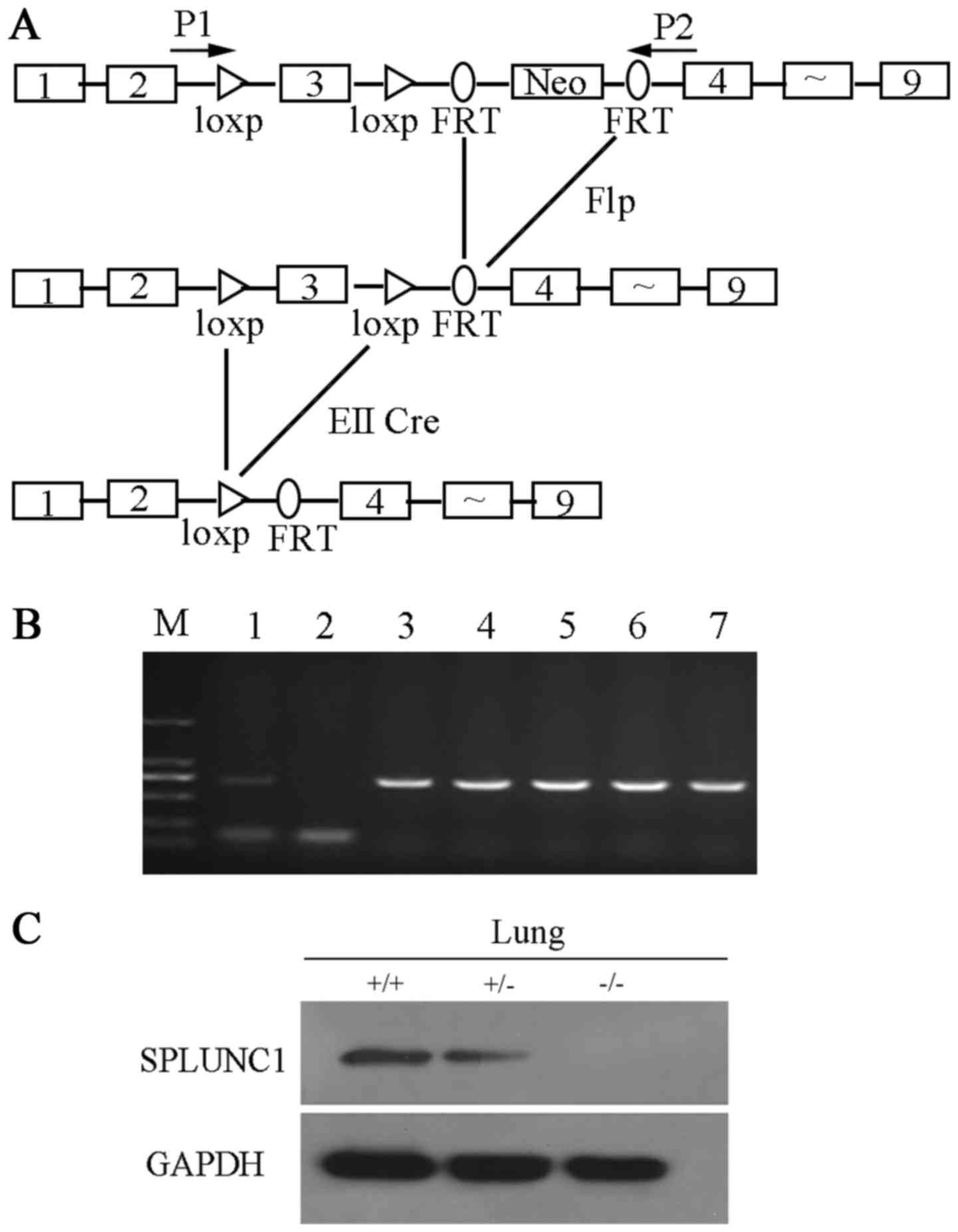
|
1
|
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E,
Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, Stern EJ and Hudson LD: Incidence and
outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 353:1685–1693. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abraham E: Neutrophils and acute lung
injury. Crit Care Med. 31 Suppl 4:S195–S199. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bingle CD and Bingle L: Characterisation
of the human plunc gene, a gene product with an upper airways and
nasopharyngeal restricted expression pattern. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1493:363–367. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bingle CD and Craven CJ: Comparative
analysis of the PLUNC (palate, lung and nasal epithelium clone)
protein families. Biochem Soc Trans. 31:806–809. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang B, Nie X, Xiao B, Xiang J, Shen S,
Gong J, Zhou M, Zhu S, Zhou J, Qian J, et al: Identification of
tissue-specific genes in nasopharyngeal epithelial tissue and
differentially expressed genes in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
suppression subtractive hybridization and cDNA microarray. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 38:80–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim CH, Kim K, Jik Kim H, Kim J Kook, Lee
JG and Yoon JH: Expression and regulation of PLUNC in human nasal
epithelium. Acta Otolaryngol. 126:1073–1078. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Campos MA, Abreu AR, Nlend MC, Cobas MA,
Conner GE and Whitney PL: Purification and characterization of
PLUNC from human tracheobronchial secretions. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 30:184–192. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sung YK, Moon C, Yoo JY, Moon C, Pearse D,
Pevsner J and Ronnett GV: Plunc, a member of the secretory gland
protein family, is up-regulated in nasal respiratory epithelium
after olfactory bulbectomy. J Biol Chem. 277:12762–12769. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang W, Zeng Z, Wei F, Chen P, Schmitt
DC, Fan S, Guo X, Liang F, Shi L, Liu Z, et al: SPLUNC1 is
associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma prognosis and plays an
important role in all-trans-retinoic acid-induced growth inhibition
and differentiation in nasopharyngeal cancer cells. FEBS J.
281:4815–4829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou HD, Li XL, Li GY, Zhou M, Liu HY,
Yang YX, Deng T, Ma J and Sheng SR: Effect of SPLUNC1 protein on
the Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Epstein-Barr virus. Mol Cell
Biochem. 309:191–197. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ou C, Sun Z, Zhang H, Xiong W, Ma J, Zhou
M, Lu J, Zeng Z, Bo X, Chen P, et al: SPLUNC1 reduces the
inflammatory response of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells infected
with the EB virus by inhibiting the TLR9/NF-κB pathway. Oncol Rep.
33:2779–2788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen P, Guo X, Zhou H, Zhang W, Zeng Z,
Liao Q, Li X, Xiang B, Yang J, Ma J, et al: SPLUNC1 regulates cell
progression and apoptosis through the miR-141-PTEN/p27 pathway, but
is hindered by LMP1. PLoS One. 8:e569292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gally F, Di YP, Smith SK, Minor MN, Liu Y,
Bratton DL, Frasch SC, Michels NM, Case SR and Chu HW: SPLUNC1
promotes lung innate defense against Mycoplasma pneumoniae
infection in mice. Am J Pathol. 178:2159–2167. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lukinskiene L, Liu Y, Reynolds SD, Steele
C, Stripp BR, Leikauf GD, Kolls JK and Di YP: Antimicrobial
activity of PLUNC protects against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
infection. J Immunol. 187:382–390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Bartlett JA, Di ME, Bomberger JM,
Chan YR, Gakhar L, Mallampalli RK, McCray PB Jr and Di YP:
SPLUNC1/BPIFA1 contributes to pulmonary host defense against
Klebsiella pneumoniae respiratory infection. Am J Pathol.
182:1519–1531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartlett JA, Meyerholz DK, Wohlford-Lenane
CL, Naumann PW, Salzman NH and McCray PB Jr: Increased
susceptibility to otitis media in a Splunc1-deficient mouse model.
Dis Model Mech. 8:501–508. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mitas M, Hoover L, Silvestri G, Reed C,
Green M, Turrisi AT, Sherman C, Mikhitarian K, Cole DJ, Block MI,
et al: Lunx is a superior molecular marker for detection of
non-small cell lung cancer in peripheral blood [corrected]. J Mol
Diagn. 5:237–242. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gabrilovich DI and Nagaraj S:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune
system. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:162–174. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rabinovich GA, Gabrilovich D and Sotomayor
EM: Immunosuppressive strategies that are mediated by tumor cells.
Annu Rev Immunol. 25:267–296. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kusmartsev S, Nefedova Y, Yoder D and
Gabrilovich DI: Antigen-specific inhibition of CD8+ T cell response
by immature myeloid cells in cancer is mediated by reactive oxygen
species. J Immunol. 172:989–999. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fu C, Jiang L, Xu X, Zhu F, Zhang S, Wu X,
Liu Z, Yang X and Li S: STAT4 knockout protects LPS-induced lung
injury by increasing of MDSC and promoting of macrophage
differentiation. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 223:16–22. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou Y, Wang W, Zheng D, Peng S, Xiong W,
Ma J, Zeng Z, Wu M, Zhou M, Xiang J, et al: Risk of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma associated with polymorphic lactotransferrin haplotypes.
Med Oncol. 29:1456–1462. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xiao S, Zhou Y, Yi W, Luo G, Jiang B, Tian
Q, Li Y and Xue M: Fra-1 is downregulated in cervical cancer
tissues and promotes cervical cancer cell apoptosis by p53
signaling pathway in vitro. Int J Oncol. 46:1677–1684. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng D, Liao S, Zhu G, Luo G, Xiao S, He
J, Pei Z, Li G and Zhou Y: CD38 is a putative functional marker for
side population cells in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines.
Mol Carcinog. 55:300–311. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hara A and Okayasu I: Cyclooxygenase-2 and
inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in human astrocytic
gliomas: Correlation with angiogenesis and prognostic significance.
Acta Neuropathol. 108:43–48. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thaikoottathil JV, Martin RJ, Di PY, Minor
M, Case S, Zhang B, Zhang G, Huang H and Chu HW: SPLUNC1 deficiency
enhances airway eosinophilic inflammation in mice. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 47:253–260. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gakhar L, Bartlett JA, Penterman J,
Mizrachi D, Singh PK, Mallampalli RK, Ramaswamy S and McCray PB Jr:
PLUNC is a novel airway surfactant protein with anti-biofilm
activity. PLoS One. 5:e90982010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sayeed S, Nistico L, St Croix C and Di YP:
Multifunctional role of human SPLUNC1 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
infection. Infect Immun. 81:285–291. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen H, Bai C and Wang X: The value of the
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in respiratory
medicine. Expert Rev Respir Med. 4:773–783. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matuschak GM and Lechner AJ: Acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: Pathophysiology
and treatment. Mo Med. 107:252–258. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gaudry S, Ricard JD and Dreyfuss D: Acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Rev Prat. 62:1197–1203. 2012.(In
French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mei SH, McCarter SD, Deng Y, Parker CH,
Liles WC and Stewart DJ: Prevention of LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice by mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing
angiopoietin 1. PLoS Med. 4:e2692007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang X, Sun CY, Zhang YB, Guo HZ, Feng
XX, Peng SZ, Yuan J, Zheng RB, Chen WP, Su ZR, et al: Kegan Liyan
oral liquid ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury through inhibition of TLR4-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway
and MMP-9 expression. J Ethnopharmacol. 186:91–102. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bhatia M, Zemans RL and Jeyaseelan S: Role
of chemokines in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 46:566–572. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim JW, Gerwick L and Park CI: Molecular
identification and expression analysis of two distinct BPI/LBPs
(bactericidal permeability-increasing protein/LPS-binding protein)
from rock bream, Oplegnathus fasciatus. Fish Shellfish Immunol.
33:75–84. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Krasity BC, Troll JV, Weiss JP and
McFall-Ngai MJ: LBP/BPI proteins and their relatives: Conservation
over evolution and roles in mutualism. Biochem Soc Trans.
39:1039–1044. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vaknin I, Blinder L, Wang L, Gazit R,
Shapira E, Genina O, Pines M, Pikarsky E and Baniyash M: A common
pathway mediated through Toll-like receptors leads to T- and
natural killer-cell immunosuppression. Blood. 111:1437–1447. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Delano MJ, Scumpia PO, Weinstein JS, Coco
D, Nagaraj S, Kelly-Scumpia KM, O'Malley KA, Wynn JL, Antonenko S,
Al-Quran SZ, et al: MyD88-dependent expansion of an immature
GR-1+CD11b+ population induces T cell suppression and Th2
polarization in sepsis. J Exp Med. 204:1463–1474. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
De Wilde V, van Rompaey N, Hill M, Lebrun
JF, Lemaître P, Lhommé F, Kubjak C, Vokaer B, Oldenhove G,
Charbonnier LM, et al: Endotoxin-induced myeloid-derived suppressor
cells inhibit alloimmune responses via heme oxygenase-1. Am J
Transplant. 9:2034–2047. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
McCubbrey AL, Barthel L, Mould KJ, Mohning
MP, Redente EF and Janssen WJ: Selective and inducible targeting of
CD11b+ mononuclear phagocytes in the murine lung with hCD68-rtTA
transgenic systems. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
311:L87–L100. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bunt SK, Yang L, Sinha P, Clements VK,
Leips J and Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Reduced inflammation in the tumor
microenvironment delays the accumulation of myeloid-derived
suppressor cells and limits tumor progression. Cancer Res.
67:10019–10026. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gabrilovich D, Ishida T, Oyama T, Ran S,
Kravtsov V, Nadaf S and Carbone DP: Vascular endothelial growth
factor inhibits the development of dendritic cells and dramatically
affects the differentiation of multiple hematopoietic lineages in
vivo. Blood. 92:4150–4166. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Serafini P, Carbley R, Noonan KA, Tan G,
Bronte V and Borrello I: High-dose granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor-producing vaccines impair the immune
response through the recruitment of myeloid suppressor cells.
Cancer Res. 64:6337–6343. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bronte V, Chappell DB, Apolloni E,
Cabrelle A, Wang M, Hwu P and Restifo NP: Unopposed production of
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor by tumors inhibits
CD8+ T cell responses by dysregulating antigen-presenting cell
maturation. J Immunol. 162:5728–5737. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Islam MN, Das SR, Emin MT, Wei M, Sun L,
Westphalen K, Rowlands DJ, Quadri SK, Bhattacharya S and
Bhattacharya J: Mitochondrial transfer from bone-marrow-derived
stromal cells to pulmonary alveoli protects against acute lung
injury. Nat Med. 18:759–765. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kotton DN, Ma BY, Cardoso WV, Sanderson
EA, Summer RS, Williams MC and Fine A: Bone marrow-derived cells as
progenitors of lung alveolar epithelium. Development.
128:5181–5188. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|