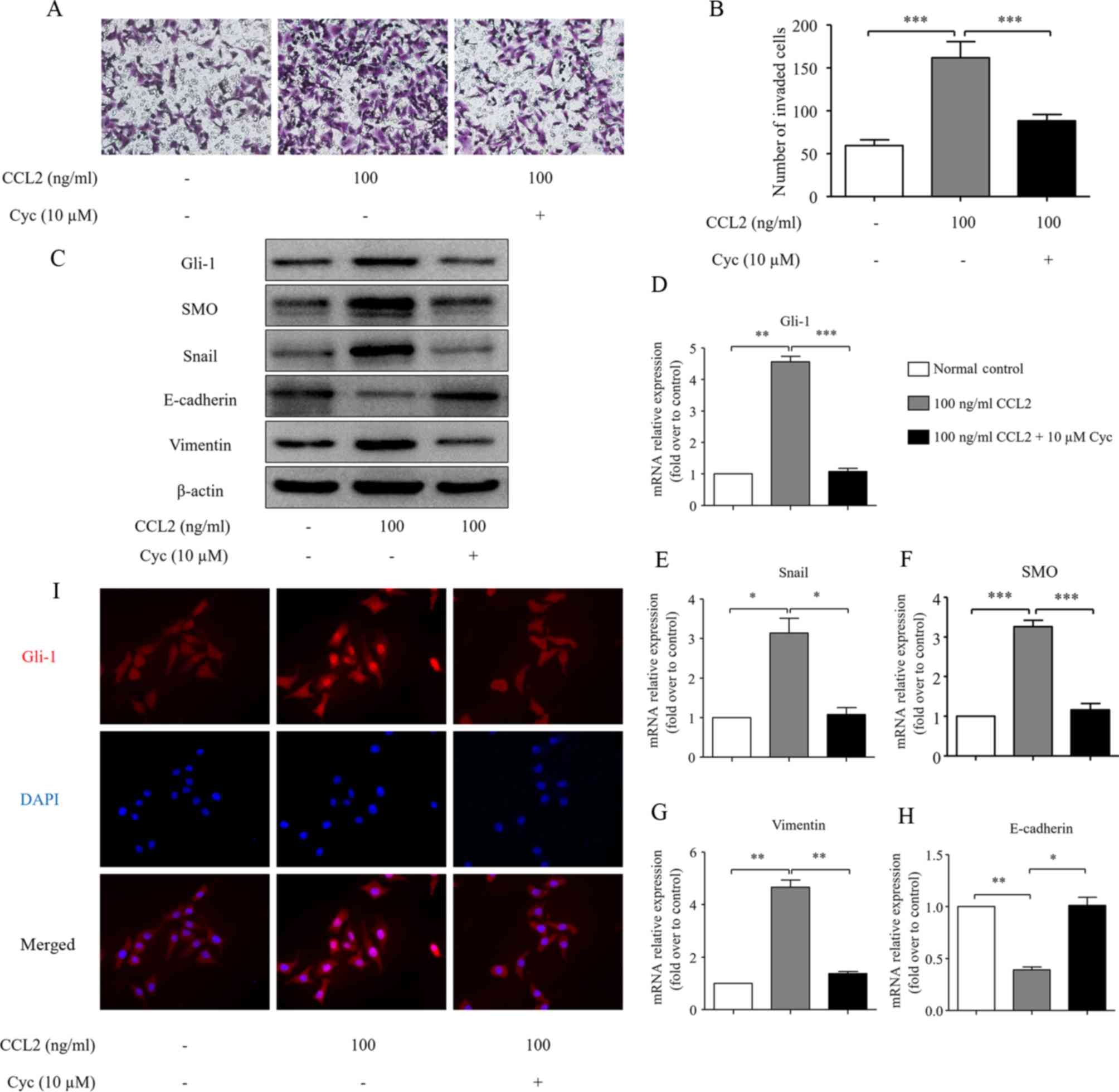
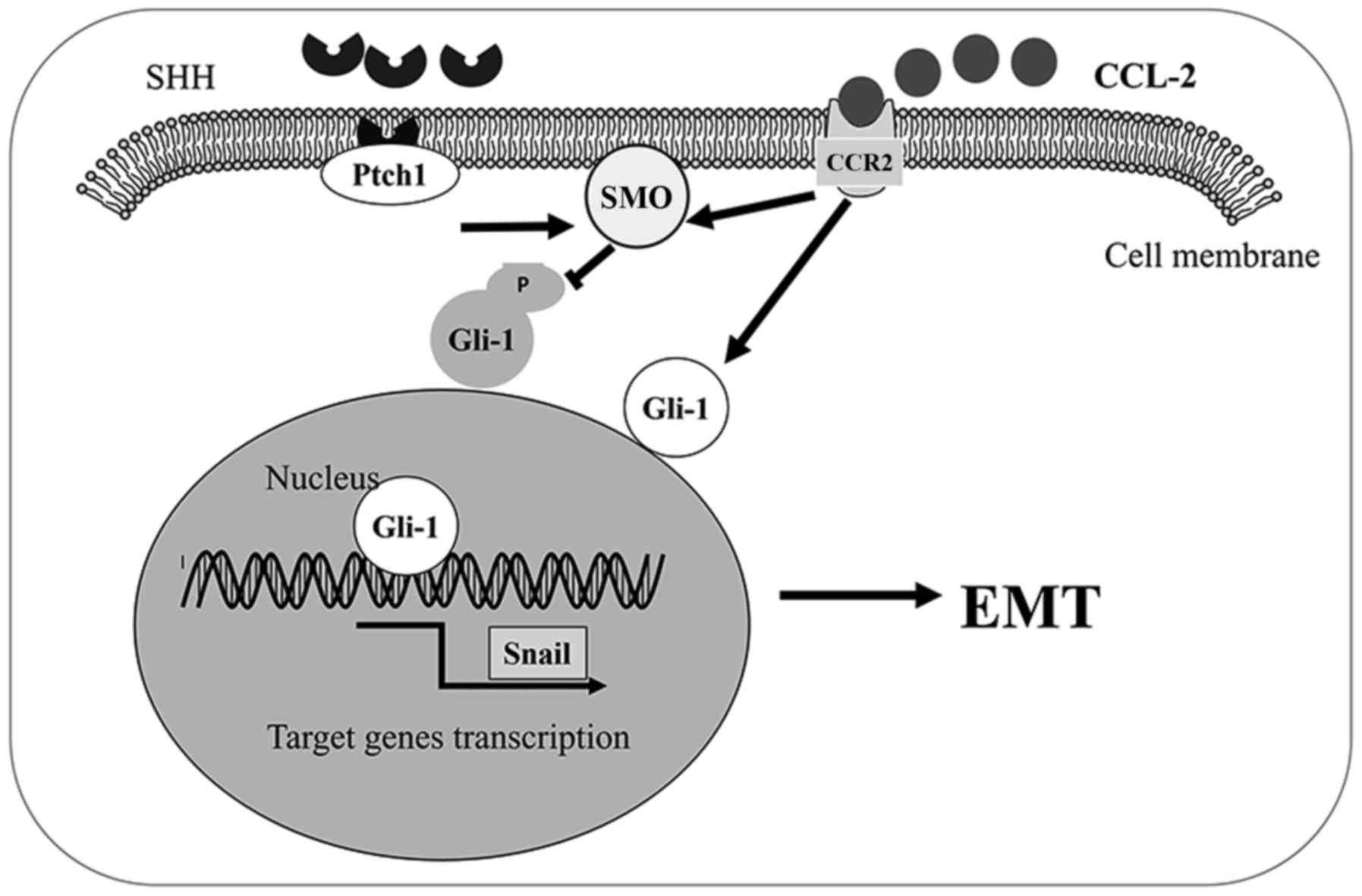
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu Q, Wang Z, Chen X, Duan W, Lei J, Zong
L, Li X, Sheng L, Ma J, Han L, et al: Stromal-derived
factor-1α/CXCL12-CXCR4 chemotactic pathway promotes perineural
invasion in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 6:4717–4732. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Z, Xie H, Zhou L, Liu Z, Fu H, Zhu Y,
Xu L and Xu J: CCL2/CCR2 axis is associated with postoperative
survival and recurrence of patients with non-metastatic clear-cell
renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:51525–51534. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang Y, Zhai C, Chang Y, Zhou L, Shi T,
Tan C, Xu L and Xu J: High expression of chemokine CCL2 is
associated with recurrence after surgery in clear-cell renal cell
carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 34:238.e19–238.e26. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang J, Patel L and Pienta KJ: CC
chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) promotes prostate cancer tumorigenesis
and metastasis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:41–48. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lim SY, Yuzhalin AE, Gordon-Weeks AN and
Muschel RJ: Targeting the CCL2-CCR2 signaling axis in cancer
metastasis. Oncotarget. 7:28697–28710. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rao Q, Chen Y, Yeh CR, Ding J, Li L, Chang
C and Yeh S: Recruited mast cells in the tumor microenvironment
enhance bladder cancer metastasis via modulation of ERβ/CCL2/CCR2
EMT/MMP9 signals. Oncotarget. 7:7842–7855. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li X, Yao W, Yuan Y, Chen P, Li B, Li J,
Chu R, Song H, Xie D, Jiang X and Wang H: Targeting of
tumour-infiltrating macrophages via CCL2/CCR2 signalling as a
therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut.
66:157–167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shih YT, Wang MC, Zhou J, Peng HH, Lee DY
and Chiu JJ: Endothelial progenitors promote hepatocarcinoma
intrahepatic metastasis through monocyte chemotactic protein-1
induction of microRNA-21. Gut. 64:1132–1147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li X, Wang Z, Ma Q, Xu Q, Liu H, Duan W,
Lei J, Ma J, Wang X, Lv S, et al: Sonic hedgehog paracrine
signaling activates stromal cells to promote perineural invasion in
pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 20:4326–4338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Ma Q, Xu Q, Liu H, Lei J, Duan W,
Bhat K, Wang F, Wu E and Wang Z: SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling induces
pancreatic cancer cell invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in vitro through non-canonical activation of Hedgehog
pathway. Cancer Lett. 322:169–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Diao Y, Azatyan A, Rahman MF, Zhao C, Zhu
J, Dahlman-Wright K and Zaphiropoulos PG: Blockade of the Hedgehog
pathway downregulates estrogen receptor alpha signaling in breast
cancer cells. Oncotarget. 7:71580–71593. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Han C, Lu L, Magliato S and Wu T:
Hedgehog signaling pathway regulates autophagy in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology. 58:995–1010. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Villavicencio EH, Walterhouse DO and
Iannaccone PM: The sonic hedgehog-patched-gli pathway in human
development and disease. Am J Hum Genet. 67:1047–1054. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lei J, Ma J, Ma Q, Li X, Liu H, Xu Q, Duan
W, Sun Q, Xu J, Wu Z and Wu E: Hedgehog signaling regulates hypoxia
induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition and invasion in
pancreatic cancer cells via a ligand-independent manner. Mol
Cancer. 12:662013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng X, Zeng W, Gai X, Xu Q, Li C, Liang
Z, Tuo H and Liu Q: Role of the Hedgehog pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma (Review). Oncol Rep. 30:2020–2026. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Q, Liu Z, Xu M, Xue Y, Yao B, Dou C,
Jia Y, Wang Y, Tu K, Zheng X and Yao Y: PCAF inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by inhibition of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting Gli-1. Cancer Lett.
375:190–198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
An J, Xue Y, Long M, Zhang G, Zhang J and
Su H: Targeting CCR2 with its antagonist suppresses viability,
motility and invasion by downregulating MMP-9 expression in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:39230–39240.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Che L, Yuan YH, Jia J and Ren J:
Activation of sonic hedgehog signaling pathway is an independent
potential prognosis predictor in human hepatocellular carcinoma
patients. Chin J Cancer Res. 24:323–331. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kasper M, Regl G, Frischauf AM and Aberger
F: GLI transcription factors: Mediators of oncogenic Hedgehog
signalling. Eur J Cancer. 42:437–445. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li Y, Yang W, Yang Q and Zhou S: Nuclear
localization of GLI1 and elevated expression of FOXC2 in breast
cancer is associated with the basal-like phenotype. Histol
Histopathol. 27:475–484. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK and Beachy
PA: Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of
cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev. 16:2743–2748. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sahin H, Trautwein C and Wasmuth HE:
Functional role of chemokines in liver disease models. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:682–690. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mandrekar P, Ambade A, Lim A, Szabo G and
Catalano D: An essential role for monocyte chemoattractant
protein-1 in alcoholic liver injury: Regulation of proinflammatory
cytokines and hepatic steatosis in mice. Hepatology. 54:2185–2197.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Baeck C, Wehr A, Karlmark KR, Heymann F,
Vucur M, Gassler N, Huss S, Klussmann S, Eulberg D, Luedde T, et
al: Pharmacological inhibition of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1)
diminishes liver macrophage infiltration and steatohepatitis in
chronic hepatic injury. Gut. 61:416–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qian BZ, Li J, Zhang H, Kitamura T, Zhang
J, Campion LR, Kaiser EA, Snyder LA and Pollard JW: CCL2 recruits
inflammatory monocytes to facilitate breast-tumour metastasis.
Nature. 475:222–225. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huber MA, Kraut N and Beug H: Molecular
requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor
progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:548–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wan Z, Pan H, Liu S, Zhu J, Qi W, Fu K,
Zhao T and Liang J: Downregulation of SNAIL sensitizes
hepatocellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis by
regulating the NF-κB pathway. Oncol Rep. 33:1560–1566. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang M, Dong X, Zhang D, Chen X and Zhu
X: High expression of Snail and NF-κB predicts poor survival in
Chinese hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Oncotarget. 8:4543–4548.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee CC, Ho HC, Su YC, Lee MS, Hung SK and
Lin CH: MCP1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in head and
neck cancer by AKT activation. Anticancer Res. 35:3299–3306.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang Z, Koehler AN and Wang L: A novel
small molecule activator of nuclear receptor SHP inhibits HCC cell
migration via suppressing Ccl2. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:2294–2301.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang J, Peng Y, Liu Y, Yang J, Huang M and
Tan W: AT-101 inhibits hedgehog pathway activity and cancer growth.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 76:461–469. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mimeault M, Rachagani S, Muniyan S,
Seshacharyulu P, Johansson SL, Datta K, Lin MF and Batra SK:
Inhibition of hedgehog signaling improves the anti-carcinogenic
effects of docetaxel in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 6:3887–3903.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zuo M, Rashid A, Churi C, Vauthey JN,
Chang P, Li Y, Hung MC, Li D and Javle M: Novel therapeutic
strategy targeting the Hedgehog signalling and mTOR pathways in
biliary tract cancer. Br J Cancer. 112:1042–1051. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang S, He J, Zhang X, Bian Y, Yang L,
Xie G, Zhang K, Tang W, Stelter AA, Wang Q, et al: Activation of
the hedgehog pathway in human hepatocellular carcinomas.
Carcinogenesis. 27:1334–1340. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chuang PT and McMahon AP: Vertebrate
Hedgehog signalling modulated by induction of a Hedgehog-binding
protein. Nature. 397:617–621. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cai H, Li H, Li J, Li X, Li Y, Shi Y and
Wang D: Sonic hedgehog signaling pathway mediates development of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:16199–16205. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Huang XH, Chen JS, Wang Q, Chen XL, Wen L,
Chen LZ, Bi J, Zhang LJ, Su Q and Zeng WT: miR-338-3p suppresses
invasion of liver cancer cell by targeting smoothened. J Pathol.
225:463–472. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pienta KJ, Machiels JP, Schrijvers D,
Alekseev B, Shkolnik M, Crabb SJ, Li S, Seetharam S, Puchalski TA,
Takimoto C, et al: Phase 2 study of carlumab (CNTO 888), a human
monoclonal antibody against CC-chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), in
metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Invest New Drugs.
31:760–768. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|