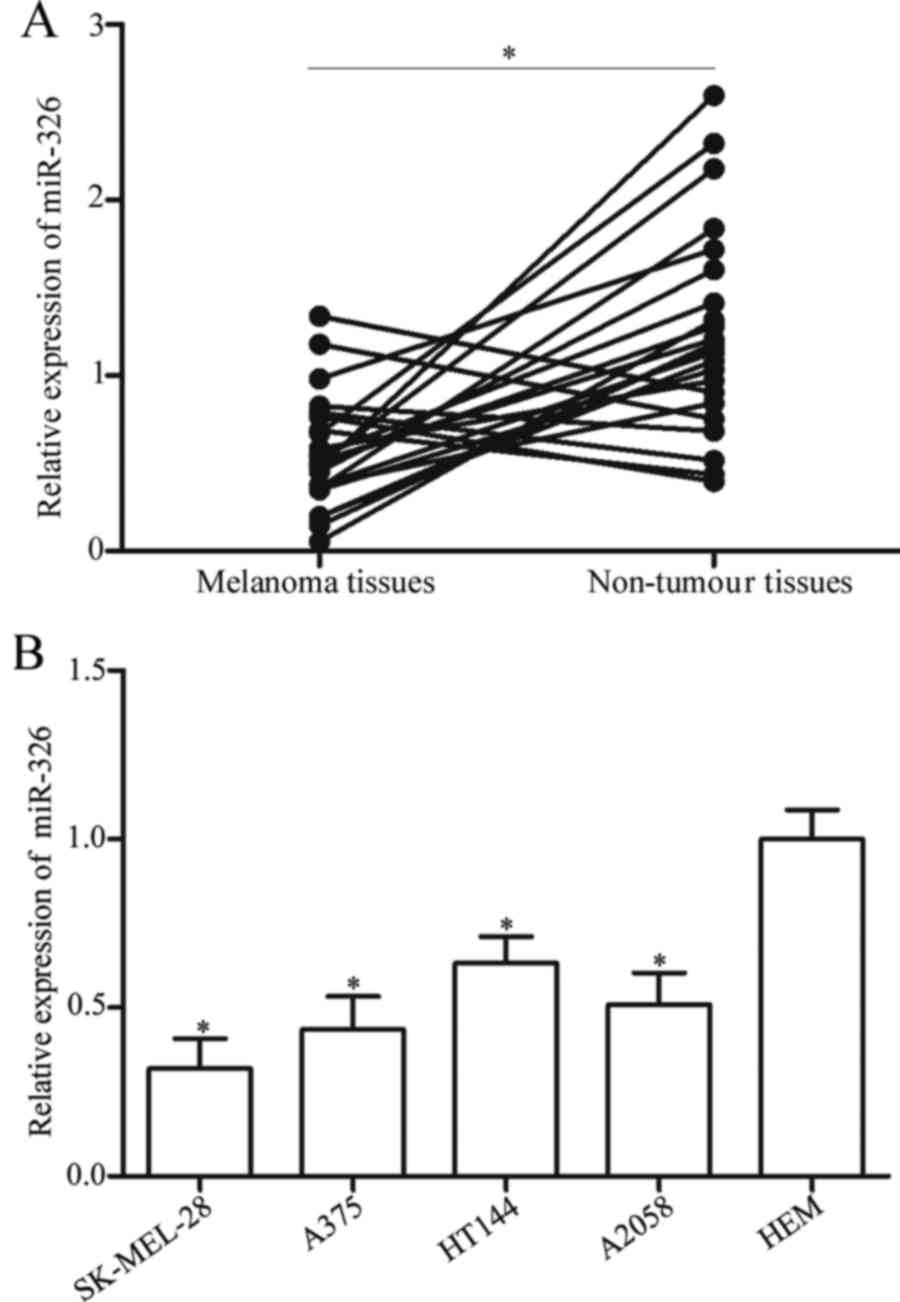
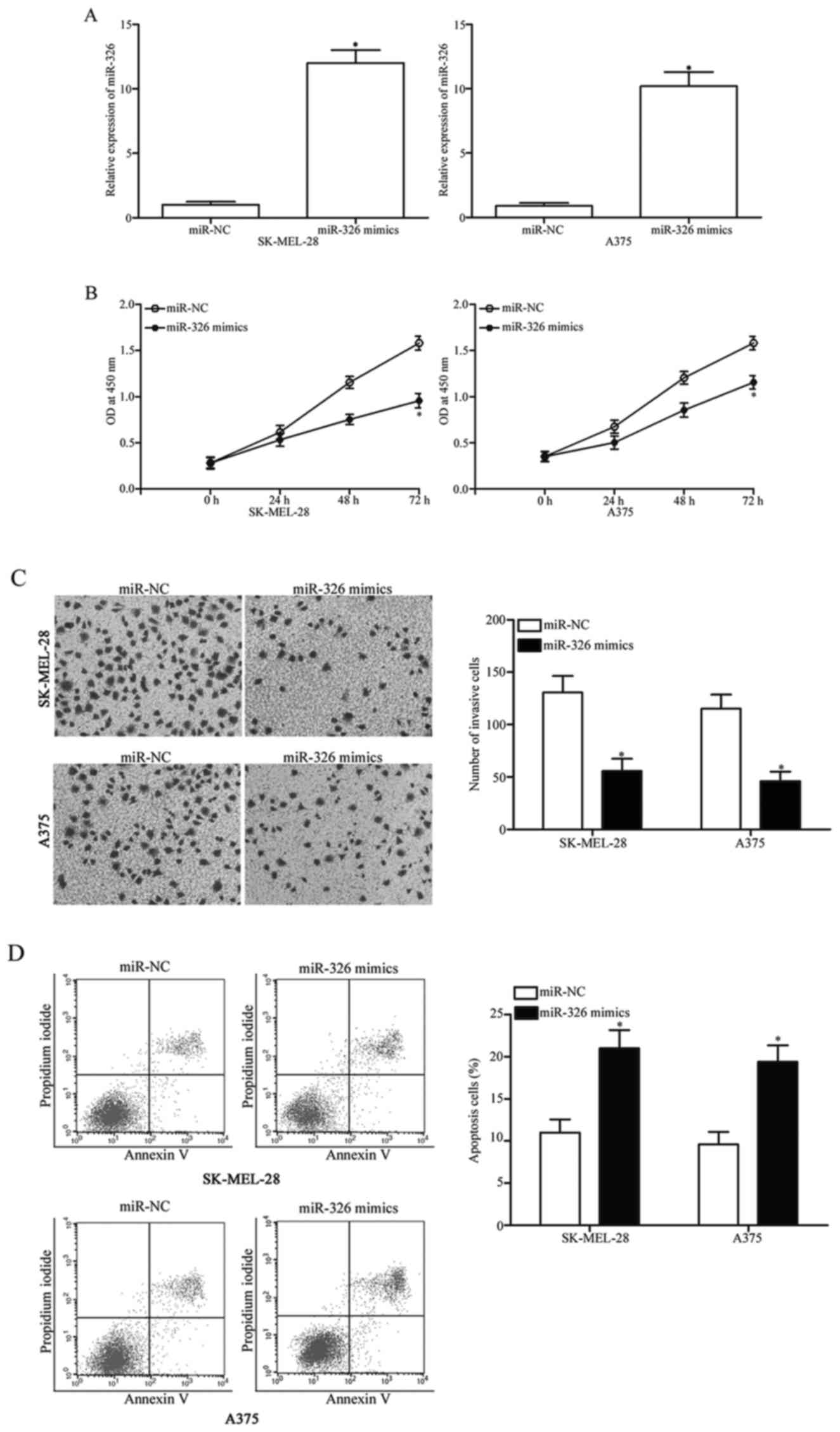
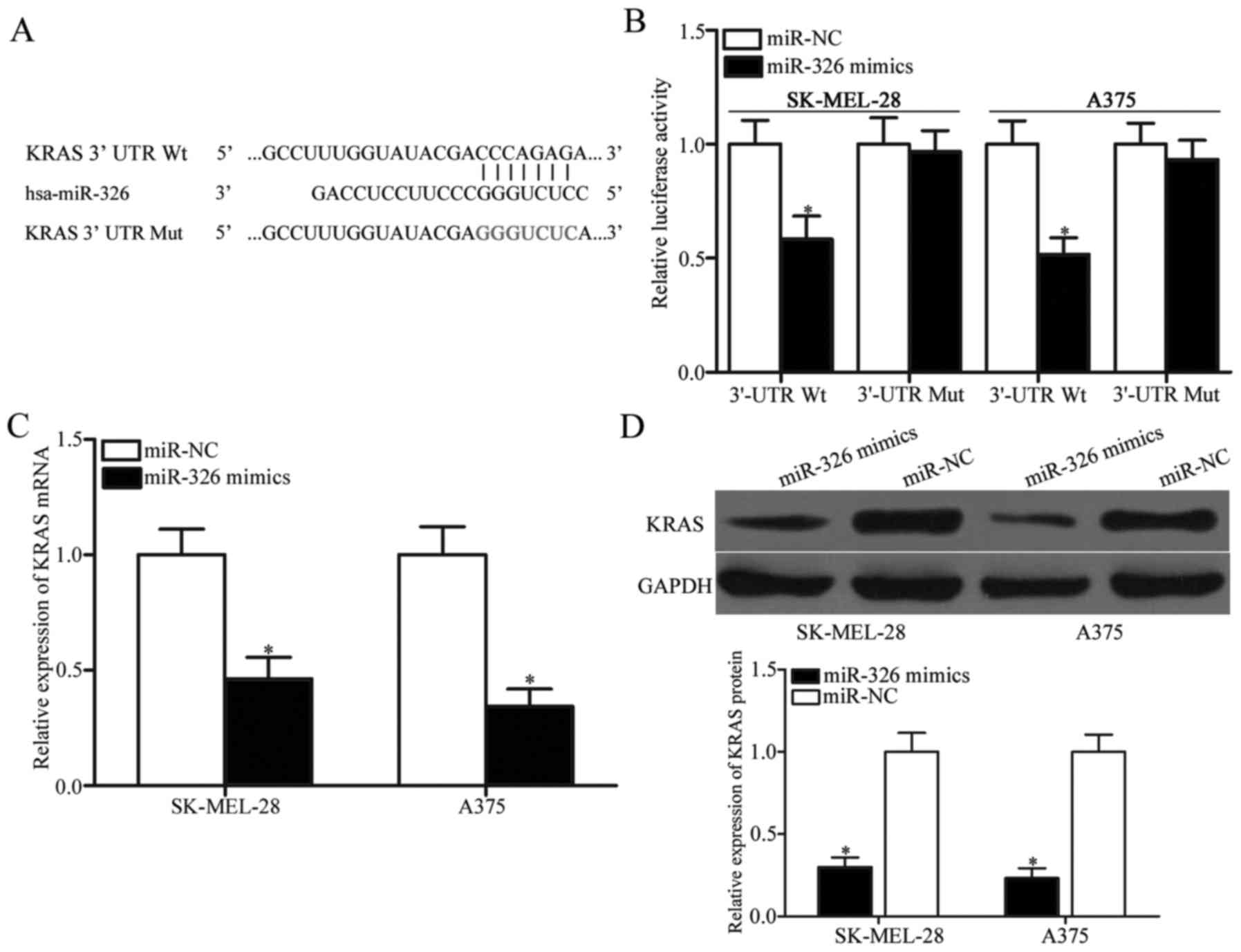
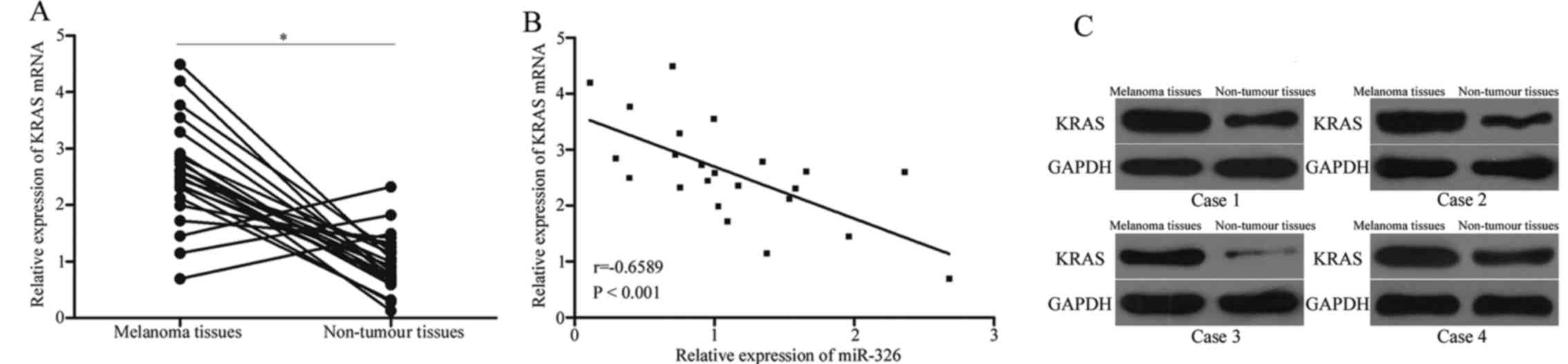
|
1
|
Trotter SC, Sroa N, Winkelmann RR, Olencki
T and Bechtel M: A global review of melanoma follow-up guidelines.
J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 6:18–26. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Linos E, Swetter SM, Cockburn MG, Colditz
GA and Clarke CA: Increasing burden of melanoma in the United
States. J Invest Dermatol. 129:1666–1674. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Terando A, Sabel MS and Sondak VK:
Melanoma: Adjuvant therapy and other treatment options. Curr Treat
Options Oncol. 4:187–199. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eggermont AM, Suciu S, Rutkowski P, Kruit
WH, Punt CJ, Dummer R, Salès F, Keilholz U, de Schaetzen G and
Testori A; EORTC Melanoma Group, : Long term follow up of the EORTC
18952 trial of adjuvant therapy in resected stage IIB-III cutaneous
melanoma patients comparing intermediate doses of
interferon-alpha-2b (IFN) with observation: Ulceration of primary
is key determinant for IFN-sensitivity. Eur J Cancer. 55:111–121.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eberle J, Kurbanov BM, Hossini AM, Trefzer
U and Fecker LF: Overcoming apoptosis deficiency of melanoma-hope
for new therapeutic approaches. Drug Resist Updat. 10:218–234.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mimeault M and Batra SK: Novel biomarkers
and therapeutic targets for optimizing the therapeutic management
of melanomas. World J Clin Oncol. 3:32–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lelli D, Pedone C and Sahebkar A: Curcumin
and treatment of melanoma: The potential role of microRNAs. Biomed
Pharmacother. 88:832–834. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kozomara A and Griffiths-Jones S: miRBase:
Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic
Acids Res. 39(Database): D152–D157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu X, Li Z and Liu J: MiRNAs in primary
cutaneous lymphomas. Cell Prolif. 48:271–277. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bai J, Zhang Z, Li X and Liu H:
MicroRNA-365 inhibits growth, invasion and metastasis of malignant
melanoma by targeting NRP1 expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:4913–4922. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren JW, Li ZJ and Tu C: MiR-135
post-transcriptionally regulates FOXO1 expression and promotes cell
proliferation in human malignant melanoma cells. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:6356–6366. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun M, Wang X, Tu C, Wang S, Qu J and Xiao
S: microRNA-216b inhibits cell proliferation and migration in human
melanoma by targeting FOXM1 in vitro and in vivo. Cell Biol Int.
Feb 22–2017.(Epub ahead of print). https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.10754 View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
He L, Qu L, Wei L, Chen Y and Suo J:
Reduction of miR 132 3p contributes to gastric cancer proliferation
by targeting MUC13. Mol Med Rep. 15:3055–3061. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yin Z, Xu M and Li P: miRNA-221 acts as an
oncogenic role by directly targeting TIMP2 in non-small-cell lung
carcinoma. Gene. 620:46–53. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abdelmaksoud-Dammak R, Chamtouri N, Triki
M, Saadallah-Kallel A, Ayadi W, Charfi S, Khabir A, Ayadi L,
Sallemi-Boudawara T and Mokdad-Gargouri R: Overexpression of
miR-10b in colorectal cancer patients: Correlation with TWIST-1 and
E-cadherin expression. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283176959162017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu Y, Zhao H, Rao M and Xu S:
MicroRNA-365 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of
glioma by targeting PIK3R3. Oncol Rep. 37:2185–2192. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shenouda SK and Alahari SK: MicroRNA
function in cancer: Oncogene or a tumor suppressor? Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 28:369–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu L, Hui H, Wang LJ, Wang H, Liu QF and
Han SX: MicroRNA-326 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal
cancer by targeting the nin one binding protein. Oncol Rep.
33:2309–2318. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang ZL, Bai ZH, Wang XB, Bai L, Miao F
and Pei HH: miR-186 and 326 predict the prognosis of pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma and affect the proliferation and migration of
cancer cells. PLoS One. 10:e01188142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun C, Huang C, Li S, Yang C, Xi Y, Wang
L, Zhang F, Fu Y and Li D: Hsa-miR-326 targets CCND1 and inhibits
non-small cell lung cancer development. Oncotarget. 7:8341–8359.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li M, Liu W, Zhu YF, Chen YL, Zhang BZ and
Wang R: Correlation of COX-2 and K-ras expression to clinical
outcome in gastric cancer. Acta Oncol. 45:1115–1119. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chang Z, Ju H, Ling J, Zhuang Z, Li Z,
Wang H, Fleming JB, Freeman JW, Yu D, Huang P, et al: Cooperativity
of oncogenic K-ras and downregulated p16/INK4A in human pancreatic
tumorigenesis. PLoS One. 9:e1014522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Przybojewska B, Jagiello A and Jalmuzna P:
H-RAS, K-RAS, and N-RAS gene activation in human bladder cancers.
Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 121:73–77. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hubbard PA, Moody CL and Murali R:
Allosteric modulation of Ras and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway:
Emerging therapeutic opportunities. Front Physiol. 5:4782014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Calvo F, Agudo-Ibáñez L and Crespo P: The
Ras-ERK pathway: Understanding site-specific signaling provides
hope of new anti-tumor therapies. BioEssays. 32:412–421. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Latchana N, Ganju A, Howard JH and Carson
WE III: MicroRNA dysregulation in melanoma. Surg Oncol. 25:184–189.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cui L, Li Y, Lv X, Li J, Wang X, Lei Z and
Li X: Expression of MicroRNA-301a and its functional roles in
malignant melanoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:230–244. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wozniak M, Mielczarek A and Czyz M: miRNAs
in melanoma: tumor suppressors and oncogenes with prognostic
potential. Curr Med Chem. 23:3136–3153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Varamo C, Occelli M, Vivenza D, Merlano M
and Lo Nigro C: MicroRNAs role as potential biomarkers and key
regulators in melanoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 56:3–10. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu J, Li J, Ren J and Zhang D:
MicroRNA-485-5p represses melanoma cell invasion and proliferation
by suppressing Frizzled7. Biomed Pharmacother. 90:303–310. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Luan W, Qian Y, Ni X, Bu X, Xia Y, Wang J,
Ruan H, Ma S and Xu B: miR-204-5p acts as a tumor suppressor by
targeting matrix metalloproteinases-9 and B-cell lymphoma-2 in
malignant melanoma. Onco Targets Ther. 10:1237–1246. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cao L, Wang J and Wang PQ: MiR-326 is a
diagnostic biomarker and regulates cell survival and apoptosis by
targeting Bcl-2 in osteosarcoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 84:828–835.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li Y, Gao Y, Xu Y, Ma H and Yang M:
Down-regulation of miR-326 is associated with poor prognosis and
promotes growth and metastasis by targeting FSCN1 in gastric
cancer. Growth Factors. 33:267–274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang S, Lu S, Geng S, Ma S, Liang Z and
Jiao B: Expression and clinical significance of microRNA-326 in
human glioma miR-326 expression in glioma. Med Oncol. 30:3732013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ji S, Zhang B, Kong Y, Ma F and Hua Y:
miR-326 inhibits gastric cancer cell growth through down regulating
NOB1. Oncol Res. 25:853–861. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou J, Xu T, Yan Y, Qin R, Wang H, Zhang
X, Huang Y, Wang Y, Lu Y, Fu D, et al: MicroRNA-326 functions as a
tumor suppressor in glioma by targeting the Nin one binding protein
(NOB1). PLoS One. 8:e684692013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kefas B, Comeau L, Erdle N, Montgomery E,
Amos S and Purow B: Pyruvate kinase M2 is a target of the
tumor-suppressive microRNA-326 and regulates the survival of glioma
cells. Neuro Oncol. 12:1102–1112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang R, Chen X, Xu T, Xia R, Han L, Chen
W, De W and Shu Y: miR-326 regulates cell proliferation and
migration in lung cancer by targeting phox2a and is regulated by
HOTAIR. Am J Cancer Res. 6:173–186. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li J, Li S, Chen Z, Wang J, Chen Y, Xu Z,
Jin M and Yu W: miR-326 reverses chemoresistance in human lung
adenocarcinoma cells by targeting specificity protein 1. Tumour
Biol. 37:13287–13294. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cai M, Wang Z, Zhang J, Zhou H, Jin L, Bai
R and Weng Y: Adam17, a target of mir-326, promotes EMT-induced
cells invasion in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:1175–1185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Du W, Liu X, Chen L, Dou Z, Lei X, Chang
L, Cai J, Cui Y, Yang D, Sun Y, et al: Targeting the SMO oncogene
by miR-326 inhibits glioma biological behaviors and stemness. Neuro
Oncol. 17:243–253. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Janssen KP, Alberici P, Fsihi H, Gaspar C,
Breukel C, Franken P, Rosty C, Abal M, El Marjou F, Smits R, et al:
APC and oncogenic KRAS are synergistic in enhancing Wnt signaling
in intestinal tumor formation and progression. Gastroenterology.
131:1096–1109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
de Mello RA, Marques DS, Medeiros R and
Araújo AM: Epidermal growth factor receptor and K-Ras in non-small
cell lung cancer-molecular pathways involved and targeted
therapies. World J Clin Oncol. 2:367–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kim RK, Suh Y, Yoo KC, Cui YH, Kim H, Kim
MJ, Gyu Kim I and Lee SJ: Activation of KRAS promotes the
mesenchymal features of basal-type breast cancer. Exp Mol Med.
47:e1372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ryu MJ, Liu Y, Zhong X, Du J, Peterson N,
Kong G, Li H, Wang J, Salamat S, Chang Q, et al: Oncogenic Kras
expression in postmitotic neurons leads to S100A8-S100A9 protein
overexpression and gliosis. J Biol Chem. 287:22948–22958. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Deng M, Tang H, Zhou Y, Zhou M, Xiong W,
Zheng Y, Ye Q, Zeng X, Liao Q, Guo X, et al: miR-216b suppresses
tumor growth and invasion by targeting KRAS in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. J Cell Sci. 124:2997–3005. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lièvre A, Bachet JB, Le Corre D, Boige V,
Landi B, Emile JF, Côté JF, Tomasic G, Penna C, Ducreux M, et al:
KRAS mutation status is predictive of response to cetuximab therapy
in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 66:3992–3995. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bhattacharya S, Socinski MA and Burns TF:
KRAS mutant lung cancer: Progress thus far on an elusive
therapeutic target. Clin Transl Med. 4:352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Schubbert S, Shannon K and Bollag G:
Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 7:295–308. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bodemann BO and White MA: Ral GTPases and
cancer: Linchpin support of the tumorigenic platform. Nat Rev
Cancer. 8:133–140. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|