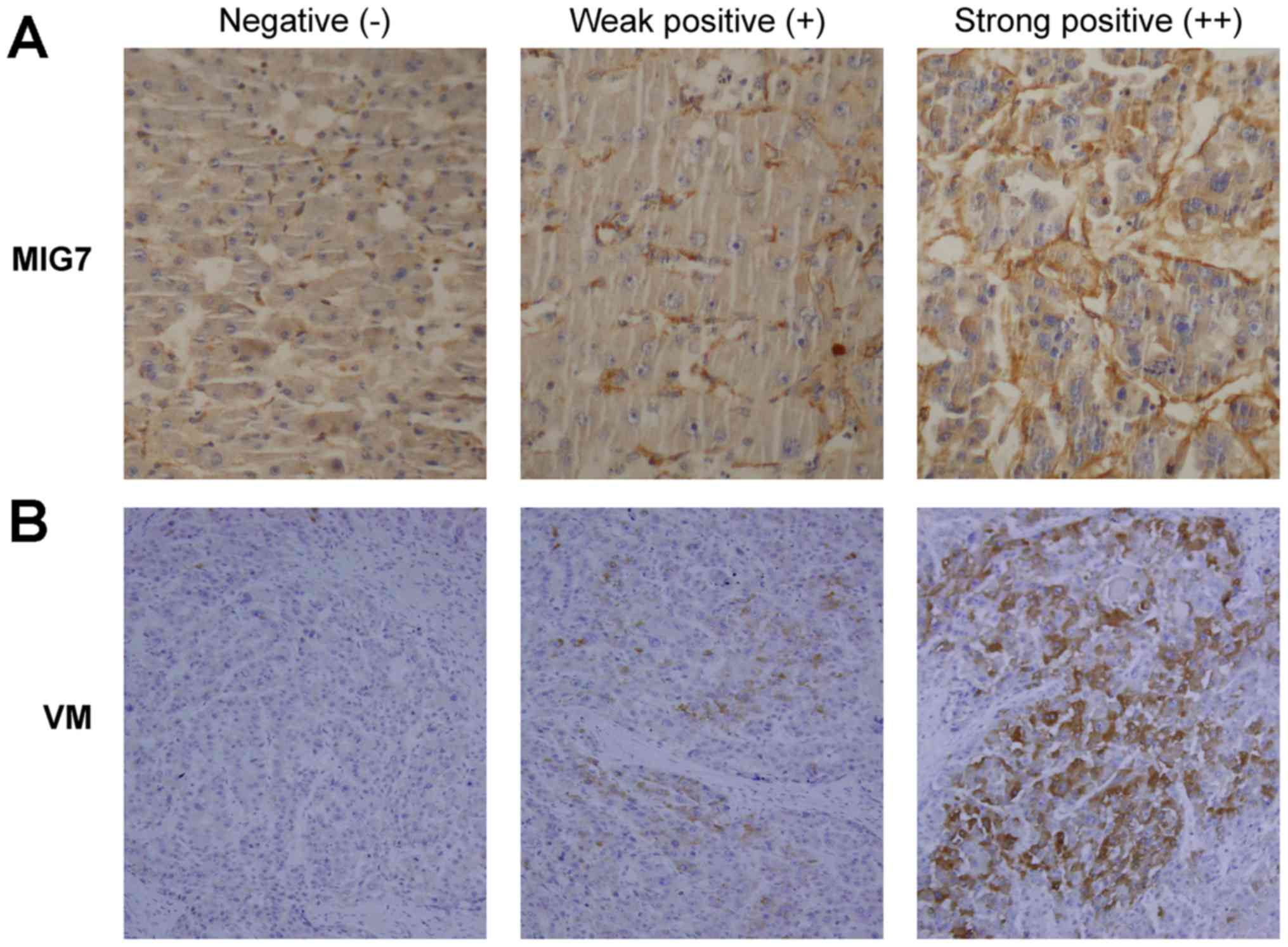
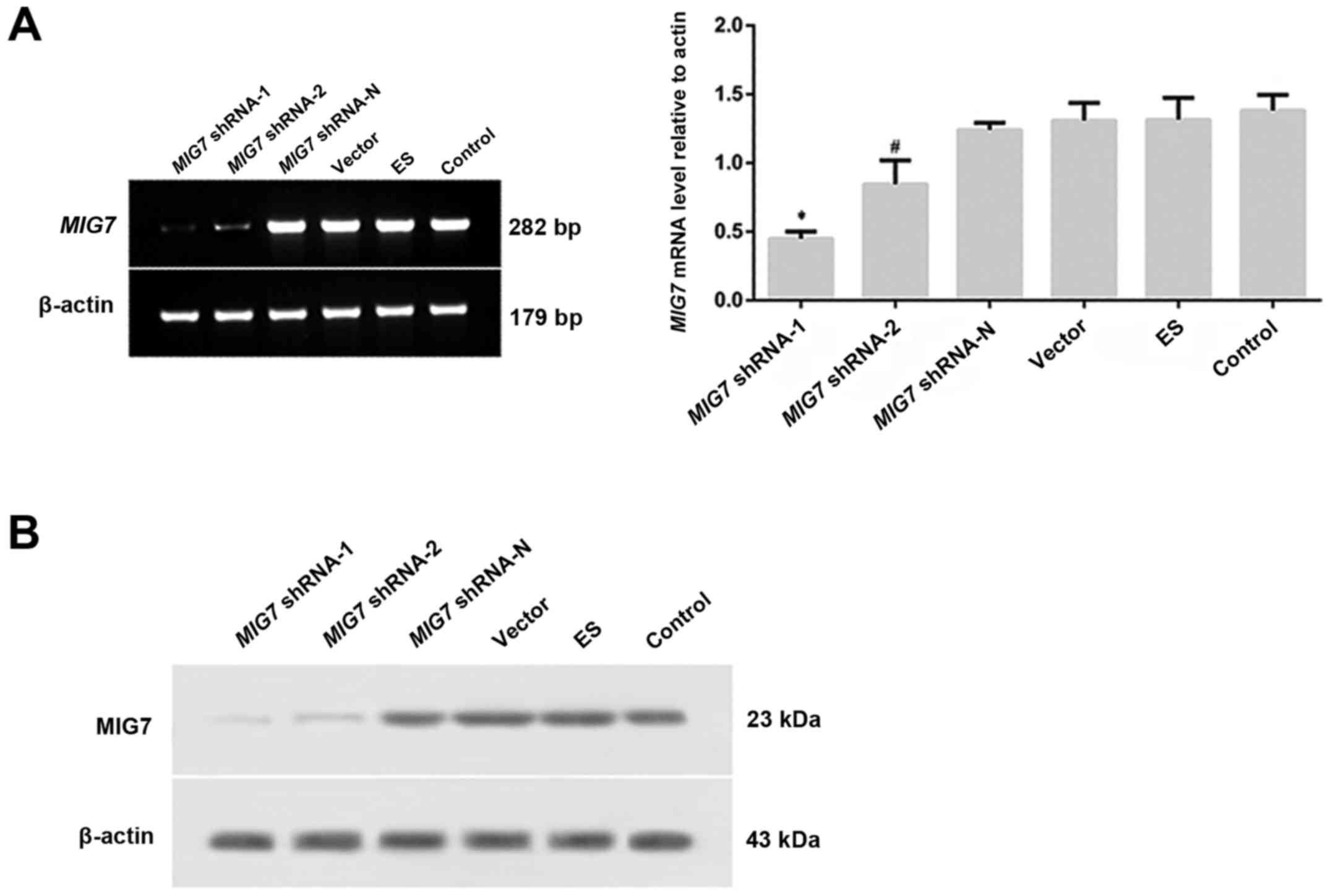
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
European Association for Study of Liver, ;
European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer, .
EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 48:599–641. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Folberg R, Hendrix MJC and Maniotis AJ:
Vasculogenic mimicry and tumor angiogenesis. Am J Pathol.
156:361–381. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen L, He Y, Sun S, Sun B and Tang X:
Vasculogenic mimicry is a major feature and novel predictor of poor
prognosis in patients with orbital rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncol Lett.
10:1635–1641. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang JP, Liao YD, Mai DM, Xie P, Qiang YY,
Zheng LS, Wang MY, Mei Y, Meng DF, Xu L, et al: Tumor vasculogenic
mimicry predicts poor prognosis in cancer patients: A
meta-analysis. Angiogenesis. 19:191–200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao N, Sun BC, Zhao XL, Wang Y, Meng J,
Che N, Dong XY and Gu Q: Role of Bcl-2 and its associated miRNAs in
vasculogenic mimicry of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:15759–15768. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang J, Wang J, Fan L, Li X, Liu N, Luo W,
Wang J and Wang Y and Wang Y: cRGD inhibits vasculogenic mimicry
formation by down-regulating uPA expression and reducing EMT in
ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 7:24050–24062. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Seftor RE, Chao JT,
Chien DS and Chu YW: Tumor cell vascular mimicry: Novel targeting
opportunity in melanoma. Pharmacol Ther. 159:83–92. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ren K, Yao N, Wang G, Tian L, Ma J, Shi X,
Zhang L, Zhang J, Zhou X, Zhou G, et al: Vasculogenic mimicry: A
new prognostic sign of human osteosarcoma. Hum Pathol.
45:2120–2129. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Luo F, Yang K, Liu RL, Meng C, Dang RF and
Xu Y: Formation of vasculogenic mimicry in bone metastasis of
prostate cancer: Correlation with cell apoptosis and senescence
regulation pathways. Pathol Res Pract. 210:291–295. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Folkman J: Antiangiogenesis in cancer
therapy - endostatin and its mechanisms of action. Exp Cell Res.
312:594–607. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Skovseth DK, Veuger MJ, Sorensen DR, De
Angelis PM and Haraldsen G: Endostatin dramatically inhibits
endothelial cell migration, vascular morphogenesis, and
perivascular cell recruitment in vivo. Blood. 105:1044–1051. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alahuhta I, Aikio M, Väyrynen O,
Nurmenniemi S, Suojanen J, Teppo S, Pihlajaniemi T, Heljasvaara R,
Salo T and Nyberg P: Endostatin induces proliferation of oral
carcinoma cells but its effect on invasion is modified by the tumor
microenvironment. Exp Cell Res. 336:130–140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qu B, Guo L, Ma J and Lv Y:
Antiangiogenesis therapy might have the unintended effect of
promoting tumor metastasis by increasing an alternative circulatory
system. Med Hypotheses. 74:360–361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eikesdal HP and Kalluri R: Drug resistance
associated with antiangiogenesis therapy. Semin Cancer Biol.
19:310–317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu YR, Sun B, Zhao XL, Gu Q, Liu ZY, Dong
XY, Che N and Mo J: Basal caspase-3 activity promotes migration,
invasion, and vasculogenic mimicry formation of melanoma cells.
Melanoma Res. 23:243–253. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Linder M and Tschernig T: Vasculogenic
mimicry: Possible role of effector caspase-3, caspase-6 and
caspase-7. Ann Anat. 204:114–117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Petty AP, Garman KL, Winn VD, Spidel CM
and Lindsey JS: Overexpression of carcinoma and embryonic
cytotrophoblast cell-specific Mig-7 induces invasion and
vessel-like structure formation. Am J Pathol. 170:1763–1780. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feng X, Yao J, Gao X, Jing Y, Kang T,
Jiang D, Jiang T, Feng J, Zhu Q, Jiang X, et al: Multi-targeting
peptide-functionalized nanoparticles recognized vasculogenic
mimicry, tumor neovasculature and glioma cells for enhanced
anti-glioma therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 7:27885–27899.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ho MY, Liang CM and Liang SM: MIG-7 and
phosphorylated prohibitin coordinately regulate lung cancer
invasion/metastasis. Oncotarget. 6:381–393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li WL and Gao Q: Mig-7 enhances
vasculogenic mimicry in gastric cancer cells. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian
Yi Xue Za Zhi. 28:1142–1145. 2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lissitzky JC, Parriaux D, Ristorcelli E,
Vérine A, Lombardo D and Verrando P: Cyclic AMP signaling as a
mediator of vasculogenic mimicry in aggressive human melanoma cells
in vitro. Cancer Res. 69:802–809. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu WB, Xu GL, Jia WD, Li JS, Ma JL, Chen
K, Wang ZH, Ge YS, Ren WH, Yu JH, et al: Prognostic significance
and mechanisms of patterned matrix vasculogenic mimicry in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 28 Suppl 1:S228–S238. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang Z, Sun B, Zhao X, Shao B, An J, Gu Q,
Wang Y, Dong X, Zhang Y and Qiu Z: Erythropoietin and
erythropoietin receptor in hepatocellular carcinoma: Correlation
with vasculogenic mimicry and poor prognosis. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:4033–4043. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li S, Meng W, Guan Z, Guo Y and Han X: The
hypoxia-related signaling pathways of vasculogenic mimicry in tumor
treatment. Biomed Pharmacother. 80:127–135. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Wang JH, Li S, Li LL, Huang M,
Zhang YH, Liu Y, Yang YT, Ding R and Ke YQ: Histone deacetylase 3
expression correlates with vasculogenic mimicry through the
phosphoinositide3-kinase/ERK-MMP-laminin5γ2 signaling pathway.
Cancer Sci. 106:857–866. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin H, Pan JC, Zhang FM, Huang B, Chen X,
Zhuang JT, Wang H, Mo CQ, Wang DH and Qiu SP: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 is required for vasculogenic mimicry by clear
cell renal carcinoma cells. Urol Oncol. 33:168.e9–168.e16. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zang M, Zhang Y, Zhang B, Hu L, Li J, Fan
Z, Wang H, Su L, Zhu Z, Li C, et al: CEACAM6 promotes tumor
angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry in gastric cancer via FAK
signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:1020–1028. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao N, Sun H, Sun B, Zhu D, Zhao X, Wang
Y, Gu Q, Dong X, Liu F, Zhang Y, et al: miR-27a-3p suppresses tumor
metastasis and VM by down-regulating VE-cadherin expression and
inhibiting EMT: An essential role for Twist-1 in HCC. Sci Rep.
6:230912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vukoja V, Brandenbusch T, Tura A, Nassar
K, Rohrbach DJ, Lüke M, Grisanti S and Lüke J: Expression of EphA2
in metastatic and non-metastatic primary uveal melanoma. Klin
Monatsbl Augenheilkd. 232:290–297. 2016.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liao S and Gao Q: Expressions and clinical
significance of vasculogenic mimicry and related protein Mig-7 and
MMP-2 in gastric carcinoma. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi.
29:194–196. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xue R, Li R, Guo H, Guo L, Su Z, Ni X, Qi
L, Zhang T, Li Q, Zhang Z, et al: Variable intra-tumor genomic
heterogeneity of multiple lesions in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 150:998–1008. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|