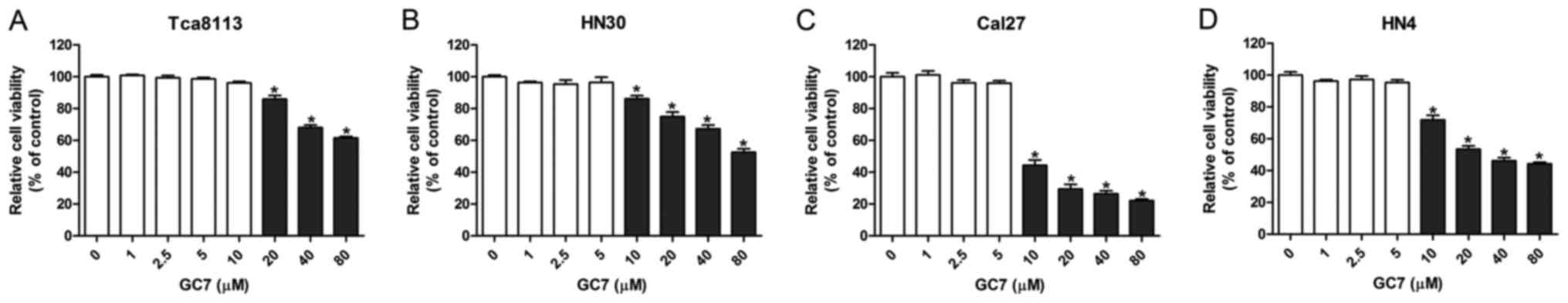
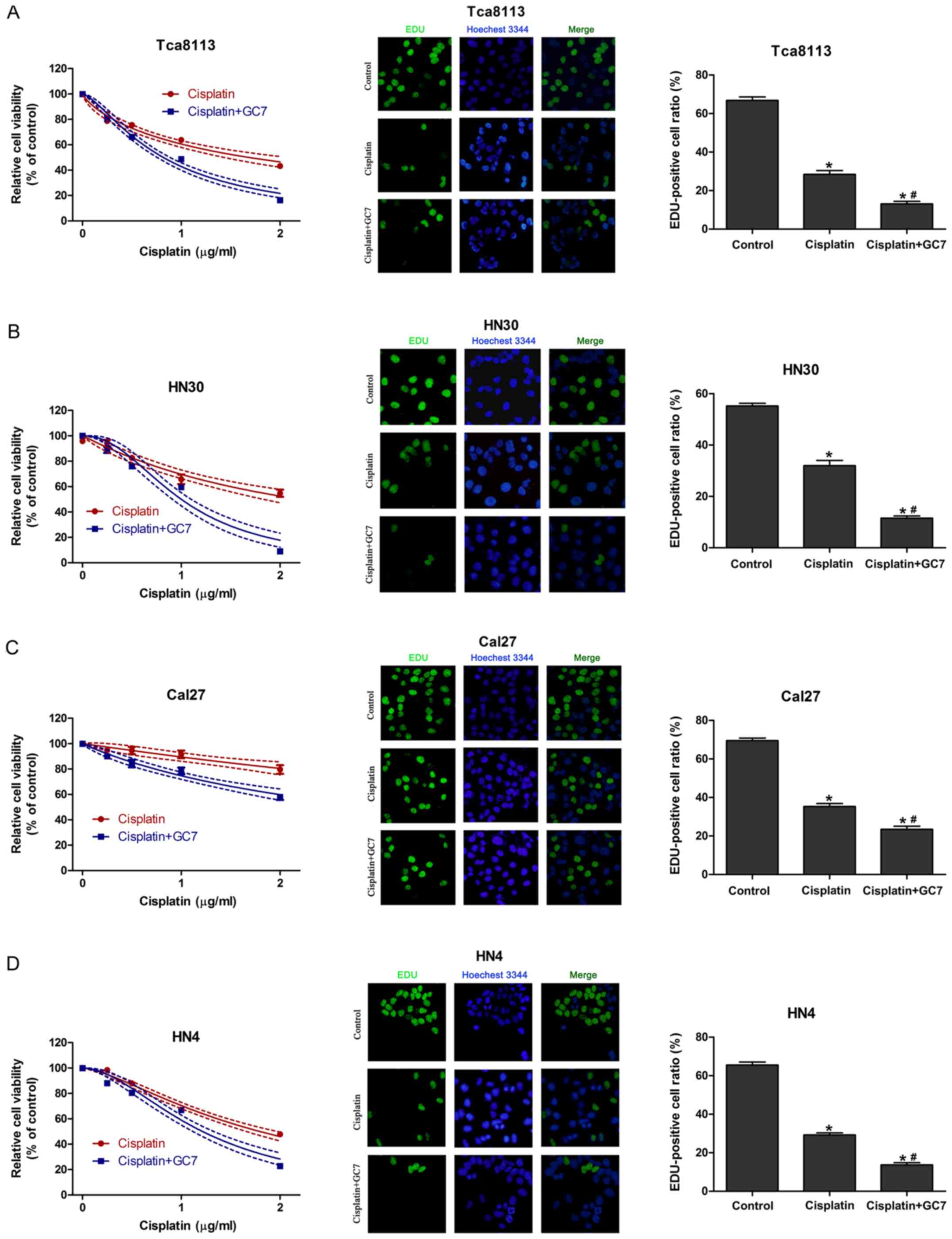
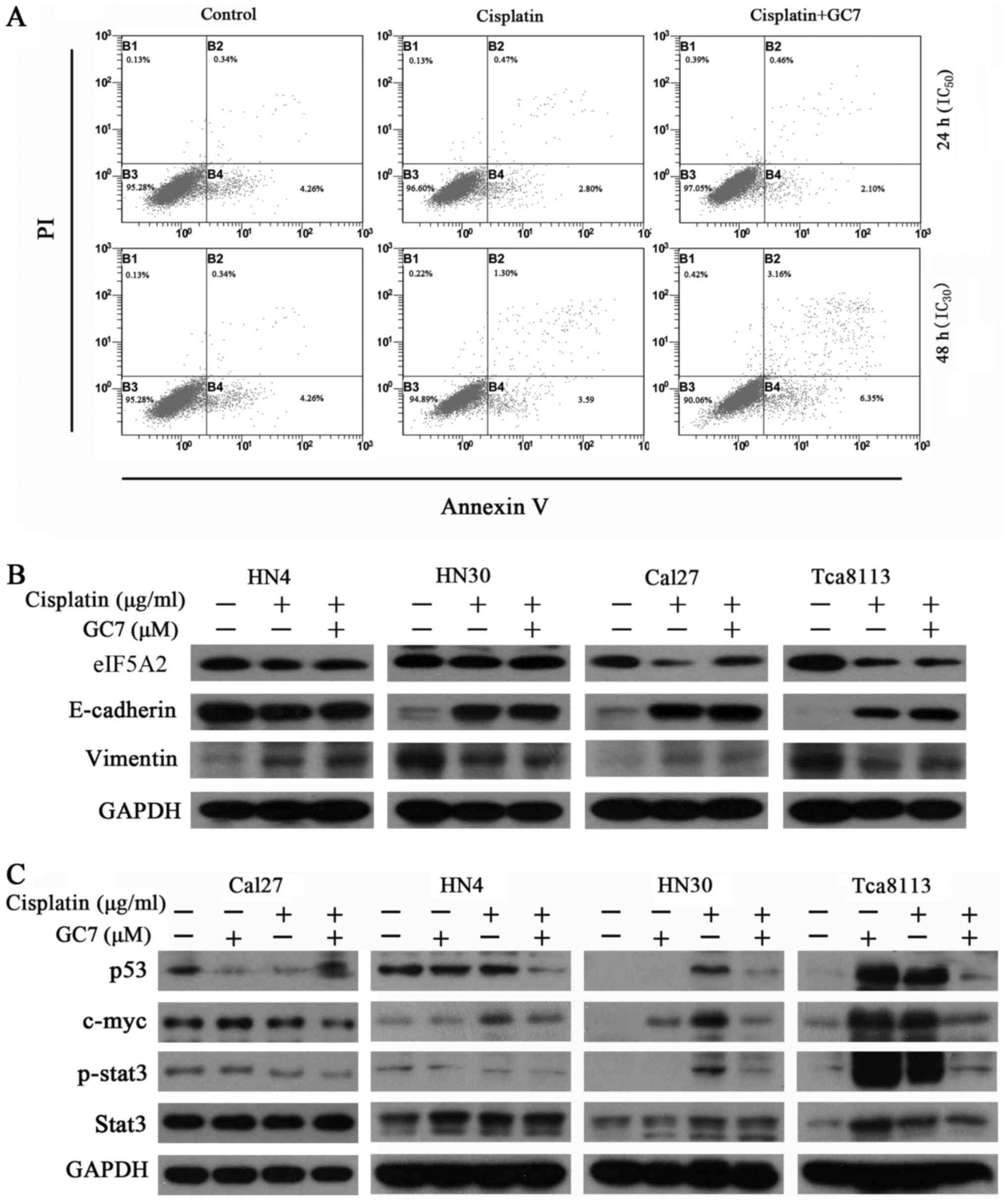
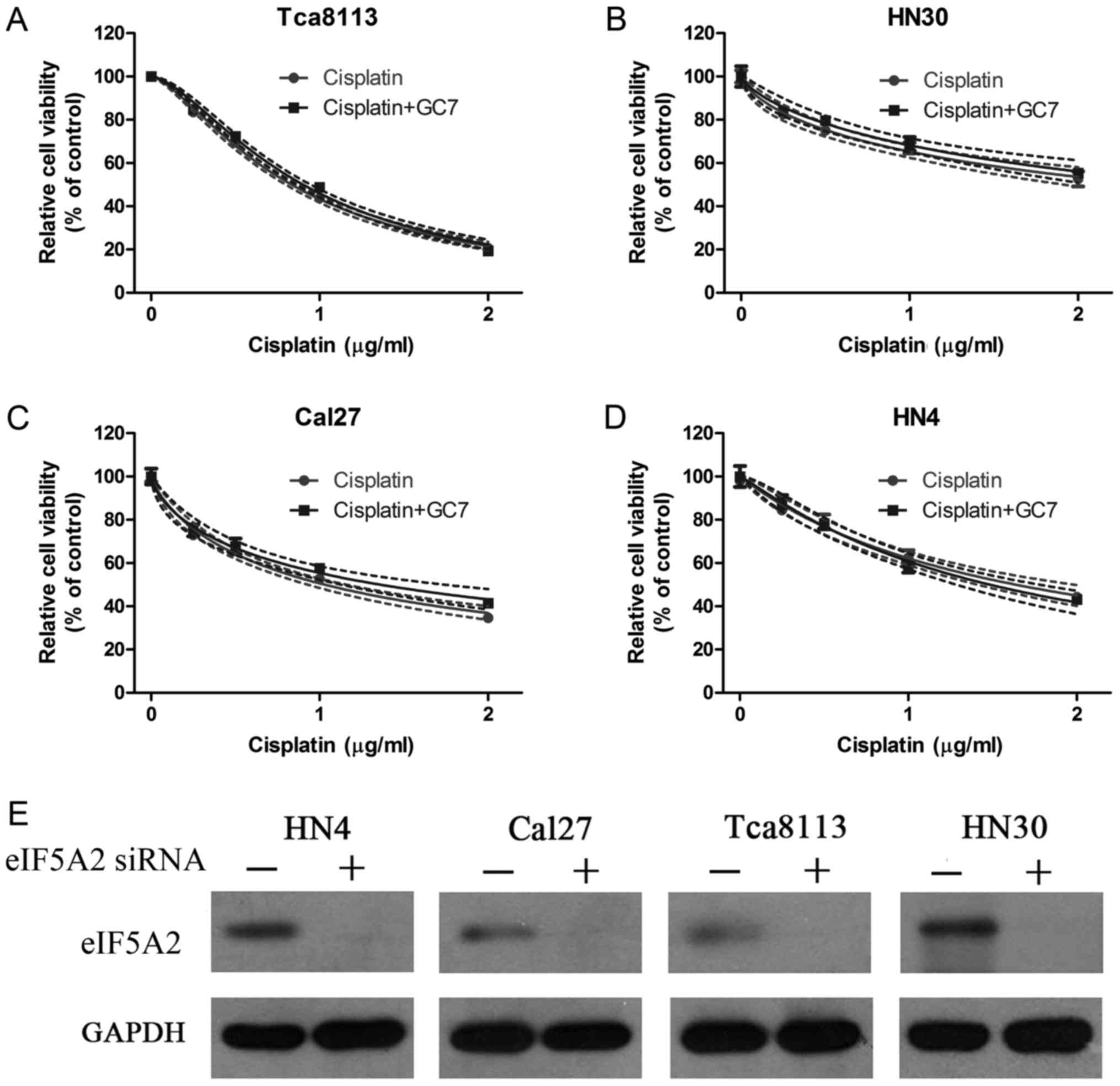
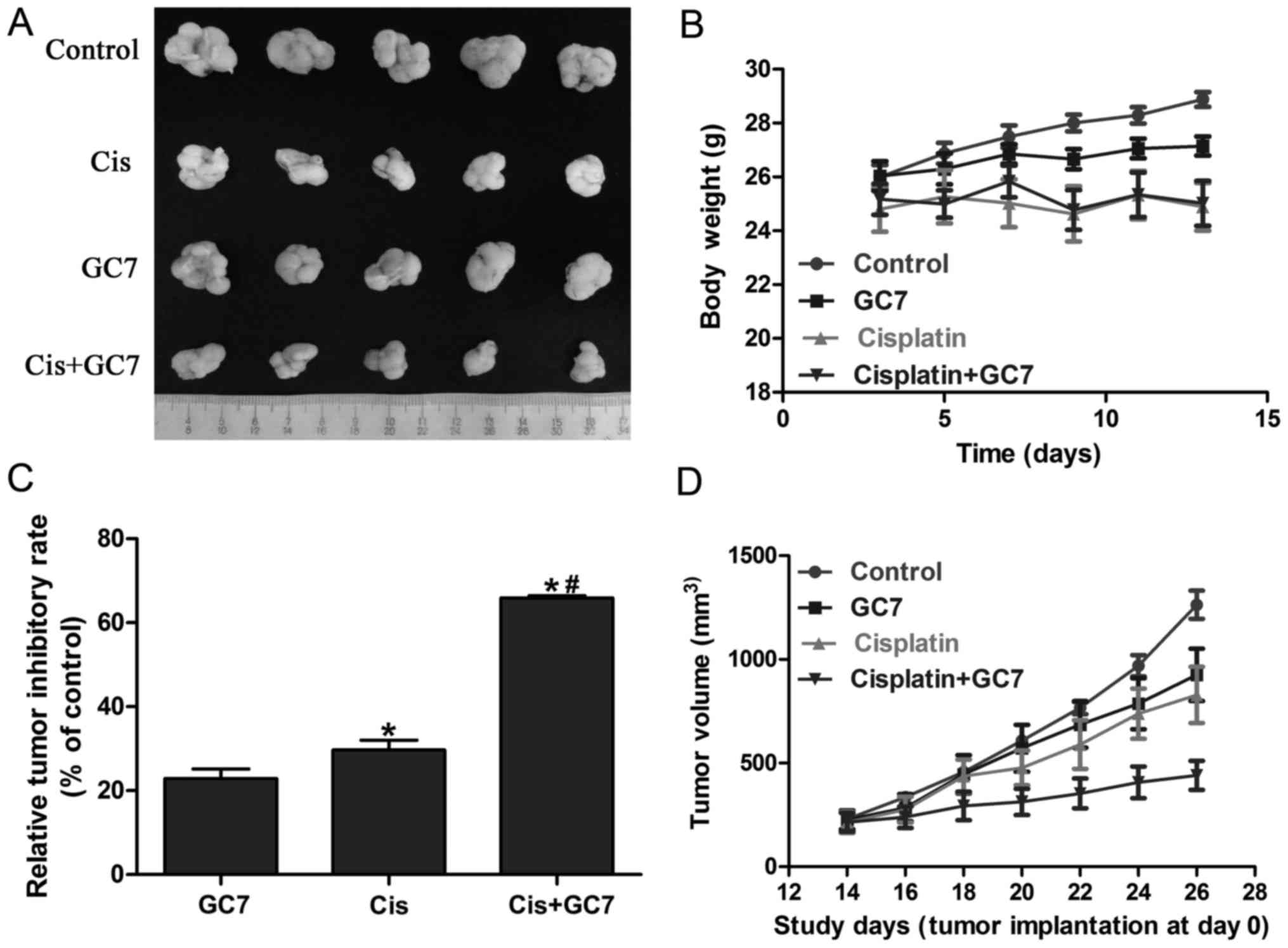
|
1
|
Cancer Stat Facts SEER: Oral Cavity and
Pharynx Cancer. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/oralcav.html
|
|
2
|
Rohde S, Kovács AF, Turowski B, Yan B,
Zanella F and Berkefeld J: Intra-arterial high-dose chemotherapy
with cisplatin as part of a palliative treatment concept in oral
cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 26:1804–1809. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kovács AF: Chemoembolization using
cisplatin crystals as neoadjuvant treatment of oral cancer. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 20:267–279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Andreadis C, Vahtsevanos K, Sidiras T,
Thomaidis I, Antoniadis K and Mouratidou D: 5-Fluorouracil and
cisplatin in the treatment of advanced oral cancer. Oral Oncol.
39:380–385. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
da Silva SD, Hier M, Mlynarek A, Kowalski
LP and Alaoui-Jamali MA: Recurrent oral cancer: Current and
emerging therapeutic approaches. Front Pharmacol. 3:1492012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mehrotra R, Ibrahim R, Eckardt A, Driemel
O and Singh M: Novel strategies in therapy of head and neck cancer.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 11:465–478. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smith A, Teknos TN and Pan Q: Epithelial
to mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Oral Oncol. 49:287–292. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chang JY, Wright JM and Svoboda KK: Signal
transduction pathways involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
in oral cancer compared with other cancers. Cells Tissues Organs.
185:40–47. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kajiyama H, Shibata K, Terauchi M,
Yamashita M, Ino K, Nawa A and Kikkawa F: Chemoresistance to
paclitaxel induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and enhances
metastatic potential for epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells. Int J
Oncol. 31:277–283. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lewin B, Siu A, Baker C, Dang D, Schnitt
R, Eisapooran P and Ramos DM: Expression of Fyn kinase modulates
EMT in oral cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 30:2591–2596.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sasahira T, Kirita T and Kuniyasu H:
Update of molecular pathobiology in oral cancer: A review. Int J
Clin Oncol. 19:431–436. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Attramadal CG, Kumar S, Boysen ME, Dhakal
HP, Nesland JM and Bryne M: Tumor budding, EMT and cancer stem
cells in T1-2/N0 oral squamous cell carcinomas. Anticancer Res.
35:6111–6120. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Z, Filho MS and Nör JE: The biology
of head and neck cancer stem cells. Oral Oncol. 48:1–9. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mathews MB and Hershey JWB: The
translation factor eIF5A and human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1849:836–844. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Clement PMJ, Henderson CA, Jenkins ZA,
Smit-McBride Z, Wolff EC, Hershey JW, Park MH and Johansson HE:
Identification and characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor
5A-2. Eur J Biochem. 270:4254–4263. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xing ZH, Wei JH, Cheang TY, Wang ZR, Zhou
X, Wang SS, Chen W, Wang SM, Luo JH and Xu AW: Bifunctional
pH-sensitive Zn(II)-curcumin nanoparticles/siRNA effectively
inhibit growth of human bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.
J Mater Chem B Mater Biol Med. 2:2714–2724. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang FW, Guan XY and Xie D: Roles of
eukaryotic initiation factor 5A2 in human cancer. Int J Biol Sci.
9:1013–1020. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang DJ, Dong SS, Ma NF, Xie D, Chen L, Fu
L, Lau SH, Li Y, Li Y and Guan XY: Overexpression of eukaryotic
initiation factor 5A2 enhances cell motility and promotes tumor
metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 51:1255–1263.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Y, Liu R, Fu P, Du F, Hong Y, Yao M,
Zhang X and Zheng S: N1-Guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane sensitizes
estrogen receptor negative breast cancer cells to doxorubicin by
preventing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of
eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 activation. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 36:2494–2503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang J, Yu H, Shen M, Wei W, Xia L and
Zhao P: N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane sensitizes bladder cancer
cells to doxorubicin by preventing epithelial-mesenchymal
transition through inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation
factor 5A2 activation. Cancer Sci. 105:219–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu G, Yu H, Shi X, Sun L, Zhou Q, Zheng D,
Shi H, Li N, Zhang X and Shao G: Cisplatin sensitivity is enhanced
in non-small cell lung cancer cells by regulating
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition of eukaryotic
translation initiation factor 5A2. BMC Pulm Med. 14:1742014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lou B, Fan J, Wang K, Chen W, Zhou X,
Zhang J, Lin S, Lv F and Chen Y: N1-guanyl-1,7-diaminoheptane (GC7)
enhances the therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin by inhibiting
activation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2)
and preventing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Exp Cell Res. 319:2708–2717. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bao Y, Lu Y, Wang X, Feng W, Sun X, Guo H,
Tang C, Zhang X, Shi Q and Yu H: Eukaryotic translation initiation
factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer
through epithelial mesenchymal transition. Cancer Cell Int.
15:1092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tomayko MM and Reynolds CP: Determination
of subcutaneous tumor size in athymic (nude) mice. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 24:148–154. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dykes DJ, Harrison SD Jr, Mayo JG and
Griswold DP Jr: Excision assay for initial evaluation of antitumor
drug activity in mice bearing human tumor xenografts. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 84:528–530. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee NP, Tsang FH, Shek FH, Mao M, Dai H,
Zhang C, Dong S, Guan XY, Poon RT and Luk JM: Prognostic
significance and therapeutic potential of eukaryotic translation
initiation factor 5A (eIF5A) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 127:968–976. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakanishi S and Cleveland JL: Targeting
the polyamine-hypusine circuit for the prevention and treatment of
cancer. Amino Acids. 48:2353–2362. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang L, Mosel AJ, Oakley GG and Peng A:
Deficient DNA damage signaling leads to chemoresistance to
cisplatin in oral cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:2401–2409. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu ZW, Zhong LP, Ji T, Zhang P, Chen WT
and Zhang CP: MicroRNAs contribute to the chemoresistance of
cisplatin in tongue squamous cell carcinoma lines. Oral Oncol.
46:317–322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Z, Yu T, Zhou B, Wei J, Fang Y, Lu J,
Guo L, Chen W, Liu ZP and Luo J: Mg(II)-Catechin nanoparticles
delivering siRNA targeting EIF5A2 inhibit bladder cancer cell
growth in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 81:125–134. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tian SB, Yu JC, Liu YQ, Kang WM, Ma ZQ, Ye
X and Yan C: MiR-30b suppresses tumor migration and invasion by
targeting EIF5A2 in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
21:9337–9347. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meng QB, Kang WM, Yu JC, Liu YQ, Ma ZQ,
Zhou L, Cui QC and Zhou WX: Overexpression of eukaryotic
translation initiation factor 5A2 (EIF5A2) correlates with cell
aggressiveness and poor survival in gastric cancer. PLoS One.
10:e01192292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Du F, Chen W, Yao M, Lv K and Fu P:
EIF5A2 is a novel chemoresistance gene in breast cancer. Breast
Cancer. 22:602–607. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee WY, Shin DY, Kim HJ, Ko YH, Kim S and
Jeong HS: Prognostic significance of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of extracapsular spread tumors in lymph node metastases
of head and neck cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 21:1904–1911. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Harada K, Ferdous T and Ueyama Y:
Establishment of 5-fluorouracil-resistant oral squamous cell
carcinoma cell lines with epithelial to mesenchymal transition
changes. Int J Oncol. 44:1302–1308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Aggarwal BB, Sethi G, Ahn KS, Sandur SK,
Pandey MK, Kunnumakkara AB, Sung B and Ichikawa H: Targeting
signal-transducer-and-activator-of-transcription-3 for prevention
and therapy of cancer: Modern target but ancient solution. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1091:151–169. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yadav A, Kumar B, Datta J, Teknos TN and
Kumar P: IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling
pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1658–1667. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gkouveris I, Nikitakis N, Karanikou M,
Rassidakis G and Sklavounou A: Erk1/2 activation and modulation of
STAT3 signaling in oral cancer. Oncol Rep. 32:2175–2182. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Buettner R, Mora LB and Jove R: Activated
STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for
therapeutic intervention. Clin Cancer Res. 8:945–954.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu W, Cai MY, Tong ZT, Dong SS, Mai SJ,
Liao YJ, Bian XW, Lin MC, Kung HF, Zeng YX, et al: Overexpression
of EIF5A2 promotes colorectal carcinoma cell aggressiveness by
upregulating MTA1 through C-myc to induce
epithelial-mesenchymaltransition. Gut. 61:562–575. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|