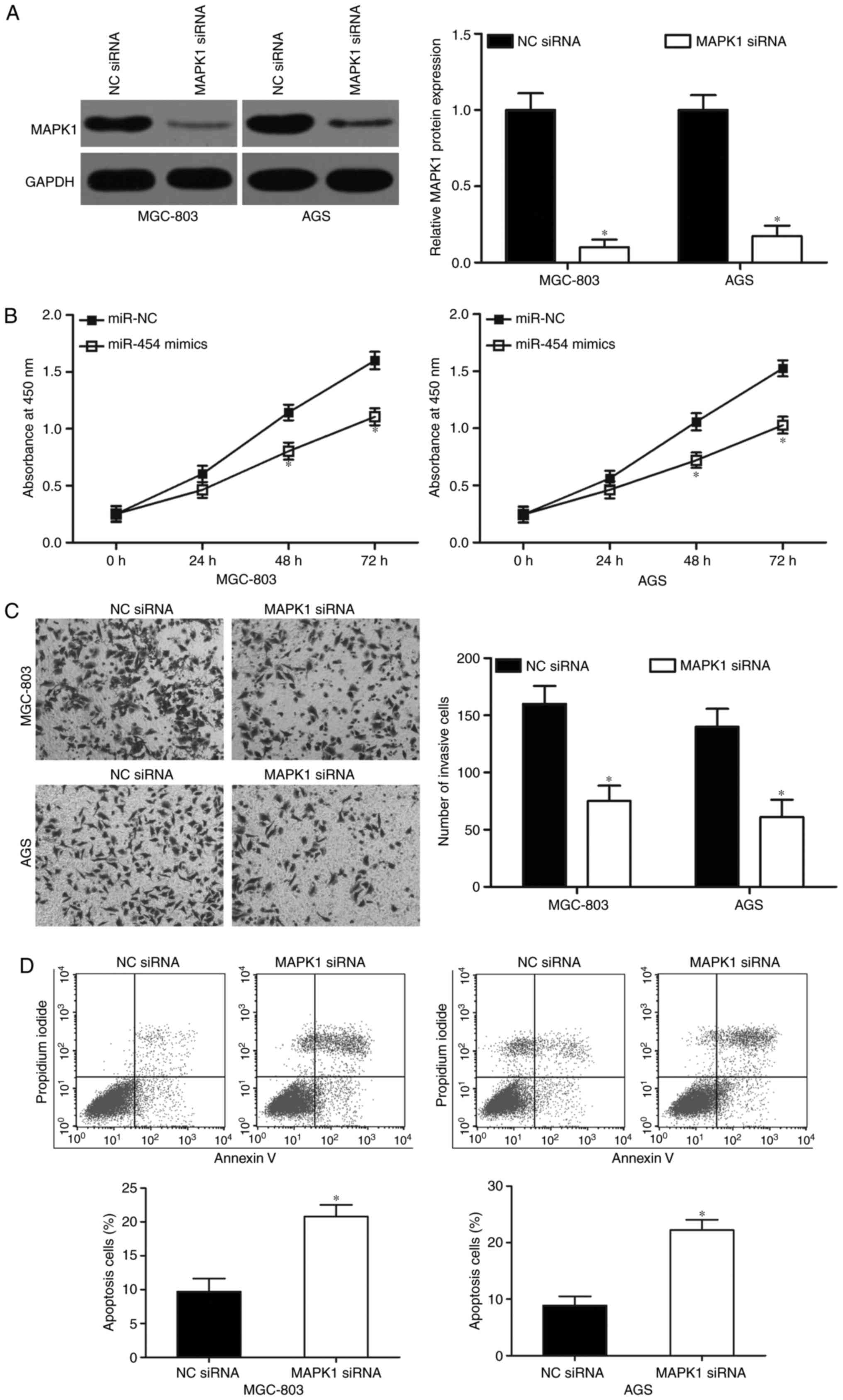
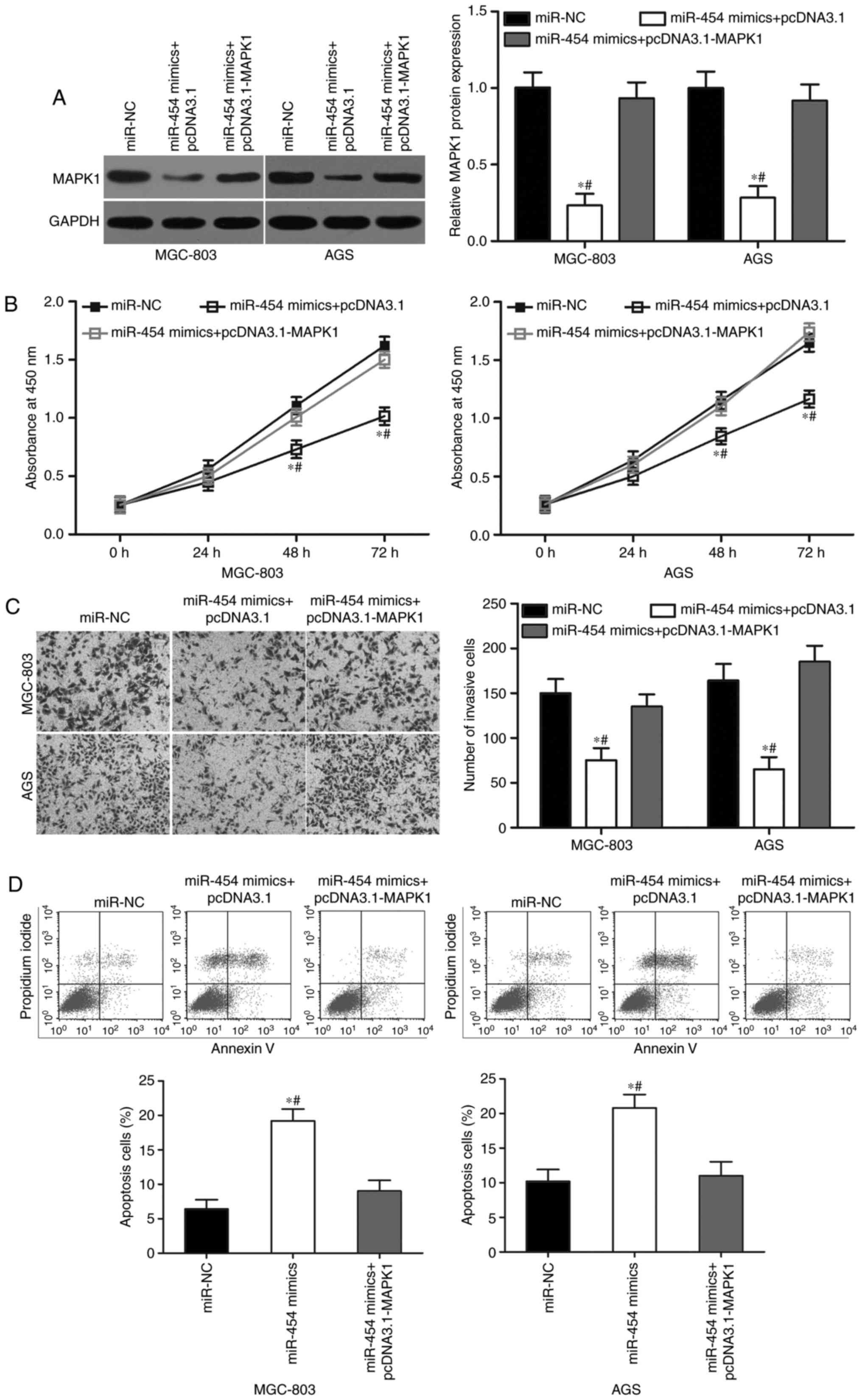
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chiba T: Factors contributing to the
development of gastric cancer due to Helicobacter pylori infection.
Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 4:267–268. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma.
Nature. 513:202–209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lent MR, Hayes SM, Wood GC, Napolitano MA,
Argyropoulos G, Gerhard GS, Foster GD and Still CD: Smoking and
alcohol use in gastric bypass patients. Eat Behav. 14:460–463.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kanda M, Kodera Y and Sakamoto J: Updated
evidence on adjuvant treatments for gastric cancer. Expert Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:1549–1560. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Moon YW, Jeung HC, Rha SY, Yoo NC, Roh JK,
Noh SH, Kim BS and Chung HC: Changing patterns of prognosticators
during 15-year follow-up of advanced gastric cancer after radical
gastrectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy: A 15-year follow-up study at
a single korean institute. Ann Surg Oncol. 14:2730–2737. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chaffer CL and Weinberg RA: A perspective
on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 331:1559–1564. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu W, Yang Z and Lu N: Molecular targeted
therapy for the treatment of gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:12016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng N, Yang P, Wang Z and Zhou Q:
OncomicroRNAs-mediated tumorigenesis: Implication in cancer
diagnosis and targeted therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 17:40–47.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang C, Chen X, Alattar M, Wei J and Liu
H: MicroRNAs in tumorigenesis, metastasis, diagnosis and prognosis
of gastric cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 22:291–301. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ding L, Zhang S, Xu M, Zhang R, Sui P and
Yang Q: MicroRNA-27a contributes to the malignant behavior of
gastric cancer cells by directly targeting PH domain and
leucine-rich repeat protein phosphatase 2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
36:452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu D, Niu X, Pan H, Zhou Y, Qu P and Zhou
J: MicroRNA-335 is downregulated in bladder cancer and inhibits
cell growth, migration and invasion via targeting ROCK1. Mol Med
Rep. 13:4379–4385. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Y, Sun Z, Liu B, Shan Y, Zhao L and Jia
L: Tumor-suppressive miR-26a and miR-26b inhibit cell
aggressiveness by regulating FUT4 in colorectal cancer. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e28922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lv QL, Du H, Liu YL, Huang YT, Wang GH,
Zhang X, Chen SH and Zhou HH: Low expression of microRNA-320b
correlates with tumorigenesis and unfavorable prognosis in glioma.
Oncol Rep. 38:959–966. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiu J, Hao Y, Huang S, Ma Y, Li X, Li D
and Mao Y: miR-557 works as a tumor suppressor in human lung
cancers by negatively regulating LEF1 expression. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283177094672017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pan HW, Li SC and Tsai KW: MicroRNA
dysregulation in gastric cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 19:1273–1284.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wu WK, Lee CW, Cho CH, Fan D, Wu K, Yu J
and Sung JJ: MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: A new player
enters the game. Oncogene. 29:5761–5771. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang H, Jiang Z, Chen H, Wu X, Xiang J and
Peng J: MicroRNA-495 inhibits gastric cancer cell migration and
invasion possibly via targeting high mobility group AT-Hook 2
(HMGA2). Med Sci Monit. 23:640–648. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun L, Wang Q, Gao X, Shi D, Mi S and Han
Q: MicroRNA-454 functions as an oncogene by regulating PTEN in
uveal melanoma. FEBS Lett. 589:2791–2796. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liang HL, Hu AP, Li SL, Xie JP, Ma QZ and
Liu JY: miR-454 prompts cell proliferation of human colorectal
cancer cells by repressing CYLD expression. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 16:2397–2402. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fang B, Zhu J, Wang Y, Geng F and Li G:
miR-454 inhibited cell proliferation of human glioblastoma cells by
suppressing PDK1 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 75:148–152. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Niu G, Li B, Sun J and Sun L: miR-454 is
down-regulated in osteosarcomas and suppresses cell proliferation
and invasion by directly targeting c-Met. Cell Prolif. 48:348–355.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang B, Wang S, Zhu XG, Yu YX, Cui ZR and
Yu YZ: Increased expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase and
its upstream regulating signal in human gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:623–628. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Husain SS, Szabo IL, Pai R, Soreghan B,
Jones MK and Tarnawski AS: MAPK (ERK2) kinase-a key target for
NSAIDs-induced inhibition of gastric cancer cell proliferation and
growth. Life Sci. 69:3045–3054. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao Y, Zhao X, Yang B, Neuzil J and Wu K:
alpha-Tocopheryl succinate-induced apoptosis in human gastric
cancer cells is modulated by ERK1/2 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase in
a biphasic manner. Cancer Lett. 247:345–352. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mao J, Xu Z, Fang Y, Wang H, Xu J, Ye J,
Zheng S and Zhu Y: Hepatoma-derived growth factor involved in the
carcinogenesis of gastric epithelial cells through promotion of
cell proliferation by Erk1/2 activation. Cancer Sci. 99:2120–2127.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cao Y, Tu Y, Mei J, Li Z, Jie Z, Xu S, Xu
L, Wang S and Xiong Y: RNAimediated knockdown of PRL-3 inhibits
cell invasion and downregulates ERK 1/2 expression in the human
gastric cancer cell line, SGC-7901. Mol Med Rep. 7:1805–1811. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fei B and Wu H: miR-378 inhibits
progression of human gastric cancer MGC-803 cells by targeting
MAPK1 in vitro. Oncol Res. 20:557–564. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shrestha S, Hsu SD, Huang WY, Huang HY,
Chen W, Weng SL and Huang HD: A systematic review of microRNA
expression profiling studies in human gastric cancer. Cancer Med.
3:878–888. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu X, Lv M, Wang H and Guan W:
Identification of circulating microRNAs as novel potential
biomarkers for gastric cancer detection: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 59:911–919. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rao M, Zhu Y, Zhou Y, Cong X and Feng L:
MicroRNA-122 inhibits proliferation and invasion in gastric cancer
by targeting CREB1. Am J Cancer Res. 7:323–333. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cheng J, Chen Y, Zhao P, Li N, Lu J, Li J,
Liu Z, Lv Y and Huang C: Dysregulation of miR-638 in hepatocellular
carcinoma and its clinical significance. Oncol Lett. 13:3859–3865.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Maia D, de Carvalho AC, Horst MA, Carvalho
AL, Scapulatempo-Neto C and Vettore AL: Expression of miR-296-5p as
predictive marker for radiotherapy resistance in early-stage
laryngeal carcinoma. J Transl Med. 13:2622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cao ZG, Li JJ, Yao L, Huang YN, Liu YR, Hu
X, Song CG and Shao ZM: High expression of microRNA-454 is
associated with poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:64900–64909. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu DY, Li XN, Qi Y, Liu DL, Yang Y, Zhao
J, Zhang CY, Wu K and Zhao S: miR-454 promotes the progression of
human non-small cell lung cancer and directly targets PTEN. Biomed
Pharmacother. 81:79–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhou L, Qu YM, Zhao XM and Yue ZD:
Involvement of miR-454 overexpression in the poor prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:825–829.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fan Y, Shi C, Li T and Kuang T:
microRNA-454 shows anti-angiogenic and anti-metastatic activity in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting LRP6. Am J Cancer
Res. 7:139–147. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fan Y, Xu LL, Shi CY, Wei W, Wang DS and
Cai DF: MicroRNA-454 regulates stromal cell derived factor-1 in the
control of the growth of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep.
6:227932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yu L, Gong X, Sun L, Yao H, Lu B and Zhu
L: miR-454 functions as an oncogene by inhibiting CHD5 in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:39225–39234. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wei C, Luo Q, Sun X, Li D, Song H, Li X,
Song J, Hua K and Fang L: MicroRNA-497 induces cell apoptosis by
negatively regulating Bcl-2 protein expression at the
posttranscriptional level in human breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:7729–7739. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Seger R and Krebs EG: The MAPK signaling
cascade. FASEB J. 9:726–735. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li W, Liang J, Zhang Z, Lou H, Zhao L, Xu
Y and Ou R: MicroRNA-329-3p targets MAPK1 to suppress cell
proliferation, migration and invasion in cervical cancer. Oncol
Rep. 37:2743–2750. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yiwei T, Hua H, Hui G, Mao M and Xiang L:
HOTAIR Interacting with MAPK1 regulates ovarian cancer skov3 cell
proliferation, migration, and invasion. Med Sci Monit.
21:1856–1863. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
You B, Yang YL, Xu Z, Dai Y, Liu S, Mao
JH, Tetsu O, Li H, Jablons DM and You L: Inhibition of ERK1/2
down-regulates the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway in human NSCLC
cells. Oncotarget. 6:4357–4368. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kouhkan F, Mobarra N, Soufi-Zomorrod M,
Keramati F, Hosseini Rad SM, Fathi-Roudsari M, Tavakoli R,
Hajarizadeh A, Ziaei S, Lahmi R, et al: MicroRNA-129-1 acts as
tumour suppressor and induces cell cycle arrest of GBM cancer cells
through targeting IGF2BP3 and MAPK1. J Med Genet. 53:24–33. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Tsubaki M, Takeda T, Ogawa N, Sakamoto K,
Shimaoka H, Fujita A, Itoh T, Imano M, Ishizaka T, Satou T and
Nishida S: Overexpression of survivin via activation of ERK1/2,
Akt, and NF-κB plays a central role in vincristine resistance in
multiple myeloma cells. Leuk Res. 39:445–452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|