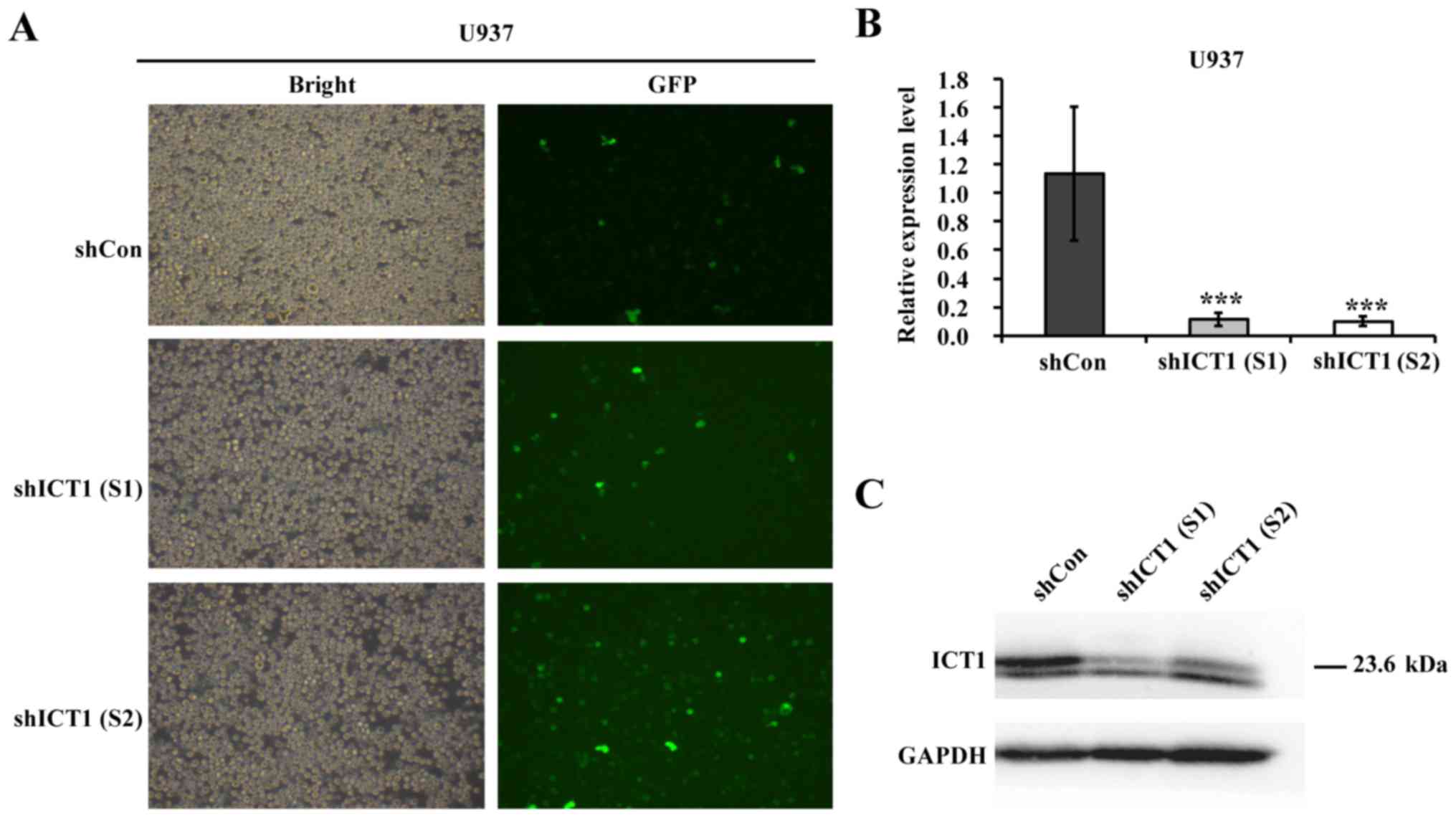
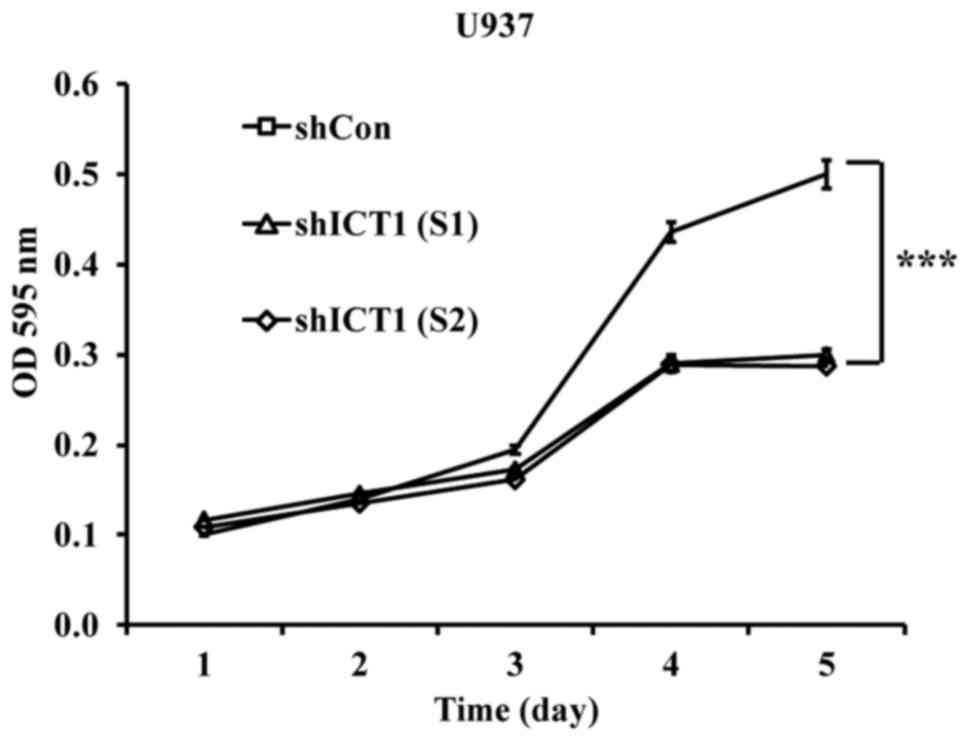
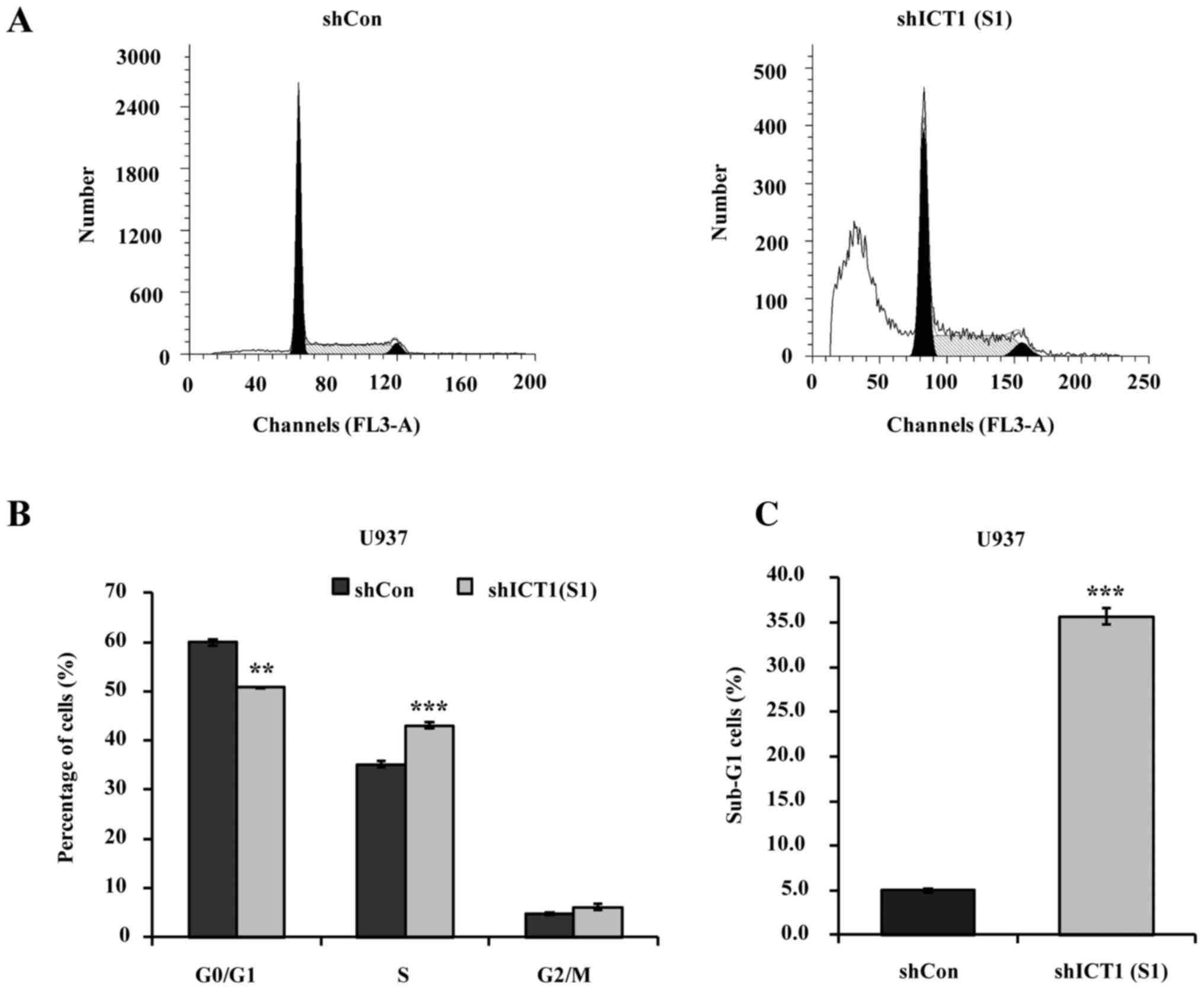
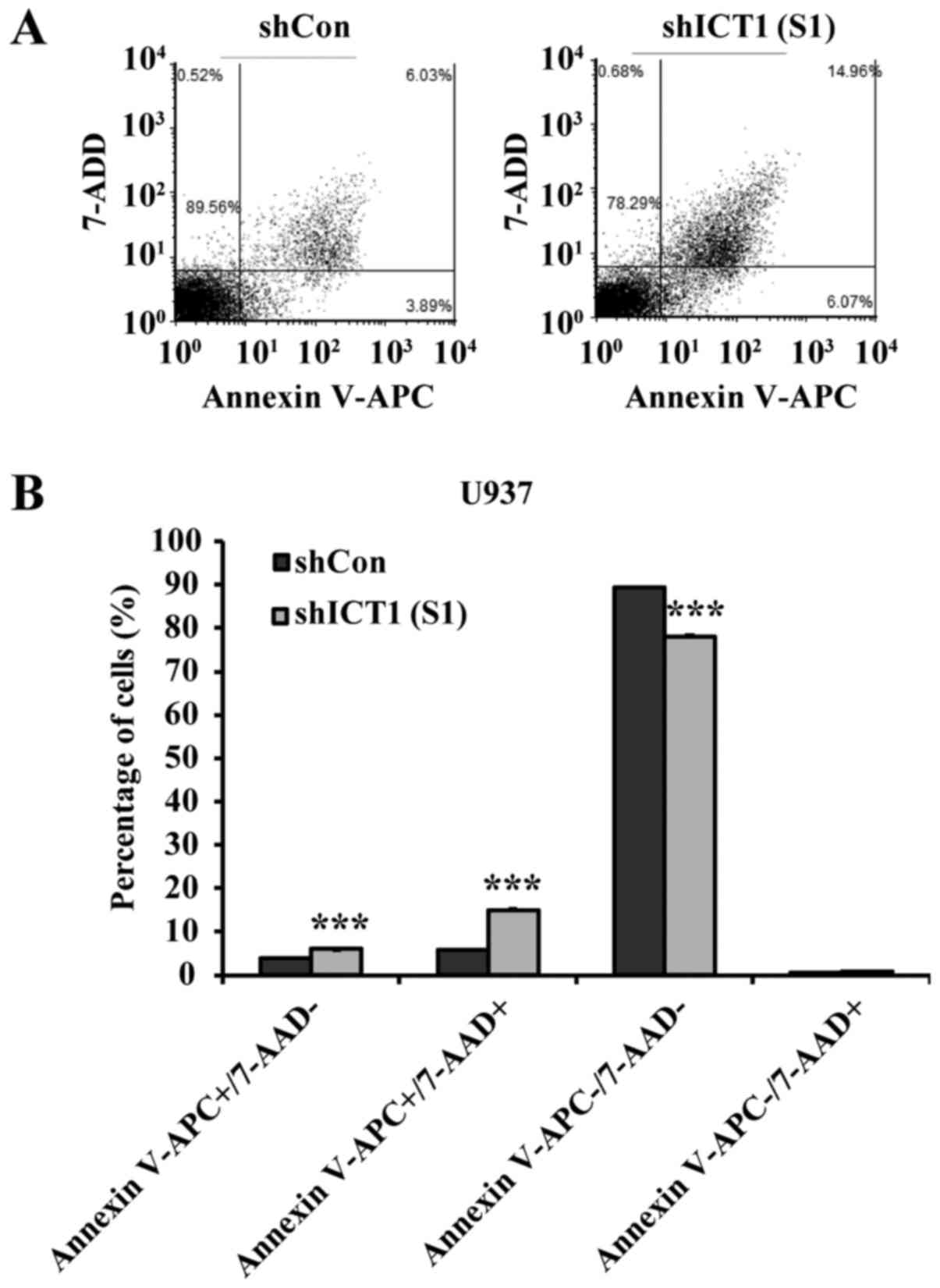
|
1
|
Mi S, Lu J, Sun M, Li Z, Zhang H, Neilly
MB, Wang Y, Qian Z, Jin J, Zhang Y, et al: MicroRNA expression
signatures accurately discriminate acute lymphoblastic leukemia
from acute myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:pp.
19971–19976. 2007; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Golub TR, Slonim DK, Tamayo P, Huard C,
Gaasenbeek M, Mesirov JP, Coller H, Loh ML, Downing JR, Caligiuri
MA, et al: Molecular classification of cancer: Class discovery and
class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science.
286:531–537. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cortes JE and Kantarjian HM: Acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. A comprehensive review with emphasis on
biology and therapy. Cancer. 76:2393–2417. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Büchner T, Berdel WE, Haferlach C,
Haferlach T, Schnittger S, Müller-Tidow C, Braess J, Spiekermann K,
Kienast J, Staib P, et al: Age-related risk profile and
chemotherapy dose response in acute myeloid leukemia: A study by
the German Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol.
27:61–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ziogas DC, Voulgarelis M and Zintzaras E:
A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of
induction treatments in acute myeloid leukemia in the elderly. Clin
Ther. 33:254–279. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Radtke S, Zolk O, Renner B, Paulides M,
Zimmermann M, Möricke A, Stanulla M, Schrappe M and Langer T:
Germline genetic variations in methotrexate candidate genes are
associated with pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and outcome in
childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 121:5145–5153. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang JJ, Cheng C, Devidas M, Cao X,
Campana D, Yang W, Fan Y, Neale G, Cox N, Scheet P, et al:
Genome-wide association study identifies germline polymorphisms
associated with relapse of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Blood. 120:4197–4204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Locatelli F, Zecca M, Rondelli R, Bonetti
F, Dini G, Prete A, Messina C, Uderzo C, Ripaldi M, Porta F, et al:
Graft versus host disease prophylaxis with low-dose cyclosporine-A
reduces the risk of relapse in children with acute leukemia given
HLA-identical sibling bone marrow transplantation: results of a
randomized trial. Blood. 95:1572–1579. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
McCormick F: Cancer gene therapy: Fringe
or cutting edge? Nat Rev Cancer. 1:130–141. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wierda WG, Cantwell MJ, Woods SJ, Rassenti
LZ, Prussak CE and Kipps TJ: CD40-ligand (CD154) gene therapy for
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. 96:2917–2924. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Renner AG, Dos Santos C, Recher C, Bailly
C, Créancier L, Kruczynski A, Payrastre B and Manenti S: Polo-like
kinase 1 is overexpressed in acute myeloid leukemia and its
inhibition preferentially targets the proliferation of leukemic
cells. Blood. 114:659–662. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wilda M, Fuchs U, Wössmann W and Borkhardt
A: Killing of leukemic cells with a BCR/ABL fusion gene by RNA
interference (RNAi). Oncogene. 21:5716–5724. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Handa Y, Hikawa Y, Tochio N, Kogure H,
Inoue M, Koshiba S, Güntert P, Inoue Y, Kigawa T, Yokoyama S, et
al: Solution structure of the catalytic domain of the mitochondrial
protein ICT1 that is essential for cell vitality. J Mol Biol.
404:260–273. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Richter R, Rorbach J, Pajak A, Smith PM,
Wessels HJ, Huynen MA, Smeitink JA, Lightowlers RN and
Chrzanowska-Lightowlers ZM: A functional peptidyl-tRNA hydrolase,
ICT1, has been recruited into the human mitochondrial ribosome.
EMBO J. 29:1116–1125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Akabane S, Ueda T, Nierhaus KH and
Takeuchi N: Ribosome rescue and translation termination at
non-standard stop codons by ICT1 in mammalian mitochondria. PLoS
Genet. 10:e10046162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie R, Zhang Y, Shen C, Cao X, Gu S and
Che X: Knockdown of immature colon carcinoma transcript-1 inhibits
proliferation of glioblastoma multiforme cells through Gap
2/mitotic phase arrest. Onco Targets Ther. 8:1119–1127.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aleman MJ, DeYoung MP, Tress M, Keating P,
Perry GW and Narayanan R: Inhibition of Single Minded 2 gene
expression mediates tumor-selective apoptosis and differentiation
in human colon cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:pp.
12765–12770. 2005; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mitchison JM: The Biology of The Cell
Cycle. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: pp. 3131971
|
|
19
|
Murray A and Hunt T: The Cell Cycle: An
Introduction. Q Rev Biol. 2:147–163. 1995.
|
|
20
|
Buckley MF, Sweeney KJ, Hamilton JA, Sini
RL, Manning DL, Nicholson RI, deFazio A, Watts CK, Musgrove EA and
Sutherland RL: Expression and amplification of cyclin genes in
human breast cancer. Oncogene. 8:2127–2133. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Murray AW, Solomon MJ and Kirschner MW:
The role of cyclin synthesis and degradation in the control of
maturation promoting factor activity. Nature. 339:280–286. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chaudhry HW, Dashoush NH, Tang H, Zhang L,
Wang X, Wu EX and Wolgemuth DJ: Cyclin A2 mediates cardiomyocyte
mitosis in the postmitotic myocardium. J Biol Chem.
279:35858–35866. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bendris N, Lemmers B, Blanchard JM and
Arsic N: Cyclin A2 mutagenesis analysis: A new insight into CDK
activation and cellular localization requirements. PLoS One.
6:e228792011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tiwari S, Roel C, Wills R, Casinelli G,
Tanwir M, Takane KK and Fiaschi-Taesch NM: Early and late G1/S
cyclins and Cdks act complementarily to enhance authentic human
β-cell proliferation and expansion. Diabetes. 64:3485–3498. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chang MW, Barr E, Lu MM, Barton K and
Leiden JM: Adenovirus-mediated over-expression of the
cyclin/cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p21 inhibits vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointima formation in the rat
carotid artery model of balloon angioplasty. J Clin Invest.
96:2260–2268. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Strasser A, O'Connor L and Dixit VM:
Apoptosis signaling. Annu Rev Biochem. 69:217–245. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Waterhouse NJ, Goldstein JC, von Ahsen O,
Schuler M, Newmeyer DD and Green DR: Cytochrome c maintains
mitochondrial transmembrane potential and ATP generation after
outer mitochondrial membrane permeabilization during the apoptotic
process. J Cell Biol. 153:319–328. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu X, Zou H, Slaughter C and Wang X: DFF,
a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to
trigger DNA fragmentation during apoptosis. Cell. 89:175–184. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huot J, Houle F, Spitz DR and Landry J:
HSP27 phosphorylation-mediated resistance against actin
fragmentation and cell death induced by oxidative stress. Cancer
Res. 56:273–279. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garrido C, Schmitt E, Candé C, Vahsen N,
Parcellier A and Kroemer G: HSP27 and HSP70: Potentially oncogenic
apoptosis inhibitors. Cell Cycle. 2:579–584. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yasuda E, Kumada T, Takai S, Ishisaki A,
Noda T, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Yoshimi N, Kato K, Toyoda H,
Kaneoka Y, et al: Attenuated phosphorylation of heat shock protein
27 correlates with tumor progression in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 337:337–342.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Landry J, Lambert H, Zhou M, Lavoie JN,
Hickey E, Weber LA and Anderson CW: Human HSP27 is phosphorylated
at serines 78 and 82 by heat shock and mitogen-activated kinases
that recognize the same amino acid motif as S6 kinase II. J Biol
Chem. 267:794–803. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|