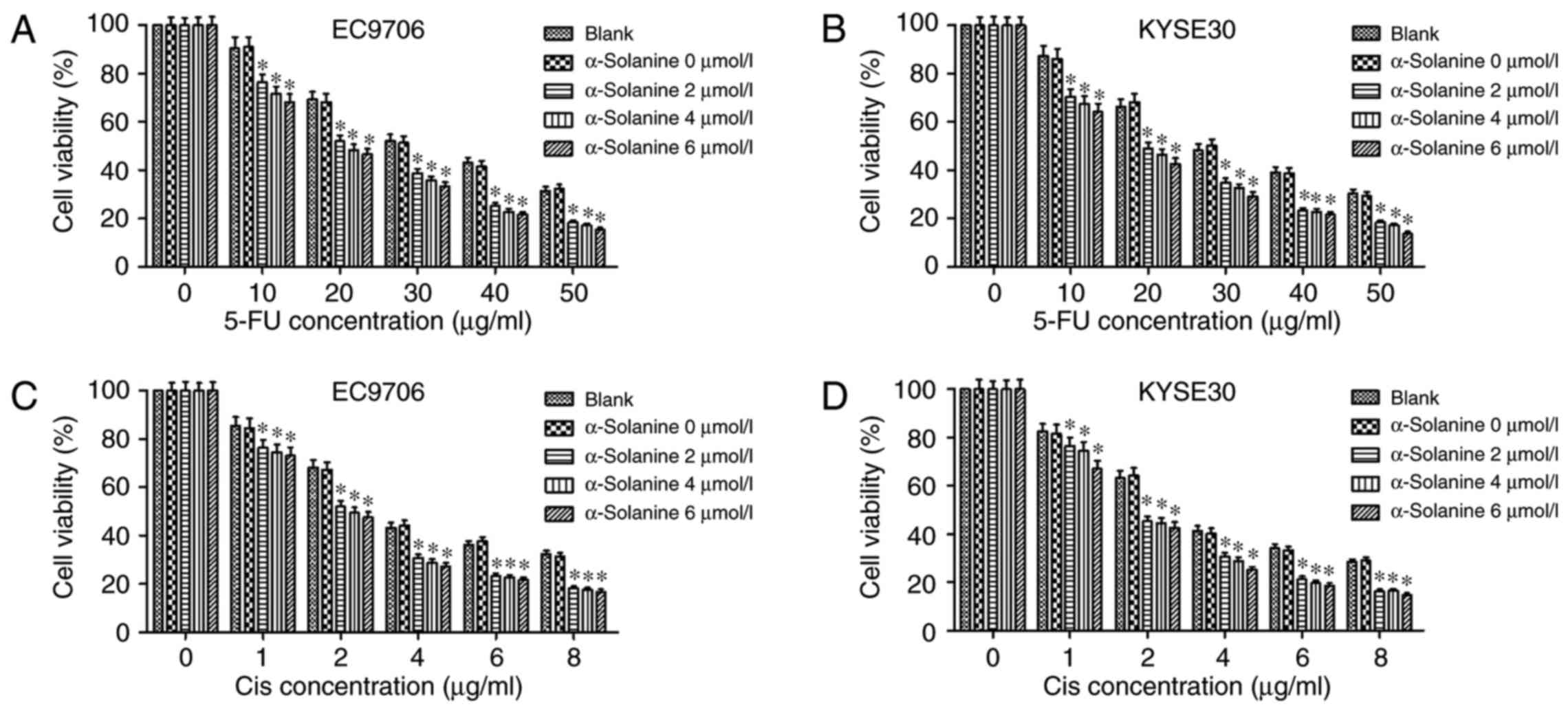
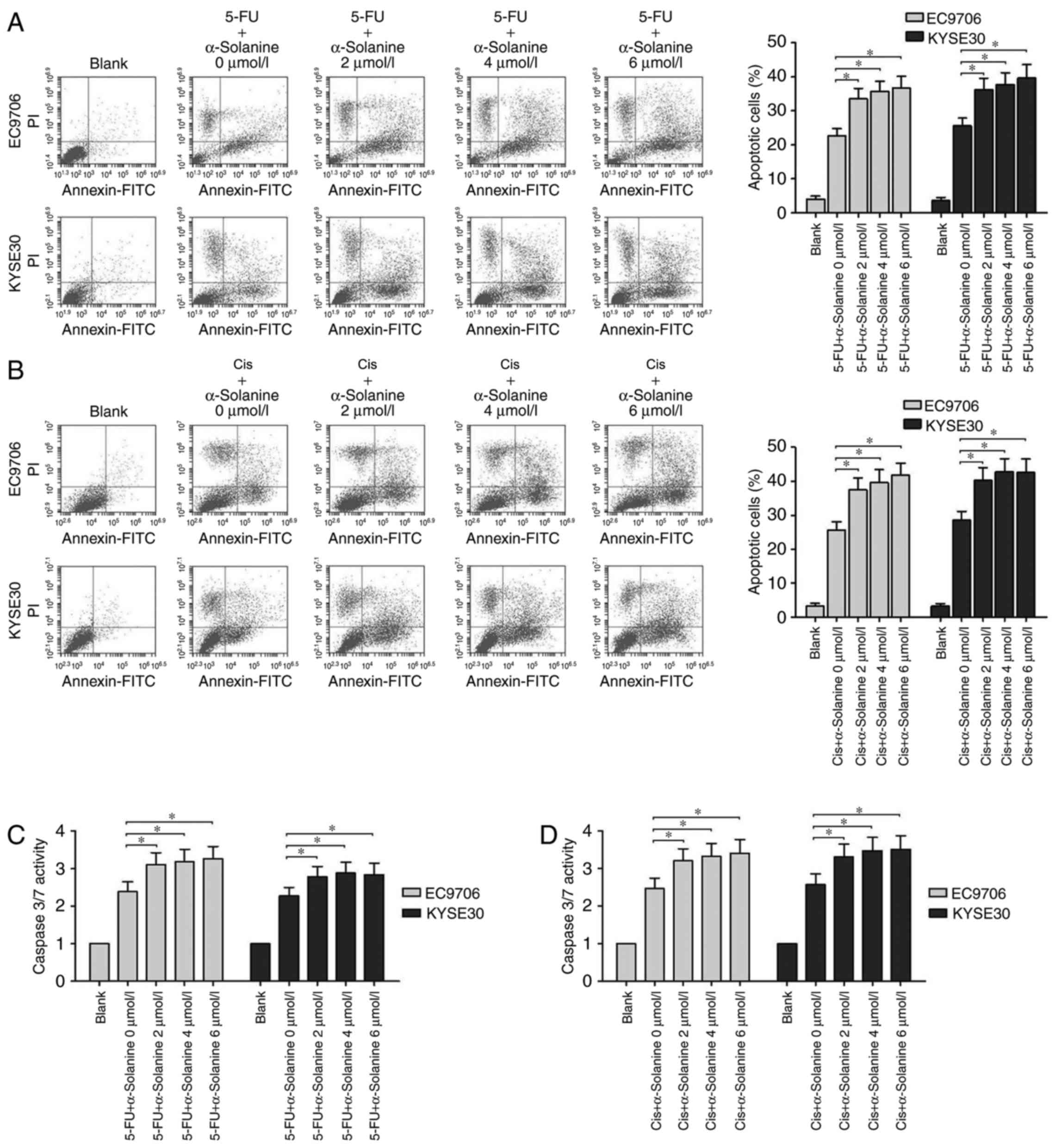
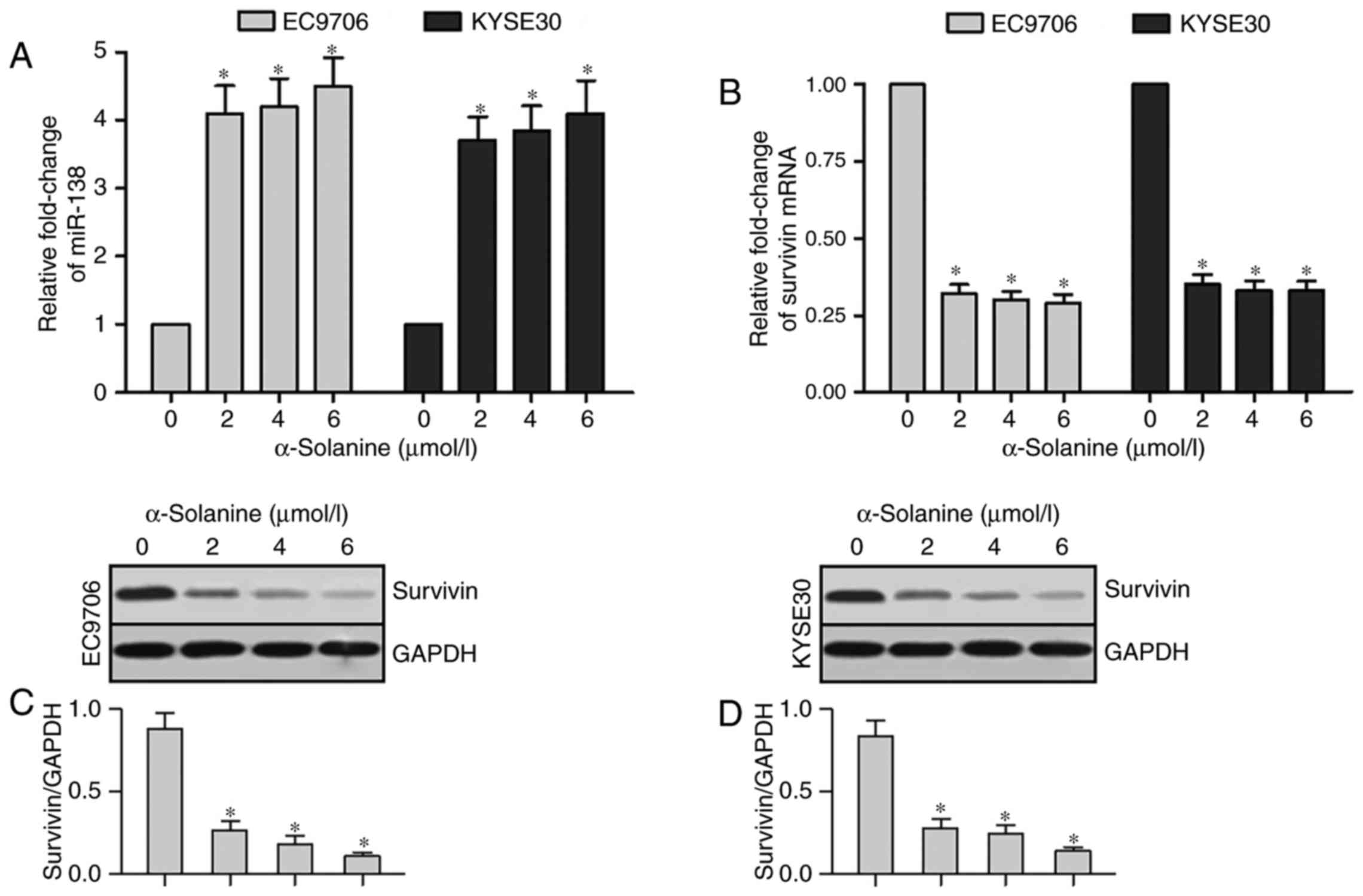
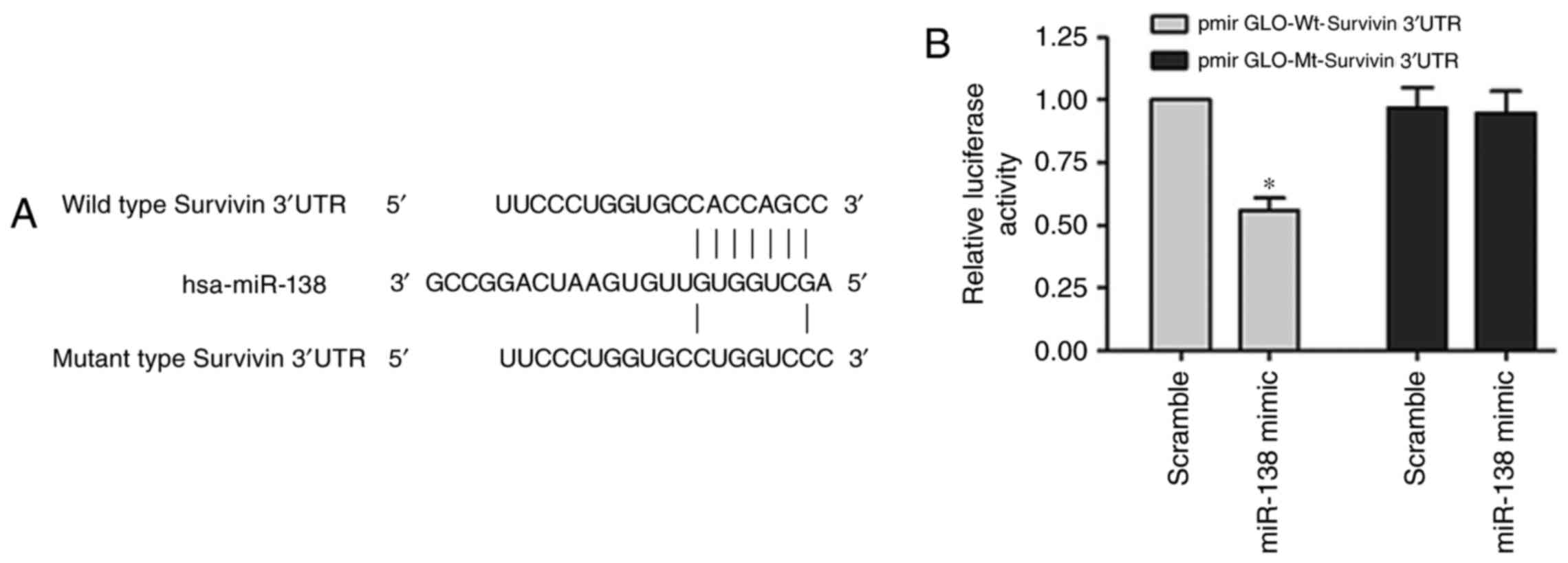
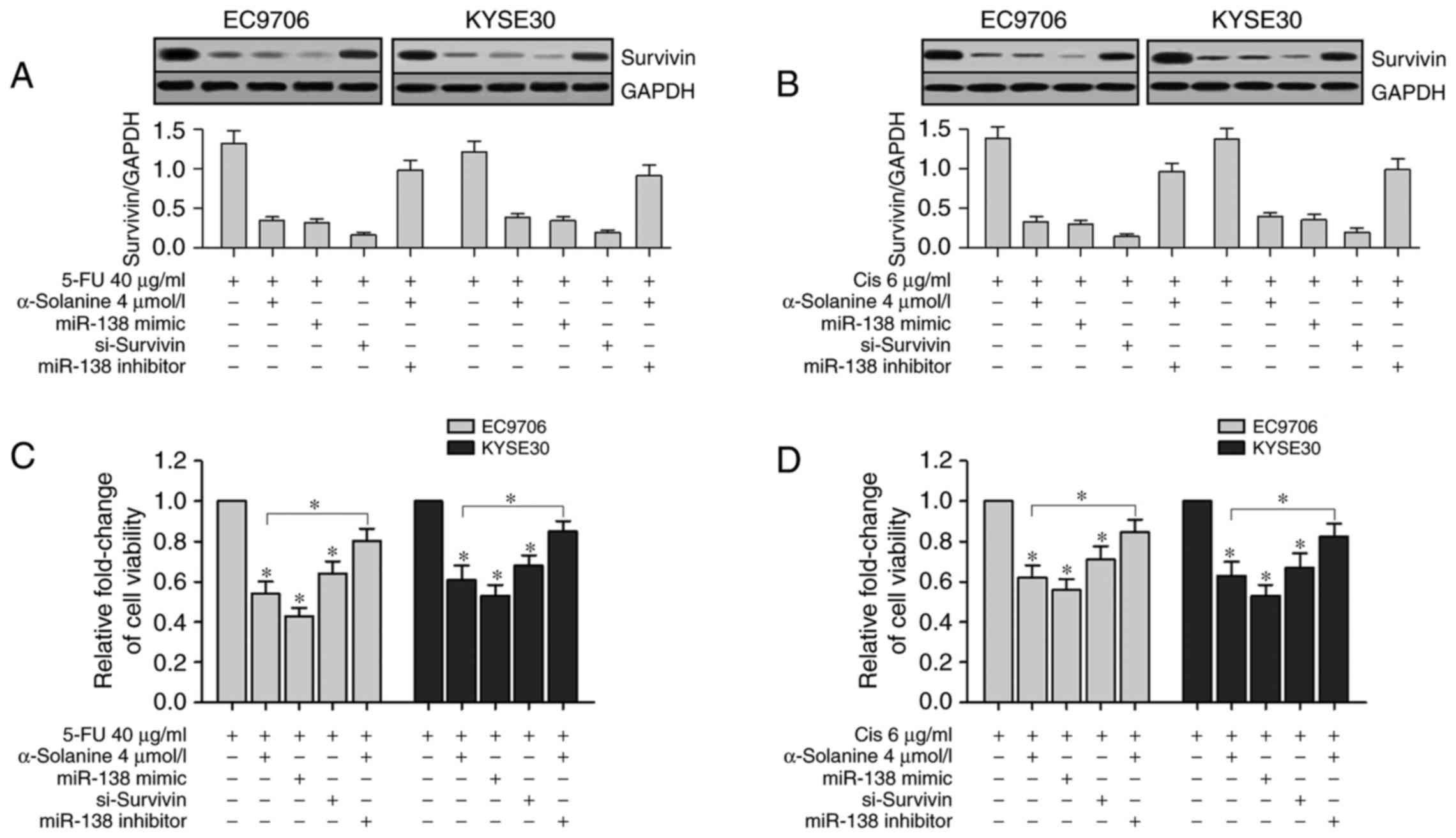
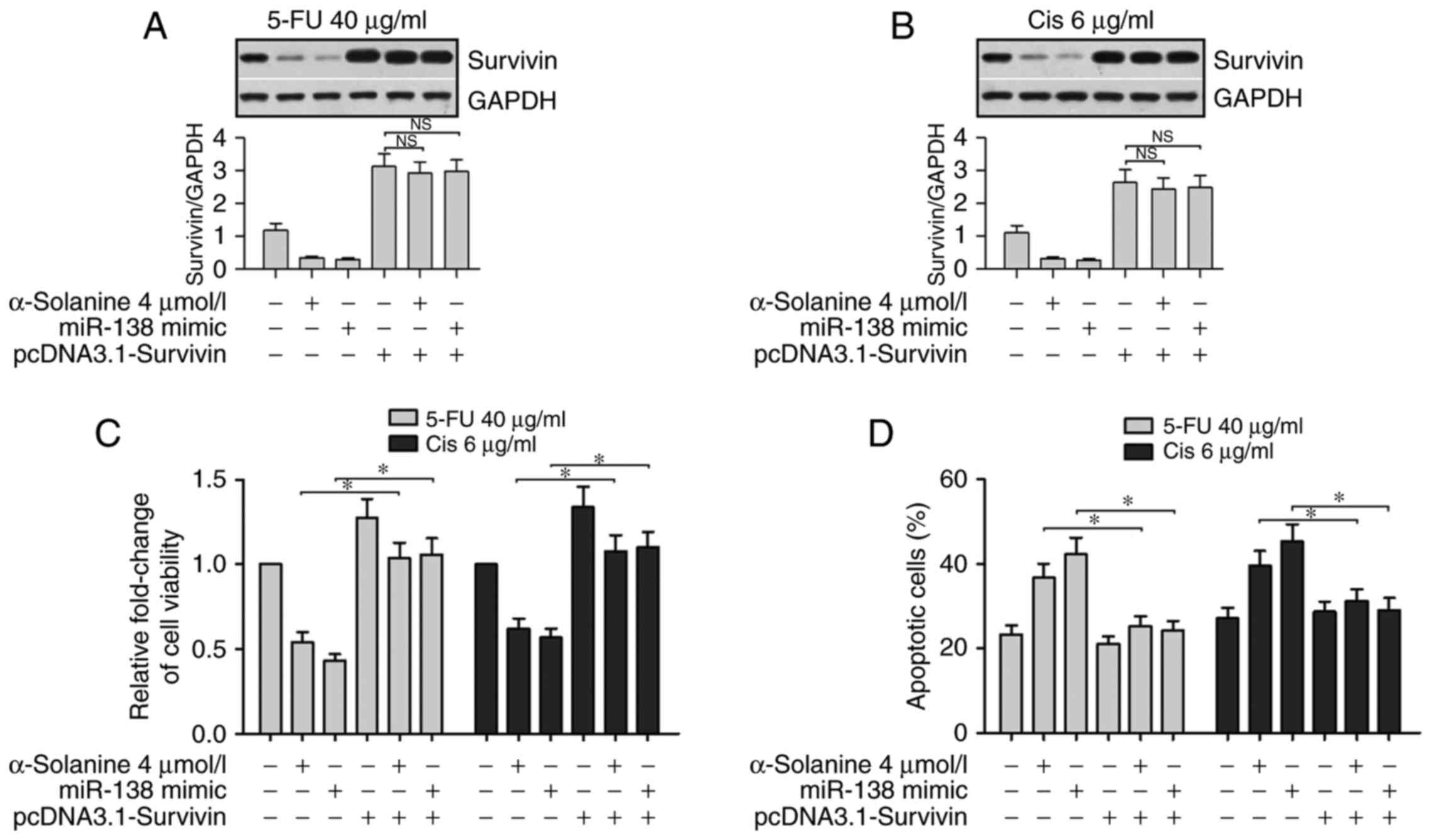
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rustgi AK and El-Serag HB: Esophageal
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 371:2499–2509. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
He SM, Li R, Kanwar JR and Zhou SF:
Structural and functional properties of human multidrug resistance
protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1). Curr Med Chem. 18:439–481. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, Scudiero DA,
Vigna N, Oltersdorf T and Reed JC: IAP-family protein survivin
inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax,
caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 58:5315–5320.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rathore R, McCallum JE, Varghese E, Florea
AM and Büsselberg D: Overcoming chemotherapy drug resistance by
targeting inhibitors of apoptosis proteins (IAPs). Apoptosis.
22:898–919. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pennati M, Folini M and Zaffaroni N:
Targeting survivin in cancer therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
12:463–476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ye Q, Cai W, Zheng Y, Evers BM and She QB:
ERK and AKT signaling cooperate to translationally regulate
survivin expression for metastatic progression of colorectal
cancer. Oncogene. 33:1828–1839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Glienke W, Maute L, Wicht J and Bergmann
L: The dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BGT226 induces cell cycle
arrest and regulates Survivin gene expression in human pancreatic
cancer cell lines. Tumour Biol. 33:757–765. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ryan BM, Konecny GE, Kahlert S, Wang HJ,
Untch M, Meng G, Pegram MD, Podratz KC, Crown J, Slamon DJ, et al:
Survivin expression in breast cancer predicts clinical outcome and
is associated with HER2, VEGF, urokinase plasminogen activator and
PAI-1. Ann Oncol. 17:597–604. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rosato A, Pivetta M, Parenti A, Iaderosa
GA, Zoso A, Milan G, Mandruzzato S, Del Bianco P, Ruol A, Zaninotto
G, et al: Survivin in esophageal cancer: An accurate prognostic
marker for squamous cell carcinoma but not adenocarcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 119:1717–1722. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Singh N, Krishnakumar S, Kanwar RK, Cheung
CH and Kanwar JR: Clinical aspects for survivin: A crucial molecule
for targeting drug-resistant cancers. Drug Discov Today.
20:578–587. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qian Y, Ma J, Guo X, Sun J, Yu Y, Cao B,
Zhang L, Ding X, Huang J and Shao JF: Curcumin enhances the
radiosensitivity of U87 cells by inducing DUSP-2 up-regulation.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:1381–1393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang SX, Qiu QH, Chen WB, Liang CH and
Huang B: Celecoxib enhances radiosensitivity via induction of
G2-M phase arrest and apoptosis in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 33:1484–1497. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang BF, Wang XJ, Kang HF, Bai MH, Guan
HT, Wang ZW, Zan Y, Song LQ, Min WL, Lin S, et al: Saikosaponin-D
enhances radiosensitivity of hepatoma cells under hypoxic
conditions by inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 33:37–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Punjabi S, Cook LJ, Kersey P, Marks R and
Cerio R: Solasodine glycoalkaloids: A novel topical therapy for
basal cell carcinoma. A double-blind, randomized,
placebo-controlled, parallel group, multicenter study. Int J
Dermatol. 47:78–82. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Friedman M, Lee KR, Kim HJ, Lee IS and
Kozukue N: Anticarcinogenic effects of glycoalkaloids from potatoes
against human cervical, liver, lymphoma, and stomach cancer cells.
J Agric Food Chem. 53:6162–6169. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee KR, Kozukue N, Han JS, Park JH, Chang
EY, Baek EJ, Chang JS and Friedman M: Glycoalkaloids and
metabolites inhibit the growth of human colon (HT29) and liver
(HepG2) cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem. 52:2832–2839. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lv C, Kong H, Dong G, Liu L, Tong K, Sun
H, Chen B, Zhang C and Zhou M: Antitumor efficacy of α-solanine
against pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
9:e878682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mohsenikia M, Alizadeh AM, Khodayari S,
Khodayari H, Kouhpayeh SA, Karimi A, Zamani M, Azizian S and
Mohagheghi MA: The protective and therapeutic effects of
alpha-solanine on mice breast cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 718:1–9.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Wu J, Guo W, Sun Q, Chen X, Zang
W, Dong Z and Zhao G: α-solanine modulates the radiosensitivity of
esophageal cancer cells by inducing microRNA 138 expression. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 39:996–1010. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
van Sleen Y, Wang Q, van der Geest KSM,
Westra J, Abdulahad WH, Heeringa P, Boots AMH and Brouwer E:
Involvement of Monocyte Subsets in the Immunopathology of Giant
Cell Arteritis. Sci Rep. 7:65532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meng XQ, Zhang W, Zhang F, Yin SY, Xie HY,
Zhou L and Zheng SS: Solanine-induced reactive oxygen species
inhibit the growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells.
Oncol Lett. 11:2145–2151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wen Z, Huang C, Xu Y, Xiao Y, Tang L, Dai
J, Sun H, Chen B and Zhou M: α-solanine inhibits vascular
endothelial growth factor expression by down-regulating the
ERK1/2-HIF-1α and STAT3 signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol.
771:93–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang F, Yang R, Zhang G, Cheng R, Bai Y,
Zhao H, Lu X, Li H, Chen S, Li J, et al: Anticancer function of
α-solanine in lung adenocarcinoma cells by inducing microRNA-138
expression. Tumour Biol. 37:6437–6446. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu Z, Tang J, Wang J, Duan G, Zhou L and
Zhou X: miR-138 acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting EZH2 and
enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells. PLoS
One. 11:e01500262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang B, Mu W, Wang J, Lu J, Jiang S, Li
L, Xu H and Tian H: MicroRNA-138 functions as a tumor suppressor in
osteosarcoma by targeting differentiated embryonic chondrocyte gene
2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ye XW, Yu H, Jin YK, Jing XT, Xu M, Wan ZF
and Zhang XY: miR-138 inhibits proliferation by targeting
3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 in non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Clin Respir J. 9:27–33. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang J, Liu D, Feng Z, Mao J, Zhang C, Lu
Y, Li J, Zhang Q, Li Q and Li L: MicroRNA-138 modulates metastasis
and EMT in breast cancer cells by targeting vimentin. Biomed
Pharmacother. 77:135–141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu X, Wang C, Chen Z, Jin Y, Wang Y,
Kolokythas A, Dai Y and Zhou X: MicroRNA-138 suppresses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma cell
lines. Biochem J. 440:23–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao X, Yang L, Hu J and Ruan J: miR-138
might reverse multidrug resistance of leukemia cells. Leuk Res.
34:1078–1082. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Q, Zhong M, Liu W, Li J, Huang J and
Zheng L: Alterations of microRNAs in cisplatin-resistant human
non-small cell lung cancer cells (A549/DDP). Exp Lung Res.
37:427–434. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Du J, Kelly AE, Funabiki H and Patel DJ:
Structural basis for recognition of H3T3ph and Smac/DIABLO
N-terminal peptides by human Survivin. Structure. 20:185–195. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tanaka C, Uzawa K, Shibahara T, Yokoe H,
Noma H and Tanzawa H: Expression of an inhibitor of apoptosis,
survivin, in oral carcinogenesis. J Dent Res. 82:607–611. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Coumar MS, Tsai FY, Kanwar JR, Sarvagalla
S and Cheung CH: Treat cancers by targeting survivin: Just a dream
or future reality? Cancer Treat Rev. 39:802–811. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|