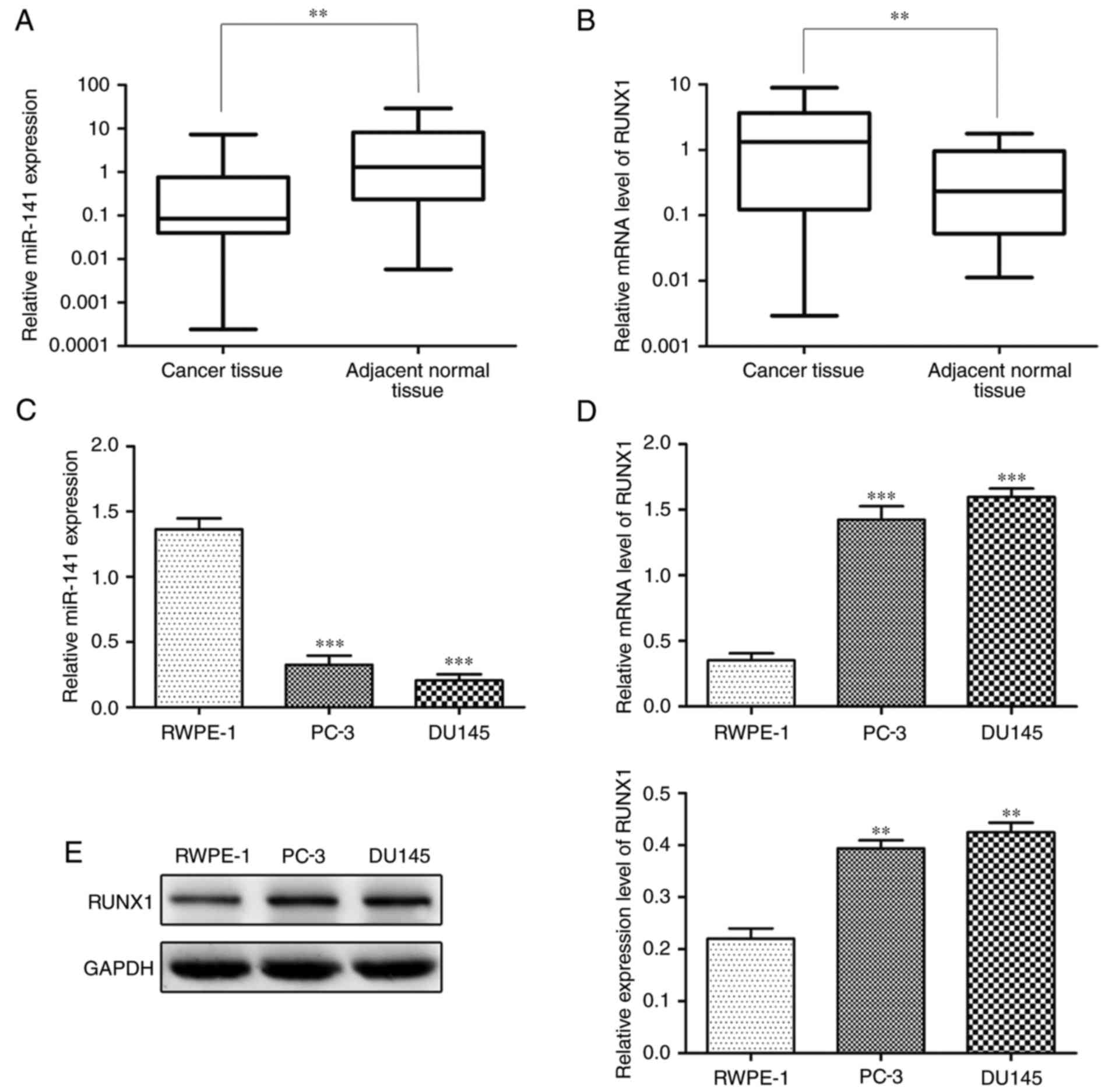
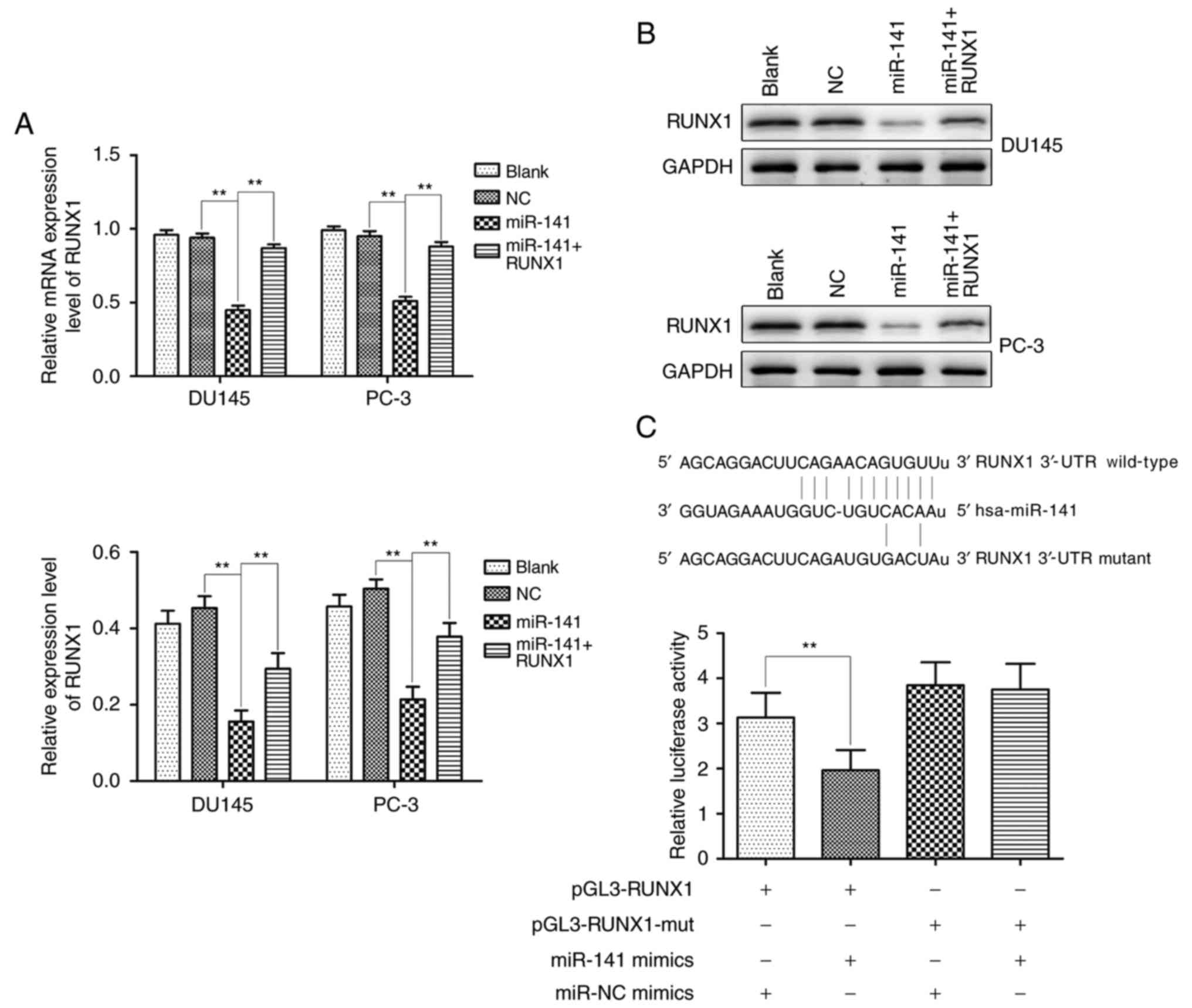
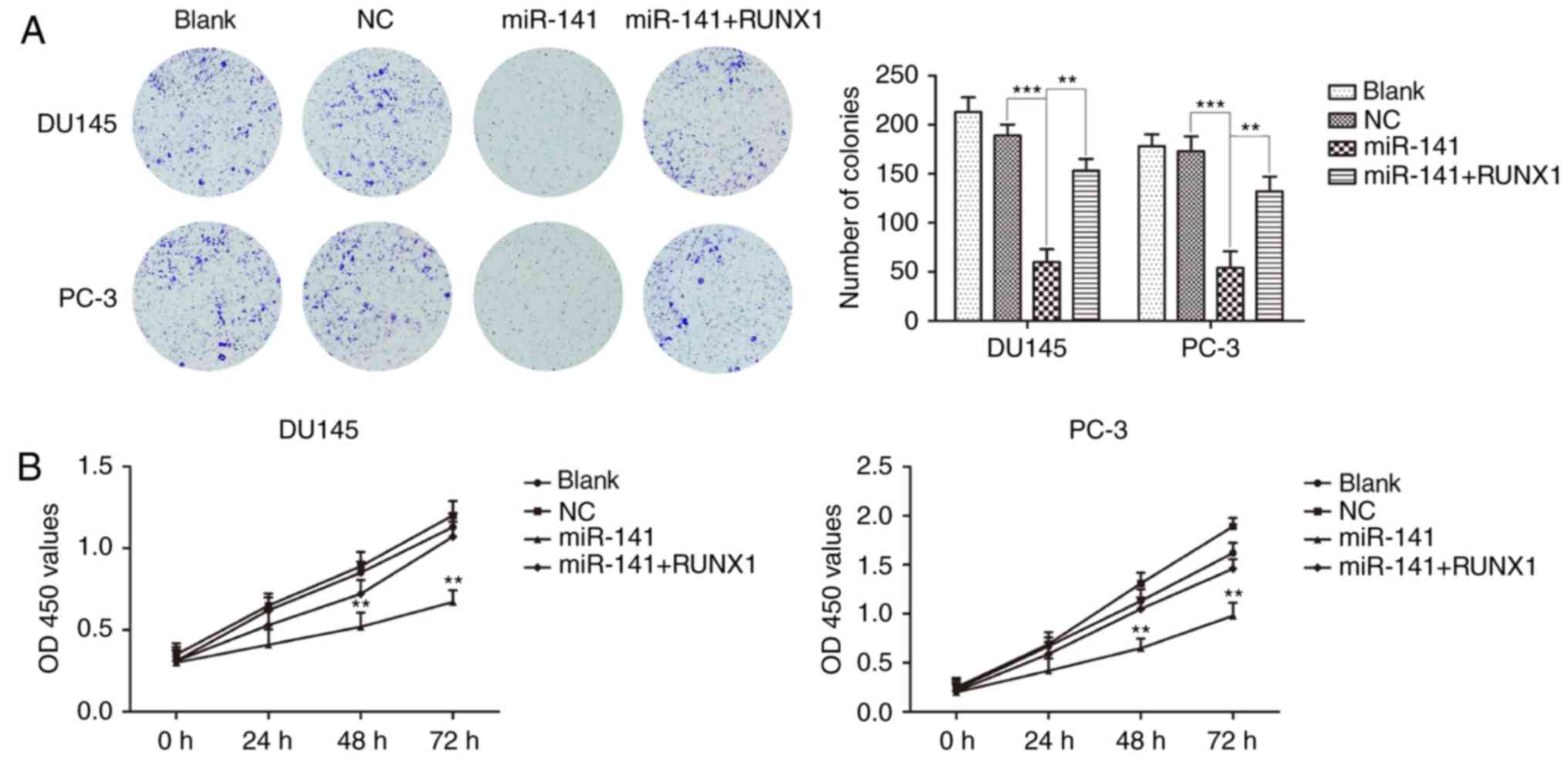
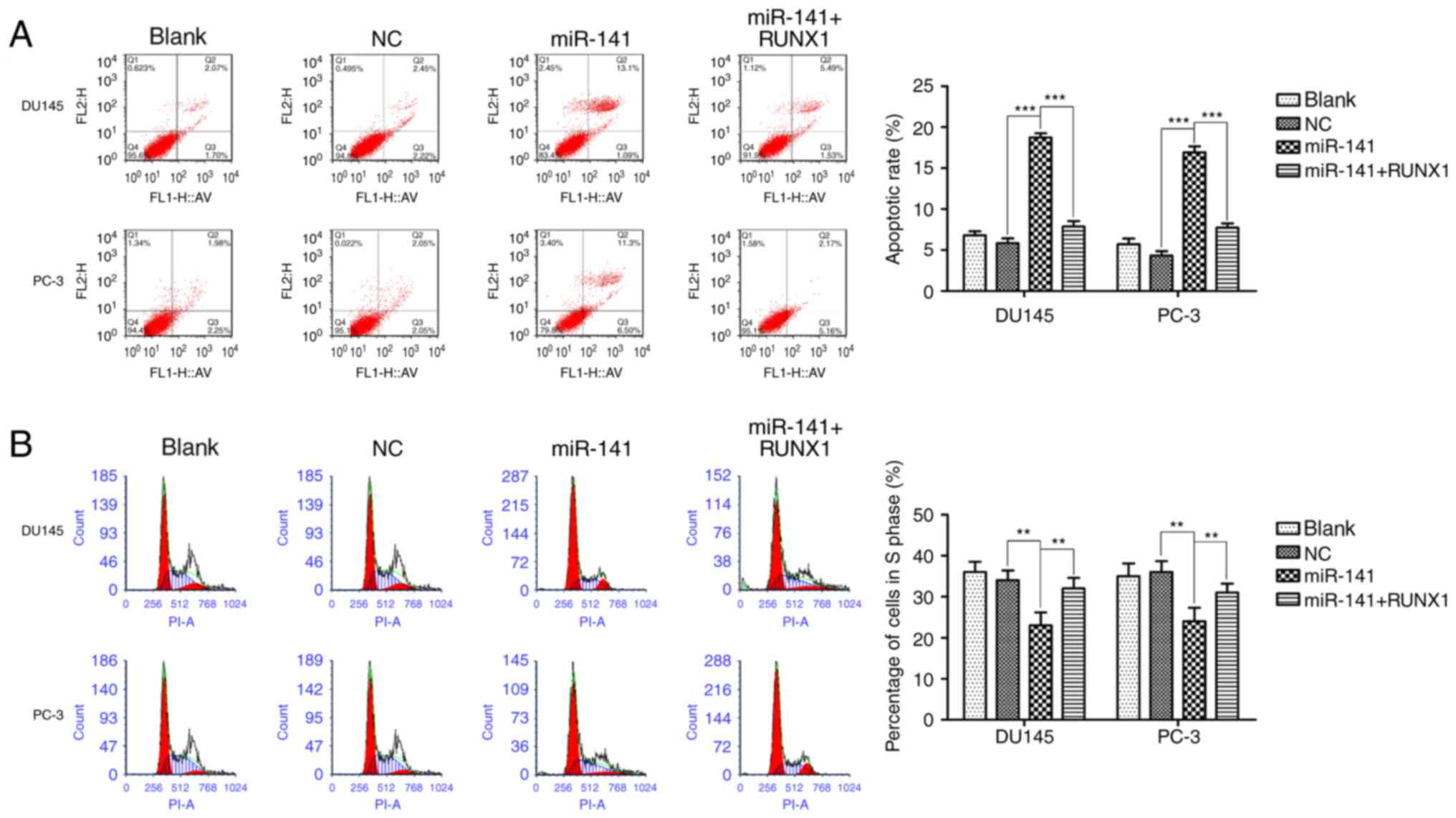
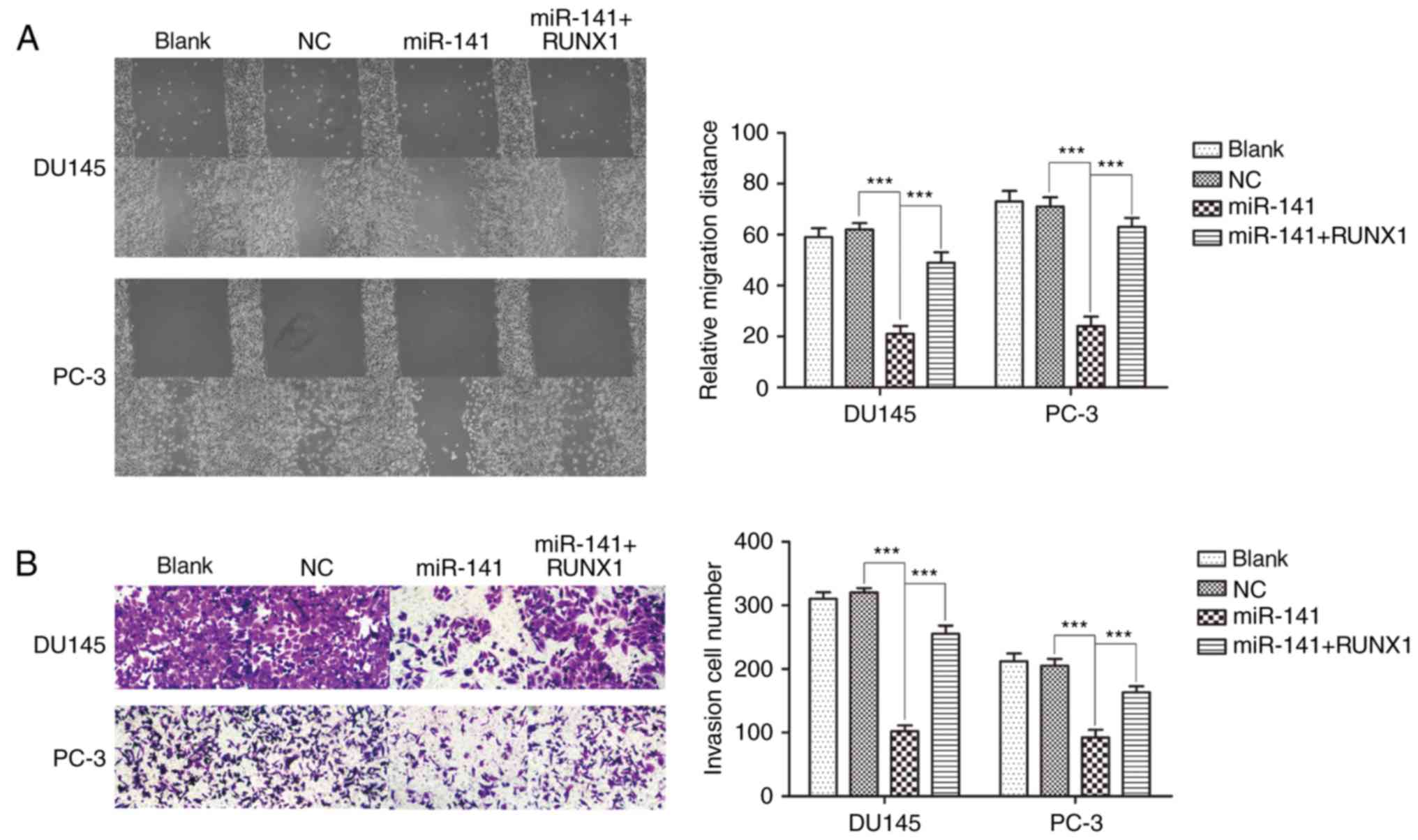
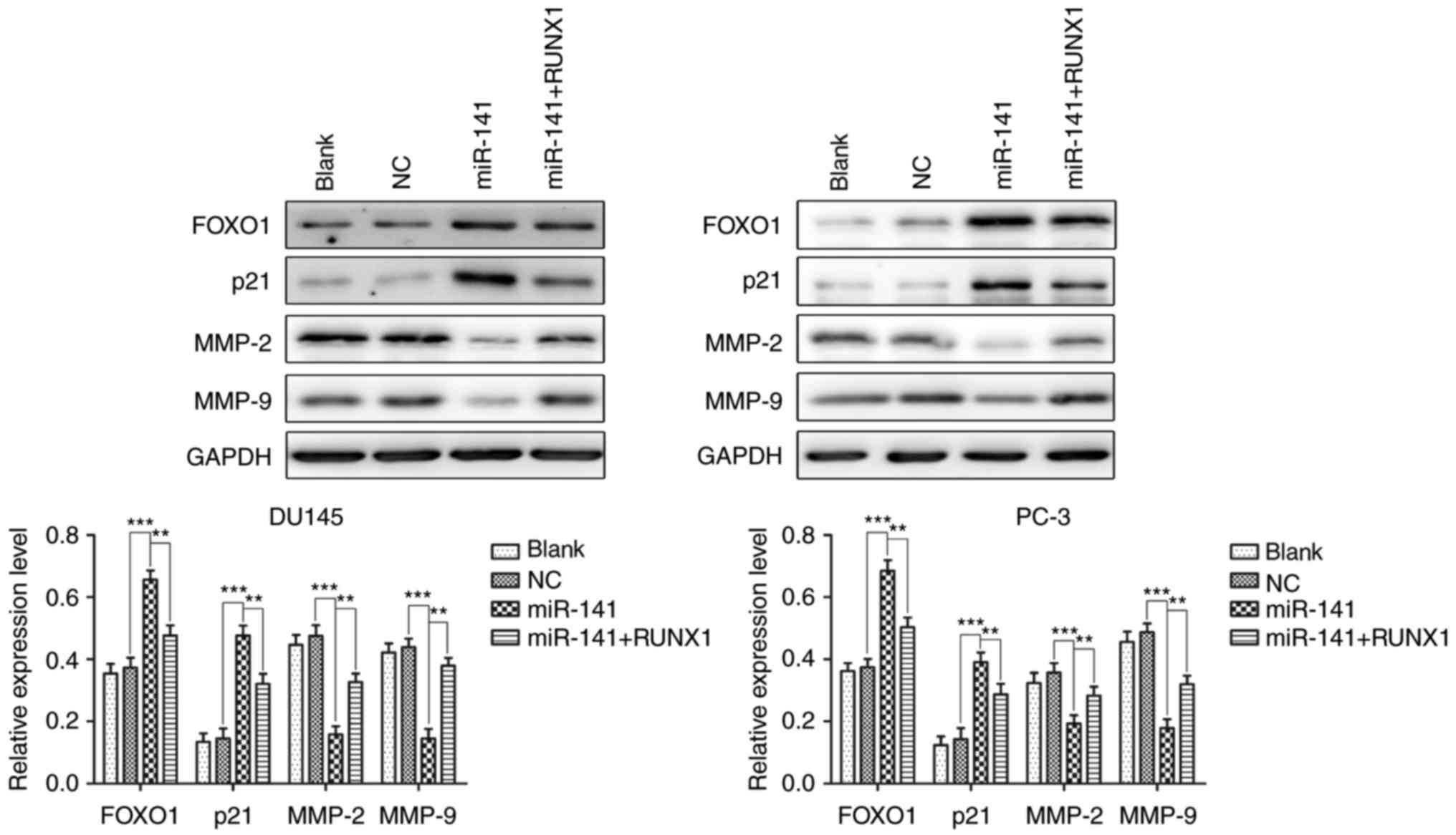
|
1
|
Wei F, Cao C, Xu X and Wang J: Diverse
functions of miR-373 in cancer. J Transl Med. 13:1622015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei W, Leng J, Shao H and Wang W: MiR-1, a
potential predictive biomarker for recurrence in prostate cancer
after radical prostatectomy. Am J Med Sci. 353:315–319. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O'Briant
KC, Allen A, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based
markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:pp.
10513–10518. 2008; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng H, Zhang L, Cogdell DE, Zheng H,
Schetter AJ, Nykter M, Harris CC, Chen K, Hamilton SR and Zhang W:
Circulating plasma MiR-141 Is a novel biomarker for metastatic
colon cancer and predicts poor prognosis. PLoS One. 6:e177452011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Madhavan D, Zucknick M, Wallwiener M, Cuk
K, Modugno C, Scharpff M, Schott S, Heil J, Turchinovich A, Yang R,
et al: Circulating miRNAs as surrogate markers for circulating
tumor cells and prognostic markers in metastatic breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:5972–5982. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Link KA, Chou FS and Mulloy JC: Core
binding factor at the crossroads: Determining the fate of the HSC.
J Cell Physiol. 222:50–56. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lam K and Zhang DE: RUNX1 and RUNX1-ETO:
Roles in hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Front Biosci.
17:1120–1139. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Friedman AD: Cell cycle and developmental
control of hematopoiesis by Runx1. J Cell Physiol. 219:520–524.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Swiers G, de Bruijn M and Speck NA:
Hematopoietic stem cell emergence in the conceptus and the role of
Runx1. Int J Dev Biol. 54:1151–1163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lund AH and van Lohuizen M: RUNX: A
trilogy of cancer genes. Cancer Cell. 1:213–215. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ito Y, Bae SC and Chuang LS: The RUNX
family: Developmental regulators in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
15:81–95. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wotton SF, Blyth K, Kilbey A, Jenkins A,
Terry A, Bernardin-Fried F, Friedman AD, Baxter EW, Neil JC and
Cameron ER: RUNX1 transformation of primary embryonic fibroblasts
is revealed in the absence of p53. Oncogene. 23:5476–5486. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Gan B, Liu D and Paik J: FoxO
family members in cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 12:253–259. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Coomans de Brachène A and Demoulin JB:
FOXO transcription factors in cancer development and therapy. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 73:1159–1172. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Georgakilas AG, Martin OA and Bonner WM:
p21: A two-faced genome guardian. Trends Mol Med. 23:310–319. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Klein T and Bischoff R: Physiology and
pathophysiology of matrix metalloproteases. Amino Acids.
41:271–290. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Overall CM: Molecular determinants of
metalloproteinase substrate specificity: Matrix metalloproteinase
substrate binding domains, modules, and exosites. Mol Biotechnol.
22:51–86. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Foda HD and Zucker S: Matrix
metalloproteinases in cancer invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis.
Drug Discovery Today. 6:478–482. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Martens-Uzunova ES, Jalava SE, Dits NF,
van Leenders GJ, Møller S, Trapman J, Bangma CH, Litman T,
Visakorpi T and Jenster G: Diagnostic and prognostic signatures
from the small non-coding RNA transcriptome in prostate cancer.
Oncogene. 31:978–991. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hulf T, Sibbritt T, Wiklund ED, Patterson
K, Song JZ, Stirzaker C, Qu W, Nair S, Horvath LG, Armstrong NJ, et
al: Epigenetic-induced repression of microRNA-205 is associated
with MED1 activation and a poorer prognosis in localized prostate
cancer. Oncogene. 32:2891–2899. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Santillan M, Devor EJ, Leslie KK, Hunter
SK and Santillan DA: A microRNA expression profile of normal
placental development. Scientific Meeting. 20:pp. 257A2013;
|
|
22
|
Karatas OF, Guzel E, Suer I, Ekici ID,
Caskurlu T, Creighton CJ, Ittmann M and Ozen M: miR-1 and miR-133b
are differentially expressed in patients with recurrent prostate
cancer. PLoS One. 9:e986752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Selth LA, Townley SL, Bert AG, Stricker
PD, Sutherland PD, Horvath LG, Goodall GJ, Butler LM and Tilley WD:
Circulating microRNAs predict biochemical recurrence in prostate
cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 109:6412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nguyen HC, Xie W, Yang M, Hsieh CL, Drouin
S, Lee GS and Kantoff PW: Expression differences of circulating
microRNAs in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer and
low-risk, localized prostate cancer. Prostate. 73:346–354. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li P, Xu T, Zhou X, Liao L, Pang G, Luo W,
Han L, Zhang J, Luo X, Xie X and Zhu K: Downregulation of miRNA-141
in breast cancer cells is associated with cell migration and
invasion: Involvement of ANP32E targeting. Cancer Med. 6:662–672.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nishijima N, Seike M, Soeno C, Chiba M,
Miyanaga A, Noro R, Sugano T, Matsumoto M, Kubota K and Gemma A:
miR-200/ZEB axis regulates sensitivity to nintedanib in non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 48:937–944. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lahat G, Lubezky N, Loewenstein S, Nizri
E, Gan S, Pasmanik-Chor M, Hayman L, Barazowsky E, Ben-Haim M and
Klausner JM: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN) is associated with
high tumor grade and adverse outcomes. Ann Surg Oncol. 21 Suppl
4:S750–S757. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tamagawa S, Beder LB, Hotomi M, Gunduz M,
Yata K, Grenman R and Yamanaka N: Role of miR-200c/miR-141 in the
regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Med. 33:879–886.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu Y, Zhao R, Wang H, Luo Y, Wang X, Niu
W, Zhou Y, Wen Q, Fan S, Li X, et al: miR-141 is involved in
BRD7-mediated cell proliferation and tumor formation through
suppression of the PTEN/AKT pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Cell Death Dis. 7:e21562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ji J, Qin Y, Ren J, Lu C, Wang R, Dai X,
Zhou R, Huang Z, Xu M, Chen M, et al: Mitochondria-related
miR-141-3p contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction in HFD-induced
obesity by inhibiting PTEN. Sci Rep. 5:162622015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jin YY, Chen QJ, Xu K, Ren HT, Bao X, Ma
YN, Wei Y and Ma HB: Involvement of microRNA-141-3p in
5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin chemo-resistance in esophageal
cancer cells via regulation of PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 422:161–170.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mao S, Frank RC, Zhang J, Miyazaki Y and
Nimer SD: Functional and physical interactions between AML1
proteins and an ETS protein, MEF: Implications for the pathogenesis
of t(8;21)-positive leukemias. Mol Cell Biol. 19:3635–3644. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Browne G, Dragon JA, Hong D, Messier TL,
Gordon JA, Farina NH, Boyd JR, VanOudenhove JJ, Perez AW, Zaidi SK,
et al: MicroRNA-378-mediated suppression of Runx1 alleviates the
aggressive phenotype of triple-negative MDA-MB-231 human breast
cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 37:88252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li N, Zhang QY, Zou JL, Li ZW, Tian TT,
Dong B, Liu XJ, Ge S, Zhu Y, Gao J and Shen L: miR-215 promotes
malignant progression of gastric cancer by targeting RUNX1.
Oncotarget. 7:4817–4828. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chiribau CB, Cheng L, Cucoranu IC, Yu YS,
Clempus RE and Sorescu D: FOXO3A regulates peroxiredoxin III
expression in human cardiac fibroblasts. J Biol Chem.
283:8211–8217. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ronnebaum SM and Patterson C: The FoxO
family in cardiac function and dysfunction. Annu Rev Physiol.
72:81–94. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gomis RR, Alarcón C, He W, Wang Q, Seoane
J, Lash A and Massagué J: A FoxO-Smad synexpression group in human
keratinocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:pp. 12747–12752. 2006;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Seoane J, Le HV, Shen L, Anderson SA and
Massagué J: Integration of Smad and Forkhead pathways in the
control of neuroepithelial and glioblastoma cell proliferation.
Cell. 117:211–223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|