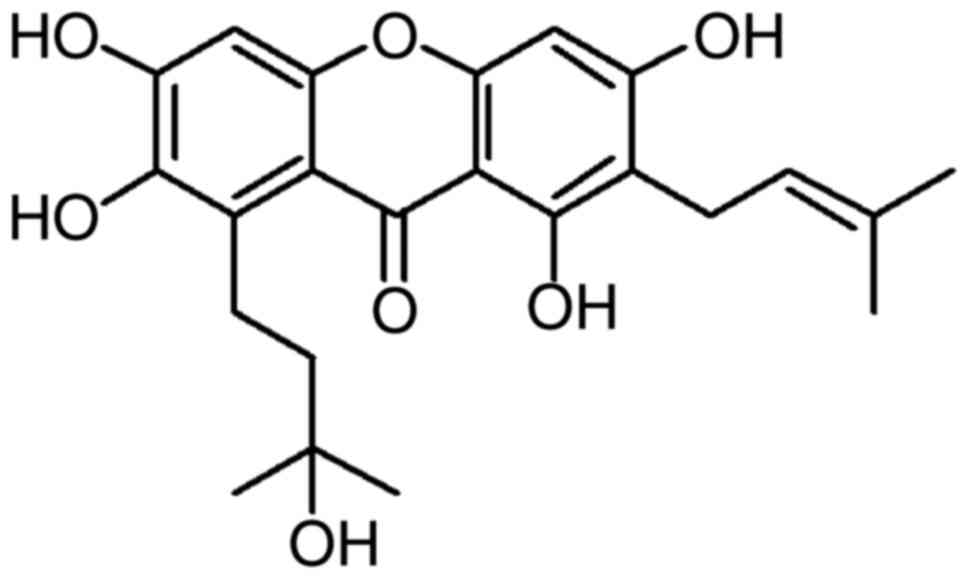
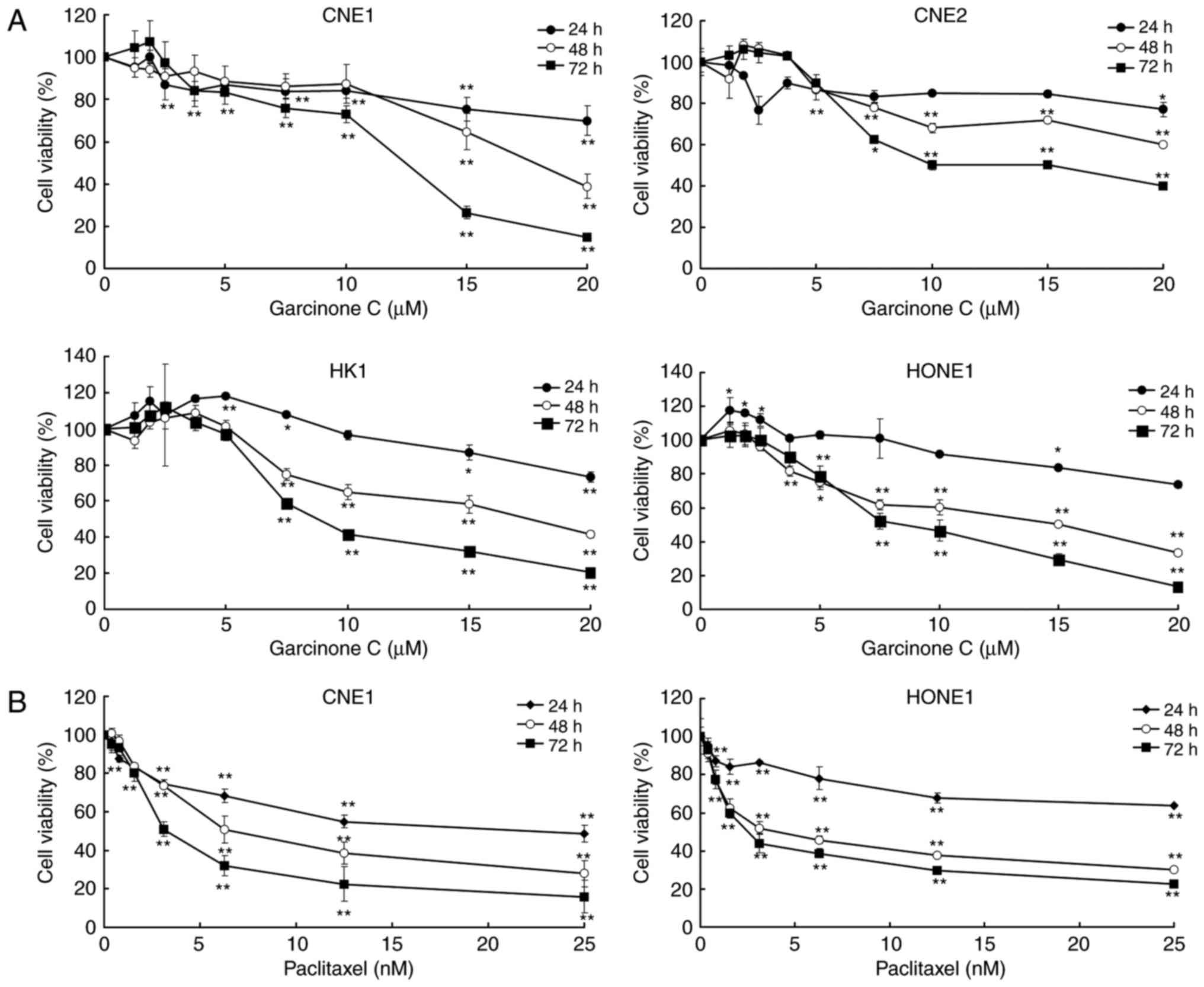
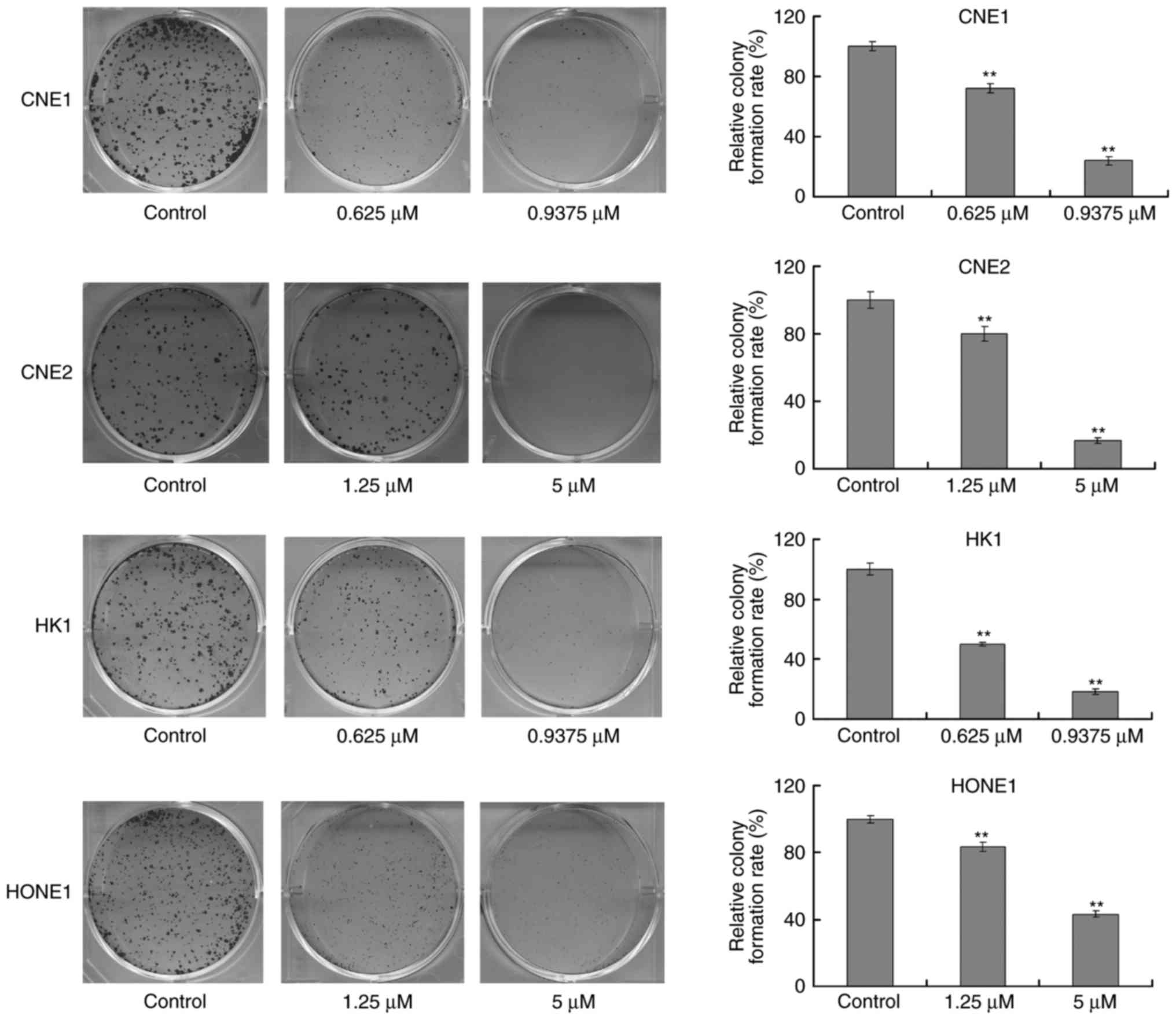
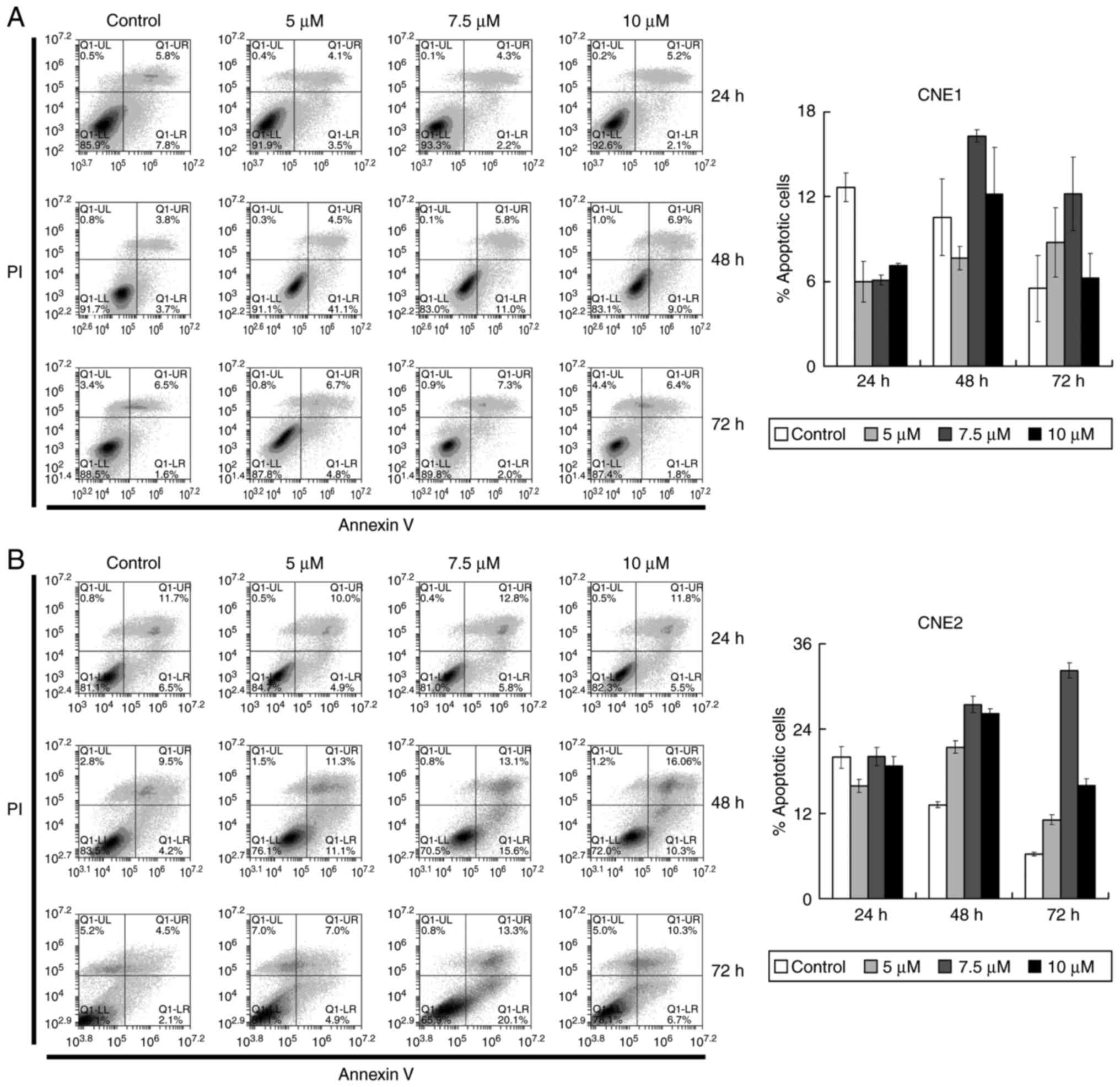
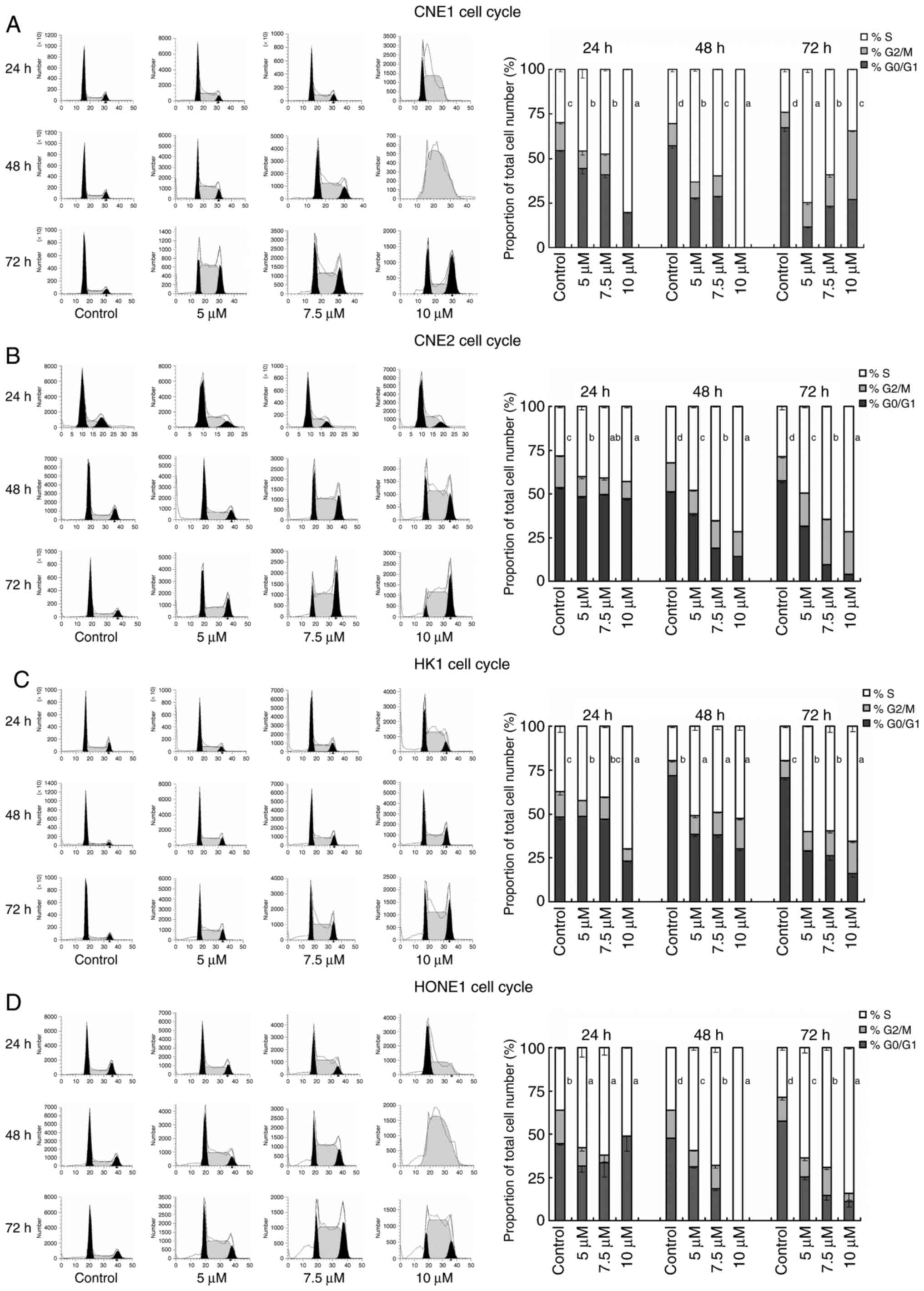
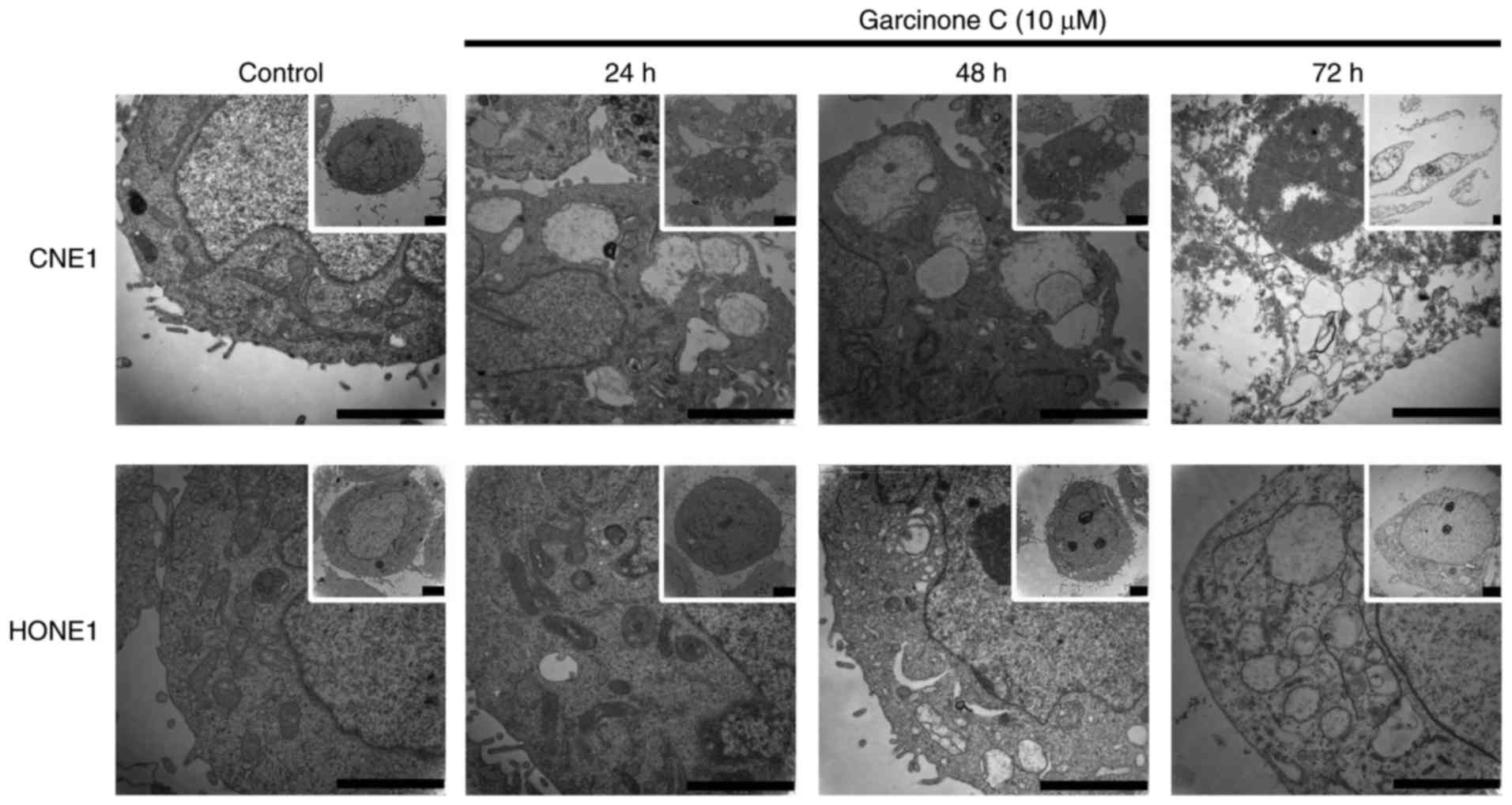
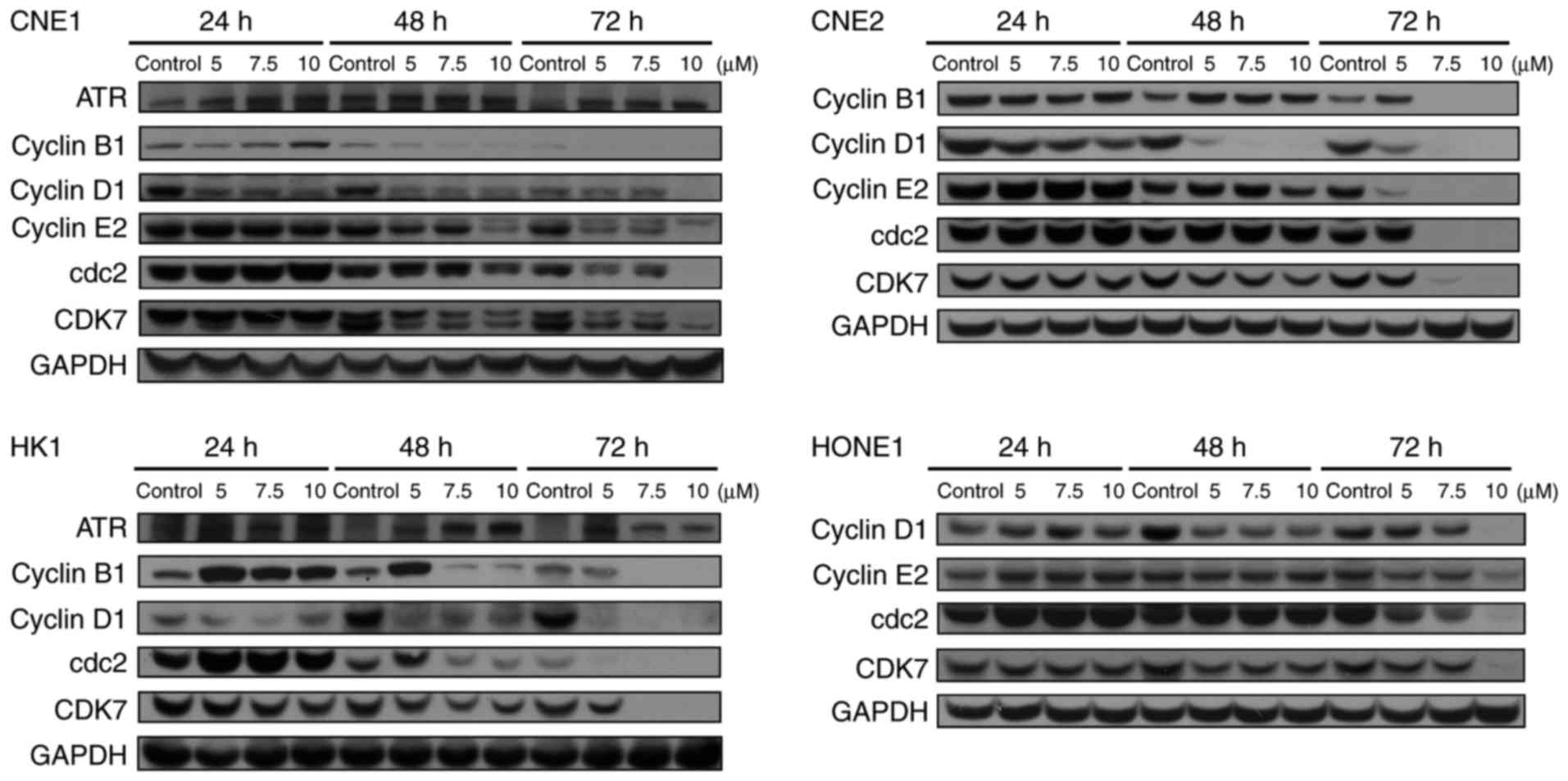
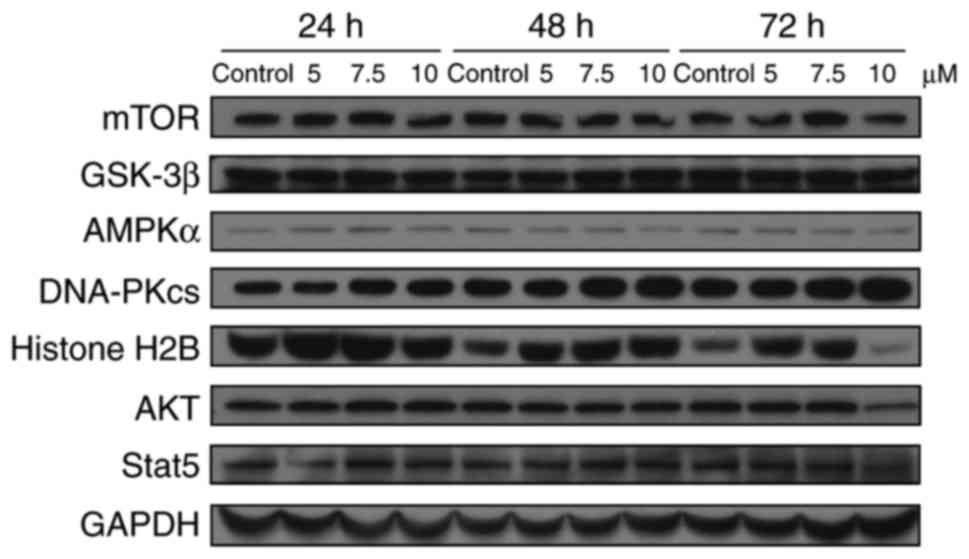
|
1
|
Zou M, Zhang X and Xu C: IL6-induced
metastasis modulators p-STAT3, MMP-2 and MMP-9 are targets of
3,3′-diindolylmethane in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
39:47–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guigay J, Temam S, Bourhis J, Pignon JP
and Armand JP: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma and therapeutic management:
The place of chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 17 Suppl 10:x304–x307. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shanmugaratnam K: Histological typing of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. IARC Sci Publ. 1–12. 1978.
|
|
4
|
Liu X, Gao Y, Lu Y, Zhang J, Li L and Yin
F: Downregulation of NEK11 is associated with drug resistance in
ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol. 45:1266–1274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang L, Kuang L, Pan X, Liu J, Wang Q, Du
B, Li D, Luo J, Liu M, Hou A and Qian M: Isoalvaxanthone inhibits
colon cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion through
inactivating Rac1 and AP-1. Int J Cancer. 127:1220–1229. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Aisha AF, Abu-Salah KM, Ismail Z and Majid
AM: In vitro and in vivo anti-colon cancer effects of Garcinia
mangostana xanthones extract. BMC Complement Altern Med.
12:1042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Panda SS, Chand M, Sakhuja R and Jain SC:
Xanthones as potential antioxidants. Curr Med Chem. 20:4481–4507.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yi T, Yi Z, Cho SG, Luo J, Pandey MK,
Aggarwal BB and Liu M: Gambogic acid inhibits angiogenesis and
prostate tumor growth by suppressing vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor 2 signaling. Cancer Res. 68:1843–1850. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rong JJ, Hu R, Song XM, Ha J, Lu N, Qi Q,
Tao L, You QD and Guo QL: Gambogic acid triggers DNA damage
signaling that induces p53/p21Waf1/CIP1 activation
through the ATR-Chk1 pathway. Cancer Lett. 296:55–64. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X and Chen W: Gambogic acid is a
novel anti-cancer agent that inhibits cell proliferation,
angiogenesis and metastasis. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
12:994–1000. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi X, Chen X, Li X, Lan X, Zhao C, Liu S,
Huang H, Liu N, Liao S, Song W, et al: Gambogic acid induces
apoptosis in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells via
inducing proteasome inhibition and caspase-dependent Bcr-Abl
downregulation. Clin Cancer Res. 20:151–163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang H, Lei Y, Yuan P, Li L, Luo C, Gao
R, Tian J, Feng Z, Nice EC and Sun J: ROS-mediated autophagy
induced by dysregulation of lipid metabolism plays a protective
role in colorectal cancer cells treated with gambogic acid. PLoS
One. 9:e964182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shibata MA, Iinuma M, Morimoto J, Kurose
H, Akamatsu K, Okuno Y, Akao Y and Otsuki Y: α-Mangostin extracted
from the pericarp of the mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana Linn)
reduces tumor growth and lymph node metastasis in an
immunocompetent xenograft model of metastatic mammary cancer
carrying a p53 mutation. BMC Med. 9:692011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jittiporn K, Suwanpradid J, Patel C, Rojas
M, Thirawarapan S, Moongkarndi P, Suvitayavat W and Caldwell RB:
Anti-angiogenic actions of the mangosteen polyphenolic xanthone
derivative α-mangostin. Microvasc Res. 93:72–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lei J, Huo X, Duan W, Xu Q, Li R, Ma J, Li
X, Han L, Li W, Sun H, et al: α-Mangostin inhibits hypoxia-driven
ROS-induced PSC activation and pancreatic cancer cell invasion.
Cancer Lett. 347:129–138. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li P, Tian W and Ma X: Alpha-mangostin
inhibits intracellular fatty acid synthase and induces apoptosis in
breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 13:1382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fu M, Qiu SX, Xu Y, Wu J, Chen Y, Yu Y and
Xiao G: A new xanthone from the pericarp of Garcinia mangostana.
Nat Prod Commun. 8:1733–1734. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Poon RY: DNA damage checkpoints in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 50:339–344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Johnson SW, Ozols RF and Hamilton TC:
Mechanisms of drug resistance in ovarian cancer. Cancer. 71(2
Supp1): S644–S649. 1993.
|
|
20
|
Sancar A, Lindsey-Boltz LA, Unsal-Kacmaz K
and Linn S: Molecular mechanisms of mammalian DNA repair and the
DNA damage checkpoints. Annu Rev Biochem. 73:39–85. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fink SL and Cookson BT: Apoptosis,
pyroptosis, and necrosis: Mechanistic description of dead and dying
eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 73:1907–1916. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G,
Zhao Y, Pestell RG, Albanese C and Darnell JE Jr: Stat3 as an
oncogene. Cell. 98:295–303. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liao Q, Zeng Z, Guo X, Li X, Wei F, Zhang
W, Li X, Chen P, Liang F, Xiang B, et al: LPLUNC1 suppresses
IL-6-induced nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell proliferation via
inhibiting the Stat3 activation. Oncogene. 33:2098–2109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Constantinou C, Elia A and Clemens MJ:
Activation of p53 stimulates proteasome-dependent truncation of
eIF4E-binding protein 1 (4E-BP1). Biol Cell. 100:279–289. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chakravarthy R, Clemens MJ, Pirianov G,
Perdios N, Mudan S, Cartwright JE and Elia A: Role of the eIF4E
binding protein 4E-BP1 in regulation of the sensitivity of human
pancreatic cancer cells to TRAIL and celastrol-induced apoptosis.
Biol Cell. 105:414–429. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ma BB, Lui VW, Hui CW, Lau CP, Wong CH,
Hui EP, Ng MH, Tsao SW, Li Y and Chan AT: Preclinical evaluation of
the AKT inhibitor MK-2206 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines.
Invest New Drugs. 31:567–575. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|