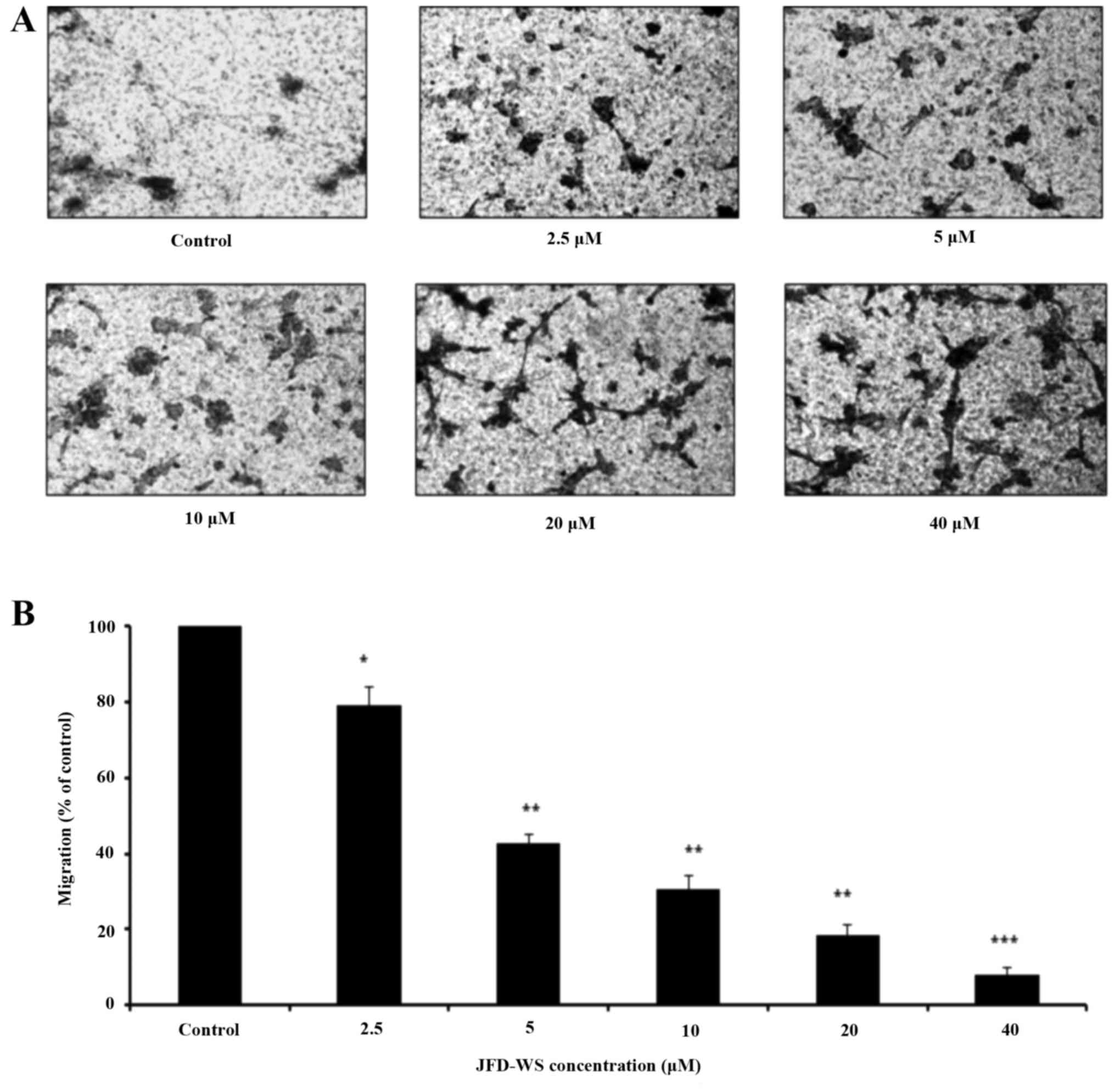
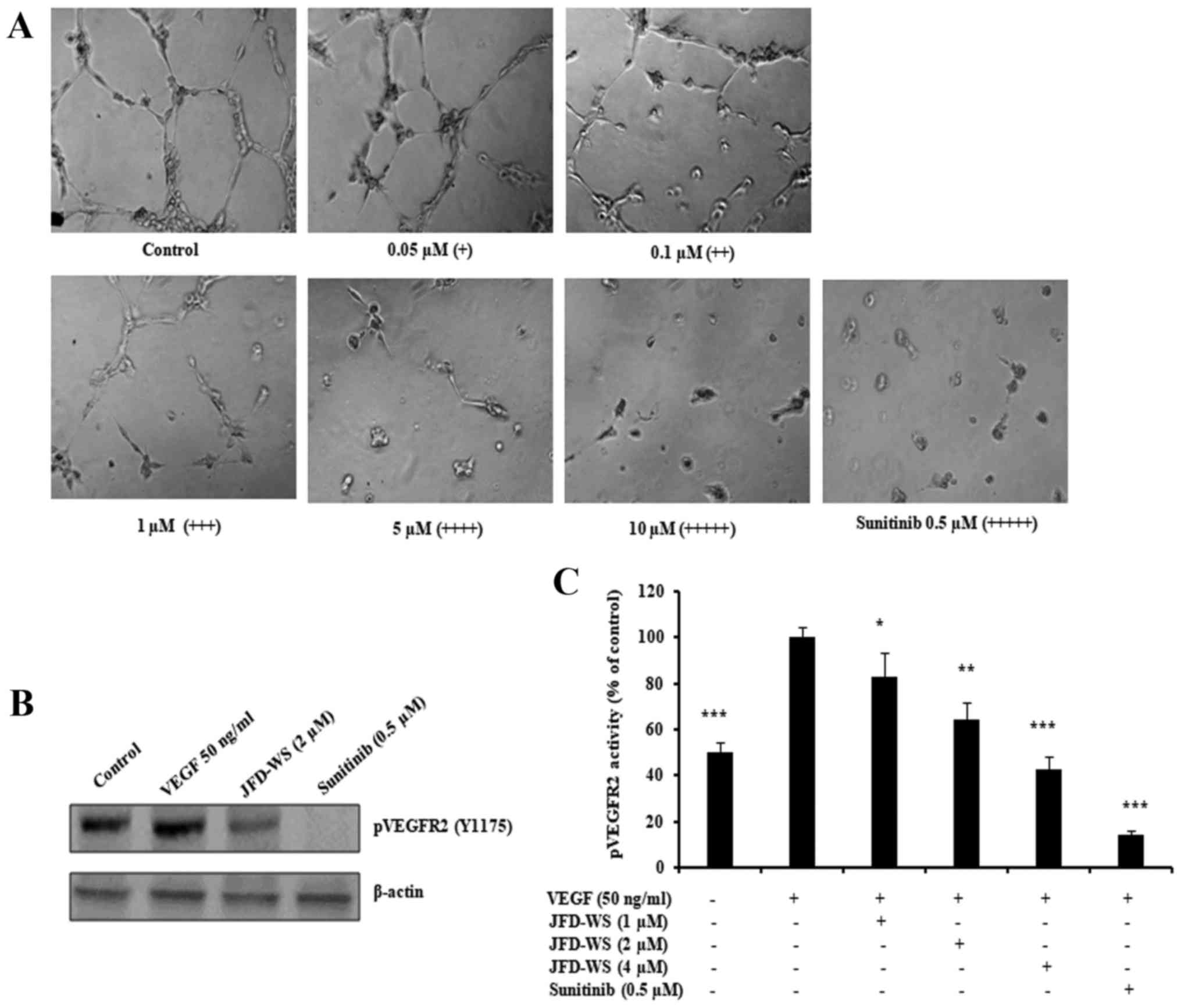
|
1
|
Folkman J: Role of angiogenesis in tumor
growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol. 29 Suppl 16:15–18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ivy SP, Wick JY and Kaufman BM: An
overview of small-molecule inhibitors of VEGFR signaling. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 6:569–579. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kamba T and McDonald DM: Mechanisms of
adverse effects of anti-VEGF therapy for cancer. Br J Cancer.
96:1788–1795. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sridhar J, Akula N, Sivanesan D,
Narasimhan M, Rathinavelu A and Pattabiraman N: Identification of
novel angiogenesis inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 15:4125–4129.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dhandayuthapani S and Rathinavelu A: JFD,
a novel small molecule for inhibiting vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor-mediated angiogenesis. Proceedings of the 105th
Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research;
2014 Apr 5–9; San Diego, CA Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res. 74
Suppl 19:Abstract nr1021. 2014;
|
|
7
|
Auerbach R, Akhtar N, Lewis RL and
Shinners BL: Angiogenesis assays: Problems and pitfalls. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 19:167–172. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mekhail TM and Markman M: Paclitaxel in
cancer therapy. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 3:755–766. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ramaswamy B and Puhalla S: Docetaxel: A
tubulin-stabilizing agent approved for the management of several
solid tumors. Drugs Today. 42:265–279. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dorr RT: Pharmacology of the taxanes.
Pharmacotherapy. 17:96S–104S. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hollstein M, Hergenhahn M, Yang Q, Bartsch
H, Wang ZQ and Hainaut P: New approaches to understanding p53 gene
tumor mutation spectra. Mutat Res. 431:199–209. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Senapati S, Das S and Batra SK:
Mucin-interacting proteins: From function to therapeutics. Trends
Biochem Sci. 35:236–245. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tampellini M, Berruti A, Gerbino A, Buniva
T, Torta M, Gorzegno G, Faggiuolo R, Cannone R, Farris A,
Destefanis M, et al: Relationship between CA 15-3 serum levels and
disease extent in predicting overall survival of breast cancer
patients with newly diagnosed metastatic disease. Br J Cancer.
75:698–702. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Morrissey JJ and Raney S: A metastatic
breast tumor cell line, GI-101A, is estrogen receptor positive and
responsive to estrogen but resistant to tamoxifen. Cell Biol Int.
22:413–419. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tamilarasan KP, Kolluru GK, Rajaram M,
Indhumathy M, Saranya R and Chatterjee S: Thalidomide attenuates
nitric oxide mediated angiogenesis by blocking migration of
endothelial cells. BMC Cell Biol. 7:172006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lamalice L, Le Boeuf F and Huot J:
Endothelial cell migration during angiogenesis. Circ Res.
100:782–794. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jimeno A and Hidalgo M: Pharmacogenomics
of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase
inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1766:217–229. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kanagasabai T, Alvarez J, Bhalani M,
Dhandayuthapani S and Rathinavelu A: The in vivo activity of a
novel anti-angiogenic compound, JFD-WS, in human breast
adenocarcinoma xenograft implanted athymic nude mice. Proceedings
of the 106th Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer
Research; 2015 Apr 18–22; Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res. 75
Suppl 15:Abstract nr13802015;
|
|
20
|
Gotink KJ and Verheul HM: Anti-angiogenic
tyrosine kinase inhibitors: What is their mechanism of action?
Angiogenesis. 13:1–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang F, Brown C, Buettner R, Hedvat M,
Starr R, Scuto A, Schroeder A, Jensen M and Jove R: Sorafenib
induces growth arrest and apoptosis of human glioblastoma cells
through the dephosphorylation of signal transducers and activators
of transcription 3. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:953–962. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Susin SA, Zamzami N, Castedo M, Daugas E,
Wang HG, Geley S, Fassy F, Reed JC and Kroemer G: The central
executioner of apoptosis: Multiple connections between protease
activation and mitochondria in Fas/APO-1/CD95- and ceramide-induced
apoptosis. J Exp Med. 186:25–37. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zamzami N, Marchetti P, Castedo M, Zanin
C, Vayssière JL, Petit PX and Kroemer G: Reduction in mitochondrial
potential constitutes an early irreversible step of programmed
lymphocyte death in vivo. J Exp Med. 181:1661–1672. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marchetti P, Castedo M, Susin SA, Zamzami
N, Hirsch T, Macho A, Haeffner A, Hirsch F, Geuskens M and Kroemer
G: Mitochondrial permeability transition is a central coordinating
event of apoptosis. J Exp Med. 184:1155–1160. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kroemer G and Reed JC: Mitochondrial
control of cell death. Nat Med. 6:513–519. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gottlieb TM, Leal JF, Seger R, Taya Y and
Oren M: Cross-talk between Akt, p53 and Mdm2: Possible implications
for the regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene. 21:1299–1303. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mukhopadhyay D, Tsiokas L and Sukhatme VP:
Wild-type p53 and v-Src exert opposing influences on human vascular
endothelial growth factor gene expression. Cancer Res.
55:6161–6165. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bouvet M, Ellis LM, Nishizaki M, Fujiwara
T, Liu W, Bucana CD, Fang B, Lee JJ and Roth JA:
Adenovirus-mediated wild-type p53 gene transfer down-regulates
vascular endothelial growth factor expression and inhibits
angiogenesis in human colon cancer. Cancer Res. 58:2288–2292.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fontanini G, Boldrini L, Vignati S, Chinè
S, Basolo F, Silvestri V, Lucchi M, Mussi A, Angeletti CA and
Bevilacqua G: Bcl2 and p53 regulate vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF)-mediated angiogenesis in non-small cell lung
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 34:718–723. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kumar P, Miller AI and Polverini PJ: p38
MAPK mediates gamma-irradiation-induced endothelial cell apoptosis,
and vascular endothelial growth factor protects endothelial cells
through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-Bcl-2 pathway. J Biol
Chem. 279:43352–43360. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Milella M, Estrov Z, Kornblau SM, Carter
BZ, Konopleva M, Tari A, Schober WD, Harris D, Leysath CE,
Lopez-Berestein G, et al: Synergistic induction of apoptosis by
simultaneous disruption of the Bcl-2 and MEK/MAPK pathways in acute
myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 99:3461–3464. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|