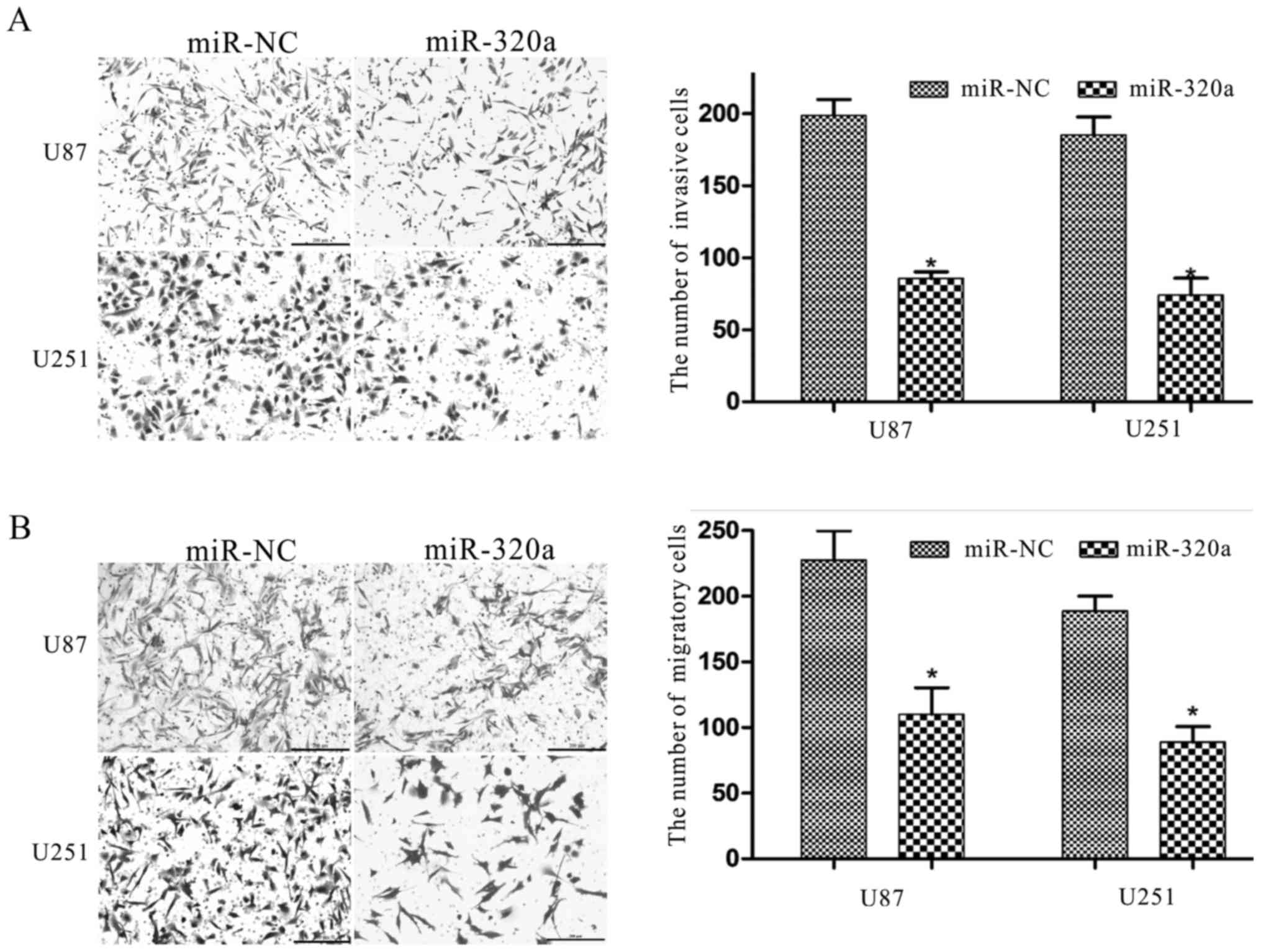
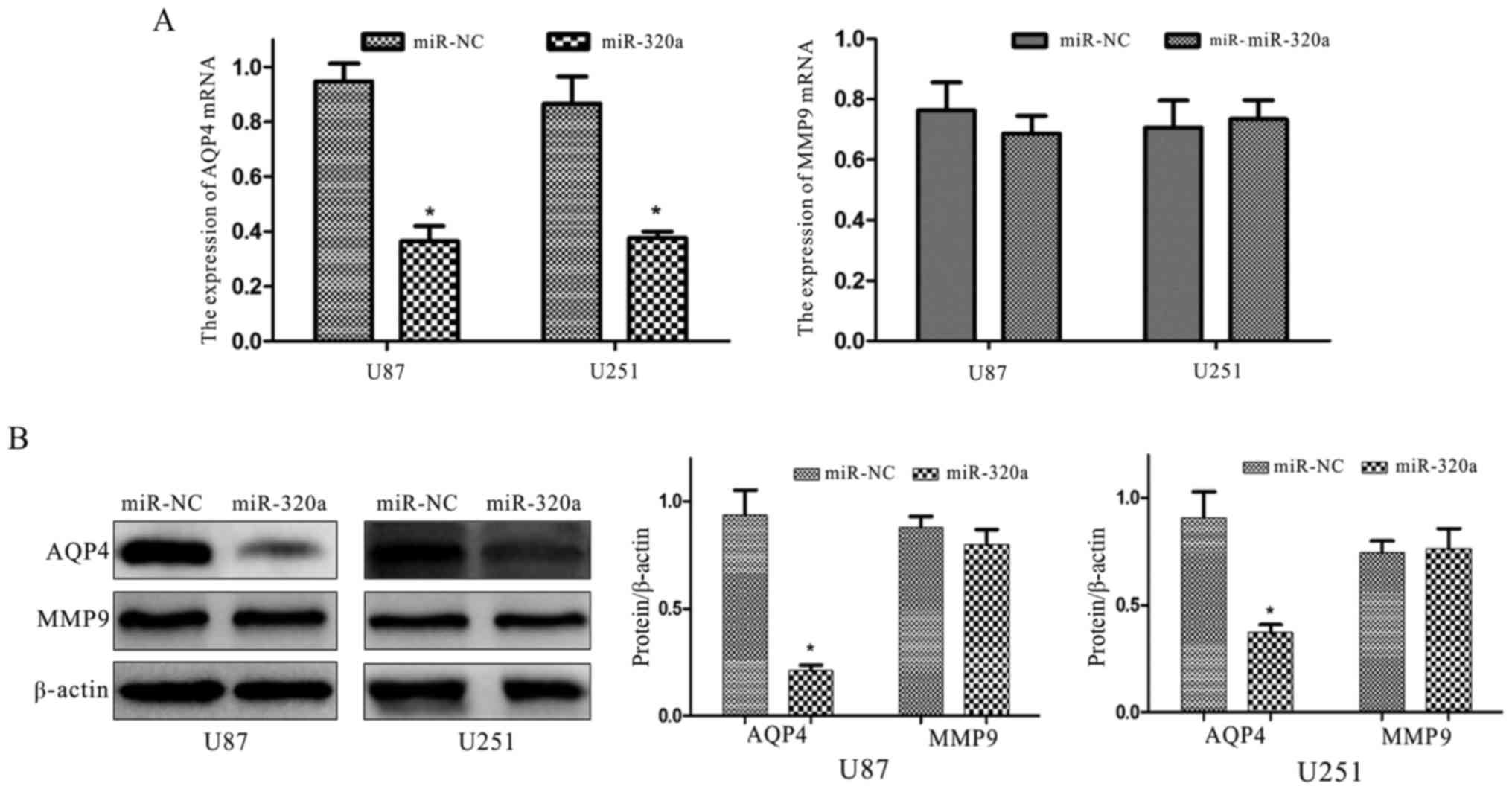
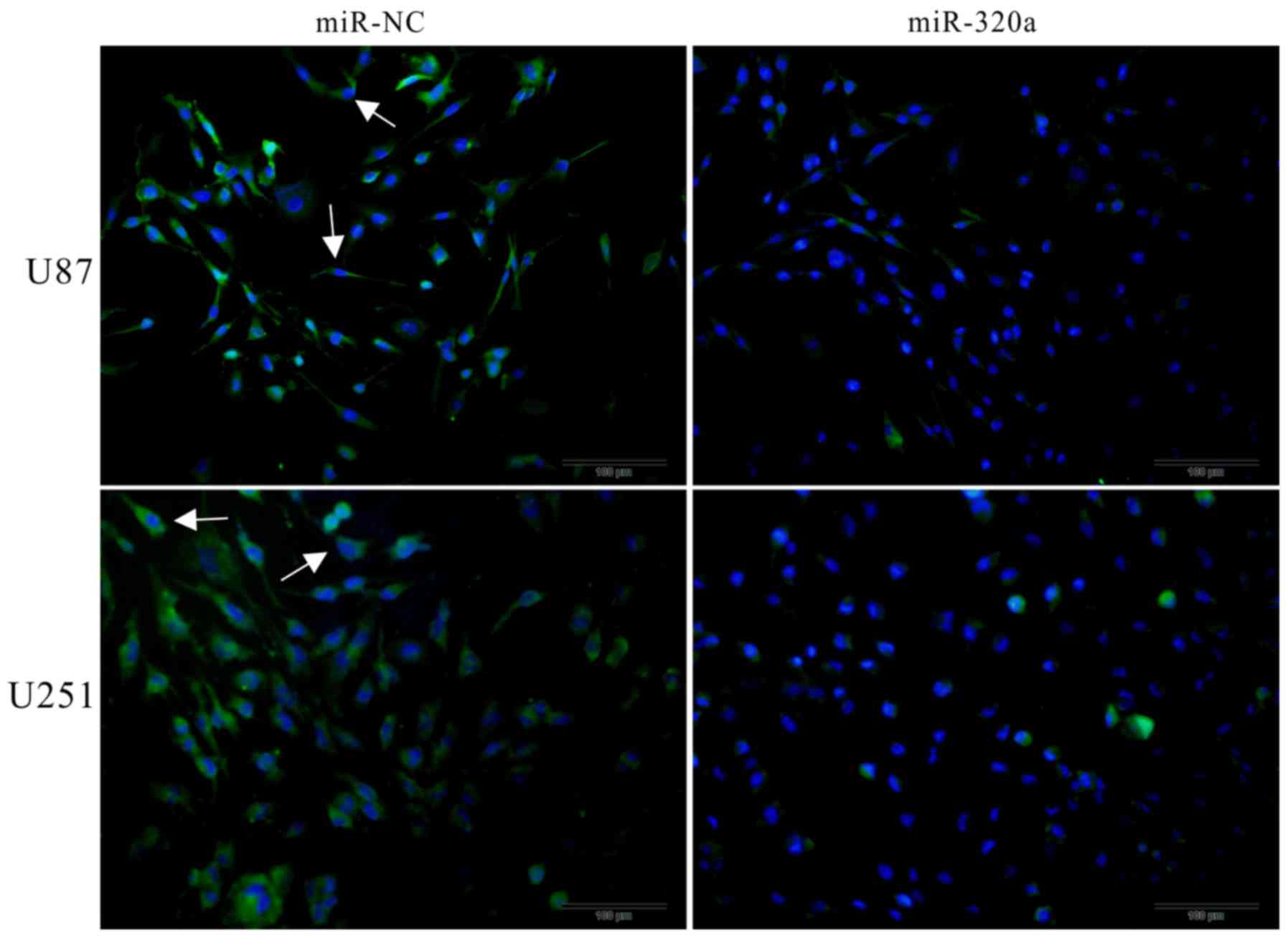
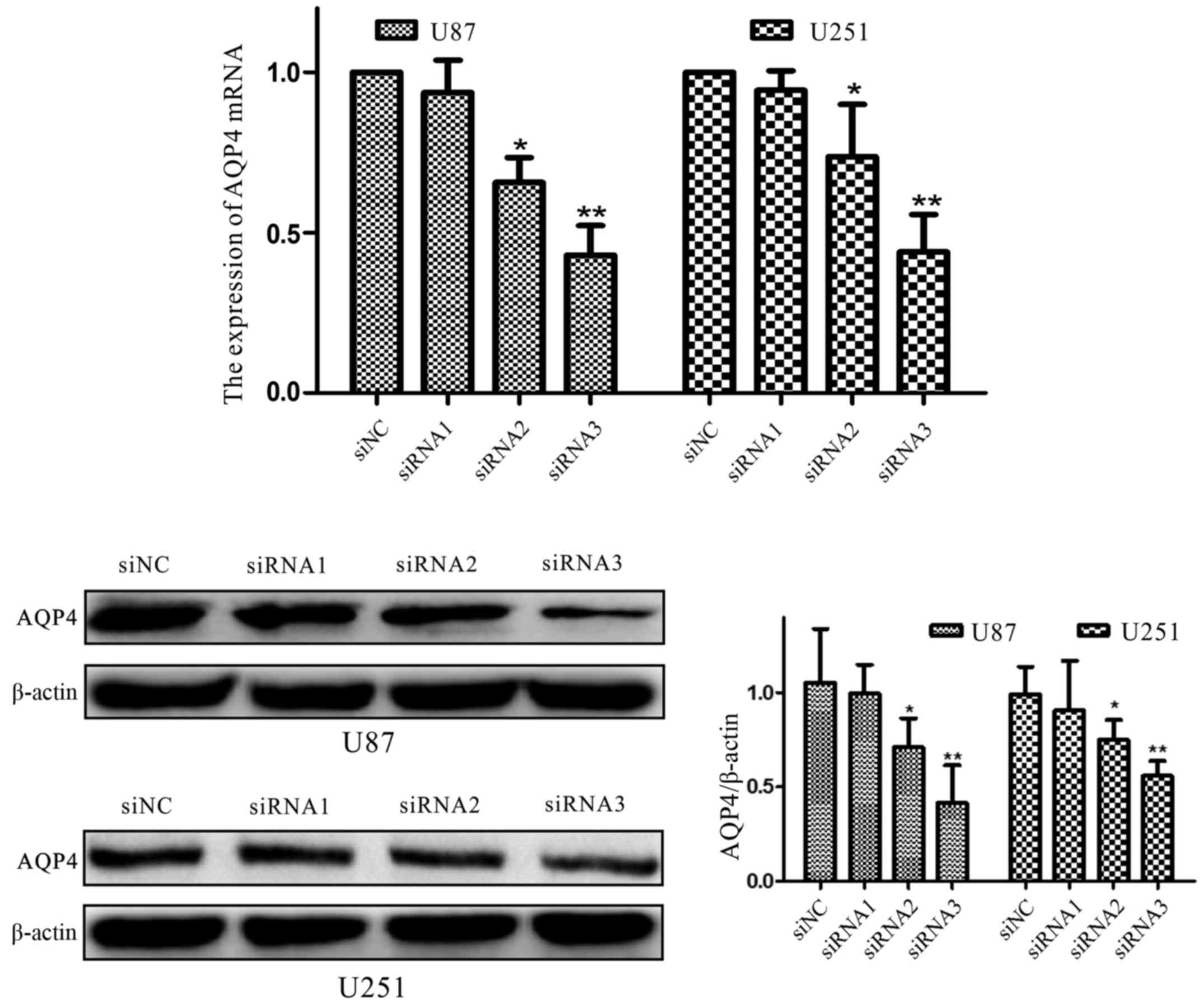
|
1
|
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Reardon DA
and Friedman HS: Experience with irinotecan for the treatment of
malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol. 11:80–91. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Katakowski M, Charteris N, Chopp M and
Khain E: Density-dependent regulation of glioma cell proliferation
and invasion mediated by miR-9. Cancer Microenviron. 9:149–159.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim Y, Jeon H and Othmer H: The role of
the tumor microenvironment in glioblastoma: A mathematical model.
IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 64:519–527. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liz J and Esteller M: lncRNAs and
microRNAs with a role in cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1859:169–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang T, Wang YR, Zeng F, Cao HY, Zhou HD
and Wang YJ: LncRNA H19 is overexpressed in glioma tissue, is
negatively associated with patient survival, and promotes tumor
growth through its derivative miR-675. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
20:4891–4897. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oberheim Bush NA and Chang S: Treatment
strategies for low-grade glioma in adults. J Oncol Pract.
12:1235–1241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Weathers SS and Gilbert MR: Toward
personalized targeted therapeutics: An overview. Neurotherapeutics.
14:256–264. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miska EA: How microRNAs control cell
division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
15:563–568. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zimmerman AL and Wu S: MicroRNAs, cancer
and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 300:10–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reid G: MicroRNAs in mesothelioma: From
tumour suppressors and biomarkers to therapeutic targets. J Thorac
Dis. 7:1031–1040. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNAs in
cancer: Small molecules with a huge impact. J Clin Oncol.
27:5848–5856. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun JY, Huang Y, Li JP, Zhang X, Wang L,
Meng YL, Yan B, Bian YQ, Zhao J, Wang WZ, et al: MicroRNA-320a
suppresses human colon cancer cell proliferation by directly
targeting β-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 420:787–792. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mittal SP, Mathai J, Kulkarni AP, Pal JK
and Chattopadhyay S: miR-320a regulates erythroid differentiation
through MAR binding protein SMAR1. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:2519–2529. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shang C, Zhang H, Guo Y, Hong Y, Liu Y and
Xue Y: miR-320a down-regulation mediates bladder carcinoma invasion
by targeting ITGB3. Mol Biol Rep. 41:2521–2527. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nagelhus EA and Ottersen OP: Physiological
roles of aquaporin-4 in brain. Physiol Rev. 93:1543–1562. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Camassa LM, Lunde LK, Hoddevik EH,
Stensland M, Boldt HB, De Souza GA, Ottersen OP and Amiry-Moghaddam
M: Mechanisms underlying AQP4 accumulation in astrocyte endfeet.
Glia. 63:2073–2091. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hubbard JA, Hsu MS, Seldin MM and Binder
DK: Expression of the astrocyte water channel aquaporin-4 in the
mouse brain. ASN Neuro. 7:17590914156054862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Badaut J, Fukuda AM, Jullienne A and Petry
KG: Aquaporin and brain diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1840:1554–1565. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lan YL, Zhao J, Ma T and Li S: The
potential roles of aquaporin 4 in Alzheimer's disease. Mol
Neurobiol. 53:5300–5309. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang WC, Zhou LJ, Zhang R, Yue ZY, Dong H,
Song CY, Qian H, Lu SJ and Chang FF: Effects of propofol and
sevoflurane on aquaporin-4 and aquaporin-9 expression in patients
performed gliomas resection. Brain Res. 1622:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lan YL, Wang X, Lou JC, Ma XC and Zhang B:
The potential roles of aquaporin 4 in malignant gliomas.
Oncotarget. 8:32345–32355. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ding T, Zhou Y, Sun K, Jiang W, Li W, Liu
X, Tian C, Li Z, Ying G, Fu L, et al: Knockdown a water channel
protein, aquaporin-4, induced glioblastoma cell apoptosis. PLoS
One. 8:e667512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hiroaki Y, Tani K, Kamegawa A, Gyobu N,
Nishikawa K, Suzuki H, Walz T, Sasaki S, Mitsuoka K, Kimura K, et
al: Implications of the aquaporin-4 structure on array formation
and cell adhesion. J Mol Biol. 355:628–639. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang L, Wang X, Zhen S, Zhang S, Kang D
and Lin Z: Aquaporin-4 upregulated expression in glioma tissue is a
reaction to glioma-associated edema induced by vascular endothelial
growth factor. Oncol Rep. 28:1633–1638. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao WJ, Zhang W, Li GL, Cui Y, Shi ZF and
Yuan F: Differential expression of MMP-9 and AQP4 in human glioma
samples. Folia Neuropathol. 50:176–186. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Peng J, Omran A, Ashhab MU, Kong H, Gan N,
He F and Yin F: Expression patterns of miR-124, miR-134, miR-132,
and miR-21 in an immature rat model and children with mesial
temporal lobe epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci. 50:291–297. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu ZH, Li J, Xia J, Jiang R, Zuo GW, Li
XP, Chen Y, Xiong W and Chen DL: Ginsenoside 20(s)-Rh2 as potent
natural histone deacetylase inhibitors suppressing the growth of
human leukemia cells. Chem Biol Interact. 242:227–234. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xishan Z, Ziying L, Jing D and Gang L:
MicroRNA-320a acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting BCR/ABL
oncogene in chronic myeloid leukemia. Sci Rep. 5:124602015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang G, Jiang G, Wang C, Zhong K, Zhang
J, Xue Q, Li X, Jin H and Li B: Decreased expression of
microRNA-320a promotes proliferation and invasion of non-small cell
lung cancer cells by increasing VDAC1 expression. Oncotarget.
7:49470–49480. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guo T, Feng Y, Liu Q, Yang X, Jiang T,
Chen Y and Zhang Q: MicroRNA-320a suppresses in GBM patients and
modulates glioma cell functions by targeting IGF-1R. Tumour Biol.
35:11269–11275. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li H, Yu L, Liu J, Bian X, Shi C, Sun C,
Zhou X, Wen Y, Hua D, Zhao S, et al: miR-320a functions as a
suppressor for gliomas by targeting SND1 and β-catenin, and
predicts the prognosis of patients. Oncotarget. 8:19723–19737.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li YB, Sun SR and Han XH: Down-regulation
of AQP4 inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of human
breast cancer cells. Folia Biol (Praha). 62:131–137.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng C, Chen ZQ and Shi XT: MicroRNA-320
inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation by directly targeting
fatty acid synthase. Tumour Biol. 35:4177–4183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lü M, Ding K, Zhang G, Yin M, Yao G, Tian
H, Lian J, Liu L, Liang M, Zhu T, et al: MicroRNA-320a sensitizes
tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells to tamoxifen by targeting
ARPP-19 and ERRγ. Sci Rep. 5:87352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Badaut J, Nehlig A, Verbavatz J, Stoeckel
M, Freund-Mercier MJ and Lasbennes F: Hypervascularization in the
magnocellular nuclei of the rat hypothalamus: Relationship with the
distribution of aquaporin-4 and markers of energy metabolism. J
Neuroendocrinol. 12:960–969. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Badaut J, Verbavatz JM, Freund-Mercier MJ
and Lasbennes F: Presence of aquaporin-4 and muscarinic receptors
in astrocytes and ependymal cells in rat brain: A clue to a common
function? Neurosci Lett. 292:75–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hsu MS, Seldin M, Lee DJ, Seifert G,
Steinhäuser C and Binder DK: Laminar-specific and developmental
expression of aquaporin-4 in the mouse hippocampus. Neuroscience.
178:21–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nielsen S, Nagelhus EA, Amiry-Moghaddam M,
Bourque C, Agre P and Ottersen OP: Specialized membrane domains for
water transport in glial cells: High-resolution immunogold
cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J Neurosci. 17:171–180.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wen H, Nagelhus EA, Amiry-Moghaddam M,
Agre P, Ottersen OP and Nielsen S: Ontogeny of water transport in
rat brain: Postnatal expression of the aquaporin-4 water channel.
Eur J Neurosci. 11:935–945. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Juryńczyk M, Tackley G, Kong Y, Geraldes
R, Matthews L, Woodhall M, Waters P, Kuker W, Craner M, Weir A, et
al: Brain lesion distribution criteria distinguish MS from
AQP4-antibody NMOSD and MOG-antibody disease. J Neurol Neurosurg
Psychiatry. 88:132–136. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Vaknin-Dembinsky A, Brill L, Kassis I,
Petrou P, Ovadia H, Ben-Hur T, Abramsky O and Karussis D: T-cell
responses to distinct AQP4 peptides in patients with neuromyelitis
optica (NMO). Mult Scler Relat Disord. 6:28–36. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Roomi MW, Monterrey JC, Kalinovsky T, Rath
M and Niedzwiecki A: Inhibition of invasion and MMPs by a nutrient
mixture in human cancer cell lines: A correlation study. Exp Oncol.
32:243–248. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Singh RD, Haridas N, Patel JB, Shah FD,
Shukla SN, Shah PM and Patel PS: Matrix metalloproteinases and
their inhibitors: Correlation with invasion and metastasis in oral
cancer. Indian J Clin Biochem. 25:250–259. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Das G, Shiras A, Shanmuganandam K and
Shastry P: Rictor regulates MMP-9 activity and invasion through
Raf-1-MEK-ERK signaling pathway in glioma cells. Mol Carcinog.
50:412–423. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ruiz-Morales JM, Dorantes-Heredia R,
Arrieta O, Chávez-Tapia NC and Motola-Kuba D: Neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) prognostic value in lung
adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 36:3601–3610. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shi W, Xiao H, Xue F and Wu J: Dynamic
changes of matrix metalloproteinase 9 in heterotopic ossification
of rat model. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.
28:1133–1138. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rimm DL, Koslov ER, Kebriaei P, Cianci CD
and Morrow JS: Alpha 1(E)-catenin is an actin-binding and -bundling
protein mediating the attachment of F-actin to the membrane
adhesion complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 92:pp. 8813–8817. 1995;
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Santhekadur PK, Akiel M, Emdad L, Gredler
R, Srivastava J, Rajasekaran D, Robertson CL, Mukhopadhyay ND,
Fisher PB and Sarkar D: Staphylococcal nuclease domain containing-1
(SND1) promotes migration and invasion via angiotensin II type 1
receptor (AT1R) and TGFβ signaling. FEBS Open Bio. 4:353–361. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Santhekadur PK, Das SK, Gredler R, Chen D,
Srivastava J, Robertson C, Baldwin AS Jr, Fisher PB and Sarkar D:
Multifunction protein staphylococcal nuclease domain containing 1
(SND1) promotes tumor angiogenesis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma through novel pathway that involves nuclear factor κB and
miR-221. J Biol Chem. 287:13952–13958. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|