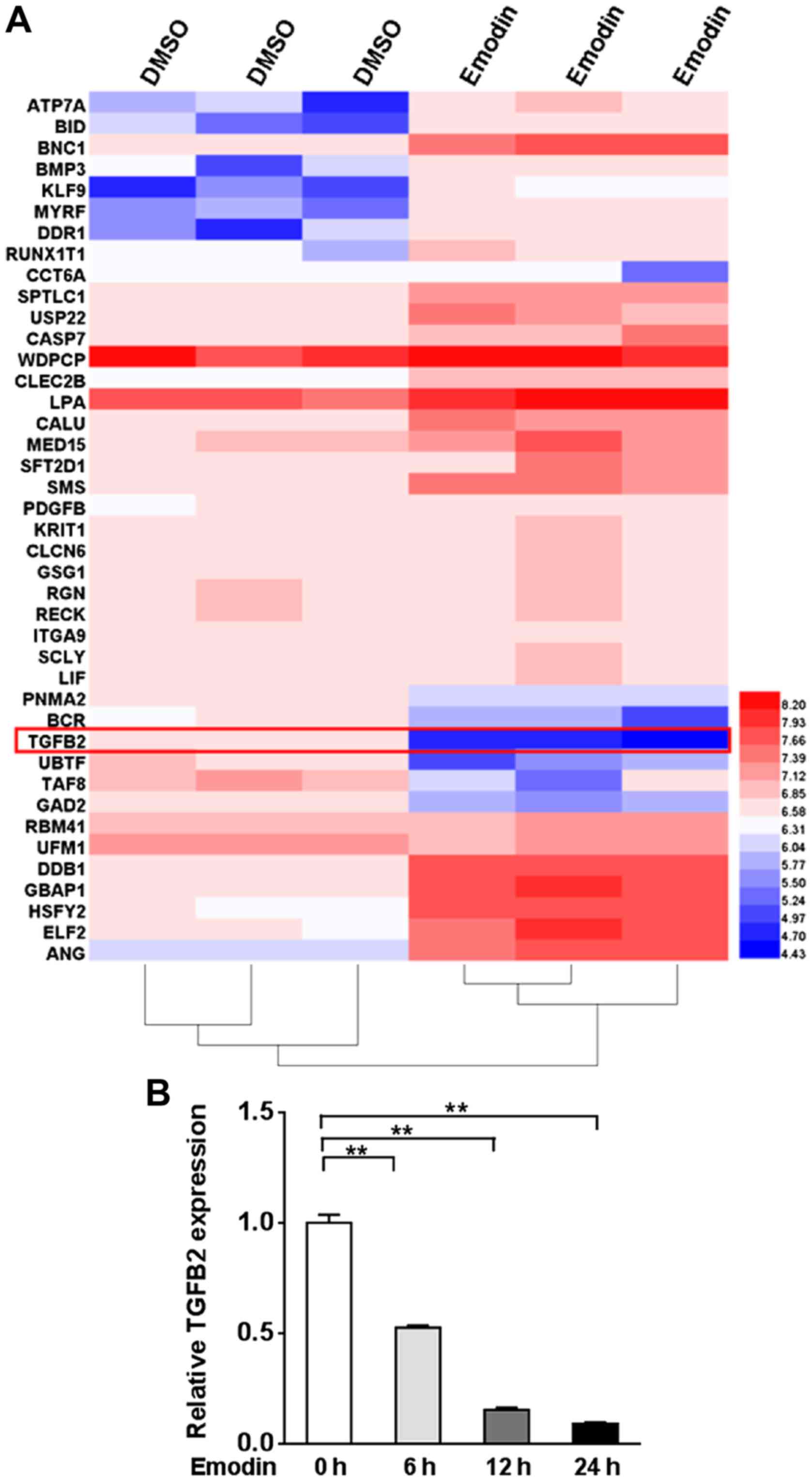
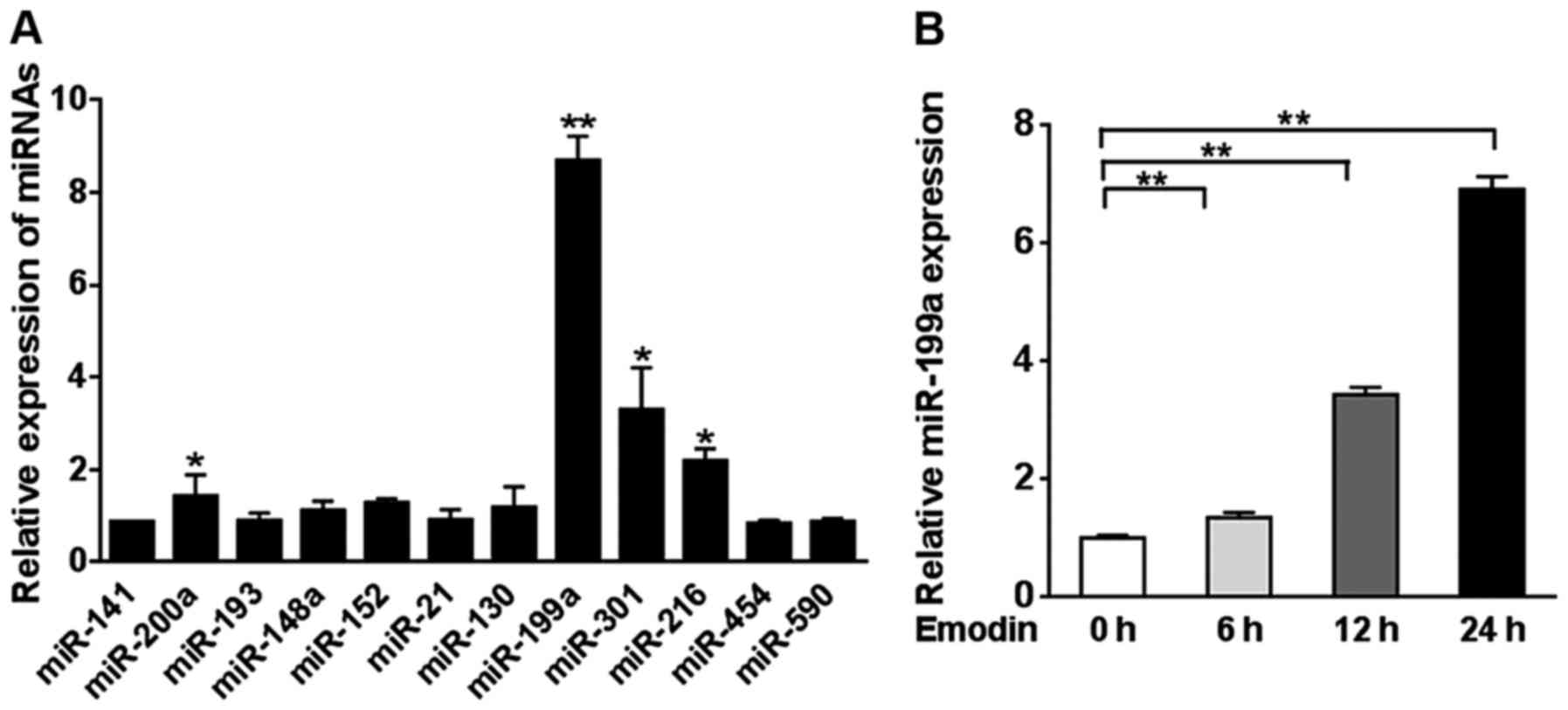
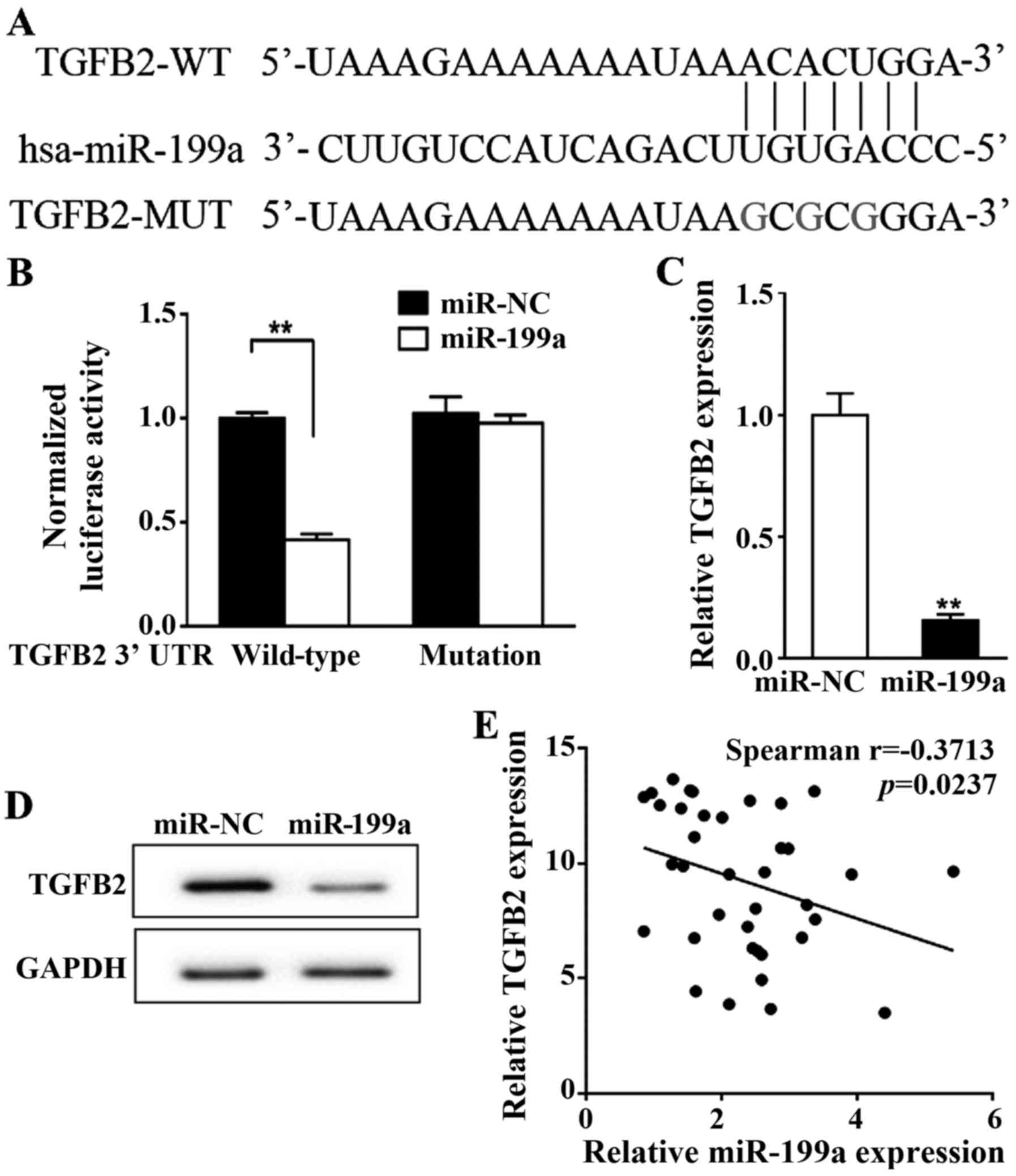
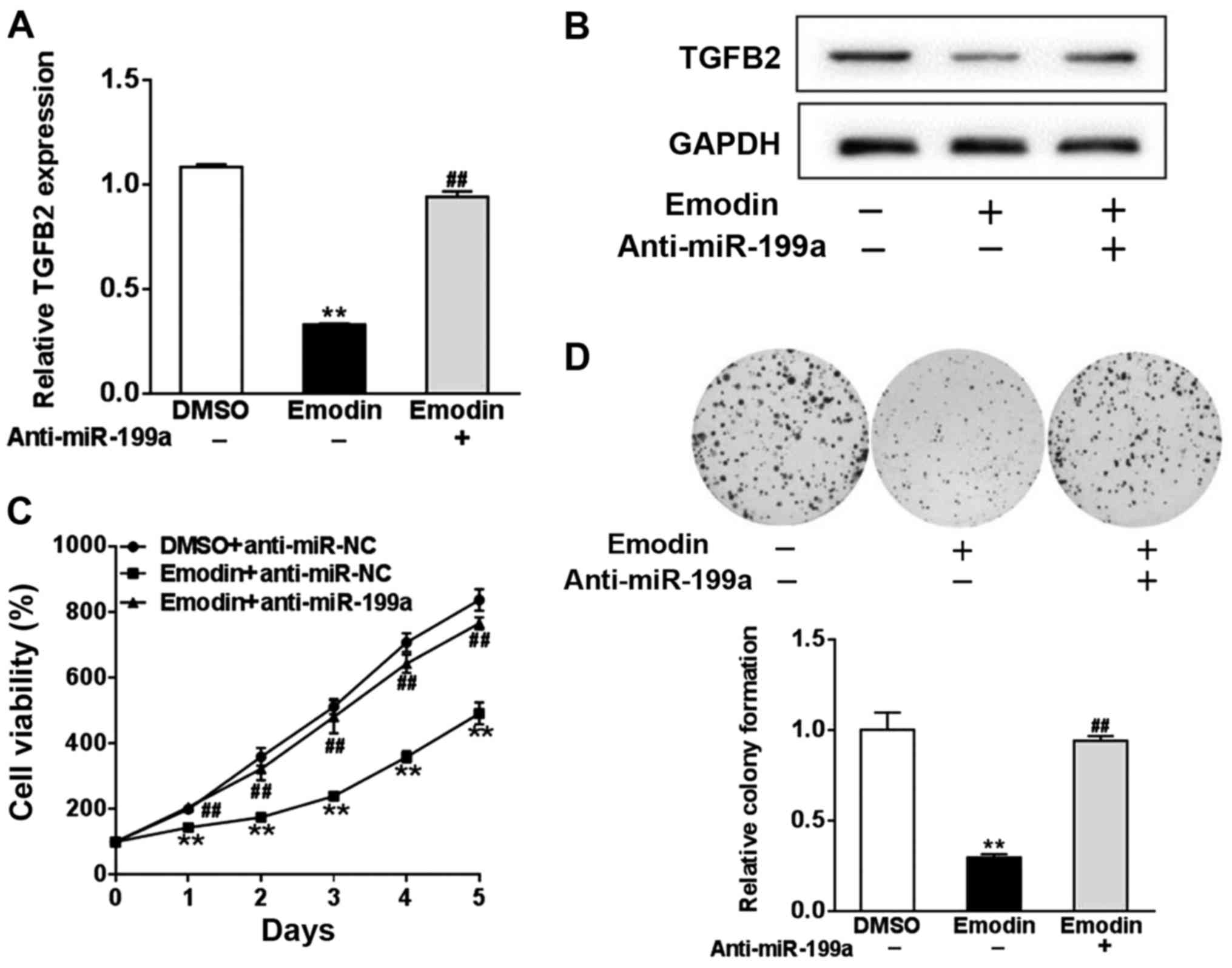
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dong X, Fu J, Yin X, Cao S, Li X, Lin L
and Ni J: Huyiligeqi: Emodin: A review of its pharmacology,
toxicity and pharmacokinetics. Phytother Res. 30:1207–1218. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lin SZ, Xu JB, Ji X, Chen H, Xu HT, Hu P,
Chen L, Guo JQ, Chen MY, Lu D, et al: Emodin inhibits angiogenesis
in pancreatic cancer by regulating the transforming growth
factor-β/drosophila mothers against decapentaplegic pathway and
angiogenesis-associated microRNAs. Mol Med Rep. 12:5865–5871. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guo J, Xiao B, Liu Q, Gong Z and Le Y:
Suppression of C-myc expression associates with anti-proliferation
of aloe-emodin on gastric cancer cells. Cancer Invest. 26:369–374.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Suboj P, Babykutty S, Srinivas P and
Gopala S: Aloe emodin induces G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
via activation of caspase-6 in human colon cancer cells.
Pharmacology. 89:91–98. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xie MJ, Ma YH, Miao L, Wang Y, Wang HZ,
Xing YY, Xi T and Lu YY: Emodin-provoked oxidative stress induces
apoptosis in human colon cancer HCT116 cells through a
p53-mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:5201–5205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gao R, Chen R, Cao Y, Wang Y, Song K,
Zhang Y and Yang J: Emodin suppresses TGF-β1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in alveolar epithelial cells
through Notch signaling pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 318:1–7.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu HC, Liu LC, Wang HY, Hung CM, Lin YC,
Ho CT and Way TD: Stromal fibroblasts from the interface zone of
triple negative breast carcinomas induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and its inhibition by emodin. PLoS One. 12:e01646612017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Liu P, Mao H, Wanga A and Zhang X:
Emodin sensitizes paclitaxel-resistant human ovarian cancer cells
to paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in vitro. Oncol Rep.
21:1605–1610. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma J, Yang J, Wang C, Zhang N, Dong Y,
Wang C, Wang Y and Lin X: Emodin augments cisplatin cytotoxicity in
platinum-resistant ovarian cancer cells via ROS-dependent MRP1
downregulation. BioMed Res Int. 2014:1076712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Auersperg N, Wong AS, Choi KC, Kang SK and
Leung PC: Ovarian surface epithelium: Biology, endocrinology, and
pathology. Endocr Rev. 22:255–288. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alsina-Sanchis E, Figueras A, Lahiguera Á,
Vidal A, Casanovas O, Graupera M, Villanueva A and Viñals F: The
TGFβ pathway stimulates ovarian cancer cell proliferation by
increasing IGF1R levels. Int J Cancer. 139:1894–1903. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin SW, Lee MT, Ke FC, Lee PP, Huang CJ,
Ip MM, Chen L and Hwang JJ: TGFbeta1 stimulates the secretion of
matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP2) and the invasive behavior in
human ovarian cancer cells, which is suppressed by MMP inhibitor
BB3103. Clin Exp Metastasis. 18:493–499. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peng H, Liu L and Zhao X: Prognostic
significance of matrix metalloproteinase-2 in gynecological cancer:
A systemic review of the literature and meta-analysis. J BUON.
18:202–210. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartlett JM, Langdon SP, Scott WN, Love
SB, Miller EP, Katsaros D, Smyth JF and Miller WR: Transforming
growth factor-beta isoform expression in human ovarian tumours. Eur
J Cancer. 33:2397–2403. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parikh A, Lee C, Joseph P, Marchini S,
Baccarini A, Kolev V, Romualdi C, Fruscio R, Shah H, Wang F, et al:
microRNA-181a has a critical role in ovarian cancer progression
through the regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Nat Commun. 5:29772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moss EG: MicroRNAs: Hidden in the genome.
Curr Biol. 12:R138–R140. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iorio MV, Visone R, Di Leva G, Donati V,
Petrocca F, Casalini P, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Alder H, et
al: MicroRNA signatures in human ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
67:8699–8707. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Perdigão-Henriques R, Petrocca F,
Altschuler G, Thomas MP, Le MT, Tan SM, Hide W and Lieberman J:
miR-200 promotes the mesenchymal to epithelial transition by
suppressing multiple members of the Zeb2 and Snail1 transcriptional
repressor complexes. Oncogene. 35:158–172. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Guo J, Li W, Shi H, Xie X, Li L, Tang H,
Wu M, Kong Y, Yang L, Gao J, et al: Synergistic effects of curcumin
with emodin against the proliferation and invasion of breast cancer
cells through upregulation of miR-34a. Mol Cell Biochem.
382:103–111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niu G, Li B, Sun L and An C: MicroRNA-153
inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation and invasion by targeting
TGF-β2. PLoS One. 10:e01192252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Peng T, Zhang S, Li W, Fu S, Luan Y and
Zuo L: MicroRNA-141 inhibits glioma cells growth and metastasis by
targeting TGF-β2. Am J Transl Res. 8:3513–3521. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu R, Ji Z, Li X, Qin J, Cui G, Chen J,
Zhai Q, Zhao C, Zhang W and Yu Z: Tumor suppressive microRNA-200a
inhibits renal cell carcinoma development by directly targeting
TGFB2. Tumour Biol. 36:6691–6700. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou Z, Zhang L, Xie B, Wang X, Yang X,
Ding N, Zhang J, Liu Q, Tan G, Feng D, et al: FOXC2 promotes
chemoresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinomas via induction of
epithelial mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 363:137–145. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu LL, Lu SX, Li M, Li LZ, Fu J, Hu W,
Yang YZ, Luo RZ, Zhang CZ and Yun JP: FoxD3-regulated microRNA-137
suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting AKT2. Oncotarget. 5:5113–5124. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He GY, Hu JL, Zhou L, Zhu XH, Xin SN,
Zhang D, Lu GF, Liao WT, Ding YQ and Liang L: The
FOXD3/miR-214/MED19 axis suppresses tumour growth and metastasis in
human colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 115:1367–1378. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng AS, Li MS, Kang W, Cheng VY, Chou
JL, Lau SS, Go MY, Lee CC, Ling TK, Ng EK, et al: Helicobacter
pylori causes epigenetic dysregulation of FOXD3 to
promote gastric carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 144:122–133.e9.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang L, Li Z, Gai F and Wang Y:
MicroRNA-137 suppresses tumor growth in epithelial ovarian cancer
in vitro and in vivo. Mol Med Rep. 12:3107–3114.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|