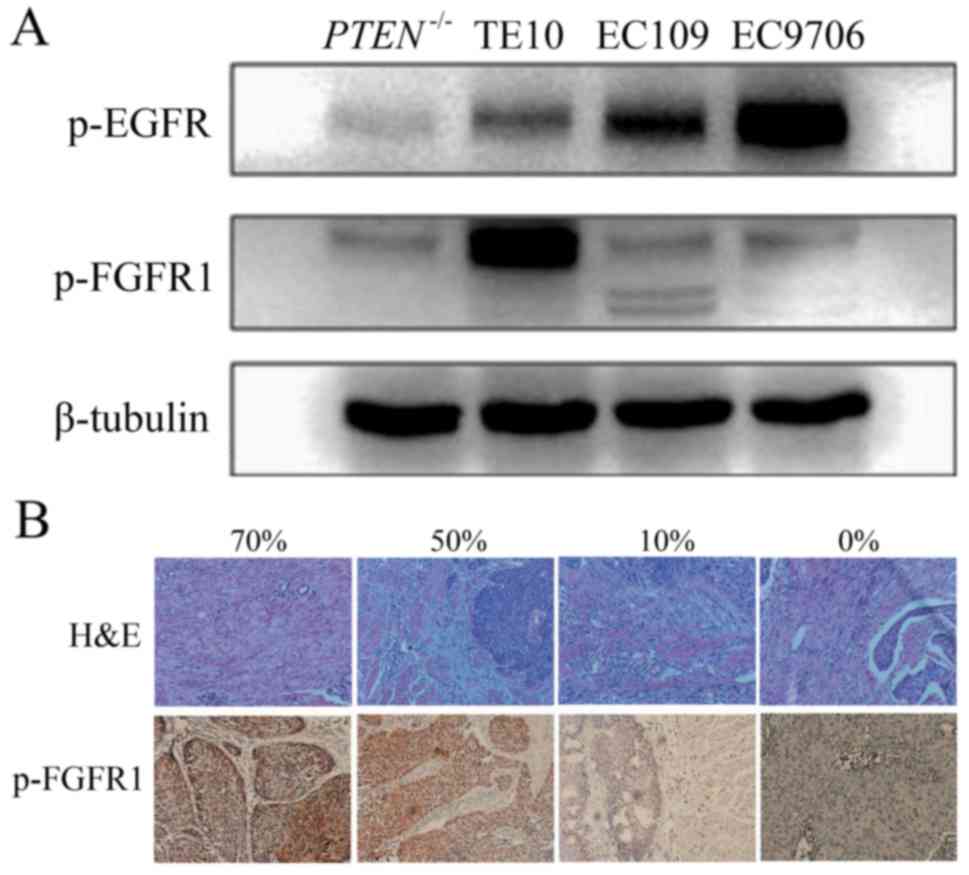
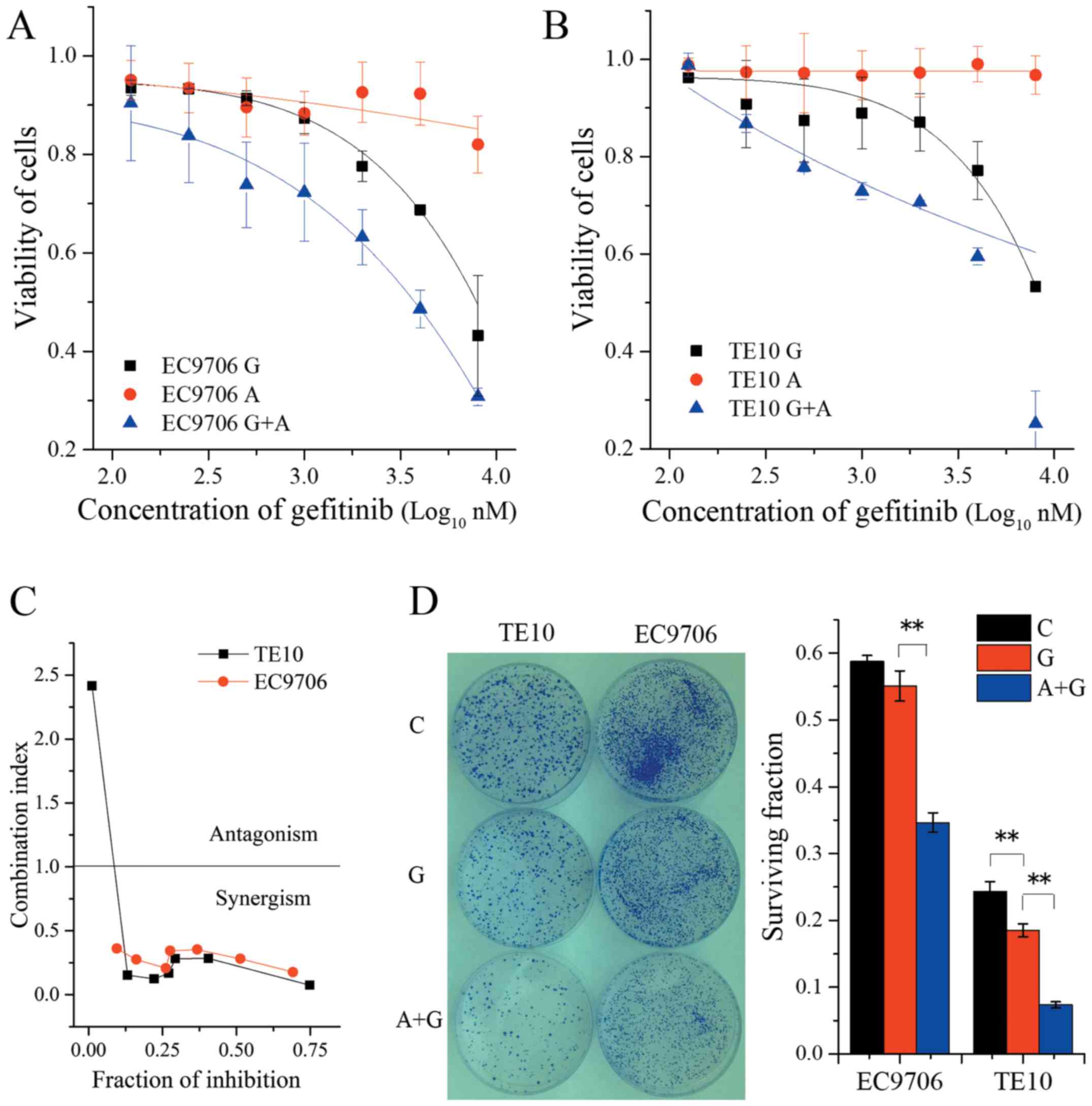
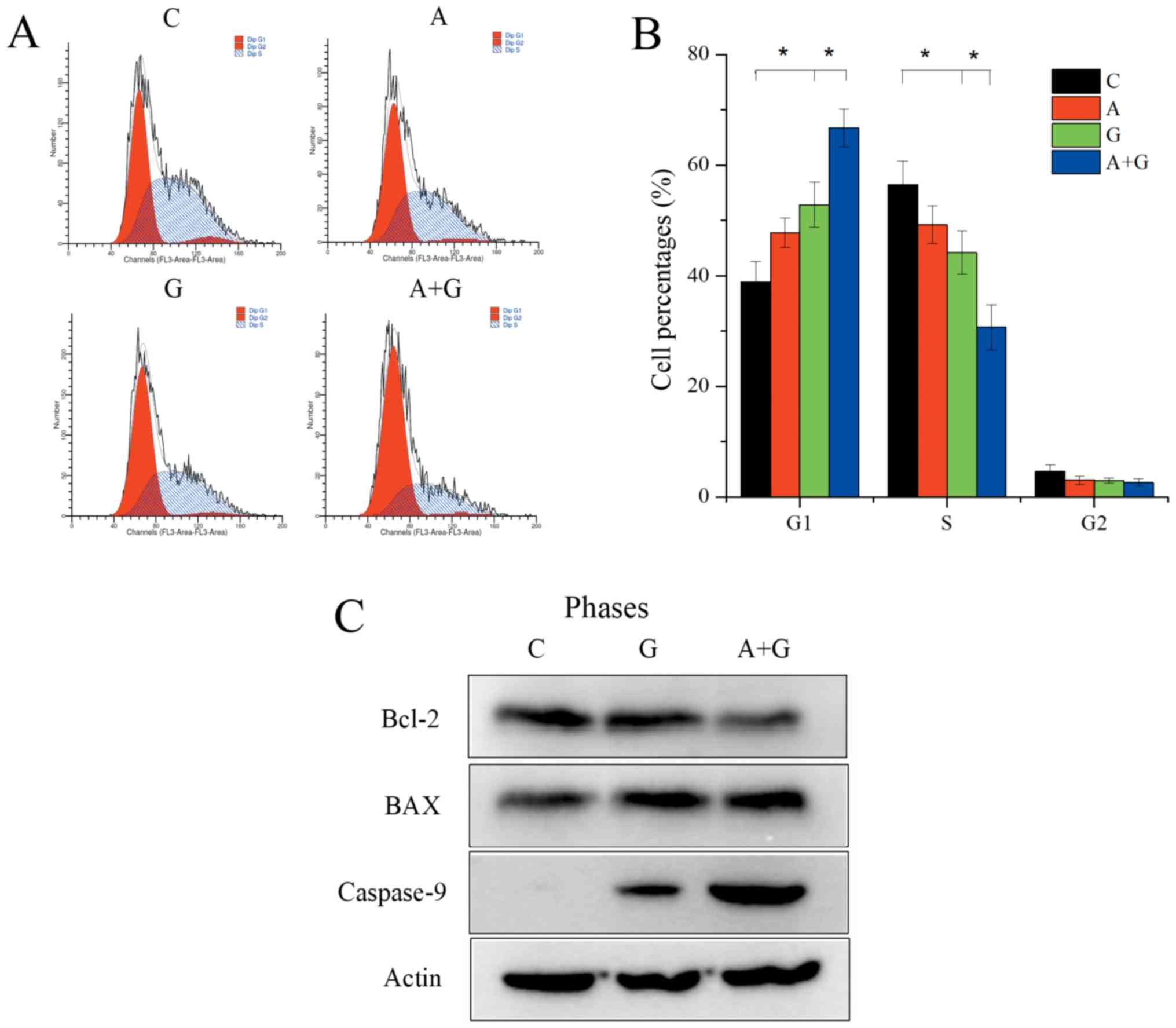
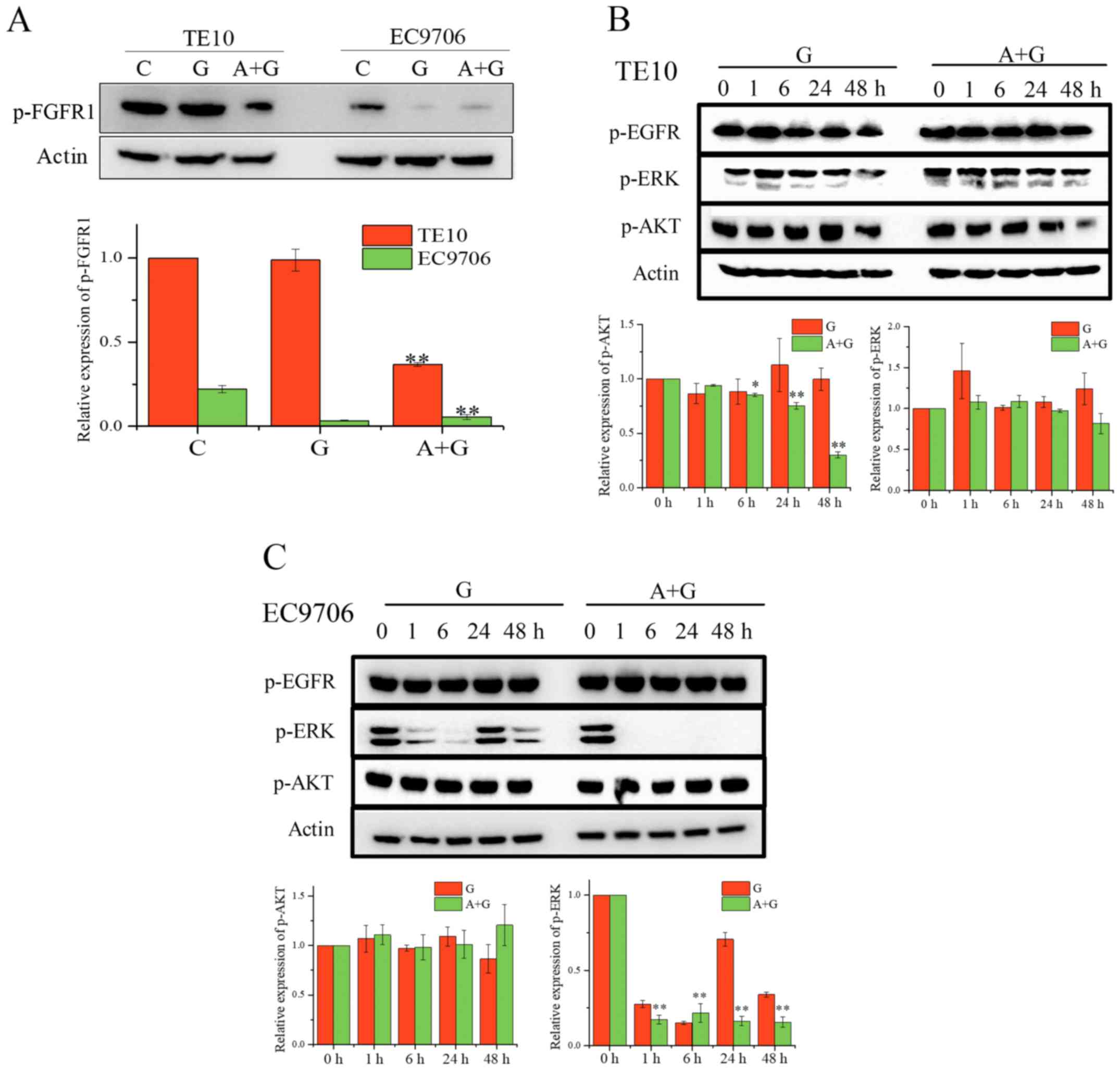
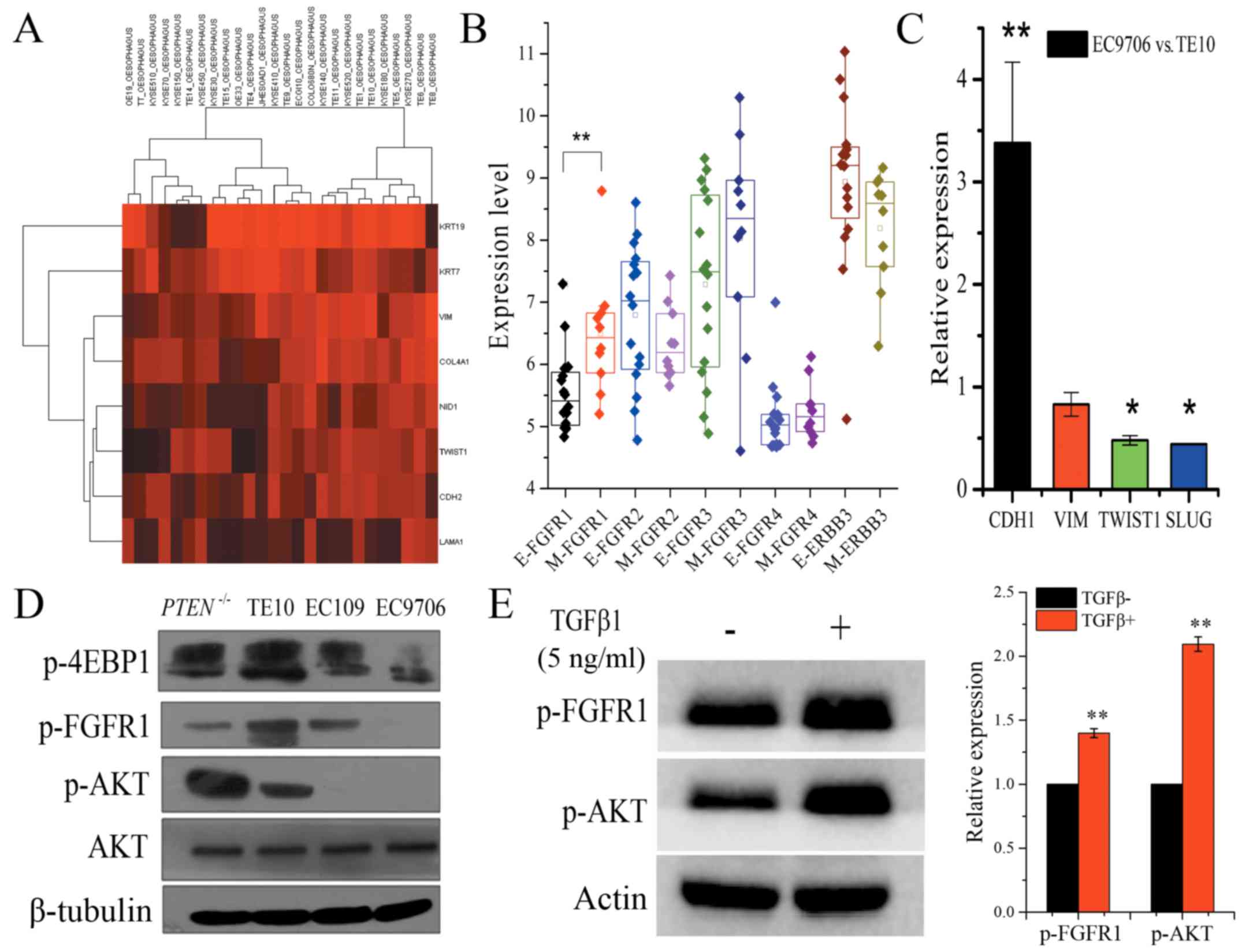
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ando N, Ozawa S, Kitagawa Y, Shinozawa Y
and Kitajima M: Improvement in the results of surgical treatment of
advanced squamous esophageal carcinoma during 15 consecutive years.
Ann Surg. 232:225–232. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pande AU, Iyer RV, Rani A, Maddipatla S,
Yang GY, Nwogu CE, Black JD, Levea CM and Javle MM: Epidermal
growth factor receptor-directed therapy in esophageal cancer.
Oncology. 73:281–289. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gibault L, Metges JP, Conan-Charlet V,
Lozac'h P, Robaszkiewicz M, Bessaguet C, Lagarde N and Volant A:
Diffuse EGFR staining is associated with reduced overall survival
in locally advanced oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Br J Cancer.
93:107–115. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hara F, Aoe M, Doihara H, Taira N, Shien
T, Takahashi H, Yoshitomi S, Tsukuda K, Toyooka S, Ohta T and
Shimizu N: Antitumor effect of gefitinib (‘Iressa’) on esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma cell lines in vitro and in vivo. Cancer
Lett. 226:37–47. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dutton SJ, Ferry DR, Blazeby JM, Abbas H,
Dahle-Smith A, Mansoor W, Thompson J, Harrison M, Chatterjee A,
Falk S, et al: Gefitinib for oesophageal cancer progressing after
chemotherapy (COG): A phase 3, multicentre, double-blind,
placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:894–904.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bandla S, Pennathur A, Luketich JD, Beer
DG, Lin L, Bass AJ, Godfrey TE and Litle VR: Comparative genomics
of esophageal adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Ann
Thorac Surg. 93:1101–1106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Pan T, Zhong X and Cheng C:
Resistance to cetuximab in EGFR-overexpressing esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma xenografts due to FGFR2 amplification and
overexpression. J Pharmacol Sci. 126:77–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Costa R, Carneiro BA, Taxter T, Tavora FA,
Kalyan A, Pai SA, Chae YK and Giles FJ: FGFR3-TACC3 fusion
in solid tumors: Mini review. Oncotarget. 7:55924–55938. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim HS, Lee SE, Bae YS, Kim DJ, Lee CG,
Hur J, Chung H, Park JC, Jung DH, Shin SK, et al: Fibroblast growth
factor receptor 1 gene amplification is associated with poor
survival in patients with resected esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:2562–2572. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Furdui CM, Lew ED, Schlessinger J and
Anderson KS: Autophosphorylation of FGFR1 kinase is mediated by a
sequential and precisely ordered reaction. Mol Cell. 21:711–717.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gavine PR, Mooney L, Kilgour E, Thomas AP,
Al-Kadhimi K, Beck S, Rooney C, Coleman T, Baker D, Mellor MJ, et
al: AZD4547: An orally bioavailable, potent, and selective
inhibitor of the fibroblast growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
family. Cancer Res. 72:2045–2056. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brown WS, Akhand SS and Wendt MK: FGFR
signaling maintains a drug persistent cell population following
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget. 7:83424–83436. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nguyen PT, Tsunematsu T, Yanagisawa S,
Kudo Y, Miyauchi M, Kamata N and Takata T: The FGFR1 inhibitor
PD173074 induces mesenchymal-epithelial transition through the
transcription factor AP-1. Br J Cancer. 109:2248–2258. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ashton JC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 1:24002015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
De Hoon MJ, Imoto S, Nolan J and Miyano S:
Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics. 20:1453–1454.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Saldanha AJ: Java Treeview-extensible
visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics. 20:3246–3248.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jo JC, Choi EK, Shin JS, Moon JH, Hong SW,
Lee HR, Kim SM, Jung SA, Lee DH, Jung SH, et al: Targeting FGFR
pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma: Expressing pFGFR and
pMET for antitumor activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:2613–2622. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koole K, Brunen D, van Kempen PM, Noorlag
R, de Bree R, Lieftink C, van Es RJ, Bernards R and Willems SM:
FGFR1 is a potential prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
22:3884–3893. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiong T, Wang M, Zhao J, Liu Q, Yang C,
Luo W, Li X, Yang H, Kristiansen K, Roy B and Zhou Y: An esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma classification system that reveals
potential targets for therapy. Oncotarget. 8:49851–49860. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xuan X, Zeng Q, Li Y, Gao Y, Wang F, Zhang
H, Wang Z, He H and Li S: Akt-mediated transforming growth
factor-b1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cultured
human esophageal squamous cancer cells. Cancer Gene Therapy.
21:238–245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
He E, Pan F, Li G and Li J: Fractionated
ionizing radiation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
human esophageal cancer cells through PTEN deficiency-mediated Akt
activation. PLoS One. 10:e01261492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tokunaga R, Imamura Y, Nakamura K,
Ishimoto T, Nakagawa S, Miyake K, Nakaji Y, Tsuda Y, Iwatsuki M,
Baba Y, et al: Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 expression, but
not its genetic amplification, is associated with tumor growth and
worse survival in esophagogastric junction adenocarcinoma.
Oncotarget. 6:19748–19761. 2016.
|
|
25
|
Brown WS, Tan L, Smith A, Gray NS and
Wendt MK: Covalent targeting of fibroblast growth factor receptor
inhibits metastatic breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 15:2096–2106.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kitai H, Ebi H, Tomida S, Floros KV,
Kotani H, Adachi Y, Oizumi S, Nishimura M, Faber AC and Yano S:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition defines feedback activation of
receptor tyrosine kinase signaling induced by MEK inhibition in
KRAS-mutant lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 6:754–769. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qian X, Anzovino A, Kim S, Suyama K, Yao
J, Hulit J, Agiostratidou G, Chandiramani N, McDaid HM, Nagi C, et
al: N-cadherin/FGFR promotes metastasis through
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem/progenitor cell-like
properties. Oncogene. 33:3411–3421. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Terry S, El-Sayed IY, Destouches D, Maillé
P, Nicolaiew N, Ploussard G, Semprez F, Pimpie C, Beltran H,
Londono-Vallejo A, et al: CRIPTO overexpression promotes
mesenchymal differentiation in prostate carcinoma cells through
parallel regulation of AKT and FGFR activities. Oncotarget.
6:11994–2008. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Petty RD, Dahle-Smith A, Stevenson DAJ,
Osborne A, Massie D, Clark C, Murray GI, Dutton SJ, Roberts C,
Chong IY, et al: Gefitinib and EGFR gene copy number
aberrations in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 35:2279–2287. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|