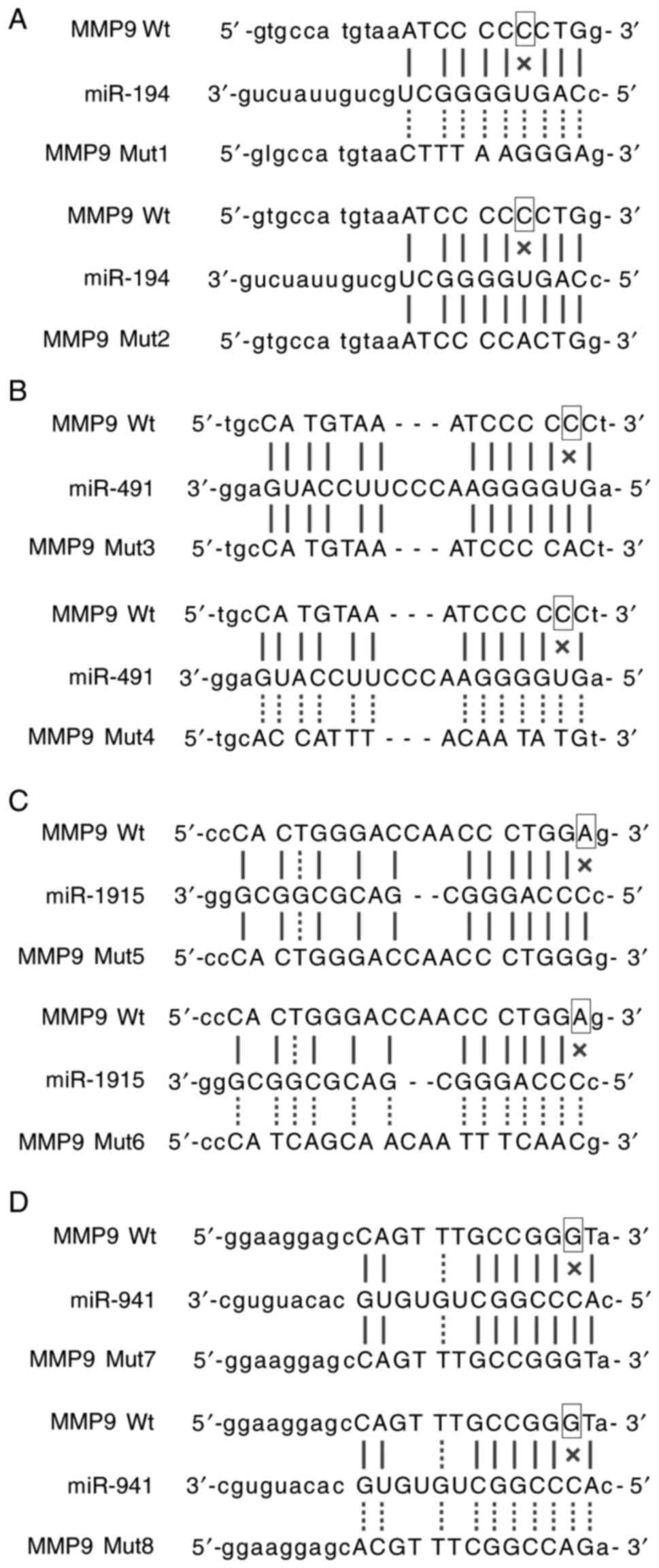
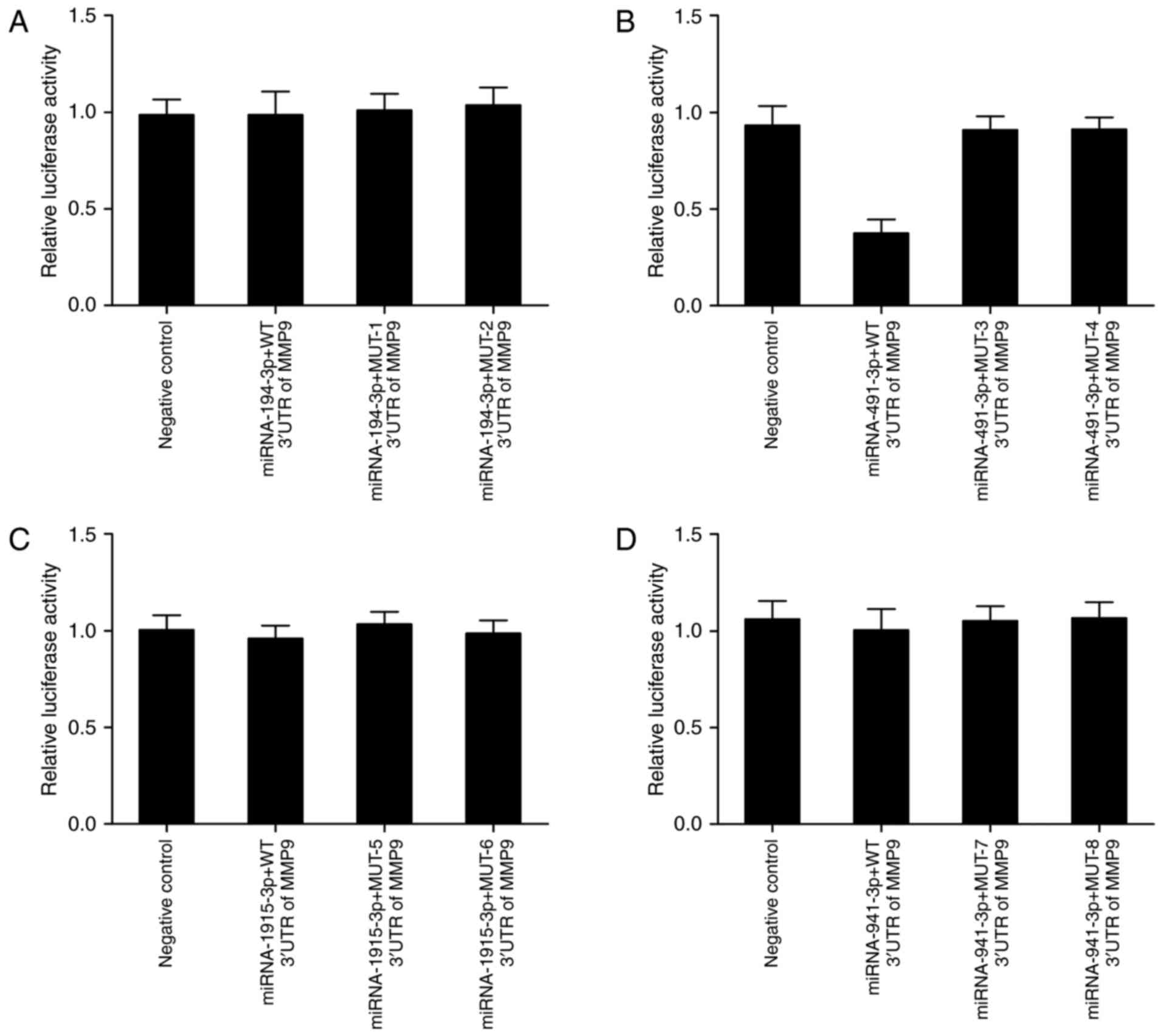
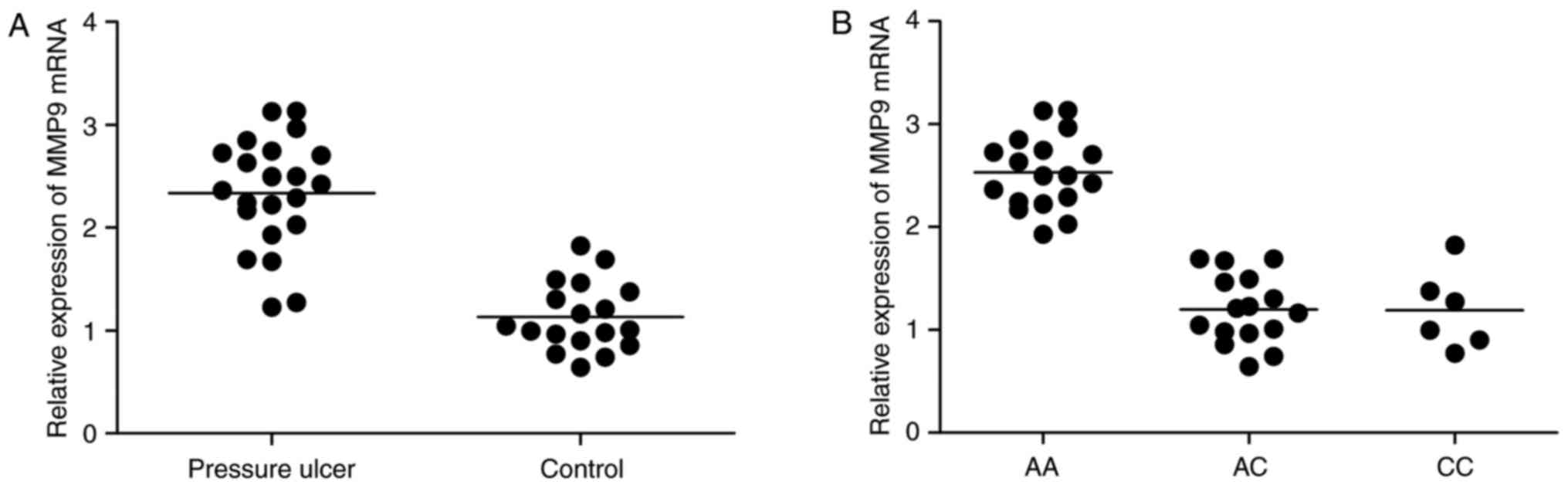
|
1
|
Bours GJ, Halfens RJ, Abu-Saad HH and Grol
RT: Prevalence, prevention, and treatment of pressure ulcers:
Descriptive study in 89 institutions in the Netherlands. Res Nurs
Health. 25:99–110. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Veronesi G, Harley K, Dugdale P and Short
SD: Governance, transparency and alignment in the Council of
Australian Governments (COAG) 2011 national health reform
agreement. Aust Health Rev. 38:288–294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Black J, Baharestani M, Cuddigan J, Dorner
B, Edsberg L, Langemo D, Posthauer ME, Ratliff C and Taler G:
National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel: National pressure ulcer
advisory panel's updated pressure ulcer staging system. Dermatol
Nurs. 19:343–349; quiz 350. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thompson D: A critical review of the
literature on pressure ulcer aetiology. J Wound Care. 14:87–90.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baumgarten M, Margolis DJ, Orwig DL,
Shardell MD, Hawkes WG, Langenberg P, Palmer MH, Jones PS, McArdle
PF, Sterling R, et al: Pressure ulcers in elderly patients with hip
fracture across the continuum of care. J Am Geriatr Soc.
57:863–870. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lindholm C, Sterner E, Romanelli M, Pina
E, Torra y Bou J, Hietanen H, Iivanainen A, Gunningberg L, Hommel
A, Klang B and Dealey C: Hip fracture and pressure ulcers-the
Pan-European Pressure Ulcer Study-intrinsic and extrinsic risk
factors. Int Wound J. 5:315–328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ladwig GP, Robson MC, Liu R, Kuhn MA, Muir
DF and Schultz GS: Ratios of activated matrix metalloproteinase-9
to tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 in wound fluids
are inversely correlated with healing of pressure ulcers. Wound
Repair Regen. 10:26–37. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bonaldo P and Sandri M: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms of muscle atrophy. Dis Model Mech. 6:25–39.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lim LP, Lau NC, Garrett-Engele P, Grimson
A, Schelter JM, Castle J, Bartel DP, Linsley PS and Johnson JM:
Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large
numbers of target mRNAs. Nature. 433:769–773. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deveci M, Catalyürek UV and Toland AE:
mrSNP: Software to detect SNP effects on microRNA binding. BMC
Bioinformatics. 15:732014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yuan M, Zhan Q, Duan X, Song B, Zeng S,
Chen X, Yang Q and Xia J: A functional polymorphism at miR-491-5p
binding site in the 3′-UTR of MMP-9 gene confers increased risk for
atherosclerotic cerebral infarction in a Chinese population.
Atherosclerosis. 226:447–452. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gumieiro DN, Rafacho BP, Gonçalves AF,
Santos PP, Azevedo PS, Zornoff LA, Pereira GJ, Matsubara LS, Paiva
SA and Minicucci MF: Serum metalloproteinases 2 and 9 as predictors
of gait status, pressure ulcer and mortality after hip fracture.
PLoS One. 8:e574242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao XL, Luo X, Wang ZX, Yang GL, Liu JZ,
Liu YQ, Li M, Chen M, Xia YM, Liu JJ, et al: Local blockage of
EMMPRIN impedes pressure ulcers healing in a rat model. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:6692–6699. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen W and Qiu Y: Ginsenoside Rh2 targets
EGFR by up-regulation of miR-491 to enhance anti-tumor activity in
hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 72:325–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li X, Liu Y, Granberg KJ, Wang Q, Moore
LM, Ji P, Gumin J, Sulman EP, Calin GA, Haapasalo H, et al: Two
mature products of MIR-491 coordinate to suppress key cancer
hallmarks in glioblastoma. Oncogene. 34:1619–1628. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakano H, Miyazawa T, Kinoshita K, Yamada
Y and Yoshida T: Functional screening identifies a microRNA,
miR-491 that induces apoptosis by targeting Bcl-X(L) in colorectal
cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 127:1072–1080. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Leivonen SK, Sahlberg KK, Mäkelä R, Due
EU, Kallioniemi O, Børresen-Dale AL and Perälä M: High-throughput
screens identify microRNAs essential for HER2 positive breast
cancer cell growth. Mol Oncol. 8:93–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Denoyelle C, Lambert B, Meryet-Figuiere M,
Vigneron N, Brotin E, Lecerf C, Abeilard E, Giffard F, Louis MH,
Gauduchon P, et al: miR-491-5p-induced apoptosis in ovarian
carcinoma depends on the direct inhibition of both BCL-XL and EGFR
leading to BIM activation. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tao K, Yang J, Guo Z, Hu Y, Sheng H, Gao H
and Yu H: Prognostic value of miR-221-3p, miR-342-3p and miR-491-5p
expression in colon cancer. Am J Transl Res. 6:391–401.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo R, Wang Y, Shi WY, Liu B, Hou SQ and
Liu L: MicroRNA miR-491-5p targeting both TP53 and Bcl-XL induces
cell apoptosis in SW1990 pancreatic cancer cells through
mitochondria mediated pathway. Molecules. 17:14733–14747. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou Y, Li Y, Ye J, Jiang R, Yan H, Yang
X, Liu Q and Zhang J: MicroRNA-491 is involved in metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibitions of matrix metalloproteinase
and epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Liver Int. 33:1271–1280.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu J, Van den Steen PE, Sang QX and
Opdenakker G: Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors as therapy for
inflammatory and vascular diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:480–498.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Roy R, Yang J and Moses MA: Matrix
metalloproteinases as novel biomarkers and potential therapeutic
targets in human cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:5287–5297. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao Q, Meijer MJ, Kubben FJ, Sier CF,
Kruidenier L, van Duijn W, van den Berg M, van Hogezand RA, Lamers
CB and Verspaget HW: Expression of matrix metalloproteinases-2 and
−9 in intestinal tissue of patients with inflammatory bowel
diseases. Dig Liver Dis. 37:584–592. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ordás I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, Baumgart
DC and Sandborn WJ: Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 380:1606–1619.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ben David D, Reznick AZ, Srouji S and
Livne E: Exposure to pro-inflammatory cytokines upregulates MMP-9
synthesis by mesenchymal stem cells-derived osteoprogenitors.
Histochem Cell Biol. 129:589–597. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rodriguez D, Morrison CJ and Overall CM:
Matrix metalloproteinases: What do they not do? New substrates and
biological roles identified by murine models and proteomics.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1803:39–54. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ram M, Sherer Y and Shoenfeld Y: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 and autoimmune diseases. J Clin Immunol.
26:299–307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Grossmann J: Molecular mechanisms of
‘detachment-induced apoptosis-Anoikis’. Apoptosis. 7:247–260. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Delclaux C, Delacourt C, D'Ortho MP, Boyer
V, Lafuma C and Harf A: Role of gelatinase B and elastase in human
polymorphonuclear neutrophil migration across basement membrane. Am
J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 14:288–295. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mast BA and Schultz GS: Interactions of
cytokines, growth factors, and proteases in acute and chronic
wounds. Wound Repair Regen. 4:411–420. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jain A and Bahuguna R: Role of matrix
metalloproteinases in dental caries, pulp and periapical
inflammation: An overview. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 5:212–218.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Latifa K, Sondess S, Hajer G, Manel BH,
Souhir K, Nadia B, Abir J, Salima F and Abdelhedi M: Evaluation of
physiological risk factors, oxidant-antioxidant imbalance,
proteolytic and genetic variations of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in
patients with pressure ulcer. Sci Rep. 6:293712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tian X and Zhang X: A single nucleotide
polymorphism (rs1056629) in 3′-UTR of MMP-9 is responsible for a
decreased risk of metastatic osteosarcoma by compromising its
interaction with microRNA-491-5p. Cell Physiol Biochem.
38:1415–1424. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|