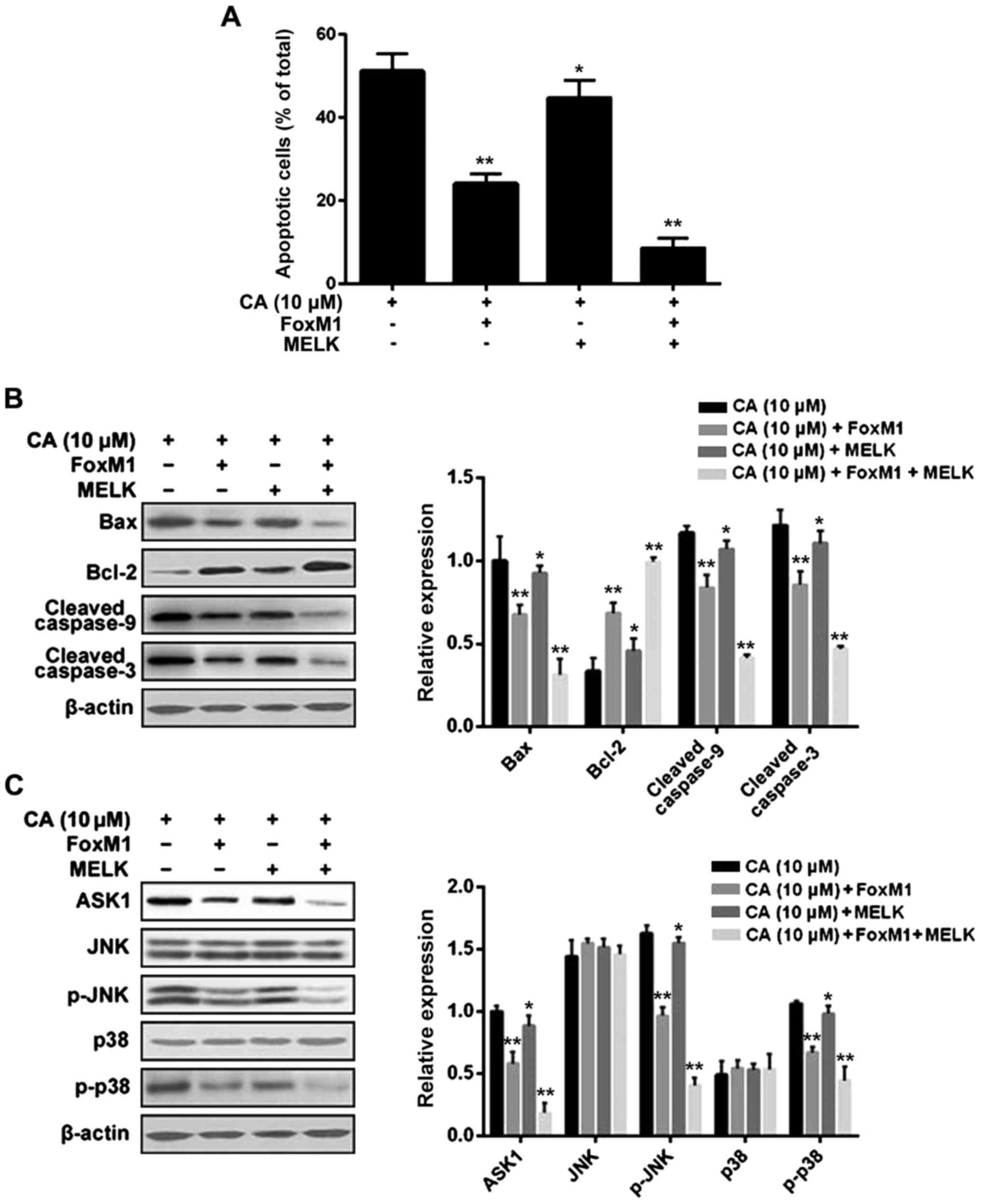
|
1
|
Kivelä T: The epidemiological challenge of
the most frequent eye cancer: Retinoblastoma, an issue of birth and
death. Br J Ophthalmol. 93:1129–1131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Park SJ, Woo SJ and Park KH: Incidence of
retinoblastoma and survival rate of retinoblastoma patients in
Korea using the Korean National Cancer Registry database
(1993–2010). Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 55:2816–2821. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Waddell KM, Kagame K, Ndamira A,
Twinamasiko A, Picton SV, Simmons IG, Johnston WT and Newton R:
Clinical features and survival among children with retinoblastoma
in Uganda. Br J Ophthalmol. 99:387–390. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McEvoy JD and Dyer MA: Genetic and
epigenetic discoveries in human retinoblastoma. Crit Rev Oncog.
20:217–225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
DiCiommo D, Gallie BL and Bremner R:
Retinoblastoma: The disease, gene and protein provide critical
leads to understand cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 10:255–269. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meel R, Radhakrishnan V and Bakhshi S:
Current therapy and recent advances in the management of
retinoblastoma. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol. 33:80–88. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim JY and Park Y: Treatment of
Retinoblastoma: The role of external beam radiotherapy. Yonsei Med
J. 56:1478–1491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ye J, Lou L, Jin K, Xu Y, Ye X, Moss T and
McBain H: Vision-related quality of life and appearance concerns
are associated with anxiety and depression after eye enucleation: A
cross-sectional study. PLoS One. 10:e01364602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Marees T, Moll AC, Imhof SM, de Boer MR,
Ringens PJ and van Leeuwen FE: Risk of second malignancies in
survivors of retinoblastoma: More than 40 years of follow-up. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 100:1771–1779. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Temming P, Arendt M, Viehmann A, Eisele L,
Le Guin CH, Schündeln MM, Biewald E, Astrahantseff K, Wieland R,
Bornfeld N, et al: Incidence of second cancers after radiotherapy
and systemic chemotherapy in heritable retinoblastoma survivors: A
report from the German reference center. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
64:71–80. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mazumder K, Tanaka K and Fukase K:
Cytotoxic activity of ursolic acid derivatives obtained by
isolation and oxidative derivatization. Molecules. 18:8929–8944.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shan JZ, Xuan YY, Zheng S, Dong Q and
Zhang SZ: Ursolic acid inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis
of HT-29 colon cancer cells by inhibiting the EGFR/MAPK pathway. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 10:668–674. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Leng S, Hao Y, Du D, Xie S, Hong L, Gu H,
Zhu X, Zhang J, Fan D and Kung HF: Ursolic acid promotes cancer
cell death by inducing Atg5-dependent autophagy. Int J Cancer.
133:2781–2790. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim SH, Ryu HG, Lee J, Shin J, Harikishore
A, Jung HY, Kim YS, Lyu HN, Oh E, Baek NI, et al: Ursolic acid
exerts anti-cancer activity by suppressing vaccinia-related kinase
1-mediated damage repair in lung cancer cells. Sci Rep.
5:145702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weng H, Tan ZJ, Hu YP, Shu YJ, Bao RF,
Jiang L, Wu XS, Li ML, Ding Q, Wang XA, et al: Ursolic acid induces
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of gallbladder carcinoma cells.
Cancer Cell Int. 14:962014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang CY, Lin CY, Tsai CW and Yin MC:
Inhibition of cell proliferation, invasion and migration by ursolic
acid in human lung cancer cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro.
25:1274–1280. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sung B, Kang YJ, Kim DH, Hwang SY, Lee Y,
Kim M, Yoon JH, Kim CM, Chung HY and Kim ND: Corosolic acid induces
apoptotic cell death in HCT116 human colon cancer cells through a
caspase-dependent pathway. Int J Mol Med. 33:943–949. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zona S, Bella L, Burton MJ, de Moraes
Nestal G and Lam EW: FOXM1: An emerging master regulator of DNA
damage response and genotoxic agent resistance. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1839:1316–1322. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koo CY, Muir KW and Lam EW: FOXM1: From
cancer initiation to progression and treatment. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1819:28–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ganguly R, Mohyeldin A, Thiel J, Kornblum
HI, Beullens M and Nakano I: MELK - a conserved kinase: Functions,
signaling, cancer, and controversy. Clin Transl Med. 4:112015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Joshi K, Banasavadi-Siddegowda Y, Mo X,
Kim SH, Mao P, Kig C, Nardini D, Sobol RW, Chow LM, Kornblum HI, et
al: MELK-dependent FOXM1 phosphorylation is essential for
proliferation of glioma stem cells. Stem Cells. 31:1051–1063. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang JS, Ren TN and Xi T: Ursolic acid
induces apoptosis by suppressing the expression of FoxM1 in MCF-7
human breast cancer cells. Med Oncol. 29:10–15. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
van Meerloo J, Kaspers GJ and Cloos J:
Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. Methods Mol Biol.
731:237–245. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu X, Wang K, Zhang K, Zhang T, Yin Y and
Xu F: Ziyuglycoside I inhibits the proliferation of MDA-MB-231
breast carcinoma cells through Inducing p53-mediated G2/M cell
cycle arrest and intrinsic/extrinsic apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci.
17:19032016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang K, Zhu X, Zhang K, Wu Z, Sun S, Zhou
F and Zhu L: Neuroprotective effect of puerarin on
glutamate-induced cytotoxicity in differentiated Y-79 cells via
inhibition of ROS generation and Ca2+ influx. Int J Mol
Sci. 17:E11092016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smale ST: Luciferase assay. Cold Spring
Harb Protoc 2010: pdb prot5421. doi: 10.1101/pdb.prot5421.
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Lee YM, Baitsch L, Huang A, Xiang
Y, Tong H, Lako A, Von T, Choi C, Lim E, et al: MELK is an
oncogenic kinase essential for mitotic progression in basal-like
breast cancer cells. eLife. 3:e017632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lin ML, Park JH, Nishidate T, Nakamura Y
and Katagiri T: Involvement of maternal embryonic leucine zipper
kinase (MELK) in mammary carcinogenesis through interaction with
Bcl-G, a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family. Breast Cancer
Res. 9:R172007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang L, Wang P, Chen L and Chen H:
Down-regulation of FoxM1 by thiostrepton or small interfering RNA
inhibits proliferation, transformation ability and angiogenesis,
and induces apoptosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:5450–5460. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ku CY, Wang YR, Lin HY, Lu SC and Lin JY:
Corosolic acid inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration by
targeting the VEGFR2/Src/FAK pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01267252015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoo KH, Park JH, Lee DY, Hwang-Bo J, Baek
NI and Chung IS: Corosolic acid exhibits anti-angiogenic and
anti-lymphangiogenic effects on in vitro endothelial cells and on
an in vivo CT-26 colon carcinoma animal model. Phytother Res.
29:714–723. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee HS, Park JB, Lee MS, Cha EY, Kim JY
and Sul JY: Corosolic acid enhances 5-fluorouracil-induced
apoptosis against SNU-620 human gastric carcinoma cells by
inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Med Rep.
12:4782–4788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wierstra I: The transcription factor FOXM1
(Forkhead box M1): Proliferation-specific expression, transcription
factor function, target genes, mouse models, and normal biological
roles. Adv Cancer Res. 118:97–398. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Laoukili J, Kooistra MR, Brás A, Kauw J,
Kerkhoven RM, Morrison A, Clevers H and Medema RH: FoxM1 is
required for execution of the mitotic programme and chromosome
stability. Nat Cell Biol. 7:126–136. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wierstra I: FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1) in
tumorigenesis: Overexpression in human cancer, implication in
tumorigenesis, oncogenic functions, tumor-suppressive properties,
and target of anticancer therapy. Adv Cancer Res. 119:191–419.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Aytes A, Mitrofanova A, Lefebvre C,
Alvarez MJ, Castillo-Martin M, Zheng T, Eastham JA, Gopalan A,
Pienta KJ, Shen MM, et al: Cross-species regulatory network
analysis identifies a synergistic interaction between FOXM1
and CENPF that drives prostate cancer malignancy. Cancer
Cell. 25:638–651. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
de Moraes Nestal G, Delbue D, Silva KL,
Robaina MC, Khongkow P, Gomes AR, Zona S, Crocamo S, Mencalha AL,
Magalhães LM, et al: FOXM1 targets XIAP and Survivin to modulate
breast cancer survival and chemoresistance. Cell Signal.
27:2496–2505. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ganguly R, Hong CS, Smith LG, Kornblum HI
and Nakano I: Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase: Key kinase
for stem cell phenotype in glioma and other cancers. Mol Cancer
Ther. 13:1393–1398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xia H, Kong SN, Chen J, Shi M, Sekar K,
Seshachalam VP, Rajasekaran M, Goh BKP, Ooi LL and Hui KM: MELK is
an oncogenic kinase essential for early hepatocellular carcinoma
recurrence. Cancer Lett. 383:85–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|