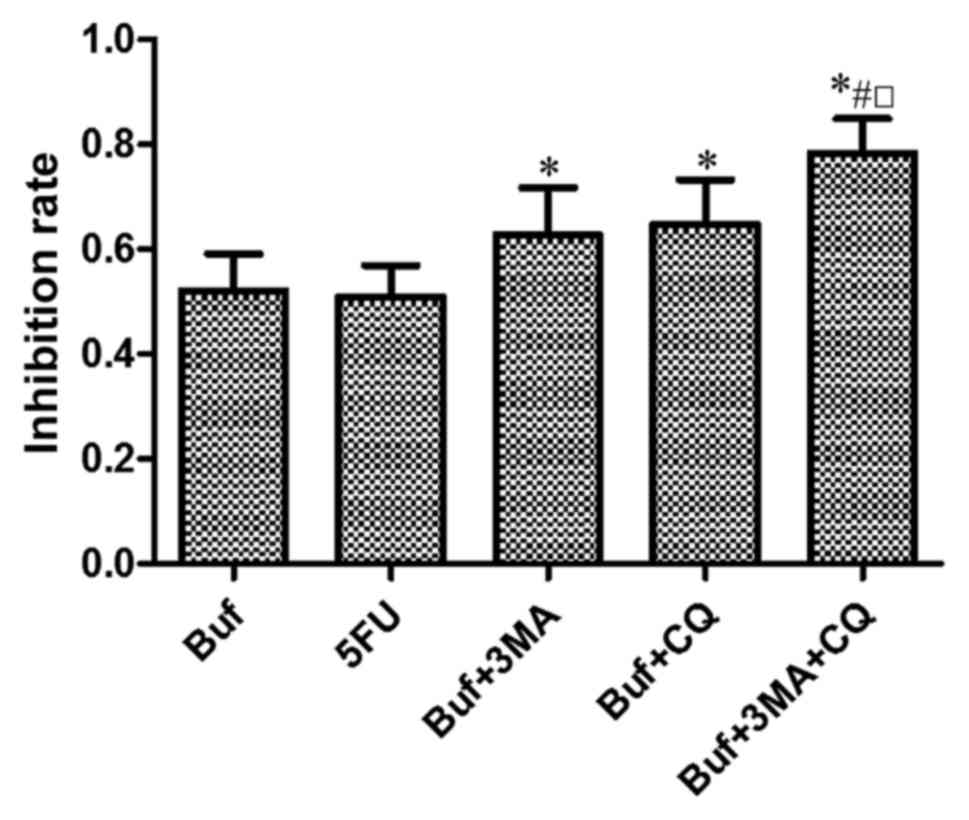
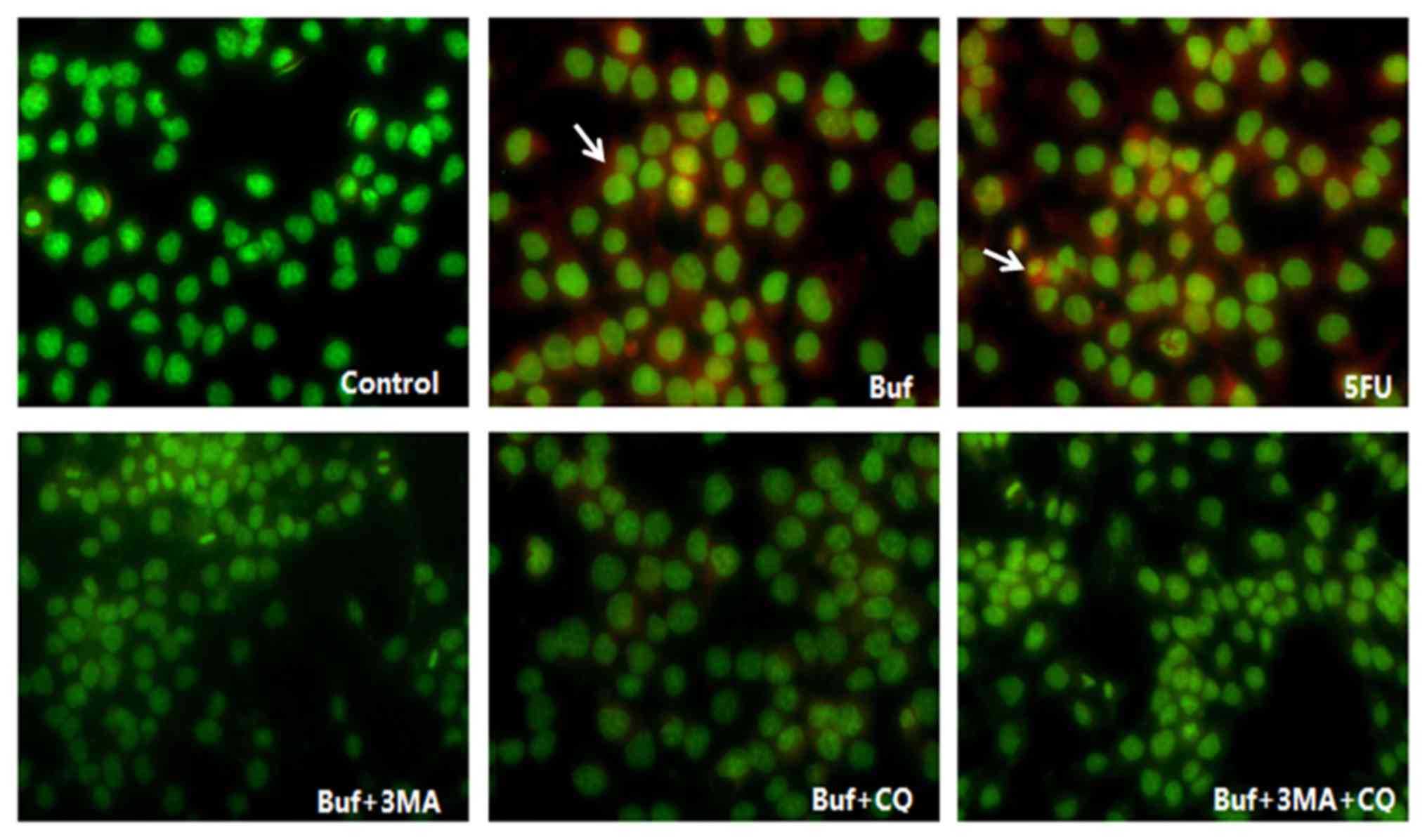
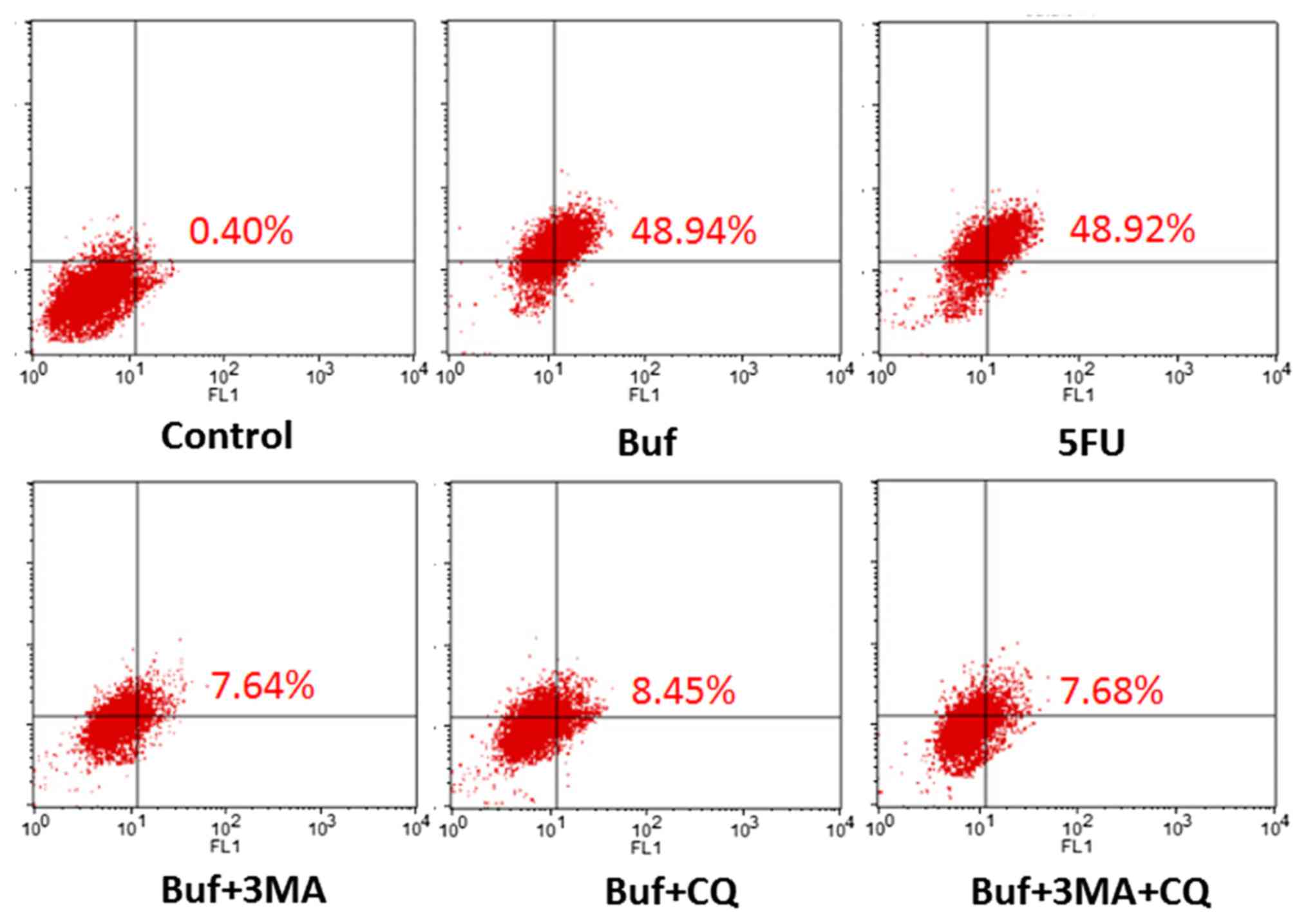
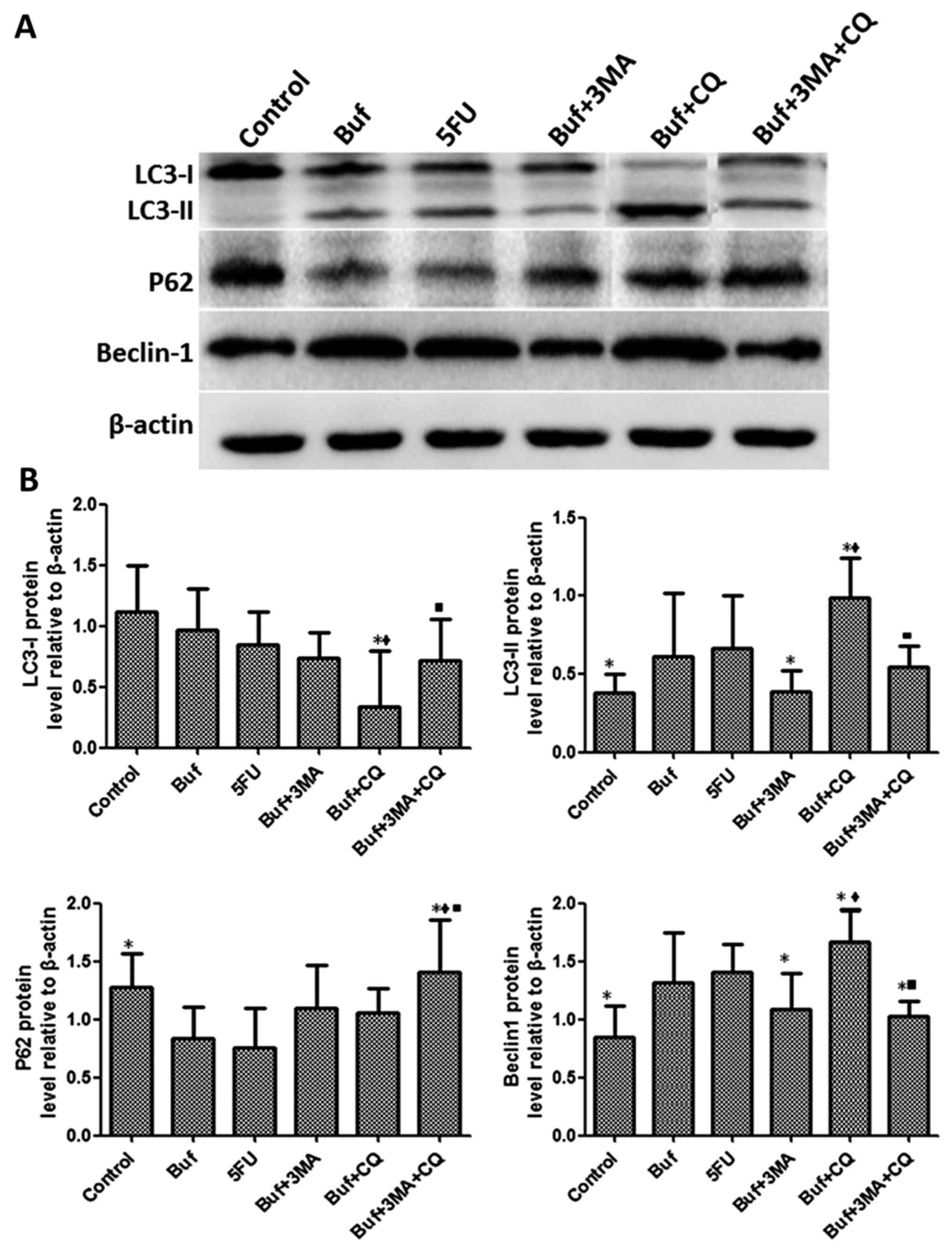
|
1
|
Hale AN, Ledbetter DJ, Gawriluk TR and
Rucker EB III: Autophagy: Regulation and role in development.
Autophagy. 9:951–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ding ZB, Shi YH, Zhou J, Qiu SJ, Xu Y, Dai
Z, Shi GM, Wang XY, Ke AW, Wu B, et al: Association of autophagy
defect with a malignant phenotype and poor prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:9167–9175. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Du H, Yang W, Chen L, Shi M, Seewoo V,
Wang J, Lin A, Liu Z and Qiu W: Role of autophagy in resistance to
oxaliplatin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep.
27:143–150. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guo XL, Li D, Hu F, Song JR, Zhang SS,
Deng WJ, Sun K, Zhao QD, Xie XQ, Song YJ, et al: Targeting
autophagy potentiates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and
proliferation inhibition in hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Letter.
320:171–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Choi KS: Autophagy and cancer. Exp Mol
Med. 44:109–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang CL and Zhu YQ: Advances in research
on antitumor activity of toads. Nat Product Res Dev. 12:67–72.
2000.
|
|
7
|
Han JT, Chen XY and Xu RC: Advances in
pharmacological activities of bufalin. Chin Remed Clin. 2:120–122.
2002.
|
|
8
|
Chen XY, Hu WL, Xu RC, Chen L and Qian J:
Effect of bufalin on cytotoxicity and growth related gene
expression of human hepatoma cell line SMMC 7721. Chin J Pharmacol
Toxicol. 15:293–296. 2001.
|
|
9
|
Gai JQ, Qin JM and Fan YZ: Experimental
study on bufalin inhibiting hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation
and invasion. World Chin J Digestol. 22:1921–1927. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sheng X, Sun X, Sun K, Sui H, Qin J and Li
Q: Inhibitory effect of bufalin combined with Hedgehog signaling
pathway inhibitors on proliferation and invasion and metastasis of
liver cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 49:1513–1524. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Change J, Sun K, Sheng X and Qin JM:
Experimental study of bufalin on inhibiting cell proliferation and
apoptosis in liver can cer cells with high metastatic potential.
Chin J Exp Surg. 32:2388–2391. 2015.
|
|
12
|
Gai JQ, Sheng X, Qin JM, Sun K, Zhao W and
Ni L: The effect and mechanism of bufalin on regulating
hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis via
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Oncol. 48:338–348. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A,
Bruun JA, Outzen H, Øvervatn A, Bjørkøy G and Johansen T:
p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of
ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem.
282:24131–24145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Levine B and Yuan J: Autophagy in cell
death: An innocent convict? J Clin Invest. 115:2679–2688. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tanida I, Nishitani T, Nemoto T, Ueno T
and Kominami E: Mammalian Apg12p, but not the Apg12p. Apg5p
conjugate, facilitates LC3 processing. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
296:1164–1170. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: In vitro
assays of lipidation of Mammalian Atg8 homologs. Curr Protoc Cell
Biol. 64:11.20.1–13. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhou ZW, Li YX, He ZX, Pan ST, Yang Y,
Zhang X, Chow K, Yang T, Qiu JX, Zhou Q, et al: Induction of
apoptosis and autophagy via sirtuin1- and PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated
pathways by plumbagin in human prostate cancer cells. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 9:1511–1554. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Koike M, Sou YS, Ueno
T, Hara T, Mizushima N, Iwata J, Ezaki J, Murata S, et al:
Homeostatic levels of p62 control cytoplasmic inclusion body
formation in autophagy-deficient mice. Cell. 131:1149–1163. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Inoue D, Suzuki T, Mitsuishi Y, Miki Y,
Suzuki S, Sugawara S, Watanabe M, Sakurada A, Endo C, Uruno A, et
al: Accumulation of p62/SQSTM1 is associated with poor prognosis in
patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 103:760–766. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duan ZL, Peng ZL and Wang ZH: Expression
and involved signal transduction pathway of autophagy gene Beclin 1
in epithelialovarian cancer. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban.
38:239–242. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Z, Yang B, Guo Y, Zheng QC, Peng Y, Ke
WB, Zhang L and Xiong J: Starvation-induced autophage promotes
invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Acta Med Univ Sci
Technol Huangzhong. 41:513–517. 2012.
|
|
22
|
Ferrari V and Cutler DJ: Uptake of
chloroquine by human erythrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 39:753–762.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hao G, Sun TS and Li SG: Advances in
detection of autophagy in mammals. Chin J Clinicians. 6:1531–1533.
2012.
|
|
24
|
Kovács AL, Molnár K and Seglen PO:
Inhibition of autophagic sequestration and endogenous protein
degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes by methylated adenosine
derivatives. FEBS Lett. 134:194–196. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen S, Zhou L, Zhang Y, Leng Y, Pei XY,
Lin H, Jones R, Orlowski RZ, Dai Y and Grant S: Targeting
SQSTM1/p62 induces cargo loading failure and converts autophagy to
apoptosis via NBK/Bik. Mol Cell Biol. 34:3435–3449. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|