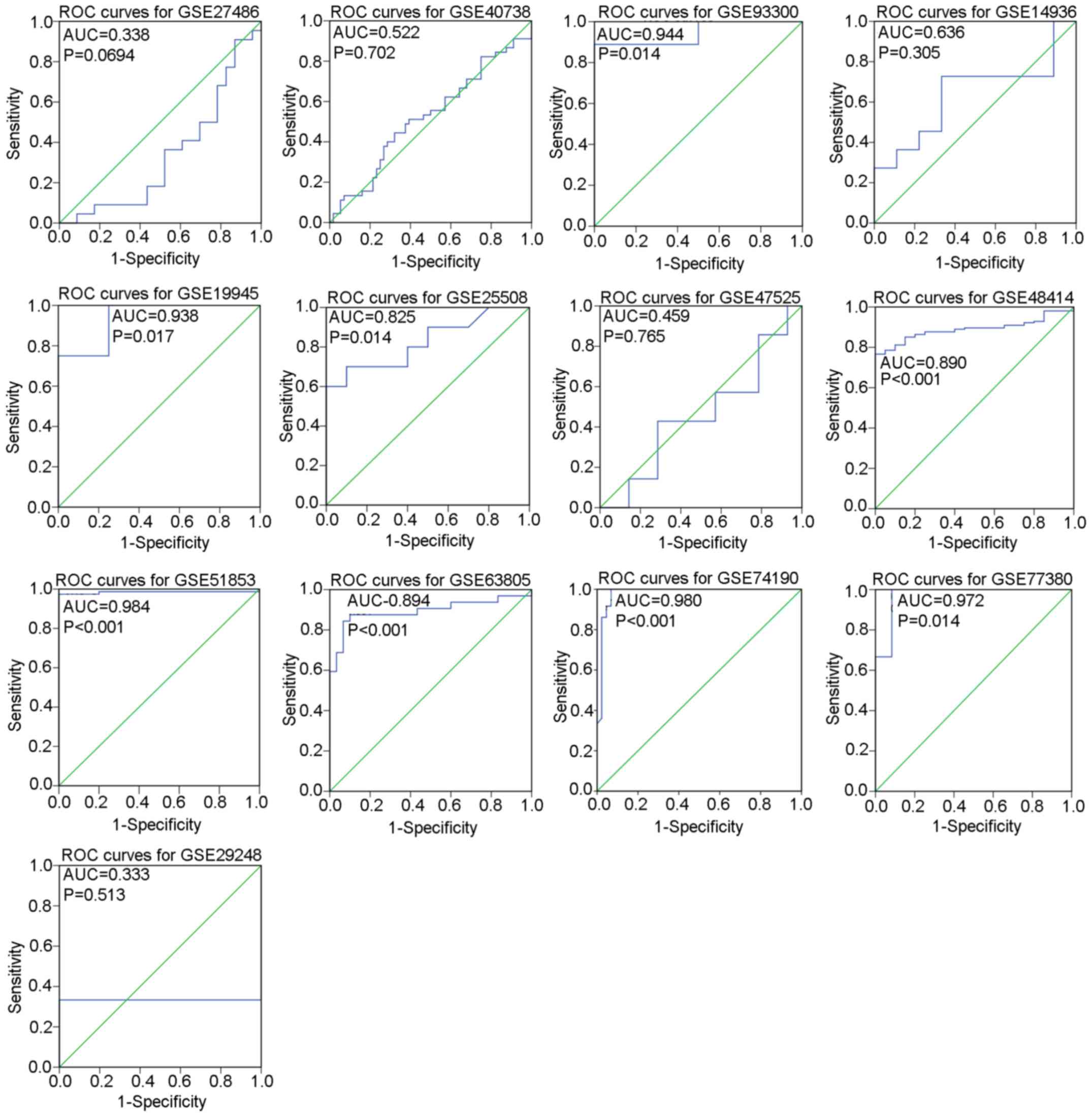
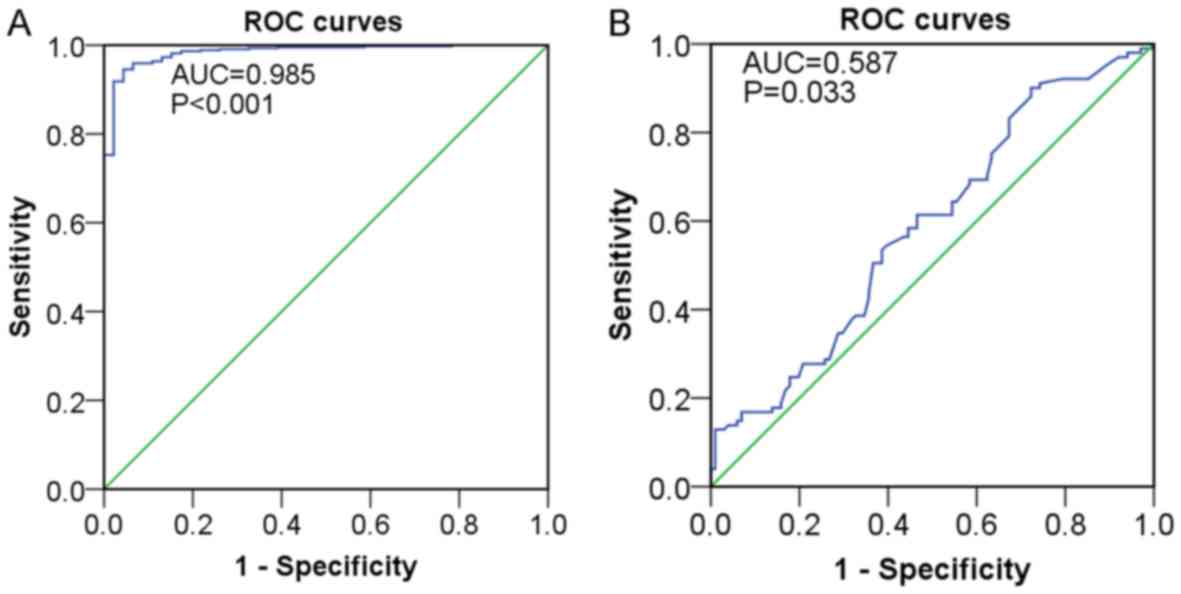
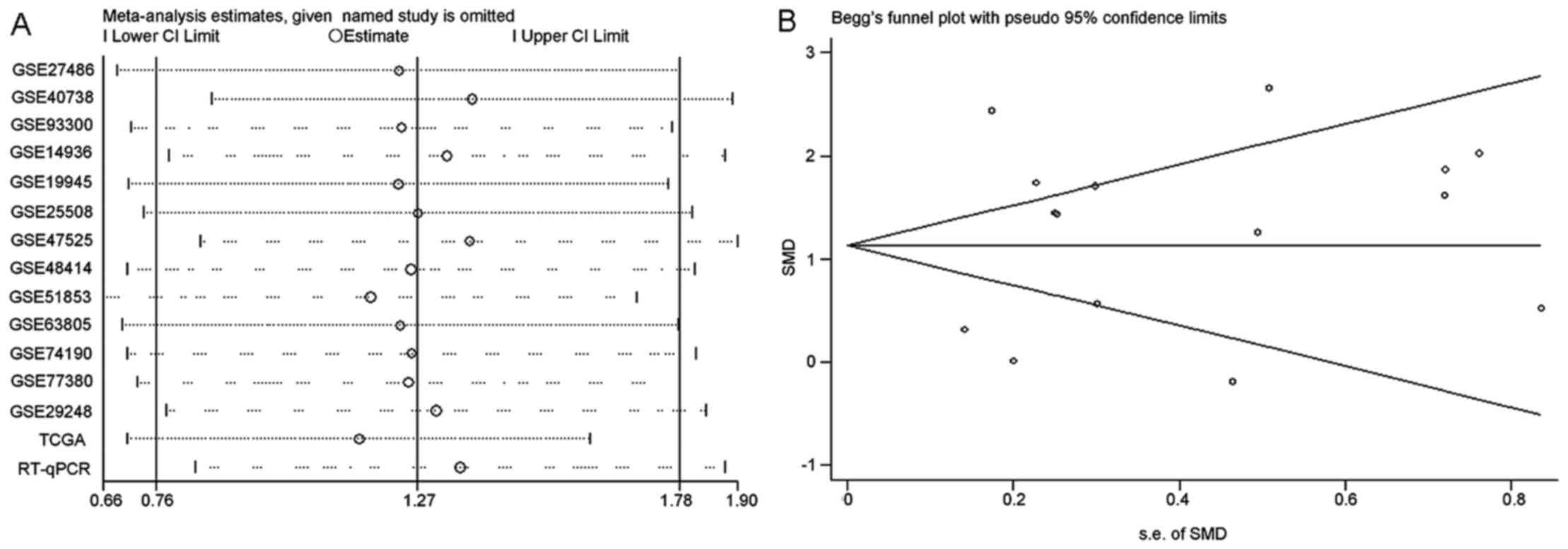
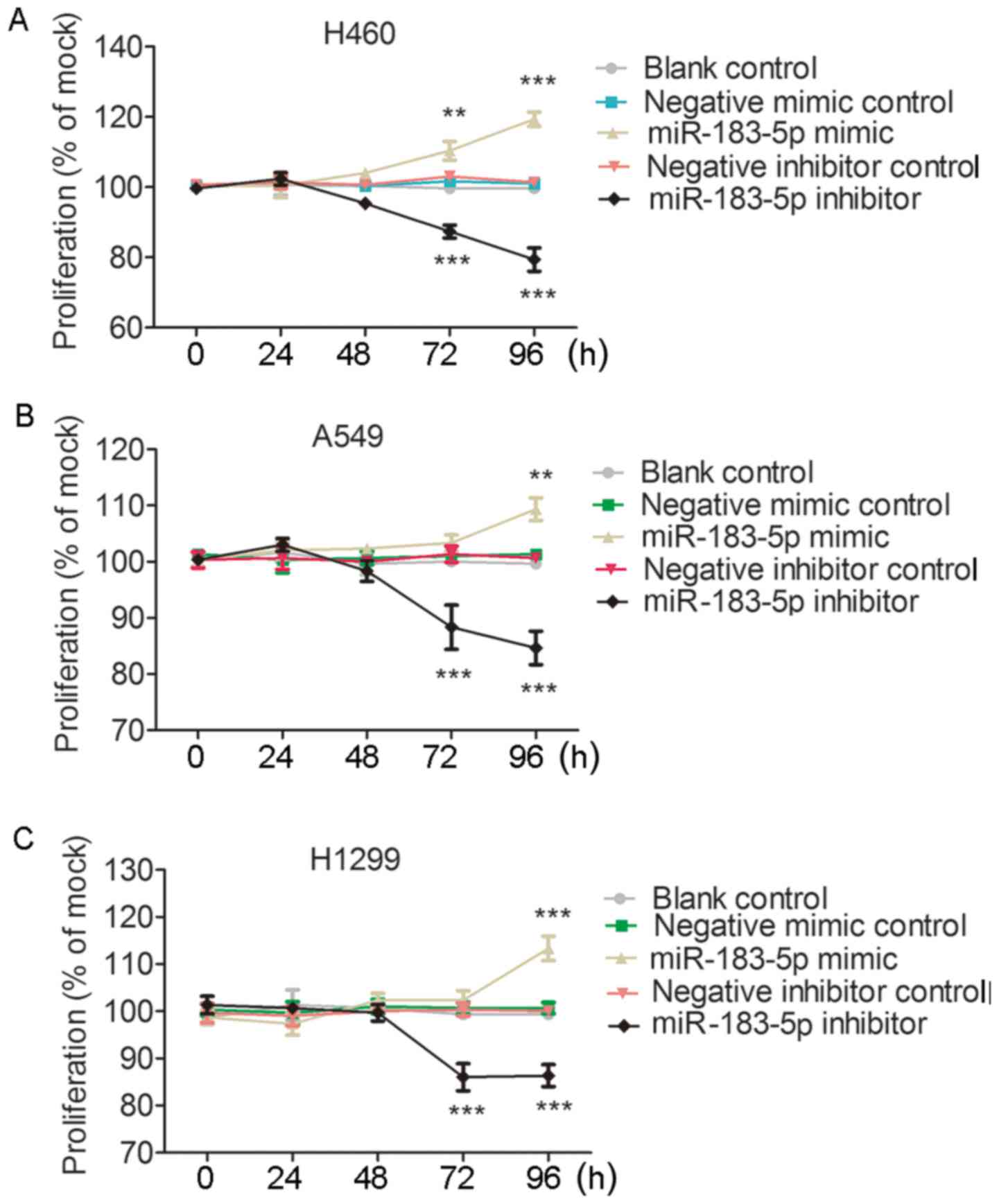
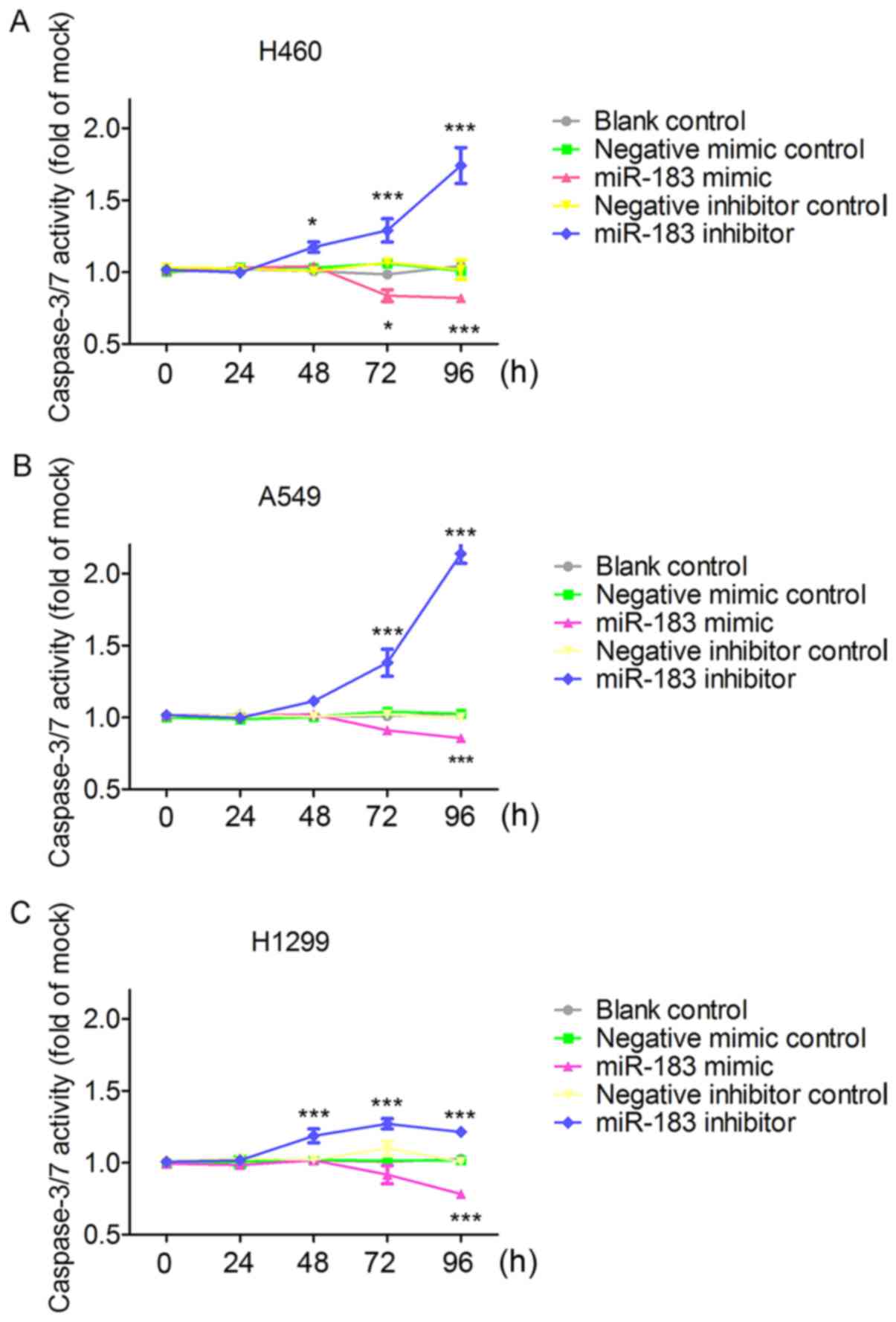
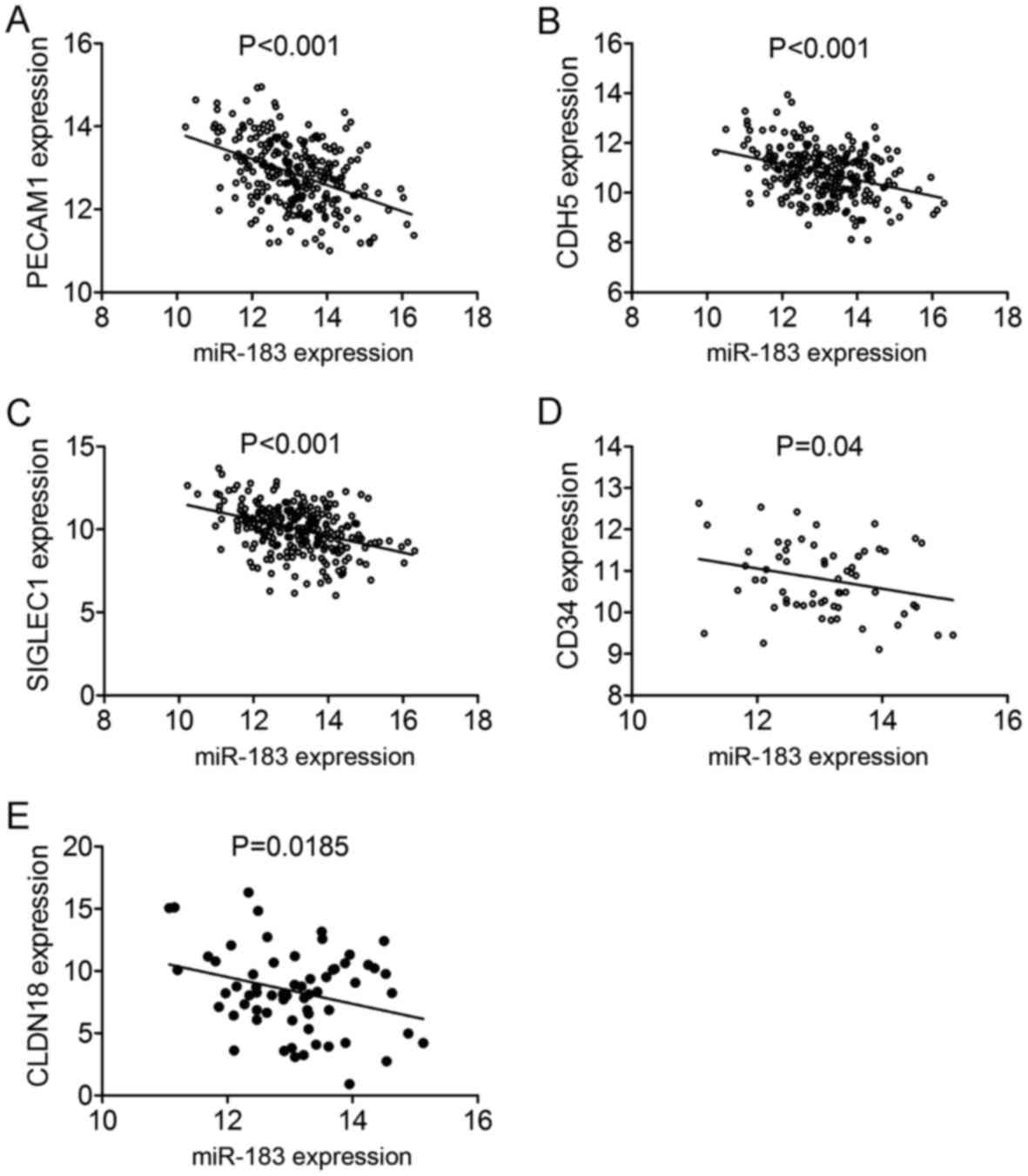
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J and Haber
DA: Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:169–181. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Choi YL, Sun JM, Cho J, Rampal S, Han J,
Parasuraman B, Guallar E, Lee G, Lee J and Shim YM: EGFR mutation
testing in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A
comprehensive evaluation of real-world practice in an East Asian
tertiary hospital. PLoS One. 8:e560112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cobo M, Gutiérrez V, Villatoro R, Trigo
JM, Ramos I, López O, Ruiz M, Godoy A, López I and Arroyo M:
Spotlight on ramucirumab in the treatment of nonsmall cell lung
cancer: Design, development, and clinical activity. Lung Cancer
(Auckl). 8:57–66. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang Q, Zhang RW, Sui PC, He HT and Ding
L: Dysregulation of non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:10956–10981. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Romero-Cordoba SL, Salido-Guadarrama I,
Rodriguez-Dorantes M and Hidalgo-Miranda A: miRNA biogenesis:
Biological impact in the development of cancer. Cancer Biol Ther.
15:1444–1455. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mulrane L, McGee SF, Gallagher WM and
O'Connor DP: miRNA dysregulation in breast cancer. Cancer Res.
73:6554–6562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Palanichamy JK and Rao DS: miRNA
dysregulation in cancer: Towards a mechanistic understanding. Front
Genet. 5:542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang H, Guan X, Tu Y, Zheng S, Long J, Li
S, Qi C, Xie X, Zhang H and Zhang Y: MicroRNA-29b attenuates
non-small cell lung cancer metastasis by targeting matrix
metalloproteinase 2 and PTEN. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:592015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dambal S, Shah M, Mihelich B and Nonn L:
The microRNA-183 cluster: The family that plays together stays
together. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:7173–7188. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen H, Zhang L, Zhang L, Du J, Wang H and
Wang B: MicroRNA-183 correlates cancer prognosis, regulates cancer
proliferation and bufalin sensitivity in epithelial ovarian caner.
Am J Transl Res. 8:1748–1755. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng Y, Xiang G, Meng Y and Dong R:
MiRNA-183-5p promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in
human breast cancer by targeting the PDCD4. Reprod Biol.
16:225–233. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan D, Wang Y, Qi P, Chen Y, Xu P, Yang X,
Jin X and Tian X: MicroRNA-183 functions as the tumor suppressor
via inhibiting cellular invasion and metastasis by targeting MMP-9
in cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 141:166–174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu F, Zhang H, Su Y, Kong J, Yu H and Qian
B: Up-regulation of microRNA-183-3p is a potent prognostic marker
for lung adenocarcinoma of female non-smokers. Clin Transl Oncol.
16:980–985. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhu WY, Zhang YK, Chai Z, Hu X, Tan L,
Wang Z, Chen Z and Le H: Identification of factors for the
preoperative prediction of tumour subtype and prognosis in patients
with T1 lung adenocarcinoma. Dis Markers. 2016:93546802016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu C, Deng X, Wu J, Zhang J, Yang H, Fu
S, Zhang Y, Han Y, Zou Y, Chen Z, et al: MicroRNA-183 promotes
migration and invasion of CD133(+)/CD326(+) lung adenocarcinoma
initiating cells via PTPN4 inhibition. Tumour Biol. 37:11289–11297.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Harbord RM, Deeks JJ, Egger M, Whiting P
and Sterne JA: A unification of models for meta-analysis of
diagnostic accuracy studies. Biostatistics. 8:239–251. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen G, Kronenberger P, Teugels E and De
Grève J: Influence of RT-qPCR primer position on EGFR interference
efficacy in lung cancer cells. Biol Proced Online. 13:12010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen G, Noor A, Kronenberger P, Teugels E,
Umelo IA and De Grève J: Synergistic effect of afatinib with
su11274 in non-small cell lung cancer cells resistant to gefitinib
or erlotinib. PLoS One. 8:e597082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen G, Umelo IA, Lv S, Teugels E, Fostier
K, Kronenberger P, Dewaele A, Sadones J, Geers C and De Grève J:
miR-146a inhibits cell growth, cell migration and induces apoptosis
in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e603172013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang R, Zhong T, Dang Y, Zhang X, Li P and
Chen G: Association between downexpression of MiR-203 and poor
prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Clin Transl
Oncol. 18:360–368. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang S, He R, Rong M, Dang Y and Chen G:
Synergistic effect of MiR-146a mimic and cetuximab on
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed Res Int.
2014:3841212014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dang YW, Zeng J, He RQ, Rong MH, Luo DZ
and Chen G: Effects of miR-152 on cell growth inhibition, motility
suppression and apoptosis induction in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:4969–4976. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dang Y, Luo D, Rong M and Chen G:
Underexpression of miR-34a in hepatocellular carcinoma and its
contribution towards enhancement of proliferating inhibitory
effects of agents targeting c-MET. PLoS One. 8:e610542013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rong M, Chen G and Dang Y: Increased
miR-221 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues and its role
in enhancing cell growth and inhibiting apoptosis in vitro. BMC
Cancer. 13:212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liang HW, Ye ZH, Yin SY, Mo WJ, Wang HL,
Zhao JC, Liang GM, Feng ZB, Chen G and Luo DZ: A comprehensive
insight into the clinicopathologic significance of miR-144-3p in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 10:3405–3419. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM,
Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson Å, Kampf C,
Sjöstedt E, Asplund A, et al: Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the
human proteome. Science. 347:12604192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Patnaik SK, Yendamuri S, Kannisto E,
Kucharczuk JC, Singhal S and Vachani A: MicroRNA expression
profiles of whole blood in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS One.
7:e460452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Patnaik SK, Kannisto ED, Mallick R,
Vachani A and Yendamuri S: Whole blood microRNA expression may not
be useful for screening non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One.
12:e01819262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Seike M, Goto A, Okano T, Bowman ED,
Schetter AJ, Horikawa I, Mathe EA, Jen J, Yang P, Sugimura H, et
al: MiR-21 is an EGFR-regulated anti-apoptotic factor in lung
cancer in never-smokers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:12085–12090.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nymark P, Guled M, Borze I, Faisal A,
Lahti L, Salmenkivi K, Kettunen E, Anttila S and Knuutila S:
Integrative analysis of microRNA, mRNA and aCGH data reveals
asbestos- and histology-related changes in lung cancer. Genes
Chromosomes Cancer. 50:585–597. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
van Jaarsveld MT, Wouters MD, Boersma AW,
Smid M, van Ijcken WF, Mathijssen RH, Hoeijmakers JH, Martens JW,
van Laere S, Wiemer EA, et al: DNA damage responsive microRNAs
misexpressed in human cancer modulate therapy sensitivity. Mol
Oncol. 8:458–468. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bjaanaes MM, Halvorsen AR, Solberg S,
Jørgensen L, Dragani TA, Galvan A, Colombo F, Anderlini M,
Pastorino U, Kure E, et al: Unique microRNA-profiles in
EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinomas. Int J Cancer. 135:1812–1821.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Arima C, Kajino T, Tamada Y, Imoto S,
Shimada Y, Nakatochi M, Suzuki M, Isomura H, Yatabe Y, Yamaguchi T,
et al: Lung adenocarcinoma subtypes definable by lung
development-related miRNA expression profiles in association with
clinicopathologic features. Carcinogenesis. 35:2224–2231. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Robles AI, Arai E, Mathé EA, Okayama H,
Schetter AJ, Brown D, Petersen D, Bowman ED, Noro R, Welsh JA, et
al: An integrated prognostic classifier for stage I lung
adenocarcinoma based on mRNA, microRNA, and DNA methylation
biomarkers. J Thorac Oncol. 10:1037–1048. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma L, Huang Y, Zhu W, Zhou S, Zhou J, Zeng
F, Liu X, Zhang Y and Yu J: An integrated analysis of miRNA and
mRNA expressions in non-small cell lung cancers. PLoS One.
6:e265022011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peng Z, Pan L, Niu Z, Li W, Dang X, Wan L,
Zhang R and Yang S: Identification of microRNAs as potential
biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma using integrating genomics
analysis. Oncotarget. 8:64143–64156. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pak MG, Lee CH, Lee WJ, Shin DH and Roh
MS: Unique microRNAs in lung adenocarcinoma groups according to
major TKI sensitive EGFR mutation status. Diagn Pathol. 10:992015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tanaka M, Oikawa K, Takanashi M, Kudo M,
Ohyashiki J, Ohyashiki K and Kuroda M: Down-regulation of miR-92 in
human plasma is a novel marker for acute leukemia patients. PLoS
One. 4:e55322009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ohyashiki K, Umezu T, Yoshizawa S, Ito Y,
Ohyashiki M, Kawashima H, Tanaka M, Kuroda M and Ohyashiki JH:
Clinical impact of down-regulated plasma miR-92a levels in
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. PLoS One. 6:e164082011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shigoka M, Tsuchida A, Matsudo T, Nagakawa
Y, Saito H, Suzuki Y, Aoki T, Murakami Y, Toyoda H, Kumada T, et
al: Deregulation of miR-92a expression is implicated in
hepatocellular carcinoma development. Pathol Int. 60:351–357. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yan D, Cai X and Feng Y: miR-183 modulates
cell apoptosis and proliferation in tongue squamous cell carcinoma
SCC25 cell line. Oncol Res. 24:399–404. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ruan H, Liang X, Zhao W, Ma L and Zhao Y:
The effects of microRNA-183 promots cell proliferation and invasion
by targeting MMP-9 in endometrial cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
89:812–818. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang X, Zuo D, Yuan Y, Yang X, Hong Z and
Zhang R: MicroRNA-183 promotes cell proliferation via regulating
programmed cell death 6 in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 143:169–180. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cui R, Kim T, Fassan M, Meng W, Sun HL,
Jeon YJ, Vicentini C, Tili E, Peng Y, Scarpa A, et al: MicroRNA-224
is implicated in lung cancer pathogenesis through targeting
caspase-3 and caspase-7. Oncotarget. 6:21802–21815. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Miao F, Zhu J, Chen Y, Tang N, Wang X and
Li X: MicroRNA-183-5p promotes the proliferation, invasion and
metastasis of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Oncol Lett.
11:134–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ren LH, Chen WX, Li S, He XY, Zhang ZM, Li
M, Cao RS, Hao B, Zhang HJ, Qiu HQ, et al: MicroRNA-183 promotes
proliferation and invasion in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma
by targeting programmed cell death 4. Br J Cancer. 111:2003–2013.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Makrilia N, Kollias A, Manolopoulos L and
Syrigos K: Cell adhesion molecules: Role and clinical significance
in cancer. Cancer Invest. 27:1023–1037. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Henderson MP, Hirte H, Hotte SJ and Kavsak
PA: Cytokines and cell adhesion molecules exhibit distinct profiles
in health, ovarian cancer, and breast cancer. Heliyon.
2:e000592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kaseda K, Ishii G, Aokage K, Takahashi A,
Kuwata T, Hishida T, Yoshida J, Kohno M, Nagai K and Ochiai A:
Identification of intravascular tumor microenvironment features
predicting the recurrence of pathological stage I lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci. 104:1262–1269. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Xu J, Lv W, Hu Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Cao J
and Hu J: Wnt3a expression is associated with
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and impacts prognosis of lung
adenocarcinoma patients. J Cancer. 8:2523–2531. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Timsah Z, Berrout J, Suraokar M, Behrens
C, Song J, Lee JJ, Ivan C, Gagea M, Shires M, Hu X, et al:
Expression pattern of FGFR2, Grb2 and Plcγ1 acts as a novel
prognostic marker of recurrence recurrence-free survival in lung
adenocarcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 5:3135–3148. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Neri S, Miyashita T, Hashimoto H, Suda Y,
Ishibashi M, Kii H, Watanabe H, Kuwata T, Tsuboi M, Goto K, et al:
Fibroblast-led cancer cell invasion is activated by
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through platelet-derived growth
factor BB secretion of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 395:20–30.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fu Q, Cash SE, Andersen JJ, Kennedy CR,
Madadi AR, Raghavendra M, Dietrich LL, Agger WA and Shelley CS:
Intracellular patterns of sialophorin expression define a new
molecular classification of breast cancer and represent new targets
for therapy. Br J Cancer. 110:146–155. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Jiang H, Li F, He C, Wang X, Li Q and Gao
H: Expression of Gli1 and Wnt2B correlates with progression and
clinical outcome of pancreatic cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:4531–4538. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu C, Li G, Ren S, Su Z, Wang Y, Tian Y,
Liu Y and Qiu Y: miR-185-3p regulates the invasion and metastasis
of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting WNT2B in vitro. Oncol
Lett. 13:2631–2636. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Catalano RD, Wilson MR, Boddy SC, McKinlay
AT, Sales KJ and Jabbour HN: Hypoxia and prostaglandin E receptor 4
signalling pathways synergise to promote endometrial adenocarcinoma
cell proliferation and tumour growth. PLoS One. 6:e192092011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mlakar V, Strazisar M, Sok M and Glavac D:
Oligonucleotide DNA microarray profiling of lung adenocarcinoma
revealed significant downregulation and deletions of vasoactive
intestinal peptide receptor 1. Cancer Invest. 28:487–494. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Strömvall K, Sundkvist K, Ljungberg B,
Halin Bergström S and Bergh A: Reduced number of CD169+
macrophages in pre-metastatic regional lymph nodes is associated
with subsequent metastatic disease in an animal model and with poor
outcome in prostate cancer patients. Prostate. 77:1468–1477. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wikman H, Westphal L, Schmid F, Pollari S,
Kropidlowski J, Sielaff-Frimpong B, Glatzel M, Matschke J, Westphal
M, Iljin K, et al: Loss of CADM1 expression is associated with poor
prognosis and brain metastasis in breast cancer patients.
Oncotarget. 5:3076–3087. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|