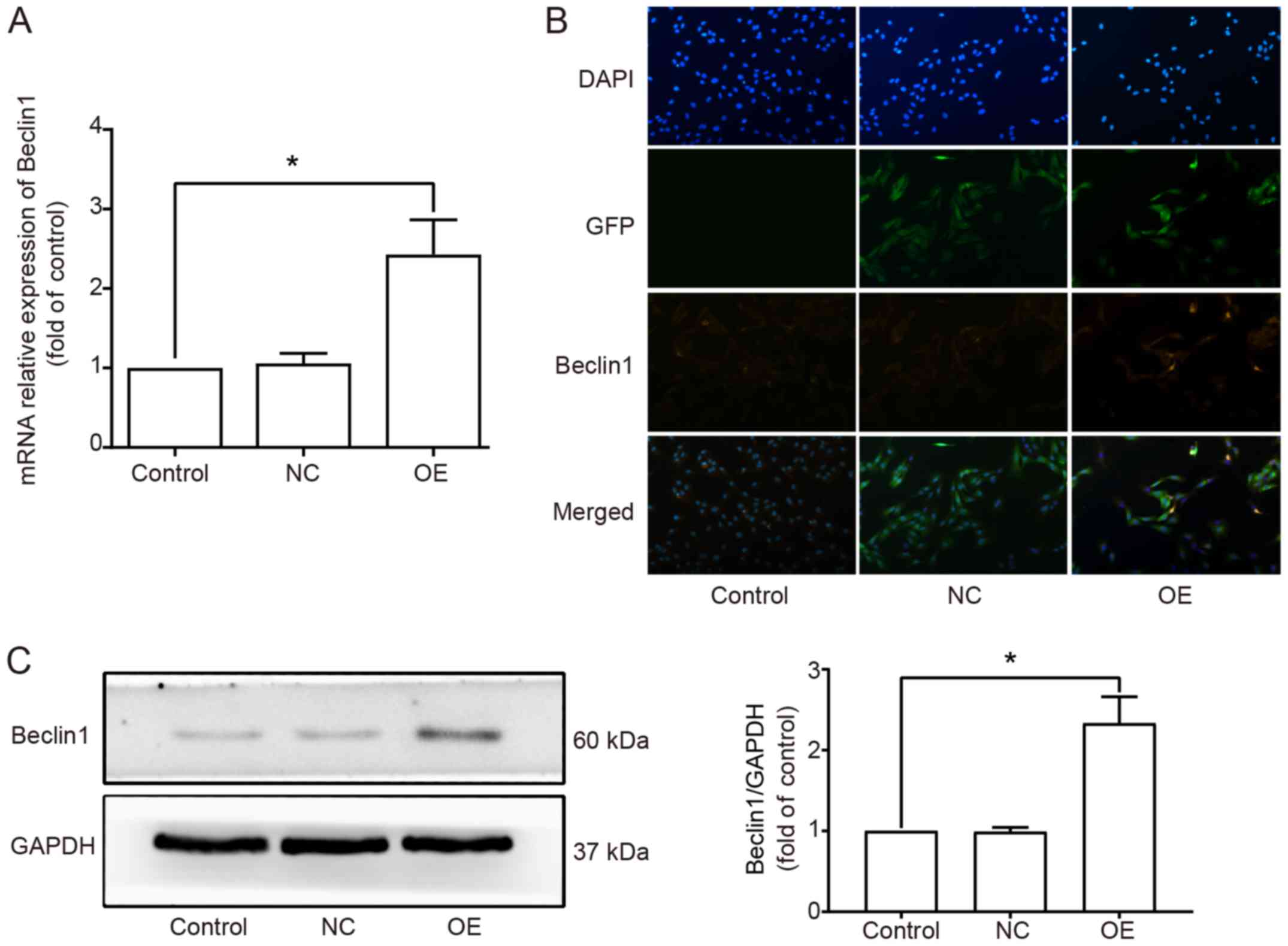
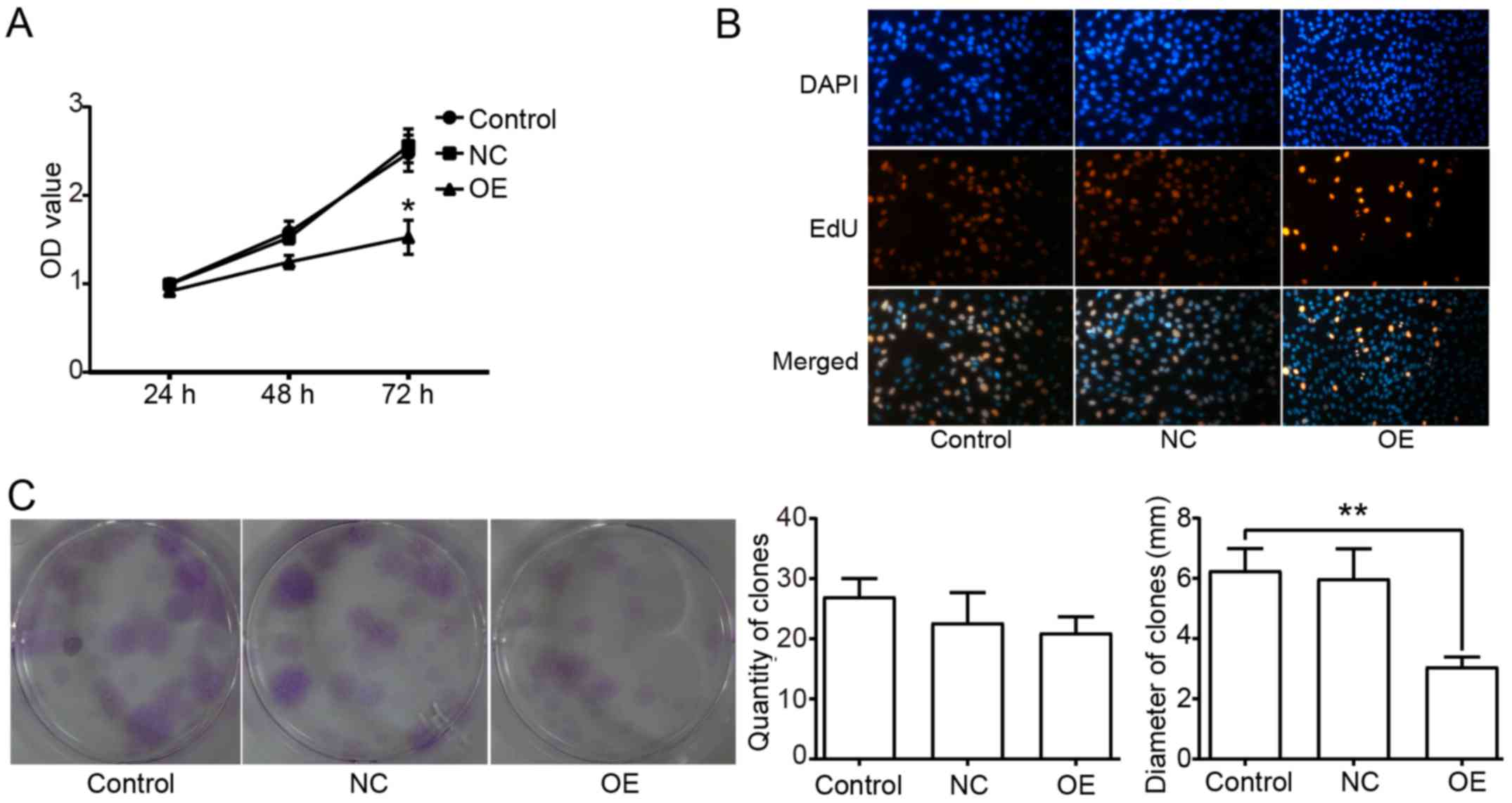
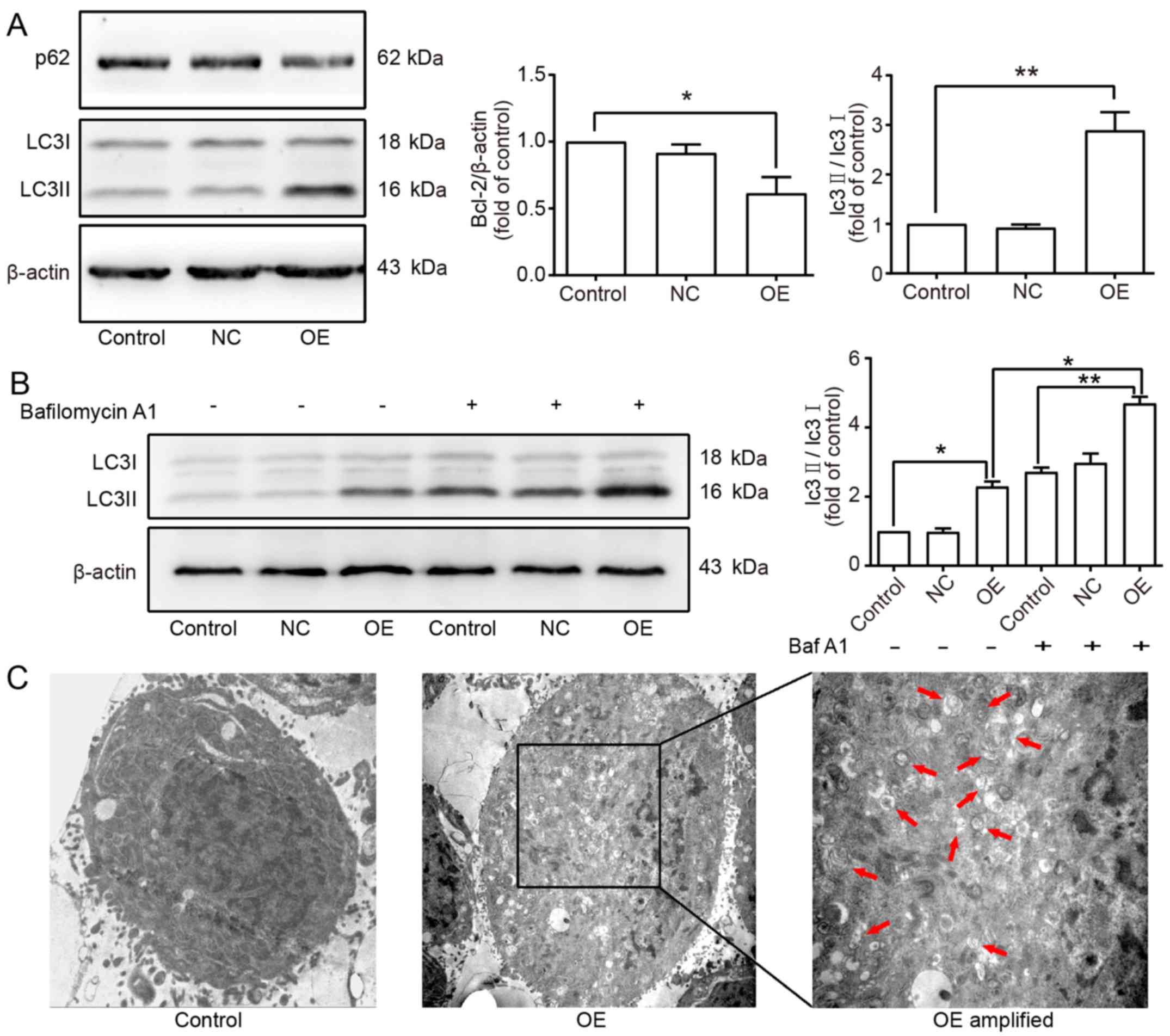
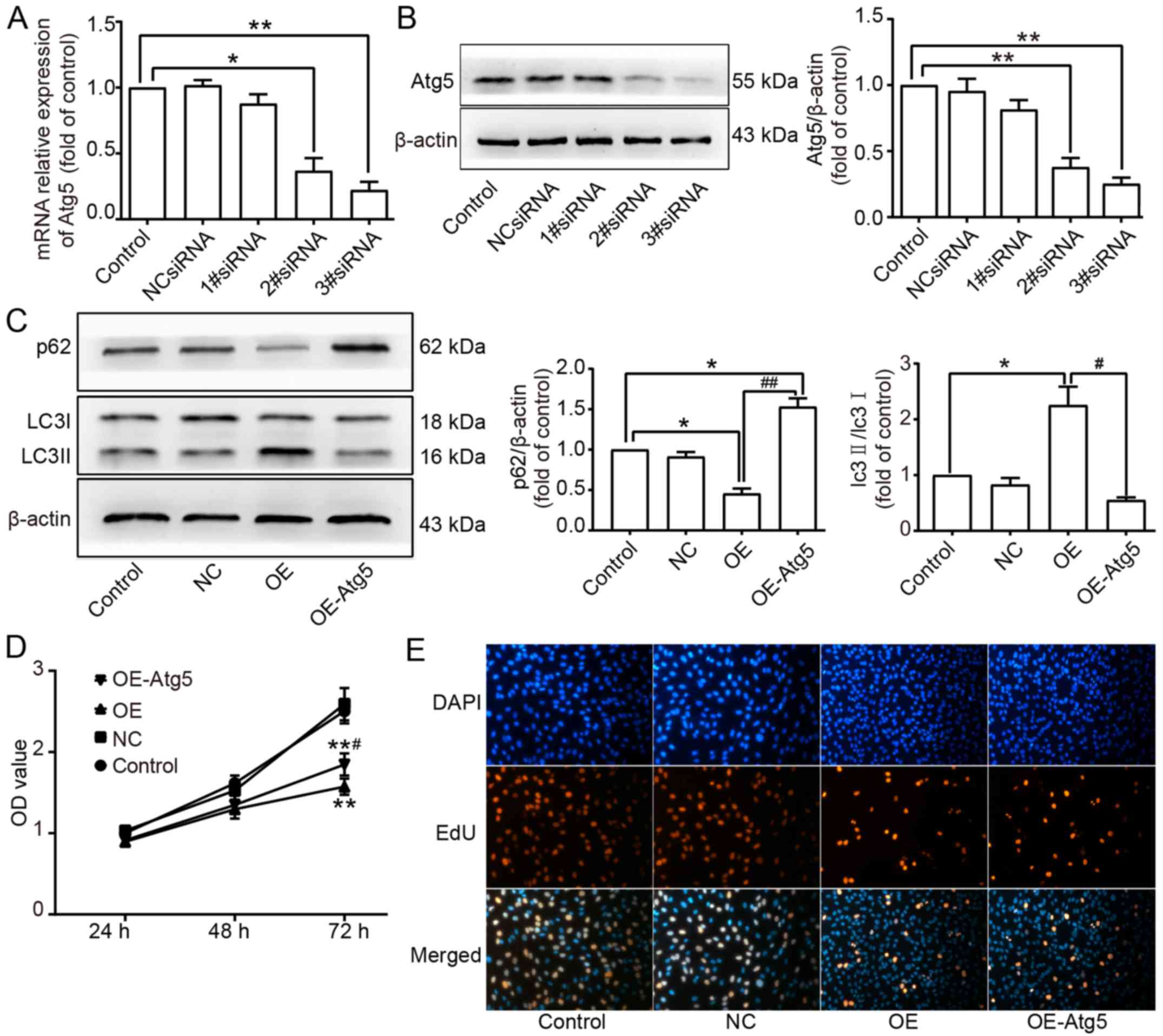
|
1
|
Yaser S, Salah S, Al-Shatti M, Abu-Sheikha
A, Shehadeh A, Sultan I, Salem A, Sughayer M, Al-Loh S and Al-Mousa
A: Prognostic factors that govern localized synovial sarcoma: A
single institution retrospective study on 51 patients. Med Oncol.
31:9582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El Beaino M, Araujo DM, Gopalakrishnan V,
Lazar AJ and Lin PP: Prognosis of T1 synovial sarcoma depends upon
surgery by oncologic surgeons. J Surg Oncol. 114:490–494. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Levine B and Klionsky DJ: Development by
self-digestion: Molecular mechanisms and biological functions of
autophagy. Dev Cell. 6:463–477. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wen YF, Zand B, Ozpolat B, Szczepanski MJ,
Lu CH, Yuca E, Carroll AR, Alpay N, Bartholomeusz C, Tekedereli I,
et al: Antagonism of tumoral prolactin receptor promotes
autophagy-related cell death. Cell Rep. 7:488–500. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Galluzzi L, Pietrocola F, Pedro Bravo-San
JM, Amaravadi RK, Baehrecke EH, Cecconi F, Codogno P, Debnath J,
Gewirtz DA, Karantza V, et al: Autophagy in malignant
transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J. 34:856–880. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liang XH, Kleeman LK, Jiang HH, Gordon G,
Goldman JE, Berry G, Herman B and Levine B: Protection against
fatal Sindbis virus encephalitis by Beclin, a novel
Bcl-2-interacting protein. J Virol. 72:8586–8596. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oberstein A, Jeffrey PD and Shi YG:
Crystal structure of the Bcl-XL-Beclin 1 peptide complex: Beclin 1
is a novel BH3-only protein. J Biol Chem. 282:13123–13132. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Park JM, Tougeron D, Huang S, Okamoto K
and Sinicrope FA: Beclin 1 and UVRAG confer protection from
radiation-induced DNA damage and maintain centrosome stability in
colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e1008192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang W, Fan H, Li X, Wu G, Zhao W, Zhang
G, Zhao G and Li L: Beclin 1 promotes apoptosis and decreases
invasion by upregulating the expression of ECRG4 in A549 human lung
adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Med Report. 14:355–360. 2016.
|
|
10
|
De Amicis F, Aquila S, Morelli C, Guido C,
Santoro M, Perrotta I, Mauro L, Giordano F, Nigro A, Andò S, et al:
Bergapten drives autophagy through the up-regulation of PTEN
expression in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 14:1302015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jung YY, Lee YK and Koo JS: The potential
of Beclin 1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment of breast
cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 20:167–178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu S, Sun C, Tian D, Li Y, Gao X, He S and
Li T: Expression and clinical significances of Beclin1, LC3 and
mTOR in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:3882–3891.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Z, Li Y, Zhang C, Yi H, Wu C, Wang J,
Liu Y, Tan J and Wen J: Downregulation of Beclin 1 and impairment
of autophagy in a small population of colorectal cancer. Dig Dis
Sci. 58:2887–2894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu YF, Lei X, Zhang HY, Ma JW, Yang WW,
Chen ML, Cui J and Zhao H: Expressions and clinical significance of
autophagy-related markers Beclin1, LC3, and EGFR in human cervical
squamous cell carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 8:2243–2249.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Z, Wang B, Yu F, Chen Q, Tian Y, Ma S
and Liu X: The roles of mitochondria in radiation-induced
autophagic cell death in cervical cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
37:4083–4091. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ju LL, Zhao CY, Ye KF, Yang H and Zhang J:
Expression and clinical implication of Beclin1, HMGB1, p62,
survivin, BRCA1 and ERCC1 in epithelial ovarian tumor tissues. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:1993–2003. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai M, Hu Z, Liu J, Gao J, Liu C, Liu D,
Tan M, Zhang D and Lin B: Beclin 1 expression in ovarian tissues
and its effects on ovarian cancer prognosis. Int J Mol Sci.
15:5292–5303. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xue S, Xiao-Hong S, Lin S, Jie B, Li-Li W,
Jia-Yao G, Shun S, Pei-Nan L, Mo-Li W, Qian W, et al: Lumbar
puncture-administered resveratrol inhibits STAT3 activation,
enhancing autophagy and apoptosis in orthotopic rat glioblastomas.
Oncotarget. 7:75790–75799. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang X, Qi Q, Hua X, Li X, Zhang W, Sun
H, Li S, Wang X and Li B: Beclin 1, an autophagy-related gene,
augments apoptosis in U87 glioblastoma cells. Oncol Rep.
31:1761–1767. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bai H, Li H, Li W, Gui T, Yang J, Cao D
and Shen K: The PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is a potential predictor of
distinct invasive and migratory capacities in human ovarian cancer
cell lines. Oncotarget. 6:25520–25532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Katagiri H, Nakayama K, Razia S, Nakamura
K, Sato E, Ishibashi T, Ishikawa M, Iida K, Ishikawa N, Otsuki Y,
et al: Loss of autophagy-related protein Beclin 1 may define poor
prognosis in ovarian clear cell carcinomas. Int J Oncol.
47:2037–2044. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Garbar C, Mascaux C, Giustiniani J,
Salesse S, Debelle L, Antonicelli F, Merrouche Y and Bensussan A:
Autophagy is decreased in triple-negative breast carcinoma
involving likely the MUC1-EGFR-NEU1 signalling pathway. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:4344–4355. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rohatgi RA, Janusis J, Leonard D, Bellvé
KD, Fogarty KE, Baehrecke EH, Corvera S and Shaw LM: Beclin 1
regulates growth factor receptor signaling in breast cancer.
Oncogene. 34:5352–5362. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shimizu S, Yoshida T, Tsujioka M and
Arakawa S: Autophagic cell death and cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
15:3145–3153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lu Y, Wang Z, Han W and Li H: Zoledronate
induces autophagic cell death in human umbilical vein endothelial
cells via Beclin-1 dependent pathway activation. Mol Med Report.
14:4747–4754. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Elgendy M, Ciro M, Abdel-Aziz AK, Belmonte
G, Dal Zuffo R, Mercurio C, Miracco C, Lanfrancone L, Foiani M and
Minucci S: Beclin 1 restrains tumorigenesis through Mcl-1
destabilization in an autophagy-independent reciprocal manner. Nat
Commun. 5:56372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rohatgi RA and Shaw LM: An
autophagy-independent function of Beclin 1 in cancer. Mol Cell
Oncol. 3:pii: e1030539. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Correa RJ, Valdes YR, Shepherd TG and
DiMattia GE: Beclin-1 expression is retained in high-grade serous
ovarian cancer yet is not essential for autophagy induction in
vitro. J Ovarian Res. 8:522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang YF, Xu YL, Tang ZH, Li T, Zhang LL,
Chen X, Lu JH, Leung CH, Ma DL, Qiang WA, et al: Baicalein induces
Beclin 1- and extracellular signal-regulated kinase-dependent
autophagy in ovarian cancer cells. Am J Chin Med. 45:123–136. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ying H, Qu D, Liu C, Ying T, Lv J, Jin S
and Xu H: Chemoresistance is associated with Beclin-1 and PTEN
expression in epithelial ovarian cancers. Oncol Lett. 9:1759–1763.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li WL, Xiong LX, Shi XY, Xiao L, Qi GY and
Meng C: IKKβ/NFκBp65 activated by interleukin-13 targets the
autophagy-related genes LC3B and beclin 1 in fibroblasts
co-cultured with breast cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. 11:1259–1264.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
De Amicis F, Guido C, Santoro M, Giordano
F, Donà A, Rizza P, Pellegrino M, Perrotta I, Bonofiglio D, Sisci
D, et al: Ligand activated progesterone receptor B drives
autophagy-senescence transition through a Beclin-1/Bcl-2 dependent
mechanism in human breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 7:57955–57969.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baspinar S, Bircan S, Orhan H, Kapucuoglu
N and Bozkurt KK: The relation of beclin 1 and bcl-2 expressions in
high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate
adenocarcinoma: A tissue microarray study. Pathol Res Pract.
210:412–418. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lian J, Wu X, He F, Karnak D, Tang W, Meng
Y, Xiang D, Ji M, Lawrence TS and Xu L: A natural BH3 mimetic
induces autophagy in apoptosis-resistant prostate cancer via
modulating Bcl-2-Beclin1 interaction at endoplasmic reticulum. Cell
Death Differ. 18:60–71. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jung G, Roh J, Lee H, Gil M, Yoon DH, Suh
C, Jang S, Park CJ, Huh J and Park CS: Autophagic markers BECLIN 1
and LC3 are associated with prognosis of multiple myeloma. Acta
Haematol. 134:17–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fukui M, Yamabe N, Choi HJ, Polireddy K,
Chen Q and Zhu BT: Mechanism of ascorbate-induced cell death in
human pancreatic cancer cells: Role of Bcl-2, Beclin 1 and
autophagy. Planta Med. 81:838–846. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Al-Shenawy HA: Expression of Beclin-1, an
autophagy-related marker, in chronic hepatitis and hepatocellular
carcinoma and its relation with apoptotic markers. APMIS.
124:229–237. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ma K, Zhang C, Huang MY, Guo YX and Hu GQ:
Crosstalk between Beclin-1-dependent autophagy and
caspase-dependent apoptosis induced by tanshinone IIA in human
osteosarcoma MG-63 cells. Oncol Rep. 36:1807–1818. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sun C, Liu Z, Li S, Yang C, Xue R, Xi Y,
Wang L, Wang S, He Q, Huang J, et al: Down-regulation of c-Met and
Bcl2 by microRNA-206, activates apoptosis, and inhibits tumor cell
proliferation, migration and colony formation. Oncotarget.
6:25533–25574. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu LS, Bai XQ, Gao Y, Wu Q, Ren Z, Li Q,
Pan LH, He NY, Peng J and Tang ZH: PCSK9 promotes oxLDL-induced
PC12 cell apoptosis through the Bcl-2/Bax-Caspase 9/3 signaling
pathway. J Alzheimers Dis. 57:723–734. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lončarević-Vasiljković N, Milanović D,
Pešić V, Tešić V, Brkić M, Lazić D, Avramović V and Kanazir S:
Dietary restriction suppresses apoptotic cell death, promotes Bcl-2
and Bcl-xl mRNA expression and increases the Bcl-2/Bax protein
ratio in the rat cortex after cortical injury. Neurochem Int.
96:69–76. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Song S, Jacobson KN, McDermott KM, Reddy
SP, Cress AE, Tang HY, Dudek SM, Black SM, Garcia JG, Makino A, et
al: ATP promotes cell survival via regulation of cytosolic [Ca2+]
and Bcl-2/Bax ratio in lung cancer cells. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 310:C99–C114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jiang N, Li Y and Ruan DY: Sa1688
aberrantly regulated dysadherin and Bcl-2/Bax2 enhances
tumorigenesis and DNA targeting drug resistance of liver cancer
stem cells. Gastroenterology. 148:S1012. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cai Y, Xu P, Yang L, Xu K, Zhu J, Wu X,
Jiang C, Yuan Q, Wang B, Li Y, et al: HMGB1-mediated autophagy
decreases sensitivity to oxymatrine in SW982 human synovial sarcoma
cells. Sci Rep. 6:378452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xu K, Cai YS, Lu SM, Li XL, Liu L, Li Z,
Liu H and Xu P: Autophagy induction contributes to the resistance
to methotrexate treatment in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like
synovial cells through high mobility group box chromosomal protein
1. Arthritis Res Ther. 17:3742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu Y and Levine B: Autosis and autophagic
cell death: The dark side of autophagy. Cell Death Differ.
22:367–376. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yu KN, Yoon TJ, Minai-Tehrani A, Kim JE,
Park SJ, Jeong MS, Ha SW, Lee JK, Kim JS and Cho MH: Zinc oxide
nanoparticle induced autophagic cell death and mitochondrial damage
via reactive oxygen species generation. Toxicol In Vitro.
27:1187–1195. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li YC, He SM, He ZX, Li M, Yang Y, Pang
JX, Zhang X, Chow K, Zhou Q, Duan W, et al: Plumbagin induces
apoptotic and autophagic cell death through inhibition of the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 344:239–259. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tai WT, Shiau CW, Chen HL, Liu CY, Lin CS,
Cheng AL, Chen PJ and Chen KF: Mcl-1-dependent activation of Beclin
1 mediates autophagic cell death induced by sorafenib and SC-59 in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 4:e4852013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wong VK, Li T, Law BY, Ma ED, Yip NC,
Michelangeli F, Law CK, Zhang MM, Lam KY, Chan PL, et al:
Saikosaponin-d, a novel SERCA inhibitor, induces autophagic cell
death in apoptosis-defective cells. Cell Death Dis. 4:e7202013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Liu C, Yan X, Wang HQ, Gao YY, Liu J, Hu
Z, Liu D, Gao J and Lin B: Autophagy-independent enhancing effects
of Beclin 1 on cytotoxicity of ovarian cancer cells mediated by
proteasome inhibitors. BMC Cancer. 12:6222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lamy L, Ngo VN, Emre NC, Shaffer AL III,
Yang Y, Tian E, Nair V, Kruhlak M, Zingone A, Landgren O, et al:
Control of autophagic cell death by caspase-10 in multiple myeloma.
Cancer Cell. 23:435–449. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yu FS, Yu CS, Chen JC, Yang JL, Lu HF,
Chang SJ, Lin MW and Chung JG: Tetrandrine induces apoptosis Via
caspase-8, −9, and −3 and poly (ADP ribose) polymerase dependent
pathways and autophagy through beclin-1/LC3-I, II signaling
pathways in human oral cancer HSC-3 cells. Environ Toxicol.
31:395–406. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao ZQ, Yu ZY, Li J and Ouyang XN:
Gefitinib induces lung cancer cell autophagy and apoptosis via
blockade of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Oncol Lett. 12:63–68. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|