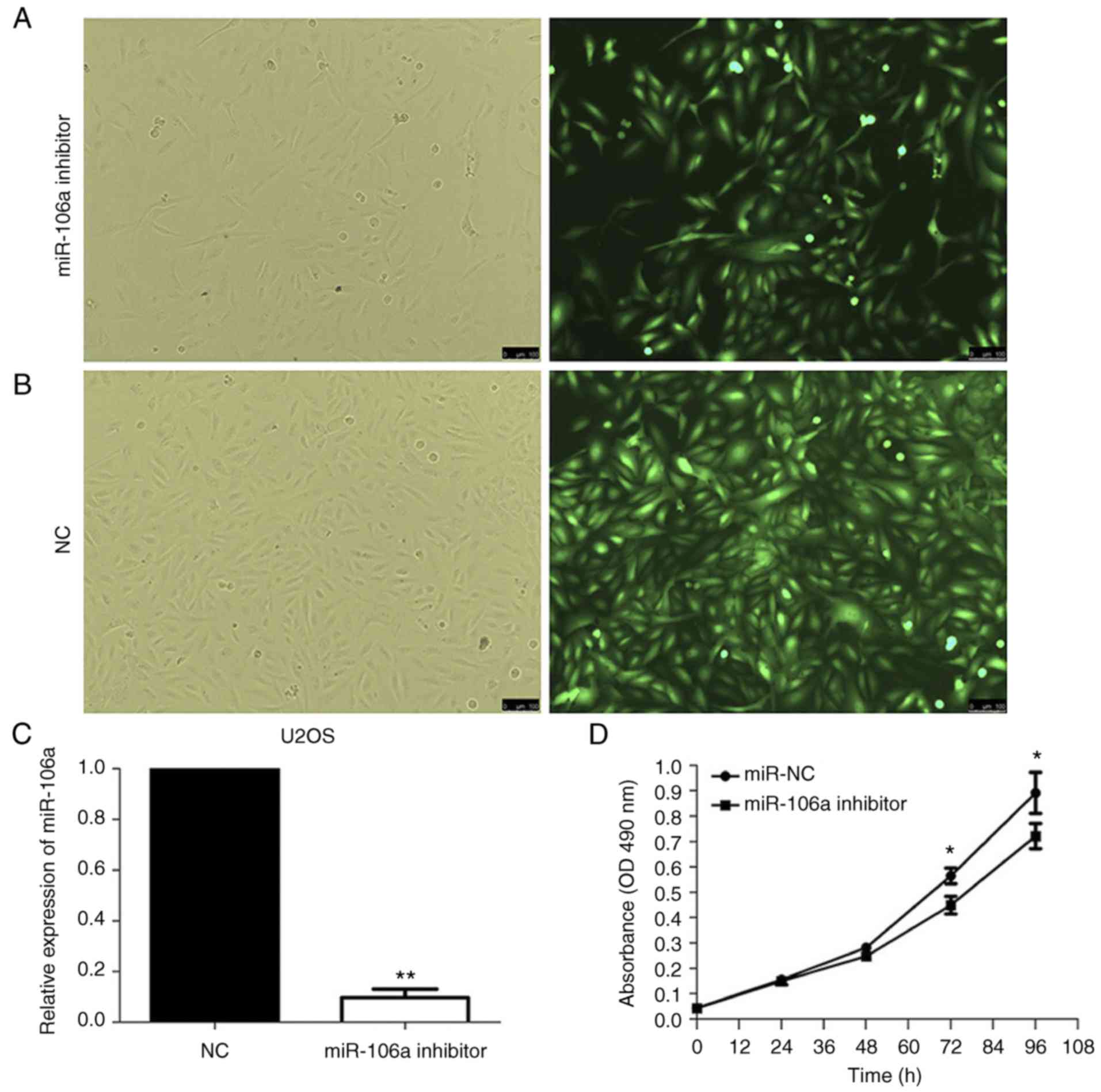
|
1
|
Ward E, DeSantis C, Robbins A, Kohler B
and Jemal A: Childhood and adolescent cancer statistics, 2014. CA
Cancer J Clin. 64:83–103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma
of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chou AJ, Kleinerman ES, Krailo MD, Chen Z,
Betcher DL, Healey JH, Conrad EU III, Nieder ML, Weiner MA, Wells
RJ, et al: Addition of muramyl tripeptide to chemotherapy for
patients with newly diagnosed metastatic osteosarcoma: A report
from the Children's Oncology Group. Cancer. 115:5339–5348. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aung L, Tin AS, Quah TC and Pho RW:
Osteogenic sarcoma in children and young adults. Ann Acad Med
Singapore. 43:305–313. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Behm-Ansmant I, Rehwinkel J and Izaurralde
E: MicroRNAs silence gene expression by repressing protein
expression and/or by promoting mRNA decay. Cold Spring Harb Symp
Quant Biol. 71:523–530. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ambros V: MicroRNA pathways in flies and
worms: Growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 113:673–676.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song L and Tuan RS: MicroRNAs and cell
differentiation in mammalian development. Birth Defects Res C
Embryo Today. 78:140–149. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Skaftnesmo KO, Prestegarden L, Micklem DR
and Lorens JB: MicroRNAs in tumorigenesis. Curr Pharm Biotechnol.
8:320–325. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lulla RR, Costa FF, Bischof JM, Chou PM,
de F Bonaldo M, Vanin EF and Soares MB: Identification of
differentially expressed MicroRNAs in osteosarcoma. Sarcoma.
2011:7326902011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, Ghoshal
K, Jacob ST and Patel T: MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the
PTEN tumor suppressor gene in human hepatocellular cancer.
Gastroenterology. 133:647–658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He L, He X, Lim LP, de Stanchina E, Xuan
Z, Liang Y, Xue W, Zender L, Magnus J, Ridzon D, et al: A microRNA
component of the p53 tumour suppressor network. Nature.
447:1130–1134. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cimmino A, Calin GA, Fabbri M, Iorio MV,
Ferracin M, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Aqeilan RI, Zupo S, Dono M, et
al: miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting
BCL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:13944–13949. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Palmini G, Marini F and Brandi ML: What is
new in the miRNAWorld regarding osteosarcoma and chondrosarcoma?
Molecule. 22:pii: E417. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Huang J, Takeda Y, Watanabe T and Sendo F:
A sandwich ELISA for detection of soluble GPI-80, a
glycosylphosphatidyl-inositol (GPI)-anchored protein on human
leukocytes involved in regulation of neutrophil adherence and
migration-its release from activated neutrophils and presence in
synovial fluid of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Microbiol Immunol.
45:467–471. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki K, Watanabe T, Sakurai S, Ohtake K,
Kinoshita T, Araki A, Fujita T, Takei H, Takeda Y, Sato Y, et al: A
novel glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-anchored protein on human
leukocytes: A possible role for regulation of neutrophil adherence
and migration. J Immunol. 162:4277–4284. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Singel KL and Segal BH: Neutrophils in the
tumor microenvironment: Trying to heal the wound that cannot heal.
Immunol Rev. 273:329–343. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eruslanov EB, Bhojnagarwala PS, Quatromoni
JG, Stephen TL, Ranganathan A, Deshpande C, Akimova T, Vachani A,
Litzky L, Hancock WW, et al: Tumor-associated neutrophils stimulate
T cell responses in early-stage human lung cancer. J Clin Invest.
124:5466–5480. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nitto T, Araki Y, Takeda Y and Sendo F:
Pharmacological analysis for mechanisms of GPI-80 release from
tumour necrosis factor-alpha-stimulated human neutrophils. Br J
Pharmacol. 137:353–360. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li P, Liu H, Zhang Z, Lv X, Wang H, Ma J,
Ma Z, Qu X and Teng YE: Expression and comparison of Cbl-b in lung
squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Med Sci Monit.
24:623–635. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Justus CR, Leffler N, Ruiz-Echevarria M
and Yang LV: In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J Vis
Exp. Jun 1–2014.doi: 10.3791/51046. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mahmood T and Yang PC: Western blot:
Technique, theory, and trouble shooting. N Am J Med Sci. 4:429–434.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, Barry
SC, Tsykin A, Farshid G, Vadas MA, Khew-Goodall Y and Goodall GJ:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom
M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, Labourier E, Reinert KL, Brown D and Slack
FJ: RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell.
120:635–647. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, Veronese A,
Spizzo R, Sabbioni S, Magri E, Pedriali M, Fabbri M, Campiglio M,
et al: MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chan JA, Krichevsky AM and Kosik KS:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H and Mo YY: MicroRNA-21
targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J
Biol Chem. 282:14328–14336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Z and Lu Y, Xiao Y and Lu Y:
Upregulation of miR-21 expression is a valuable predicator of
advanced clinicopathological features and poor prognosis in
patients with renal cell carcinoma through the p53/p21-cyclin
E2-Bax/caspase-3 signaling pathway. Oncol Rep. 37:1437–1444. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Edatt L, Maurya AK, Raji G, Kunhiraman H
and Kumar SV: MicroRNA106a regulates matrix metalloprotease 9 in a
sirtuin-1 dependent mechanism. J Cell Physiol. 233:238–248. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pan YJ, Zhuang Y, Zheng JN and Pei DS:
MiR-106a: Promising biomarker for cancer. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
26:5373–5377. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shen CT, Qiu ZL, Song HJ, Wei WJ and Luo
QY: miRNA-106a directly targeting RARB associates with the
expression of Na+/I− symporter in thyroid
cancer by regulating MAPK signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35:1012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Espinosa-Parrilla Y, Munoz X, Bonet C,
Garcia N, Venceslá A, Yiannakouris N, Naccarati A, Sieri S, Panico
S, Huerta JM, et al: Genetic association of gastric cancer with
miRNA clusters including the cancer-related genes MIR29, MIR25,
MIR93 and MIR106: Results from the EPIC-EURGAST study.
Int J Cancer. 135:2065–2076. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He QY, Wang GC, Zhang H, Tong DK, Ding C,
Liu K, Ji F, Zhu X and Yang S: miR-106a-5p suppresses the
proliferation, migration, and invasion of osteosarcoma cells by
targeting HMGA2. DNA Cell Biol. 35:506–520. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kroemer G and Pouyssegur J: Tumor cell
metabolism: Cancer's Achilles' heel. Cancer Cell. 13:472–482. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lopez-Rios F, Sanchez-Arago M,
Garcia-Garcia E, Ortega AD, Berrendero JR, Pozo-Rodríguez F,
López-Encuentra A, Ballestín C and Cuezva JM: Loss of the
mitochondrial bioenergetic capacity underlies the glucose avidity
of carcinomas. Cancer Res. 67:9013–9017. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nitto T and Onodera K: Linkage between
coenzyme a metabolism and inflammation: Roles of pantetheinase. J
Pharmacol Sci. 123:1–8. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|