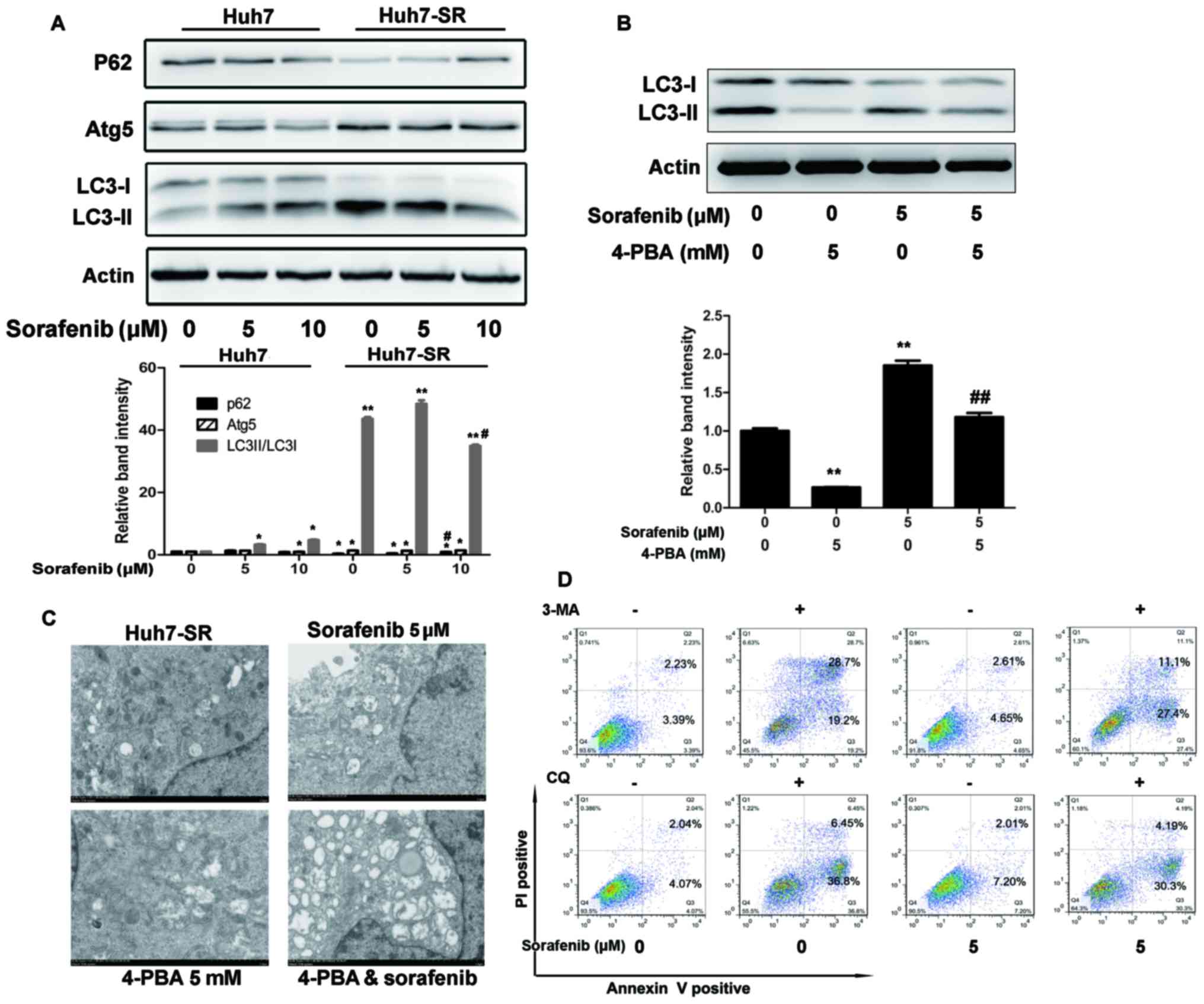
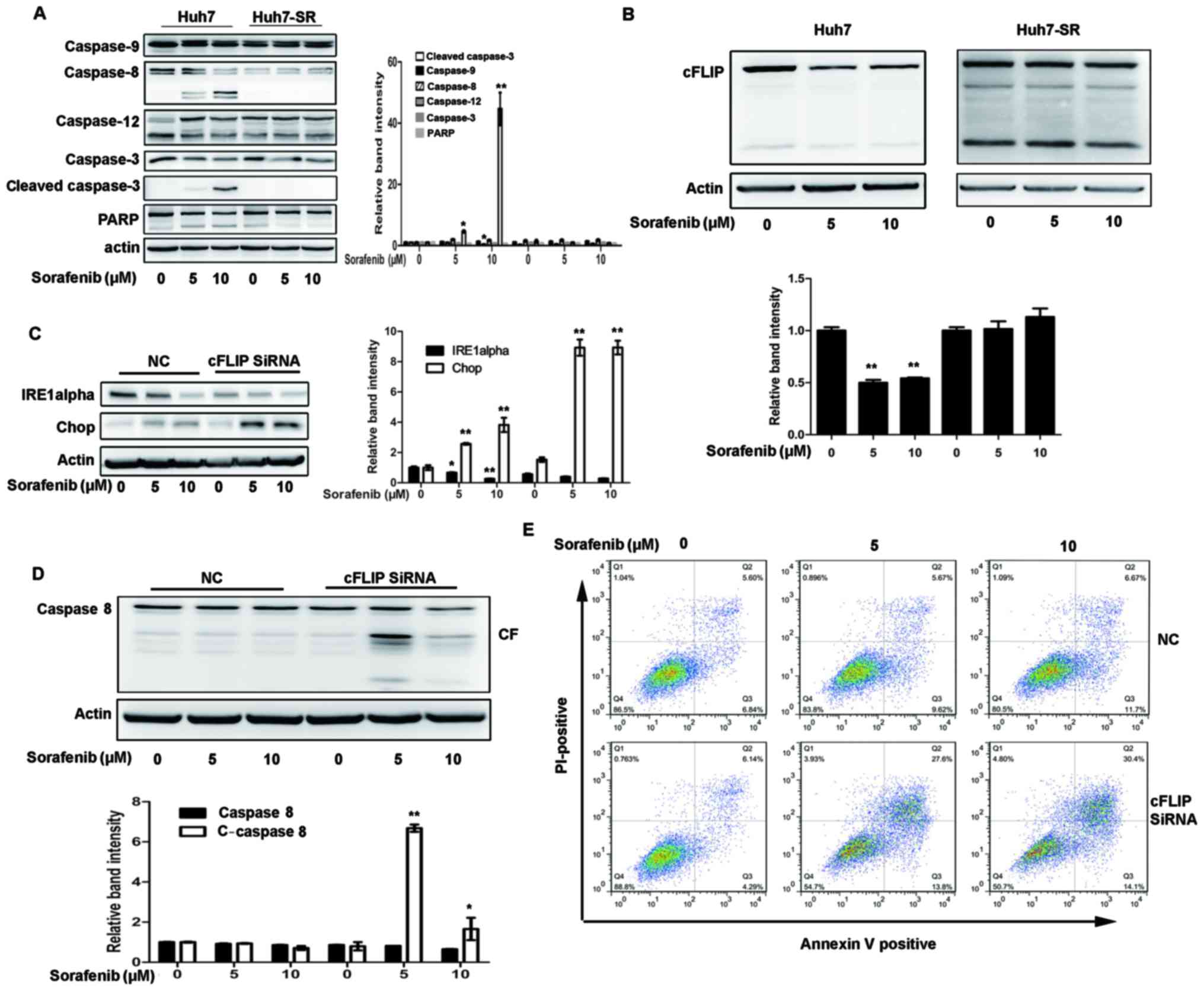
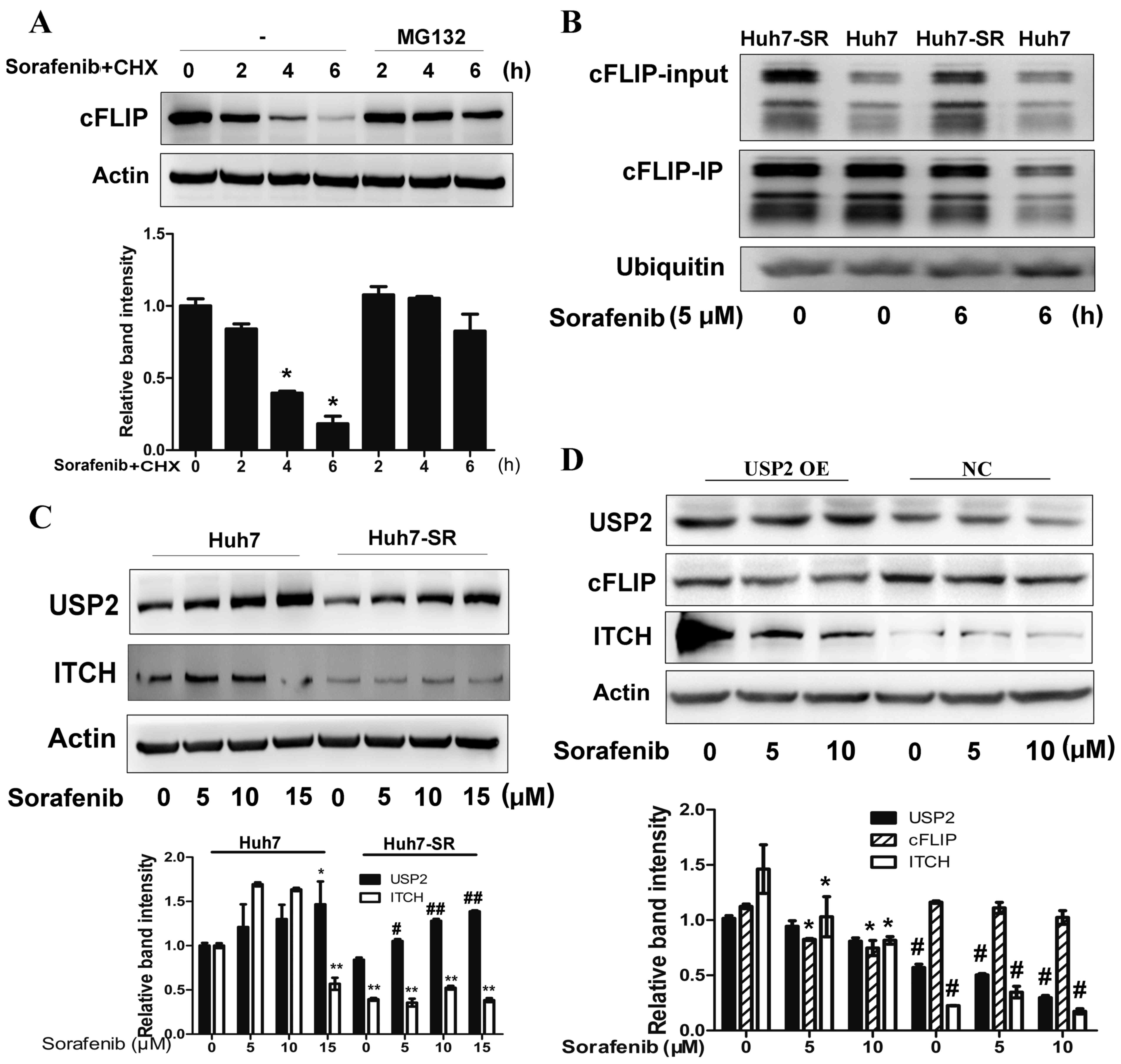
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu AX: Systemic treatment of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Dawn of a new era? Ann Surg Oncol.
17:1247–1256. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, De Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhai B and Sun XY: Mechanisms of
resistance to sorafenib and the corresponding strategies in
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 5:345–352. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hennessy BT, Smith DL, Ram PT, Lu Y and
Mills GB: Exploiting the PI3K/AKT pathway for cancer drug
discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:988–1004. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Micheau O: Cellular FLICE-inhibitory
protein: An attractive therapeutic target? Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 7:559–573. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Poukkula M, Kaunisto A, Denessiouk K,
Katajamäki T, Johnson MS, Sistonen L and Eriksson JE: Rapid
turnover of c-FLIPshort is determined by its unique C-terminal
tail. J Biol Chem. 280:27345–27355. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ueffing N, Singh KK, Christians A, Thorns
C, Feller AC, Nagl F, Fend F, Heikaus S, Marx A, Zotz RB, et al: A
single nucleotide polymorphism determines protein isoform
production of the human c-FLIP protein. Blood. 114:572–579. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chaudhary PM, Eby MT, Jasmin A, Kumar A,
Liu L and Hood L: Activation of the NF-kappaB pathway by caspase 8
and its homologs. Oncogene. 19:4451–4460. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iyer AK, Azad N, Talbot S, Stehlik C, Lu
B, Wang L and Rojanasakul Y: Antioxidant c-FLIP inhibits Fas
ligand-induced NF-kappaB activation in a phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt-dependent manner. J Immunol. 187:3256–3266. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Quintavalle C, Incoronato M, Puca L, Zanca
C, Romano G, Garofalo M, Iaboni M, Croce CM and Condorelli G:
c-FLIPL enhances anti-apoptotic Akt functions by modulation of
Gsk3beta activity. Cell Death Differ. 24:11342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ding WX and Yin XM: Sorting, recognition
and activation of the misfolded protein degradation pathways
through macroautophagy and the proteasome. Autophagy. 4:141–150.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fujita E, Kouroku Y, Isoai A, Kumagai H,
Misutani A, Matsuda C, Hayashi YK and Momoi T: Two endoplasmic
reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) systems for the novel
variant of the mutant dysferlin: Ubiquitin/proteasome ERAD(I) and
autophagy/lysosome ERAD(II). Hum Mol Genet. 16:618–629. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi YH, Ding ZB, Zhou J, Hui B, Shi GM, Ke
AW, Wang XY, Dai Z, Peng YF, Gu CY, et al: Targeting autophagy
enhances sorafenib lethality for hepatocellular carcinoma via ER
stress-related apoptosis. Autophagy. 7:1159–1172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhai B, Hu F, Jiang X, Zhao D, Liu B, Pan
S, Dong X, Tan G and Wei Z: Inhibition of Akt reverses the acquired
resistance to sorafenib by switching protective autophagy to
autophagic cell death in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:1589–1598. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Du J, Wu J, Fu X, Tse AK, Li T, Su T and
Yu ZL: Icariside II overcomes TRAIL resistance of melanoma cells
through ROS-mediated downregulation of STAT3/cFLIP signaling.
Oncotarget. 7:52218–52229. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Salim K, Fenton T, Bacha J,
Urien-Rodriguez H, Bonnert T, Skynner HA, Watts E, Kerby J, Heald
A, Beer M, et al: Oligomerization of G-protein-coupled receptors
shown by selective co-immunoprecipitation. J Biol Chem.
277:15482–15485. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Krammer PH: CD95's deadly mission in the
immune system. Nature. 407:789–795. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ciechanover A and Schwartz AL: The
ubiquitin system: Pathogenesis of human diseases and drug
targeting. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1695:3–17. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Haimerl F, Erhardt A, Sass G and Tiegs G:
Down-regulation of the de-ubiquitinating enzyme ubiquitin-specific
protease 2 contributes to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced
hepatocyte survival. J Biol Chem. 284:495–504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Berasain C: Hepatocellular carcinoma and
sorafenib: Too many resistance mechanisms? Gut. 62:1674–1675. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang CC, Yang F, Thorne RF, Zhu BK,
Hersey P and Zhang XD: Human melanoma cells under endoplasmic
reticulum stress acquire resistance to microtubule-targeting drugs
through XBP-1-mediated activation of Akt. Neoplasia. 11:436–447.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fan L, Sun G, Ma T, Zhong F, Lei Y, Li X
and Wei W: Melatonin reverses tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic
reticulum stress in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and
improves cytotoxic response to doxorubicin by increasing CHOP and
decreasing survivin. J Pineal Res. 55:184–194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fan L, Song B, Sun G, Ma T, Zhong F and
Wei W: Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced resistance to
doxorubicin is reversed by paeonol treatment in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PloS One. 8:e626272013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kato H and Nishitoh H: Stress responses
from the endoplasmic reticulum in cancer. Front Oncol. 5:932015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu F, Han J, Zhai B, Ming X, Zhuang L, Liu
Y, Pan S and Liu T: Blocking autophagy enhances the apoptosis
effect of bufalin on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells through
endoplasmic reticulum stress and JNK activation. Apoptosis.
19:210–223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang WA, Groenendyk J and Michalak M:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress associated responses in cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:2143–2149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos
K and Tschopp J: NF-kappaB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP.
Mol Cell Biol. 21:5299–5305. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song JH, Tse MC, Bellail A, Phuphanich S,
Khuri F, Kneteman NM and Hao C: Lipid rafts and nonrafts mediate
tumor necrosis factor related apoptosis-inducing ligand induced
apoptotic and nonapoptotic signals in non small cell lung carcinoma
cells. Cancer Res. 67:6946–6955. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chang L, Kamata H, Solinas G, Luo JL,
Maeda S, Venuprasad K, Liu YC and Karin M: The E3 ubiquitin ligase
itch couples JNK activation to TNFalpha-induced cell death by
inducing c-FLIP(L) turnover. Cell. 124:601–613. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|