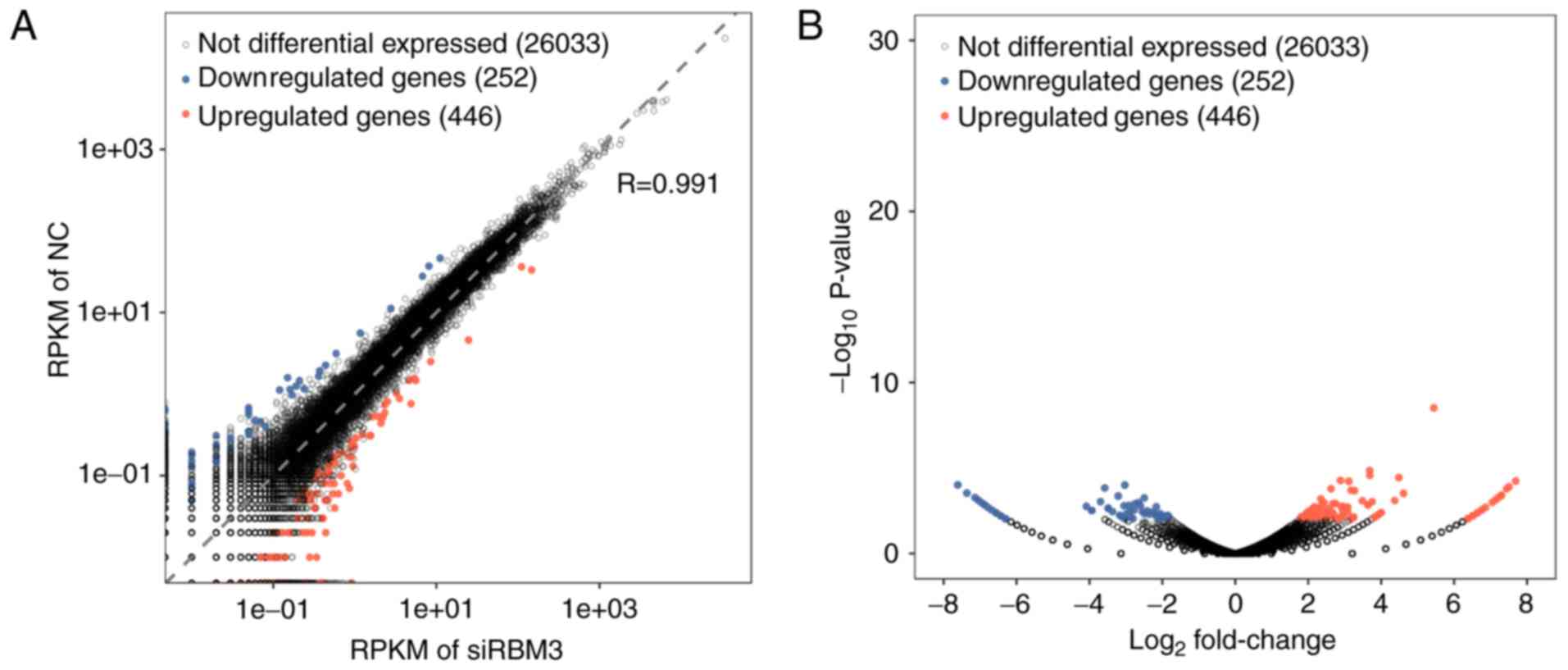
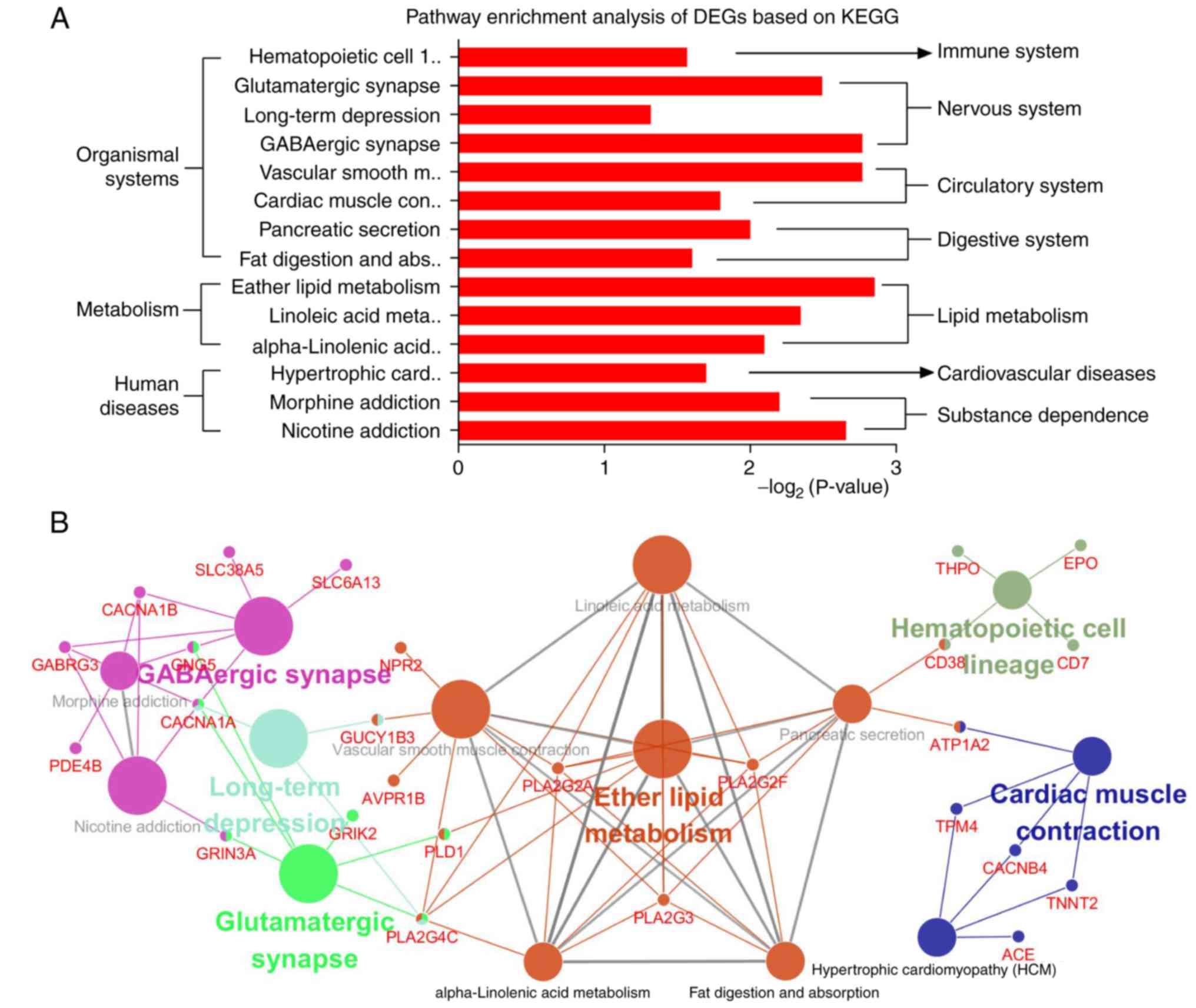
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Danno S, Nishiyama H, Higashitsuji H,
Yokoi H, Xue JH, Itoh K, Matsuda T and Fujita J: Increased
transcript level of RBM3, a member of the glycine-rich RNA-binding
protein family, in human cells in response to cold stress. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 236:804–807. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wellmann S, Truss M, Bruder E, Tornillo L,
Zelmer A, Seeger K and Bührer C: The RNA-binding protein RBM3 is
required for cell proliferation and protects against serum
deprivation-induced cell death. Pediatr Res. 67:35–41. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Peretti D, Bastide A, Radford H, Verity N,
Molloy C, Martin MG, Moreno JA, Steinert JR, Smith T, Dinsdale D,
et al: RBM3 mediates structural plasticity and protective effects
of cooling in neurodegeneration. Nature. 518:236–239. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ehlén Å, Nodin B, Rexhepaj E, Brändstedt
J, Uhlén M, Alvarado-Kristensson M, Pontén F, Brennan DJ and
Jirström K: RBM3-regulated genes promote DNA integrity and affect
clinical outcome in epithelial ovarian cancer. Transl Oncol.
4:212–221. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jögi A, Brennan DJ, Rydén L, Magnusson K,
Fernö M, Stål O, Borgquist S, Uhlen M, Landberg G, Påhlman S, et
al: Nuclear expression of the RNA-binding protein RBM3 is
associated with an improved clinical outcome in breast cancer. Mod
Pathol. 22:1564–1574. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nodin B, Fridberg M, Jonsson L, Bergman J,
Uhlén M and Jirström K: High MCM3 expression is an independent
biomarker of poor prognosis and correlates with reduced RBM3
expression in a prospective cohort of malignant melanoma. Diagn
Pathol. 7:822012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Florianova L, Xu B, Traboulsi S, Elmansi
H, Tanguay S, Aprikian A, Kassouf W and Brimo F: Evaluation of
RNA-binding motif protein 3 expression in urothelial carcinoma of
the bladder: An immunohistochemical study. World J Surg Oncol.
13:3172015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Melling N, Simon R, Mirlacher M, Izbicki
JR, Stahl P, Terracciano LM, Bokemeyer C, Sauter G and Marx AH:
Loss of RNA-binding motif protein 3 expression is associated with
right-sided localization and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer.
Histopathology. 68:191–198. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jonsson L, Gaber A, Ulmert D, Uhlén M,
Bjartell A and Jirström K: High RBM3 expression in prostate cancer
independently predicts a reduced risk of biochemical recurrence and
disease progression. Diagn Pathol. 6:912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grupp K, Wilking J, Prien K, Hube-Magg C,
Sirma H, Simon R, Steurer S, Budäus L, Haese A, Izbicki J, et al:
High RNA-binding motif protein 3 expression is an independent
prognostic marker in operated prostate cancer and tightly linked to
ERG activation and PTEN deletions. Eur J Cancer. 50:852–861. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zeng Y, Wodzenski D, Gao D, Shiraishi T,
Terada N, Li Y, Vander GDJ, Luo J, Kong C, Getzenberg RH, et al:
Stress-response protein RBM3 attenuates the stem-like properties of
prostate cancer cells by interfering with CD44 variant splicing.
Cancer Res. 73:4123–4133. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong
P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z and
Galon J: ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally
grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks.
Bioinformatics. 25:1091–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ferro M, Terracciano D, Buonerba C,
Lucarelli G, Bottero D, Perdonà S, Autorino R, Serino A, Cantiello
F, Damiano R, et al: The emerging role of obesity, diet and lipid
metabolism in prostate cancer. Future Oncol. 13:285–293. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Butler LM, Centenera MM and Swinnen JV:
Androgen control of lipid metabolism in prostate cancer: Novel
insights and future applications. Endocr Relat Cancer.
23:R219–R227. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Al KO, Traka MH, Melchini A, Troncoso-Rey
P, Jurkowski W, Defernez M, Pachori P, Mills RD, Ball RY and Mithen
RF: Increased transcriptional and metabolic capacity for lipid
metabolism in the peripheral zone of the prostate may underpin its
increased susceptibility to cancer. Oncotarget. 8:84902–84916.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamamoto S, Tomita Y, Hoshida Y, Takiguchi
S, Fujiwara Y, Yasuda T, Doki Y, Yoshida K, Aozasa K, Nakamura H,
et al: Expression of hepatoma-derived growth factor is correlated
with lymph node metastasis and prognosis of gastric carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:117–122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fijneman RJ and Cormier RT: The roles of
sPLA2-IIA (Pla2g2a) in cancer of the small and large intestine.
Front Biosci. 13:4144–4174. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kuefner MS, Pham K, Redd JR, Stephenson
EJ, Harvey I, Deng X, Bridges D, Boilard E, Elam MB and Park EA:
Secretory phospholipase A2 group IIA modulates insulin sensitivity
and metabolism. J Lipid Res. 58:1822–1833. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Six DA and Dennis EA: The expanding
superfamily of phospholipase A2 enzymes: Classification
and characterization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1488:1–19. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu S and Dong Z: Overexpression of
secretory phospholipase A2-IIa supports cancer stem cell phenotype
via HER/ERBB-elicited signaling in lung and prostate cancer cells.
Int J Oncol. 50:2113–2122. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Su Y and Wang Y, Zhou Y, Zhu Z, Zhang Q,
Zhang X, Wang W, Gu X, Guo A and Wang Y: Macrophage migration
inhibitory factor activates inflammatory responses of astrocytes
through interaction with CD74 receptor. Oncotarget. 8:2719–2730.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Asano T, Shinohara H, Morishita R, Ueda H,
Kawamura N, Katoh-Semba R, Kishikawa M and Kato K: Selective
localization of G protein gamma5 subunit in the subventricular zone
of the lateral ventricle and rostral migratory stream of the adult
rat brain. J Neurochem. 79:1129–1135. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rosanò L, Spinella F and Bagnato A:
Endothelin 1 in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:637–651. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nikolić ZZ, Pavićević DLj, Romac SP and
Brajušković GN: Genetic variants within endothelial nitric oxide
synthase gene and prostate cancer: A meta-analysis. Clin Transl
Sci. 8:23–31. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Benkisser-Petersen M, Buchner M, Dörffel
A, Dühren-von-Minden M, Claus R, Kläsener K, Leberecht K, Burger M,
Dierks C, Jumaa H, et al: Spleen tyrosine kinase is involved in the
CD38 signal transduction pathway in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
PLoS One. 11:e01691592016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karakurt S and Adali O: Tannic acid
inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion of prostate cancer and
modulates drug metabolizing and antioxidant enzymes. anticancer
agents Med Chem. 16:781–789. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|