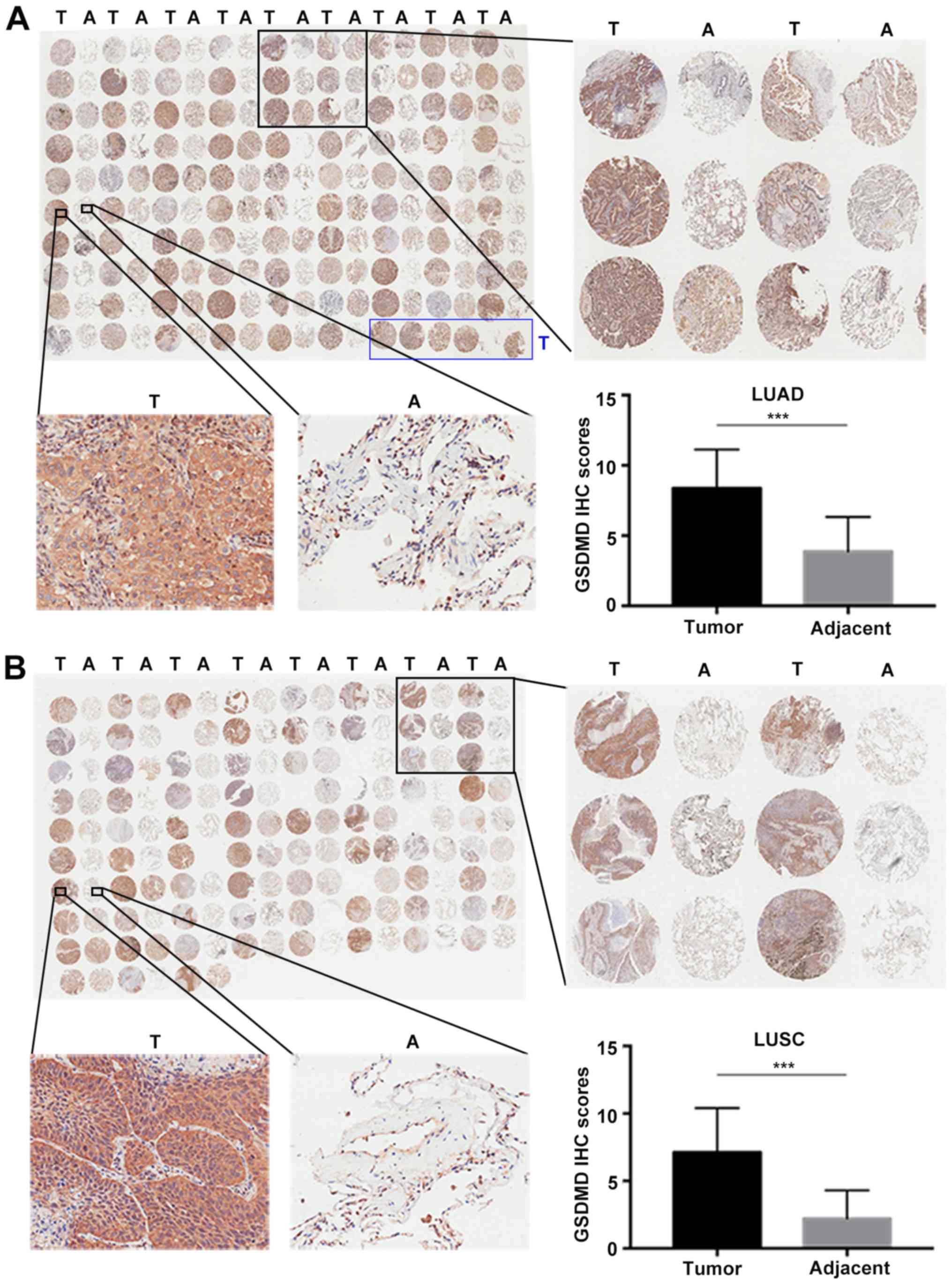
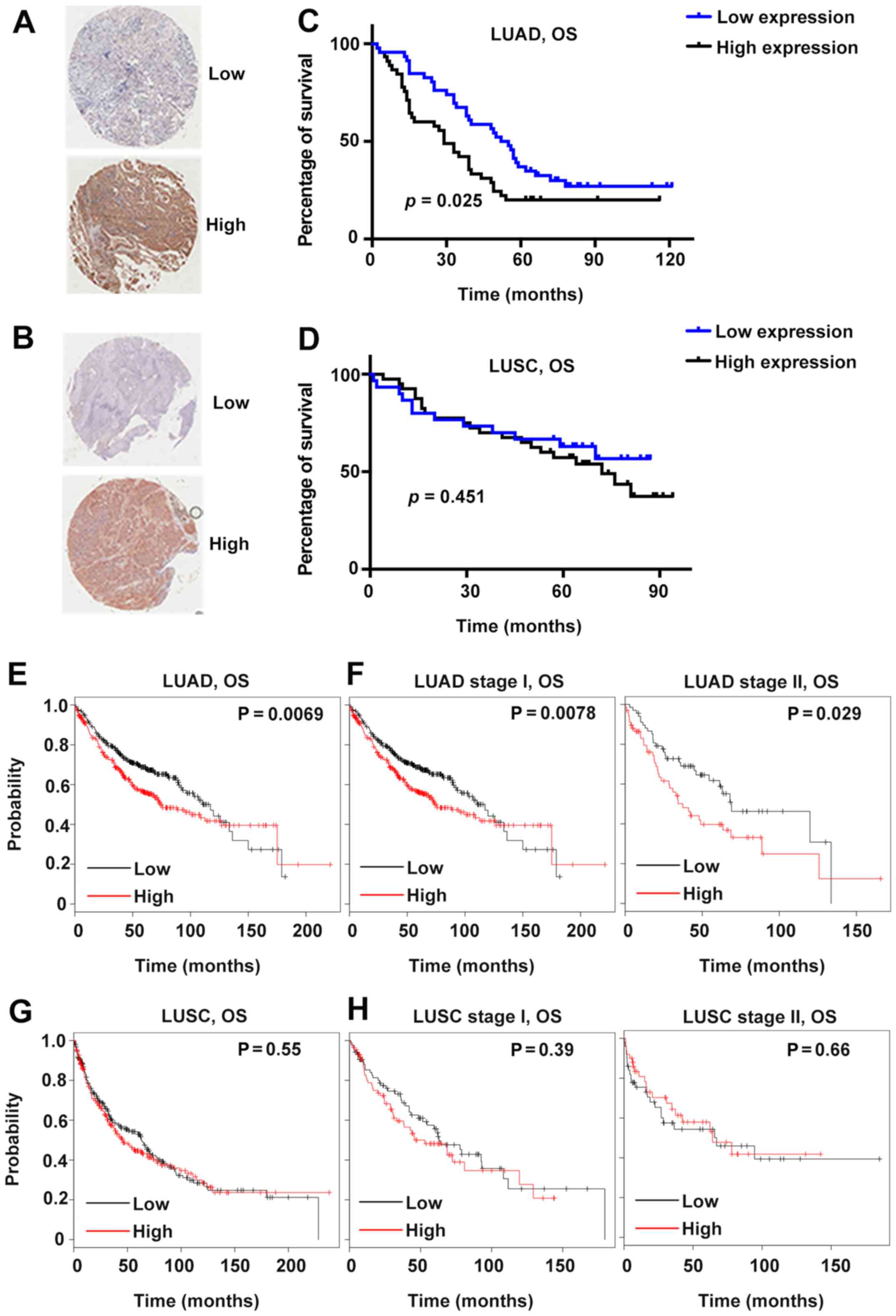
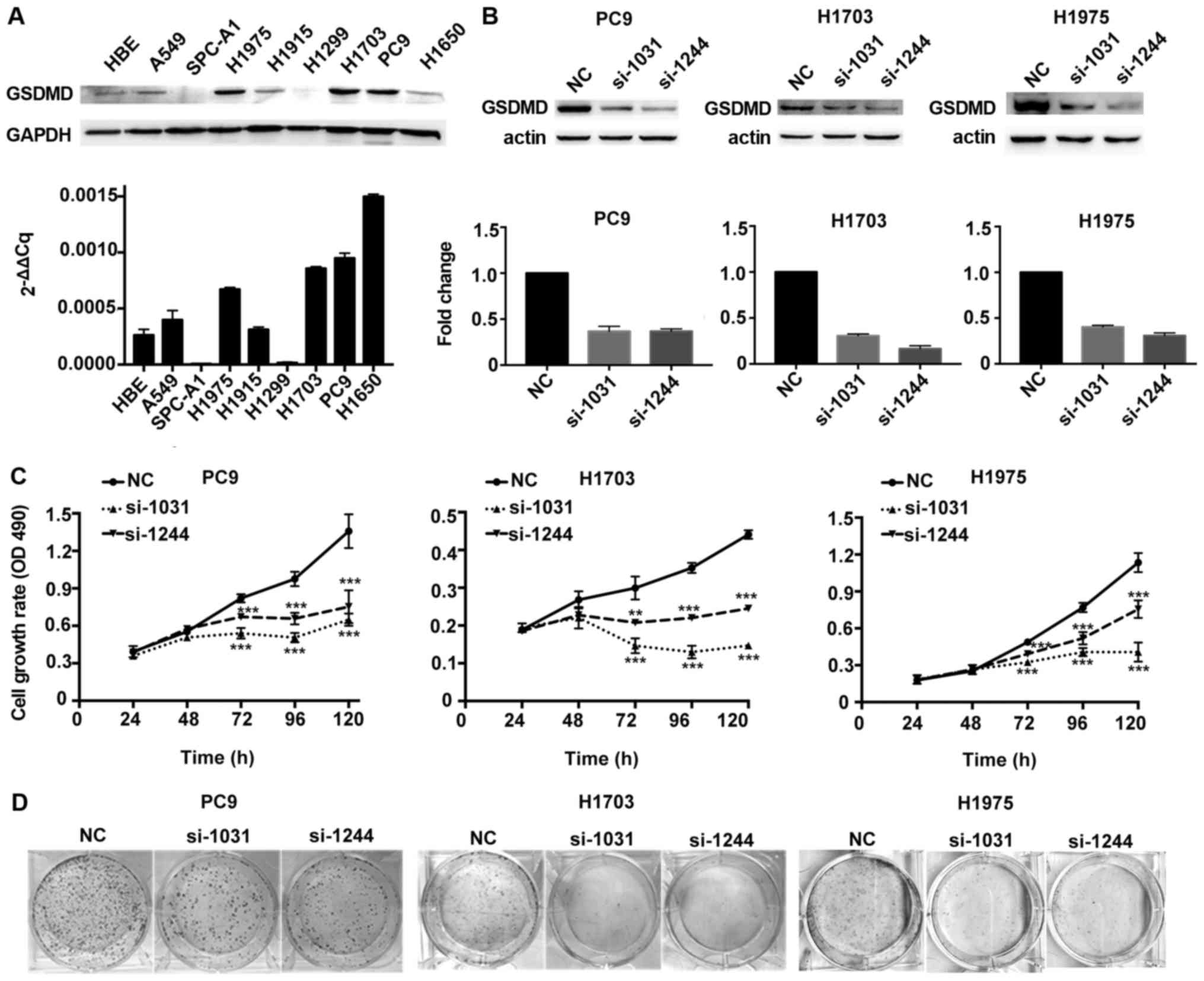
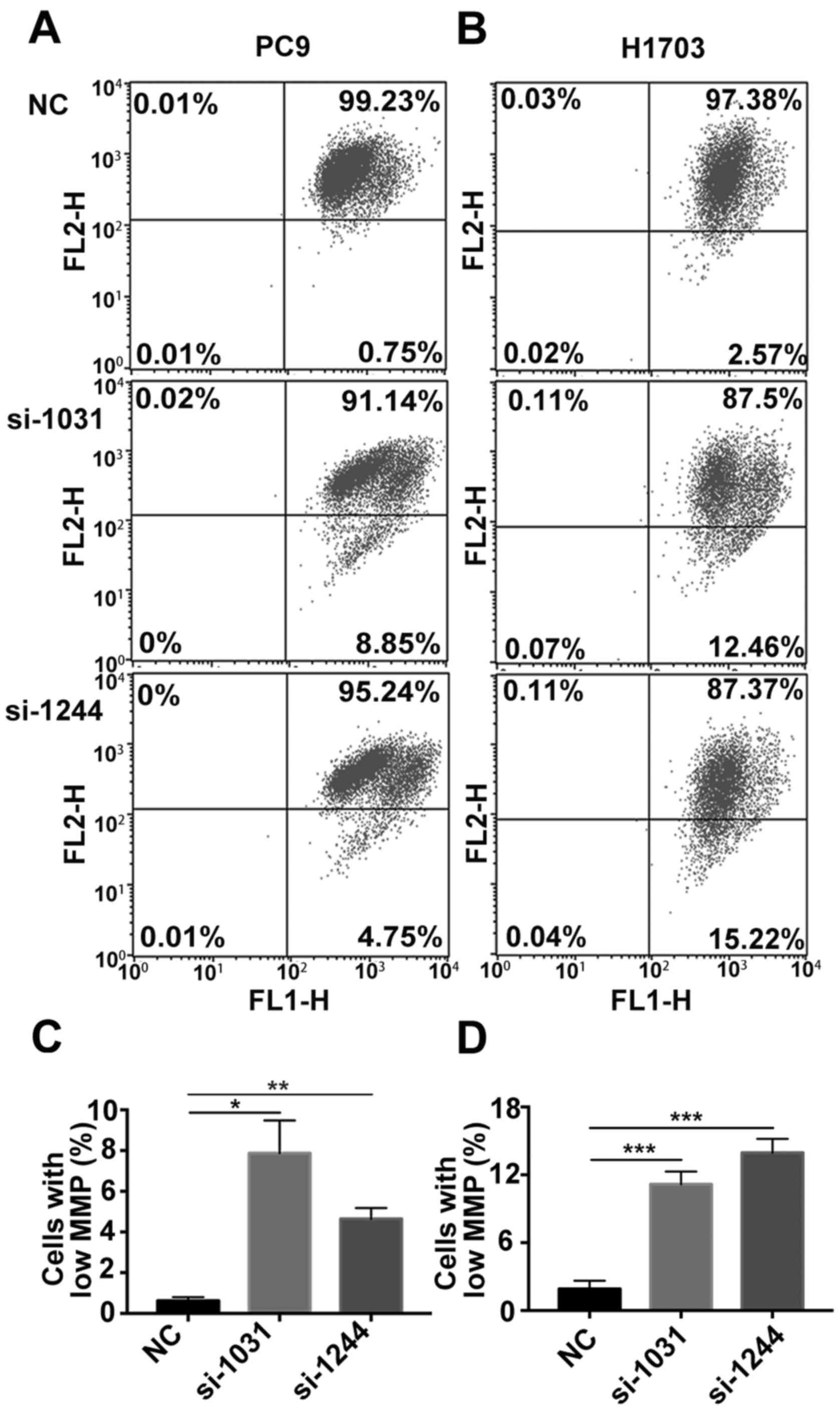
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reck M and Rabe KF: Precision diagnosis
and treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J
Med. 377:849–861. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Saeki N, Usui T, Aoyagi K, Kim DH, Sato M,
Mabuchi T, Yanagihara K, Ogawa K, Sakamoto H, Yoshida T and Sasaki
H: Distinctive expression and function of four GSDM family
genes (GSDMA-D) in normal and malignant upper
gastrointestinal epithelium. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 48:261–271.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shi J, Gao W and Shao F: Pyroptosis:
Gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem
Sci. 42:245–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kayagaki N, Stowe IB, Lee BL, O'Rourke K,
Anderson K, Warming S, Cuellar T, Haley B, Roose-Girma M, Phung QT,
et al: Caspase-11 cleaves gasdermin D for non-canonical
inflammasome signalling. Nature. 526:666–671. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y,
Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F and Shao F: Cleavage of GSDMD by
inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature.
526:660–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fink SL and Cookson BT: Apoptosis,
pyroptosis, and necrosis: Mechanistic description of dead and dying
eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun. 73:1907–1916. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aglietti RA, Estevez A, Gupta A, Ramirez
MG, Liu PS, Kayagaki N, Ciferri C, Dixit VM and Dueber EC: GsdmD
p30 elicited by caspase-11 during pyroptosis forms pores in
membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:7858–7863. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen X, He WT, Hu L, Li J, Fang Y, Wang X,
Xu X, Wang Z, Huang K and Han J: Pyroptosis is driven by
non-selective gasdermin-D pore and its morphology is different from
MLKL channel-mediated necroptosis. Cell Res. 26:1007–1020. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ding J, Wang K, Liu W, She Y, Sun Q, Shi
J, Sun H, Wang DC and Shao F: Pore-forming activity and structural
autoinhibition of the gasdermin family. Nature. 535:111–116. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sborgi L, Ruhl S and Mulvihill E: GSDMD
membrane pore formation constitutes the mechanism of pyroptotic
cell death. EMBO J. 35:1766–1778. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wallach D, Kang TB, Dillon CP and Green
DR: Programmed necrosis in inflammation: Toward identification of
the effector molecules. Science. 352:aaf21542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zitvogel L, Kepp O, Galluzzi L and Kroemer
G: Inflammasomes in carcinogenesis and anticancer immune responses.
Nat Immunol. 13:343–351. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Karki R, Man SM and Kanneganti TD:
Inflammasomes and cancer. Cancer Immunol Res. 5:94–99. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Munn LL: Cancer and inflammation. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 9:2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Allen IC, TeKippe EM, Woodford RM, Uronis
JM, Holl EK, Rogers AB, Herfarth HH, Jobin C and Ting JP: The NLRP3
inflammasome functions as a negative regulator of tumorigenesis
during colitis-associated cancer. J Exp Med. 207:1045–1056. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zaki MH, Vogel P, Body-Malapel M, Lamkanfi
M and Kanneganti TD: IL-18 production downstream of the Nlrp3
inflammasome confers protection against colorectal tumor formation.
J Immunol. 185:4912–4920. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bauer C, Duewell P, Mayer C, Lehr HA,
Fitzgerald KA, Dauer M, Tschopp J, Endres S, Latz E and Schnurr M:
Colitis induced in mice with dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) is
mediated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Gut. 59:1192–1199. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Diakos CI, Charles KA, McMillan DC and
Clarke SJ: Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness.
Lancet Oncol. 15:e493–e503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhai Z, Liu W, Kaur M, Luo Y, Domenico J,
Samson JM, Shellman YG, Norris DA, Dinarello CA, Spritz RA, et al:
NLRP1 promotes tumor growth by enhancing inflammasome activation
and suppressing apoptosis in metastatic melanoma. Oncogene.
36:3820–3830. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vande Walle L and Lamkanfi M: Pyroptosis.
Curr Biol. 26:R568–R572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taabazuing CY, Okondo MC and Bachovchin
DA: Pyroptosis and apoptosis pathways engage in bidirectional
crosstalk in monocytes and macrophages. Cell Chem Biol.
24(507–514): e5042017.
|
|
24
|
He WT, Wan H, Hu L, Chen P, Wang X, Huang
Z, Yang ZH, Zhong CQ and Han J: Gasdermin D is an executor of
pyroptosis and required for interleukin-1beta secretion. Cell Res.
25:1285–1298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Silva MT: Secondary necrosis: The natural
outcome of the complete apoptotic program. FEBS Lett.
584:4491–4499. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yuan J, Najafov A and Py BF: Roles of
caspases in necrotic cell death. Cell. 167:1693–1704. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yip PY: Phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin (PI3K-Akt-mTOR)
signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer
Res. 4:165–176. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Aglietti RA and Dueber EC: Recent insights
into the molecular mechanisms underlying pyroptosis and gasdermin
family functions. Trends Immunol. 38:261–271. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jorgensen I, Rayamajhi M and Miao EA:
Programmed cell death as a defence against infection. Nat Rev
Immunol. 17:151–164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sagulenko V, Thygesen SJ, Sester DP, Idris
A, Cridland JA, Vajjhala PR, Roberts TL, Schroder K, Vince JE, Hill
JM, et al: AIM2 and NLRP3 inflammasomes activate both apoptotic and
pyroptotic death pathways via ASC. Cell Death Differ. 20:1149–1160.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kong H, Wang Y, Zeng X, Wang Z, Wang H and
Xie W: Differential expression of inflammasomes in lung cancer cell
lines and tissues. Tumour Biol. 36:7501–7513. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Weichhart T and Saemann MD: The
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in innate immune cells: Emerging therapeutic
applications. Ann Rheum Dis. 67 Suppl 3:iii70–iii74. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Papadimitrakopoulou V: Development of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors and their application in
personalized therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Oncol. 7:1315–1326. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|