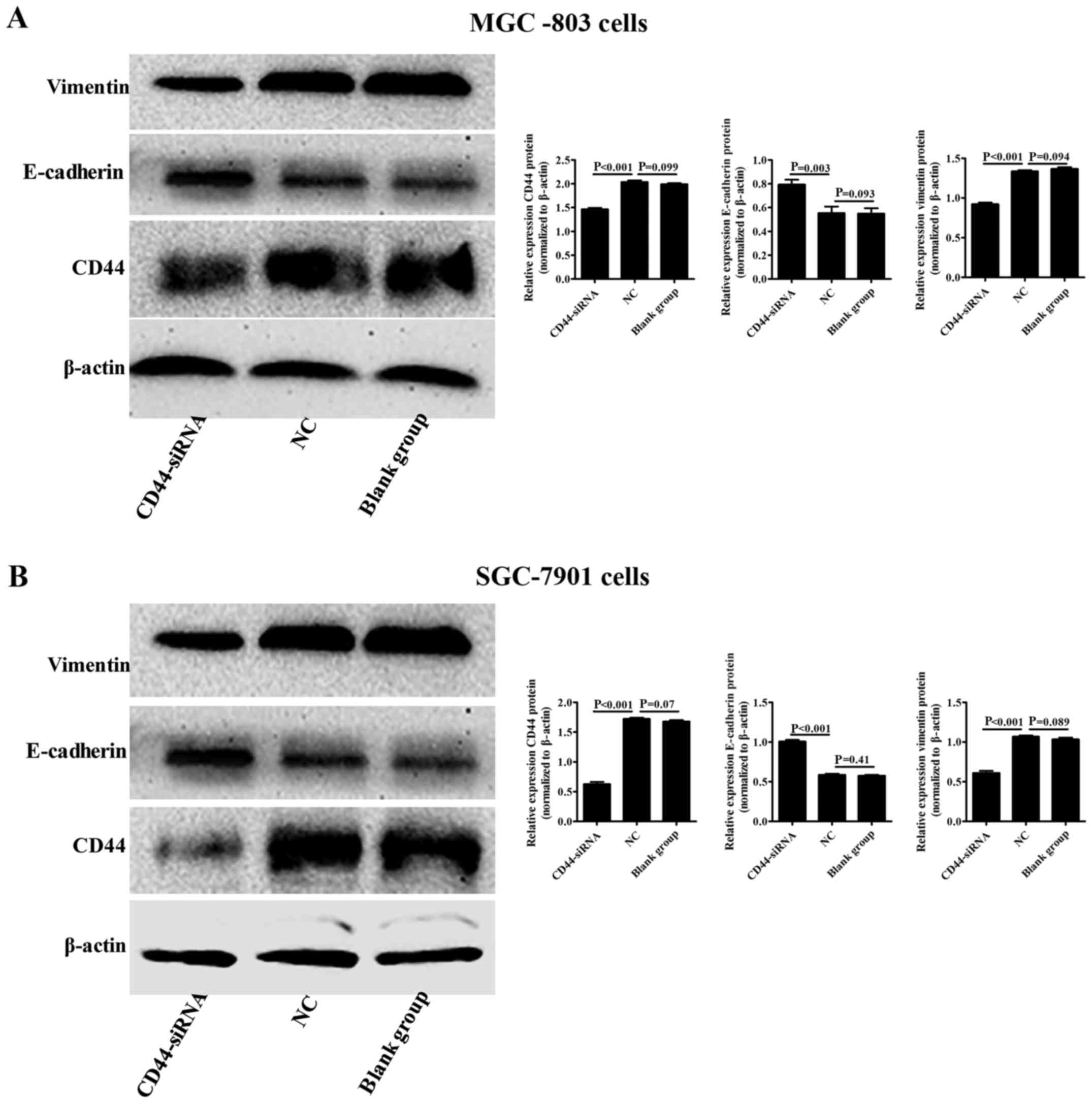
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Martin-Richard M, Custodio A, Garcia-Giron
C, Gravalos C, Gomez C, Jimenez-Fonseca P, Manzano JL, Pericay C,
Rivera F and Carrato A: Seom guidelines for the treatment of
gastric cancer 2015. Clin Transl Oncol. 17:996–1004. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yan W, Cao QJ, Arenas RB, Bentley B and
Shao R: GATA3 inhibits breast cancer metastasis through the
reversal of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Biol Chem.
285:14042–14051. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen Y, Liu J, Wang W, Xiang L, Wang J,
Liu S, Zhou H and Guo Z: High expression of hnRNPA1 promotes cell
invasion by inducing EMT in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep.
39:1993–1701. 2018.
|
|
6
|
Huang M, Wu S, Hu Q, Wu H, Wei S, Xie H,
Sun K, Li X and Fang L: Agkihpin, a novel SVAE may inhibit the
migration and invasion of liver cancer cells associated with the
inversion of EMT induced by Wnt/beta-catenin signaling inhibition.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 479:283–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Wang X, Liu F and Fu Y:
microRNA-335 inhibits colorectal cancer HCT116 cells growth and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process by targeting
Twist1. Pharmazie. 72:475–481. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ventura A and Jacks T: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 136:586–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang X, Nie Y, Du Y, Cao J, Shen B and Li
Y: MicroRNA-181a promotes gastric cancer by negatively regulating
tumor suppressor KLF6. Tumour Biol. 33:1589–1597. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen JS, Li HS, Huang JQ, Dong SH, Huang
ZJ, Yi W, Zhan GF, Feng JT, Sun JC and Huang XH: MicroRNA-379-5p
inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting FAK/AKT
signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 375:73–83.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song F, Yang D, Liu B, Guo Y, Zheng H, Li
L, Wang T, Yu J, Zhao Y, Niu R, et al: Integrated microRNA network
analyses identify a poor-prognosis subtype of gastric cancer
characterized by the miR-200 family. Clin Cancer Res. 20:878–889.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Z, Liu S, Shi R and Zhao G: miR-27
promotes human gastric cancer cell metastasis by inducing
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Genet. 204:486–491.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi Y, Shi H, Zhang B, Yan Y, Han X, Jiang
W, Qian H and Xu W: miR-373 suppresses gastric cancer metastasis by
downregulating vimentin. Mol Med Rep. 17:4027–4034. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen X, Wang G, Lu X, Gao P, Song Y, Sun
J, Li A, Xu Y, Xu H and Wang Z: Polymorphisms and haplotypes of the
miR-148/152 family are associated with the risk and
clinicopathological features of gastric cancer in a Northern
Chinese population. Mutagenesis. 29:401–407. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu X, Luo L, Wu Y, Yu X, Liu Y, Yu X, Zhao
X, Zhang X, Cui L, Ye G, et al: Gastric juice miR-129 as a
potential biomarker for screening gastric cancer. Med Oncol.
30:3652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liao A, Tan G, Chen L, Zhou W and Hu H:
RASSF1A inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation by
miR-711-mediated downregulation of CDK4 expression. Oncotarget.
7:5842–5851. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma Z, Xin Z, Hu W, Jiang S, Yang Z, Yan X,
Li X, Yang Y and Chen F: Forkhead box O proteins: Crucial
regulators of cancer EMT. Semin Cancer Biol. 50:21–31. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Boulding T, McCuaig RD, Tan A, Hardy K, Wu
F, Dunn J, Kalimutho M, Sutton CR, Forwood JK, Bert AG, et al: LSD1
activation promotes inducible EMT programs and modulates the tumour
microenvironment in breast cancer. Sci Rep. 8:732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Z, Zou Y, Liang M, Chen Y, Luo Y,
Yang B, Liu F, Qin Y, He D, Wang F and Huang O: Suppressor of fused
(Sufu) promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in cervical
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:114226–114238. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Tian XJ, Zhang H, Teng Y, Li R,
Bai F, Elankumaran S and Xing J: TGF-beta-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition proceeds through stepwise
activation of multiple feedback loops. Sci Signal. 7:ra912014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Asakura T, Yamaguchi N, Ohkawa K and
Yoshida K: Proteasome inhibitor-resistant cells cause EMT-induction
via suppression of E-cadherin by miR-200 and ZEB1. Int J Oncol.
46:2251–2260. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qin Y, Tang B, Hu CJ, Xiao YF, Xie R, Yong
X, Wu YY, Dong H and Yang SM: An hTERT/ZEB1 complex directly
regulates E-cadherin to promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:351–361. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Satelli A, Batth I, Brownlee Z, Mitra A,
Zhou S, Noh H, Rojas CR, Li H, Meng QH and Li S: EMT circulating
tumor cells detected by cell-surface vimentin are associated with
prostate cancer progression. Oncotarget. 8:49329–49337. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhai X, Zhu H, Wang W, Zhang S, Zhang Y
and Mao G: Abnormal expression of EMT-related proteins, S100A4,
vimentin and E-cadherin, is correlated with clinicopathological
features and prognosis in HCC. Med Oncol. 31:9702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ikezono Y, Koga H, Akiba J, Abe M, Yoshida
T, Wada F, Nakamura T, Iwamoto H, Masuda A, Sakaue T, et al:
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and EMT behavior are driven by the
CSC marker DCLK1. Mol Cancer Res. 15:744–752. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jayaraman A, Kumar P, Marin S, de Atauri
P, Mateo F, Thomson M T, Centelles J J, Graham F S and Cascante M:
Untargeted metabolomics reveals distinct metabolic reprogramming in
endothelial cells co-cultured with CSC and non-CSC prostate cancer
cell subpopulations. PLoS One. 13:e01921752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mateo F, Meca-Cortes O, Celia-Terrassa T,
Fernandez Y, Abasolo I, Sanchez-Cid L, Bermudo R, Sagasta A,
Rodriguez-Carunchio L, Pons M, et al: SPARC mediates metastatic
cooperation between CSC and non-CSC prostate cancer cell
subpopulations. Mol Cancer. 13:2372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ishimoto T, Oshima H, Oshima M, Kai K,
Torii R, Masuko T, Baba H, Saya H and Nagano O: CD44+
slow-cycling tumor cell expansion is triggered by cooperative
actions of Wnt and prostaglandin E2 in gastric tumorigenesis.
Cancer Sci. 101:673–678. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gadhoum SZ, Madhoun NY, Abuelela AF and
Merzaban JS: Anti-CD44 antibodies inhibit both mTORC1 and mTORC2: A
new rationale supporting CD44-induced AML differentiation therapy.
Leukemia. 30:2397–2401. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cao W, Wei W, Zhan Z, Xie D, Xie Y and
Xiao Q: Role of miR-647 in human gastric cancer suppression. Oncol
Rep. 37:1401–1411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee SY, Kim KA, Kim CH, Kim YJ, Lee JH and
Kim HR: CD44-shRNA recombinant adenovirus inhibits cell
proliferation, invasion, and migration, and promotes apoptosis in
HCT116 colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 50:329–336. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang L, Wu H, Wang L, Zhang H, Lu J, Liang
Z and Liu T: Asporin promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasion and
migration by regulating the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
(EMT) through both autocrine and paracrine mechanisms. Cancer Lett.
398:24–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao N, Yu H, Yu H, Sun M, Zhang Y, Xu M
and Gao W: MiRNA-711-SP1-collagen-I pathway is involved in the
anti-fibrotic effect of pioglitazone in myocardial infarction. Sci
China Life Sci. 56:431–439. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Boursereau R, Abou-Samra M, Lecompte S,
Noel L and Brichard SM: New targets to alleviate skeletal muscle
inflammation: Role of microRNAs regulated by adiponectin. Sci Rep.
7:434372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu JY, Yi W, Zhang MY, Xu R, Zeng LS, Long
XR, Zhou XM, Zheng XS, Kang Y and Wang HY: MicroRNA-711 is a
prognostic factor for poor overall survival and has an oncogenic
role in breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 11:2155–2163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Waseem M, Ahmad MK, Srivatava VK, Rastogi
N, Serajuddin M, Kumar S, Mishra DP, Sankhwar SN and Mahdi AA:
Evaluation of miR-711 as novel biomarker in prostate cancer
progression. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 18:2185–2191. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zheng X, Carstens JL, Kim J, Scheible M,
Kaye J, Sugimoto H, Wu CC, LeBleu VS and Kalluri R:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis
but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature.
527:525–530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fischer KR, Durrans A, Lee S, Sheng J, Li
F, Wong ST, Choi H, El Rayes T, Ryu S, Troeger J, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung
metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature. 527:472–476.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hu Y, Wang J, Qian J, Kong X, Tang J, Wang
Y, Chen H, Hong J, Zou W, Chen Y, et al: Long noncoding RNA GAPLINC
regulates CD44-dependent cell invasiveness and associates with poor
prognosis of gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 74:6890–6902. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|