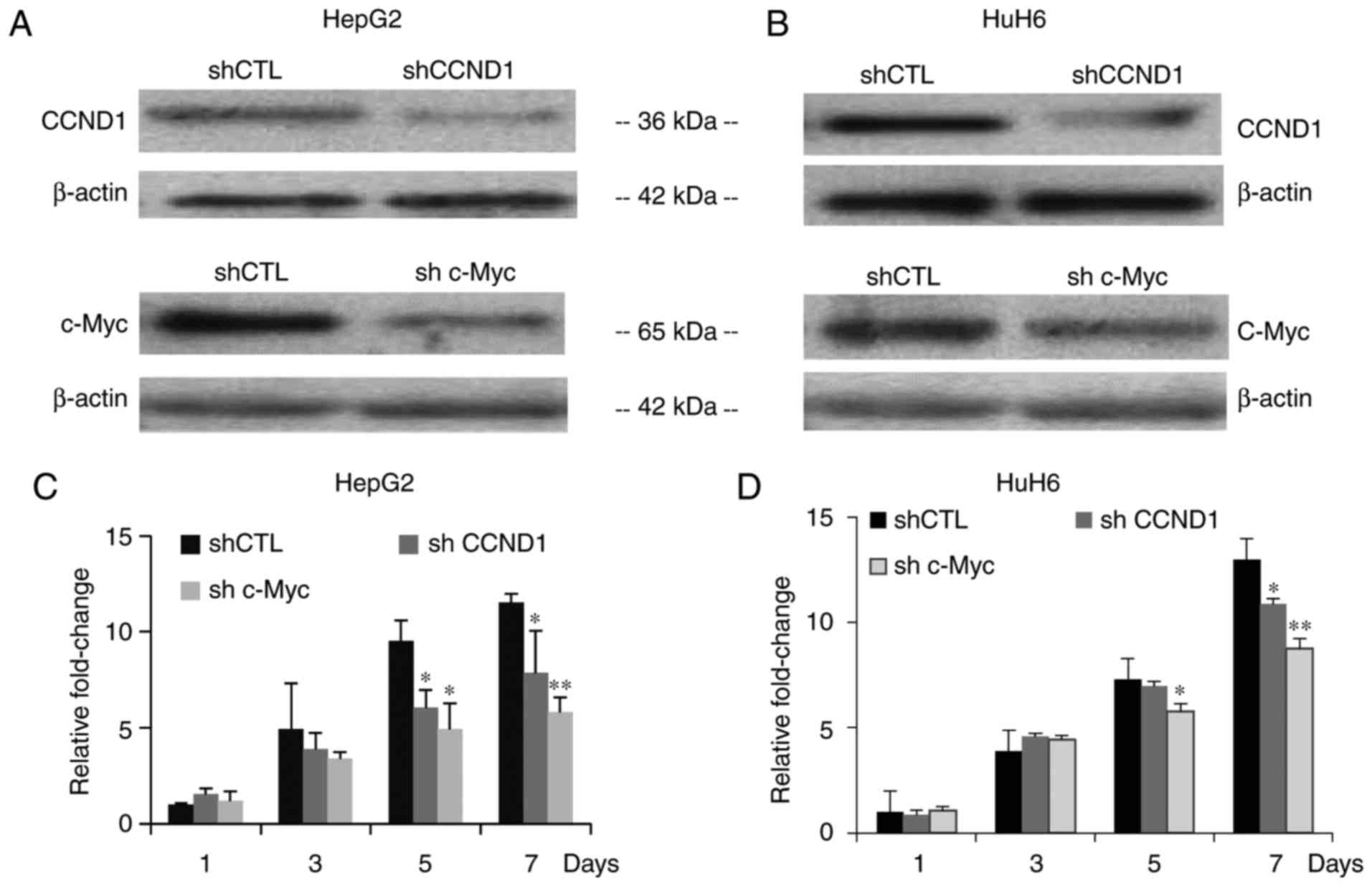
|
1
|
Buendia MA: Unravelling the genetics of
hepatoblastoma: Few mutations, what else? J Hepatol. 6:1202–4.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
von Schweinitz D: Hepatoblastoma: Recent
developments in research and treatment. Semin Pediatr Surg.
21:21–30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
von Schweinitz D: Management of liver
tumors in childhood. Semin Pediatr Surg. 15:17–24. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schmid I, Haberle B, Albert MH,
Corbacioglu S, Fröhlich B, Graf N, Kammer B, Kontny U, Leuschner I,
Scheel-Walter HG, et al: Sorafenib and cisplatin/doxorubicin
(PLADO) in pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma. Pediatr Blood
Cancer. 58:539–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Malogolowkin MH, Katzenstein HM, Krailo M,
Chen Z, Quinn JJ, Reynolds M and Ortega JA: Redefining the role of
doxorubicin for the treatment of children with hepatoblastoma. J
Clin Oncol. 26:2379–2383. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Warmann SW, Armeanu S, Frank H, Buck H,
Graepler F, Lemken ML, Heitmann H, Seitz G, Lauer UM, Bitzer M and
Fuchs J: In vitro gene targeting in human hepatoblastoma. Pediatr
Surg Int. 22:16–23. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Warmann S, Hunger M, Teichmann B, Flemming
P, Gratz KF and Fuchs J: The role of the MDR1 gene in the
development of multidrug resistance in human hepatoblastoma:
Clinical course and in vivo model. Cancer. 95:1795–1801. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fayard E, Auwerx J and Schoonjans K: LR
H-1 An orphan nuclear receptor involved in development, metabolism
and steroidogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 14:250–260. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fayard E, Schoonjans K, Annicotte JS and
Auwerx J: Liver receptor homolog 1 controls the expression of
carboxyl ester lipase. J Biol Chem. 278:35725–35731. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Petersen GM, Amundadottir L, Fuchs CS,
Kraft P, Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Jacobs KB, Arslan AA,
Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Gallinger S, Gross M, et al: A genome-wide
association study identifies pancreatic cancer susceptibility loci
on chromosomes 13q22.1, 1q32.1 and 5p15.33. Nat Genet. 42:224–228.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Annicotte JS, Fayard E, Swift GH, Selander
L, Edlund H, Tanaka T, Kodama T, Schoonjans K and Auwerx J:
Pancreatic-duodenal homeobox 1 regulates expression of liver
receptor homolog 1 during pancreas development. Mol Cell Biol.
23:6713–6724. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thiruchelvam PT, Lai CF, Hua H, Thomas RS,
Hurtado A, Hudson W, Bayly AR, Kyle FJ, Periyasamy M and Photiou A:
The liver receptor homolog-1 regulates estrogen receptor expression
in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 127:385–396. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bolado-Carrancio A, Riancho JA, Sainz J
and Rodriguez-Rey JC: Activation of nuclear receptor NR5A2
increases Glut4 expression and glucose metabolism in muscle cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 446:614–619. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin Q, Aihara A, Chung W, Li Y, Huang Z,
Chen X, Weng S, Carlson RI, Wands JR and Dong X: LRH1 as a driving
factor in pancreatic cancer growth. Cancer Lett. 345:85–90. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Botrugno OA, Fayard E, Annicotte JS, Haby
C, Brennan T, Wendling O, Tanaka T, Kodama T, Thomas W, Auwerx J
and Schoonjans K: Synergy between LRH-1 and beta-catenin induces G1
cyclin-mediated cell proliferation. Mol Cell. 15:499–509. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dube C, Bergeron F, Vaillant MJ, Robert
NM, Brousseau C and Tremblay JJ: The nuclear receptors SF1 and LRH1
are expressed in endometrial cancer cells and regulate
steroidogenic gene transcription by cooperating with AP-1 factors.
Cancer Lett. 275:127–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Whitby RJ, Stec J, Blind RD, Dixon S,
Leesnitzer LM, Orband-Miller LA, Williams SP, Willson TM, Xu R,
Zuercher WJ, et al: Small molecule agonists of the orphan nuclear
receptors steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, NR5A1) and liver receptor
homologue-1 (LRH-1, NR5A2). J Med Chem. 54:2266–2281. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Whitby RJ, Dixon S, Maloney PR, Delerive
P, Goodwin BJ, Parks DJ and Willson TM: Identification of small
molecule agonists of the orphan nuclear receptors liver receptor
homolog-1 and steroidogenic factor-1. J Med Chem. 49:6652–6655.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Corzo CA, Mari Y, Chang MR, Khan T,
Kuruvilla D, Nuhant P, Kumar N, West GM, Duckett DR, Roush WR and
Griffin PR: Antiproliferation activity of a small molecule
repressor of liver receptor homolog 1. Mol Pharmacol. 87:296–304.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Benod C, Carlsson J, Uthayaruban R, Hwang
P, Irwin JJ, Doak AK, Shoichet BK, Sablin EP and Fletterick RJ:
Structure-based discovery of antagonists of nuclear receptor LRH-1.
J Biol Chem. 288:19830–19844. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Woodfield SE, Shi Y, Patel RH, Jin J,
Major A, Sarabia SF, Starosolski Z, Zorman B, Gupta SS, Chen Z, et
al: A novel cell line based orthotopic xenograft mouse model that
recapitulates human hepatoblastoma. Sci Rep. 7:177512017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Heng JC, Feng B, Han J, Jiang J, Kraus P,
Ng JH, Orlov YL, Huss M, Yang L, Lufkin T, et al: The nuclear
receptor Nr5a2 can replace Oct4 in the reprogramming of murine
somatic cells to pluripotent cells. Cell Stem Cell. 6:167–174.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wagner RT, Xu X, Yi F, Merrill BJ and
Cooney AJ: Canonical Wnt/beta-catenin regulation of liver receptor
homolog-1 mediates pluripotency gene expression. Stem Cells.
28:1794–1804. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pelengaris S, Khan M and Evan G: c-MYC:
More than just a matter of life and death. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:764–776. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Annicotte JS, Chavey C, Servant N,
Teyssier J, Bardin A, Licznar A, Badia E, Pujol P, Vignon F,
Maudelonde T, et al: The nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog-1
is an estrogen receptor target gene. Oncogene. 24:8167–8175. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bertolin K, Gossen J, Schoonjans K and
Murphy BD: The orphan nuclear receptor Nr5a2 is essential for
luteinization in the female mouse ovary. Endocrinology.
155:1931–1943. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bayrer JR, Mukkamala S, Sablin EP, Webb P
and Fletterick RJ: Silencing LRH-1 in colon cancer cell lines
impairs proliferation and alters gene expression programs. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:2467–2472. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pietsch T, Fonatsch C, Albrecht S, Maschek
H, Wolf HK and von Schweinitz D: Characterization of the continuous
cell line HepT1 derived from a human hepatoblastoma. Lab Invest.
74:809–818. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|