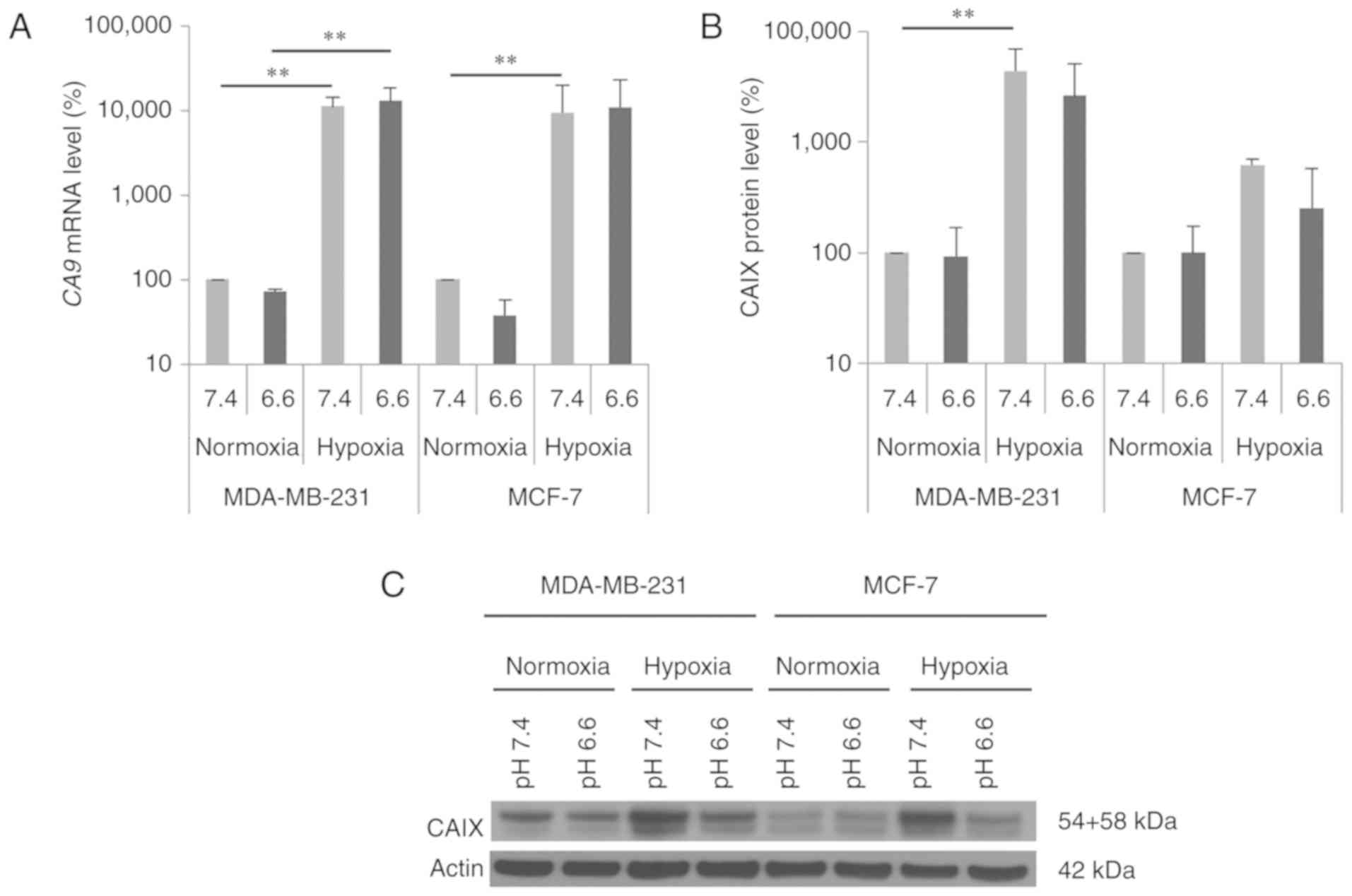
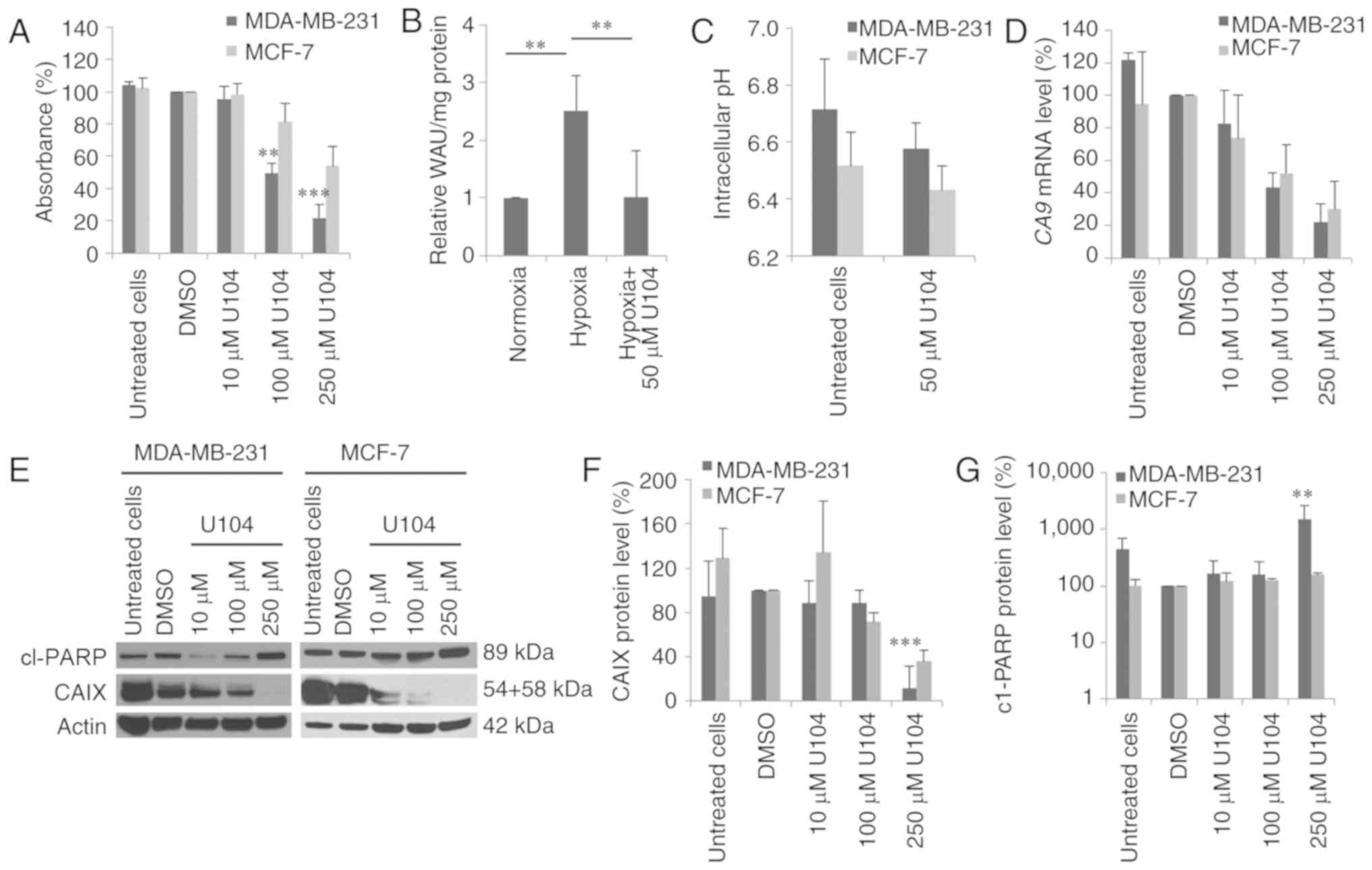
|
1
|
Brown JM and Wilson WR: Exploiting tumour
hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:437–447. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gatenby RA and Gillies RJ: Why do cancers
have high aerobic glycolysis? Nat Rev Cancer. 4:891–899. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown JM and Giaccia AJ: The unique
physiology of solid tumors: Opportunities (and problems) for cancer
therapy. Cancer Res. 58:1408–1416. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wykoff CC, Beasley NJ, Watson PH, Turner
KJ, Pastorek J, Sibtain A, Wilson GD, Turley H, Talks KL, Maxwell
PH, et al: Hypoxia-inducible expression of tumor- associated
carbonic anhydrases. Cancer Res. 60:7075–7083. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Swietach P, Vaughan-Jones RD and Harris
AL: Regulation of tumor pH and the role of carbonic anhydrase 9.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 26:299–310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lou Y, McDonald PC, Oloumi A, Chia S,
Ostlund C, Ahmadi A, Kyle A, Auf dem Keller U, Leung S, Huntsman D,
et al: Targeting tumor hypoxia: Suppression of breast tumor growth
and metastasis by novel carbonic anhydrase IX inhibitors. Cancer
Res. 71:3364–3376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Radvak P, Repic M, Svastova E, Takacova M,
Csaderova L, Strnad H, Pastorek J, Pastorekova S and Kopacek J:
Suppression of carbonic anhydrase IX leads to aberrant focal
adhesion and decreased invasion of tumor cells. Oncol Rep.
29:1147–1153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chiche J, Ilc K, Laferrière J, Trottier E,
Dayan F, Mazure NM, Brahimi-Horn MC and Pouysségur J:
Hypoxia-inducible carbonic anhydrase IX and XII promote tumor cell
growth by counteracting acidosis through the regulation of the
intracellular pH. Cancer Res. 69:358–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van Kuijk SJA, Yaromina A, Houben R,
Niemans R, Lambin P and Dubois LJ: Prognostic significance of
carbonic anhydrase IX expression in cancer patients: A
meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 6:692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hussain SA, Ganesan R, Reynolds G, Gross
L, Stevens A, Pastorek J, Murray PG, Perunovic B, Anwar MS,
Billingham L, et al: Hypoxia-regulated carbonic anhydrase IX
expression is associated with poor survival in patients with
invasive breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 96:104–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chia SK, Wykoff CC, Watson PH, Han C, Leek
RD, Pastorek J, Gatter KC, Ratcliffe P and Harris AL: Prognostic
significance of a novel hypoxia-regulated marker, carbonic
anhydrase IX, in invasive breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
19:3660–3668. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brennan DJ, Jirstrom K, Kronblad A,
Millikan RC, Landberg G, Duffy MJ, Rydén L, Gallagher WM and
O'Brien SL: CA IX is an independent prognostic marker in
premenopausal breast cancer patients with one to three positive
lymph nodes and a putative marker of radiation resistance. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:6421–6431. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin MS, Lee H, Park IA, Chung YR, Im SA,
Lee KH, Moon HG, Han W, Kim K, Kim TY, et al: Overexpression of
HIF1α and CAXI predicts poor outcome in early-stage triple negative
breast cancer. Virchows Arch. 469:183–190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dubois L, Peeters SG, van Kuijk SJ,
Yaromina A, Lieuwes NG, Saraya R, Biemans R, Rami M, Parvathaneni
NK, Vullo D, et al: Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX by
nitroimidazole based sulfamides enhances the therapeutic effect of
tumor irradiation: A new concept of dual targeting drugs. Radiother
Oncol. 108:523–528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dubois L, Peeters S, Lieuwes NG, Geusens
N, Thiry A, Wigfield S, Carta F, McIntyre A, Scozzafava A, Dogné
JM, et al: Specific inhibition of carbonic anhydrase IX activity
enhances the in vivo therapeutic effect of tumor irradiation.
Radiother Oncol. 99:424–431. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ivanova L, Zandberga E, Siliņa K, Kalniņa
Z, Ābols A, Endzeliņš E, Vendina I, Romanchikova N, Hegmane A,
Trapencieris P, et al: Prognostic relevance of carbonic anhydrase
IX expression is distinct in various subtypes of breast cancer and
its silencing suppresses self-renewal capacity of breast cancer
cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 75:235–246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McDonald PC, Chafe SC and Dedhar S:
Overcoming hypoxia-mediated tumor progression: Combinatorial
approaches targeting pH regulation, angiogenesis and immune
dysfunction. Front Cell Dev Biol. 4:272016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Winum JY, Pastorekova S, Jakubickova L,
Montero JL, Scozzafava A, Pastorek J, Vullo D, Innocenti A and
Supuran CT: Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Synthesis and inhibition
of cytosolic/tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isozymes I, II,
and IX with bis-sulfamates. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 15:579–584. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bache M, Münch C, Güttler A, Wichmann H,
Theuerkorn K, Emmerich D, Paschke R and Vordermark D: Betulinyl
sulfamates as anticancer agents and radiosensitizers in human
breast cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 16:26249–26262. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meehan J, Ward C, Turnbull A,
Bukowski-Wills J, Finch AJ, Jarman EJ, Xintaropoulou C,
Martinez-Perez C, Gray M, Pearson M, et al: Inhibition of pH
regulation as a therapeutic strategy in hypoxic human breast cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 8:42857–42875. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kessler J, Hahnel A, Wichmann H, Rot S,
Kappler M, Bache M and Vordermark D: HIF-1α inhibition by siRNA or
chetomin in human malignant glioma cells: Effects on hypoxic
radioresistance and monitoring via CA9 expression. BMC Cancer.
10:6052010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Güttler A, Giebler M, Cuno P, Wichmann H,
Keßler J, Ostheimer C, Söling A, Strauss C, Illert J, Kappler M, et
al: Osteopontin and splice variant expression level in human
malignant glioma: Radiobiologic effects and prognosis after
radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 108:535–540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Riemann A, Ihling A, Thomas J, Schneider
B, Thews O and Gekle M: Acidic environment activates inflammatory
programs in fibroblasts via a cAMP-MAPK pathway. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1853:299–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hahnel A, Wichmann H, Kappler M, Kotzsch
M, Vordermark D, Taubert H and Bache M: Effects of osteopontin
inhibition on radiosensitivity of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells.
Radiat Oncol. 5:822010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McDonald PC, Winum JY, Supuran CT and
Dedhar S: Recent developments in targeting carbonic anhydrase IX
for cancer therapeutics. Oncotarget. 3:84–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pastorek J and Pastorekova S:
Hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrase IX as a target for cancer
therapy: From biology to clinical use. Semin Cancer Biol. 31:52–64.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Riemann A, Güttler A, Haupt V, Wichmann H,
Reime S, Bache M, Vordermark D and Thews O: Inhibition of carbonic
anhydrase IX by ureidosulfonamide inhibitor U104 reduces prostate
cancer cell growth, but does not modulate daunorubicin or cisplatin
cytotoxicity. Oncol Res. 26:191–200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tang X, Lucas JE, Chen JL, LaMonte G, Wu
J, Wang MC, Koumenis C and Chi JT: Functional interaction between
responses to lactic acidosis and hypoxia regulates genomic
transcriptional outputs. Cancer Res. 72:491–502. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vordermark D, Kaffer A, Riedl S, Katzer A
and Flentje M: Characterization of carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) as
an endogenous marker of chronic hypoxia in live human tumor cells.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 61:1197–1207. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matsubara T, Diresta GR, Kakunaga S, Li D
and Healey JH: Additive influence of extracellular pH, oxygen
tension, and pressure on invasiveness and survival of human
osteosarcoma cells. Front Oncol. 3:1992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ihnatko R, Kubes M, Takacova M, Sedlakova
O, Sedlak J, Pastorek J, Kopacek J and Pastorekova S: Extracellular
acidosis elevates carbonic anhydrase IX in human glioblastoma cells
via transcriptional modulation that does not depend on hypoxia. Int
J Oncol. 29:1025–1033. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Said HM, Hagemann C, Carta F, Katzer A,
Polat B, Staab A, Scozzafava A, Anacker J, Vince GH, Flentje M and
Supuran CT: Hypoxia induced CA9 inhibitory targeting by two
different sulfonamide derivatives including acetazolamide in human
glioblastoma. Bioorg Med Chem. 21:3949–3957. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Duivenvoorden WCM, Hopmans SN, Gallino D,
Farrell T, Gerdes C, Glennie D, Lukka H and Pinthus JH: Inhibition
of carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9) sensitizes renal cell carcinoma to
ionizing radiation. Oncol Rep. 34:1968–1976. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Robertson N, Potter C and Harris AL: Role
of carbonic anhydrase IX in human tumor cell growth, survival, and
invasion. Cancer Res. 64:6160–6165. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ward C, Meehan J, Mullen P, Supuran C,
Dixon JM, Thomas JS, Winum J-Y, Lambin P, Dubois L, Pavathaneni NK,
et al: Evaluation of carbonic anhydrase IX as a therapeutic target
for inhibition of breast cancer invasion and metastasis using a
series of in vitro breast cancer models. Oncotarget. 6:24856–24870.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sedlakova O, Svastova E, Takacova M,
Kopacek J, Pastorek J and Pastorekova S: Carbonic anhydrase IX, a
hypoxia-induced catalytic component of the pH regulating machinery
in tumors. Front Physiol. 4:4002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shin HJ, Rho SB, Jung DC, Han IO, Oh ES
and Kim JY: Carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9) modulates tumor-associated
cell migration and invasion. J Cell Sci. 124:1077–1087. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vanchanagiri K, Emmerich D, Bruschke M,
Bache M, Seifert F, Csuk R, Vordermark D and Paschke R: Synthesis
and biological investigation of new carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX)
inhibitors. Chem Biol Interact. 284:12–23. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cianchi F, Vinci MC, Supuran CT, Peruzzi
B, De Giuli P, Fasolis G, Perigli G, Pastorekova S, Papucci L, Pini
A, et al: Selective inhibition of carbonic anhydrase IX decreases
cell proliferation and induces ceramide-mediated apoptosis in human
cancer cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 334:710–719. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Doyen J, Parks SK, Marcié S, Pouysségur J
and Chiche J: Knock-down of hypoxia-induced carbonic anhydrases IX
and XII radiosensitizes tumor cells by increasing intracellular
acidosis. Front Oncol. 2:1992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|