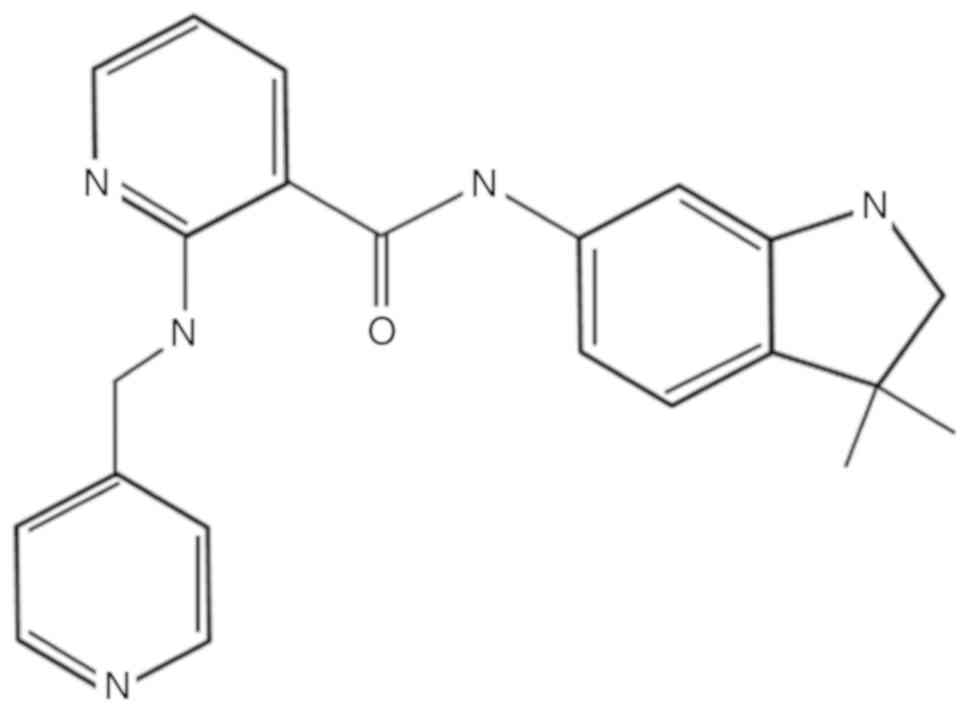
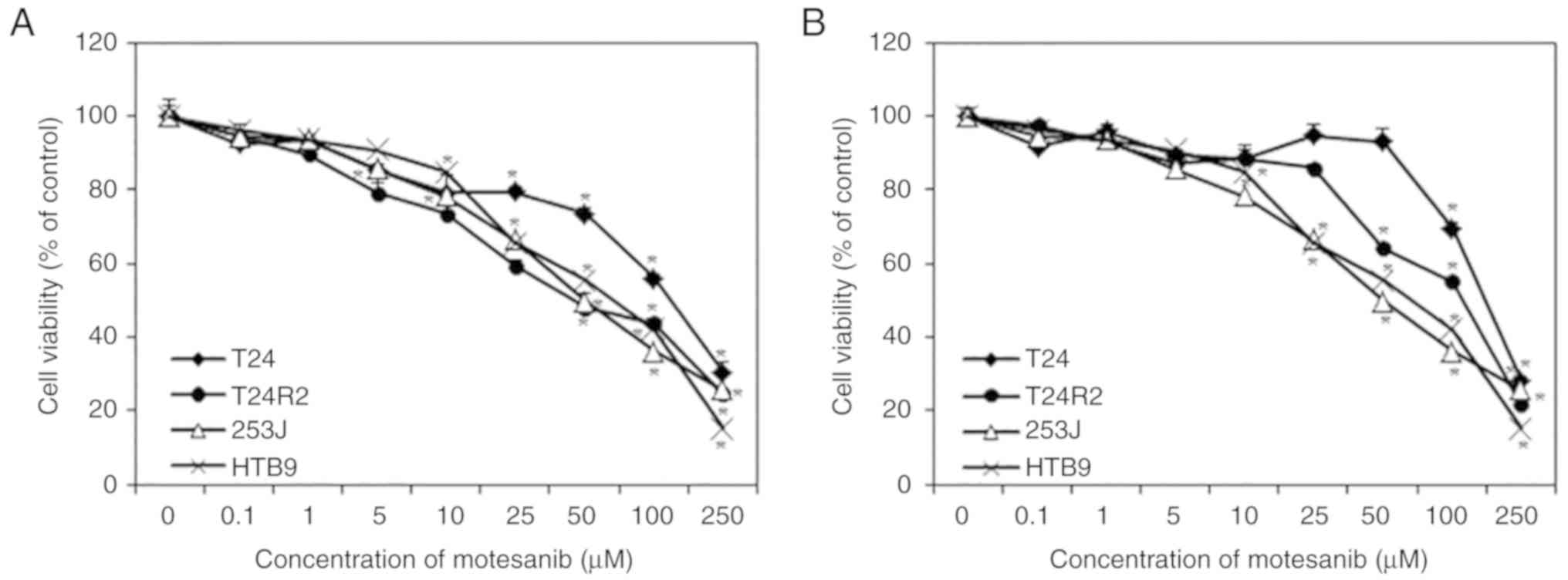
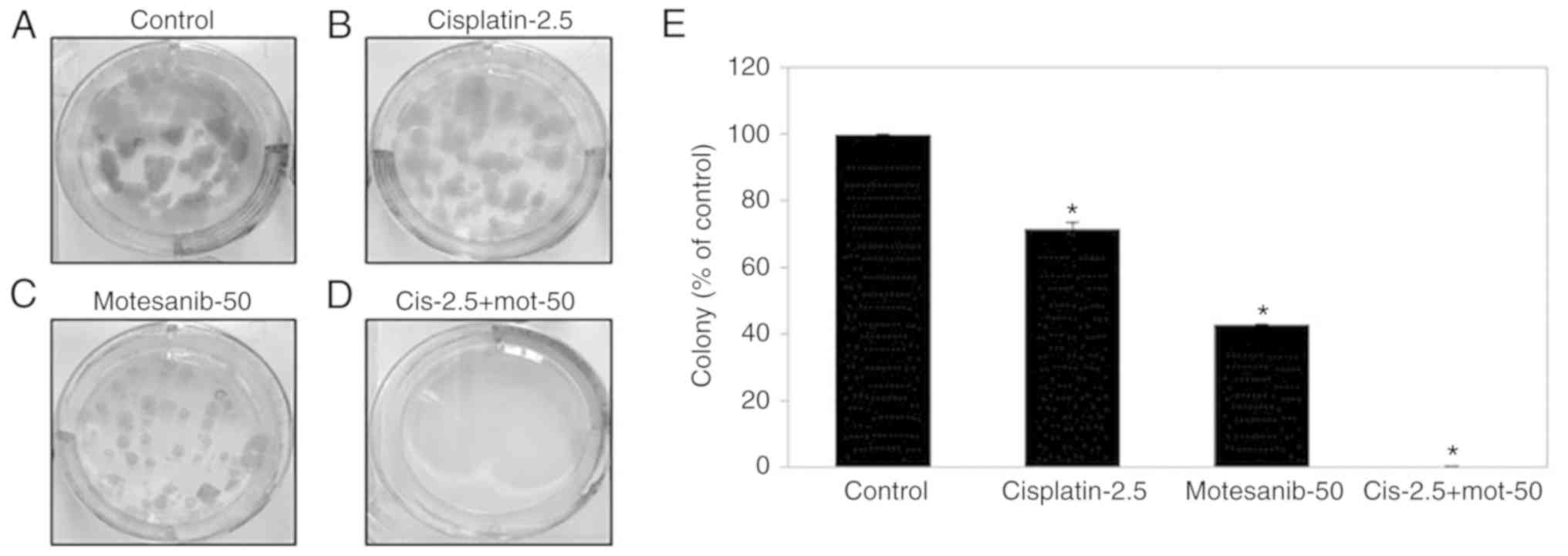
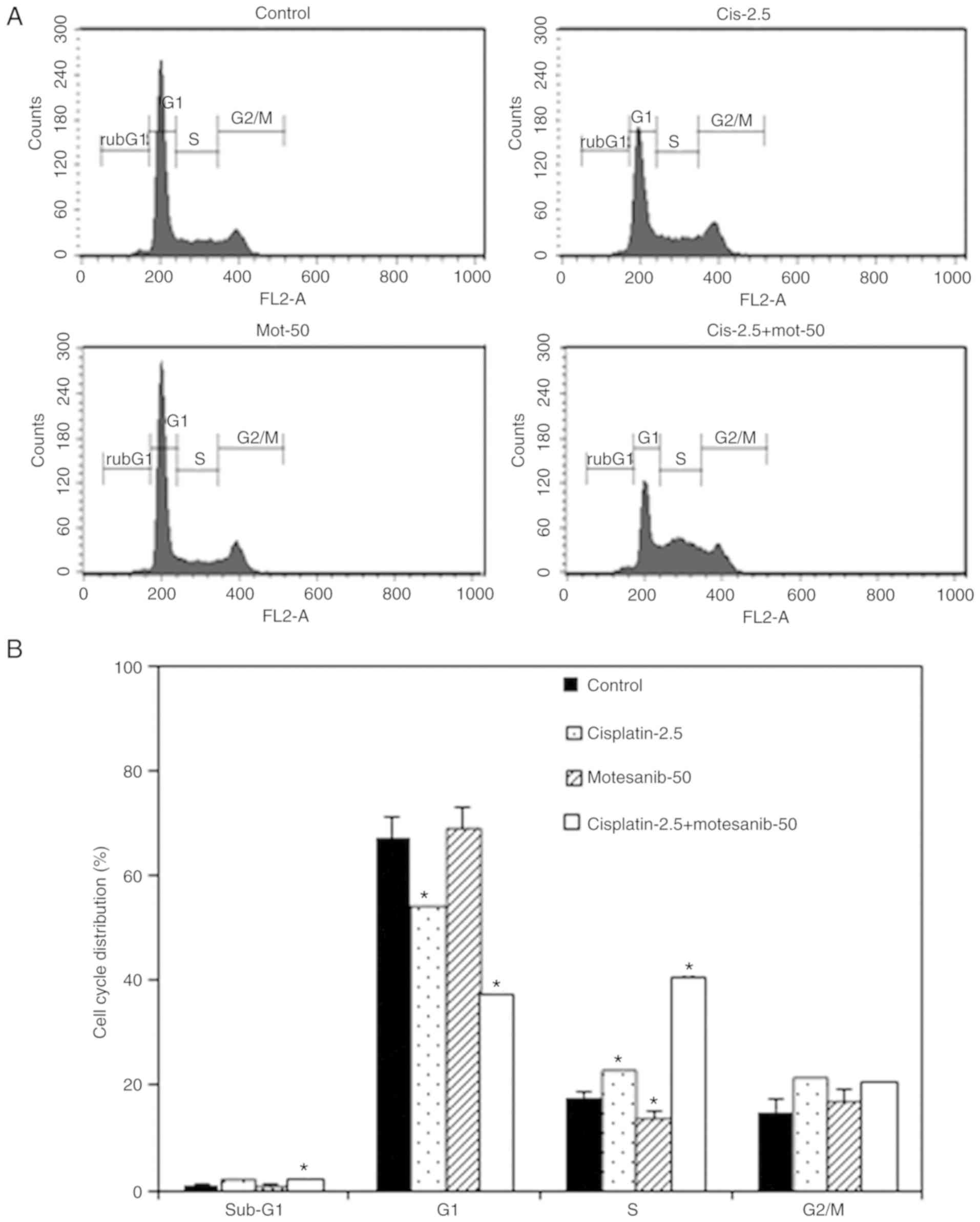
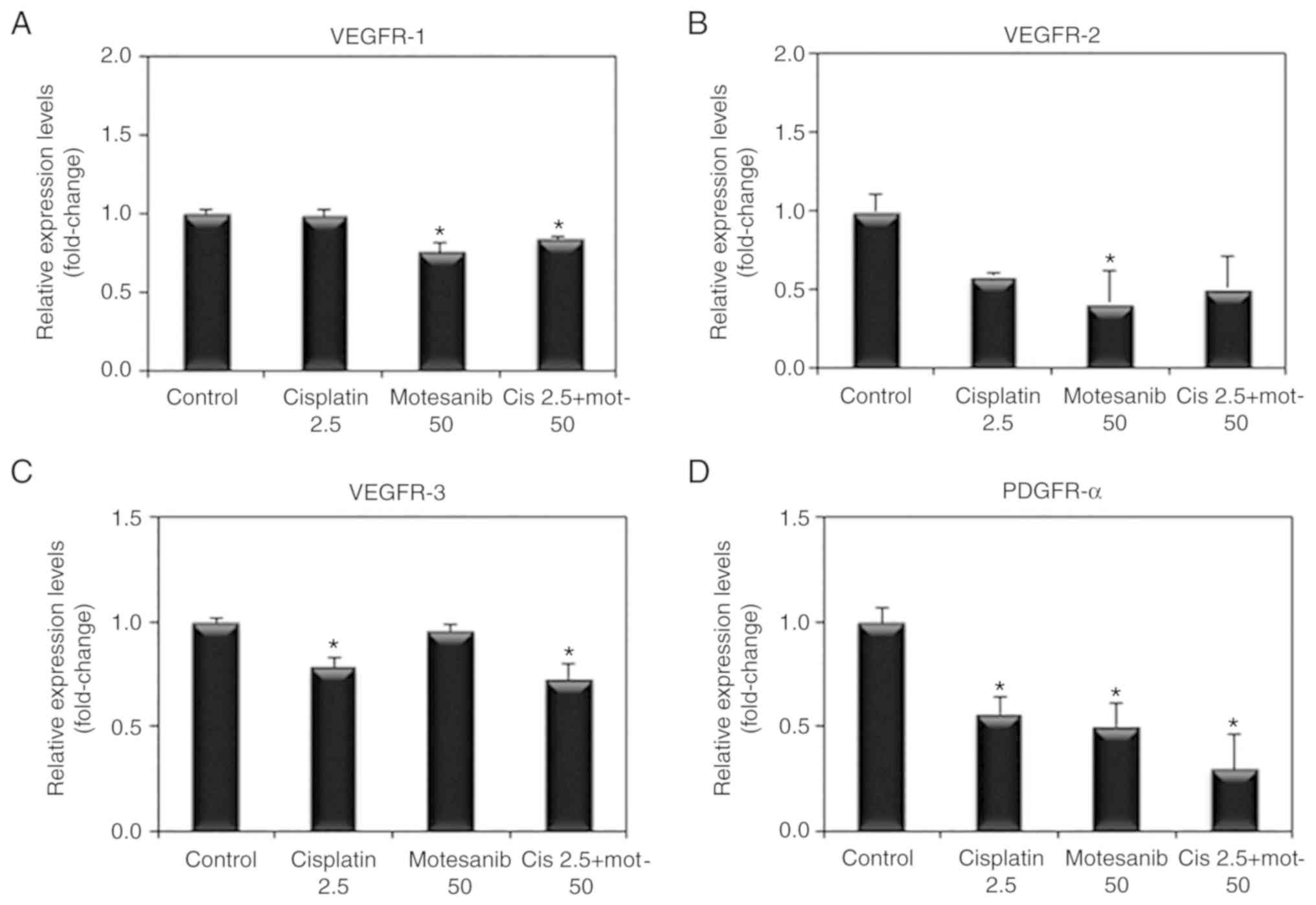
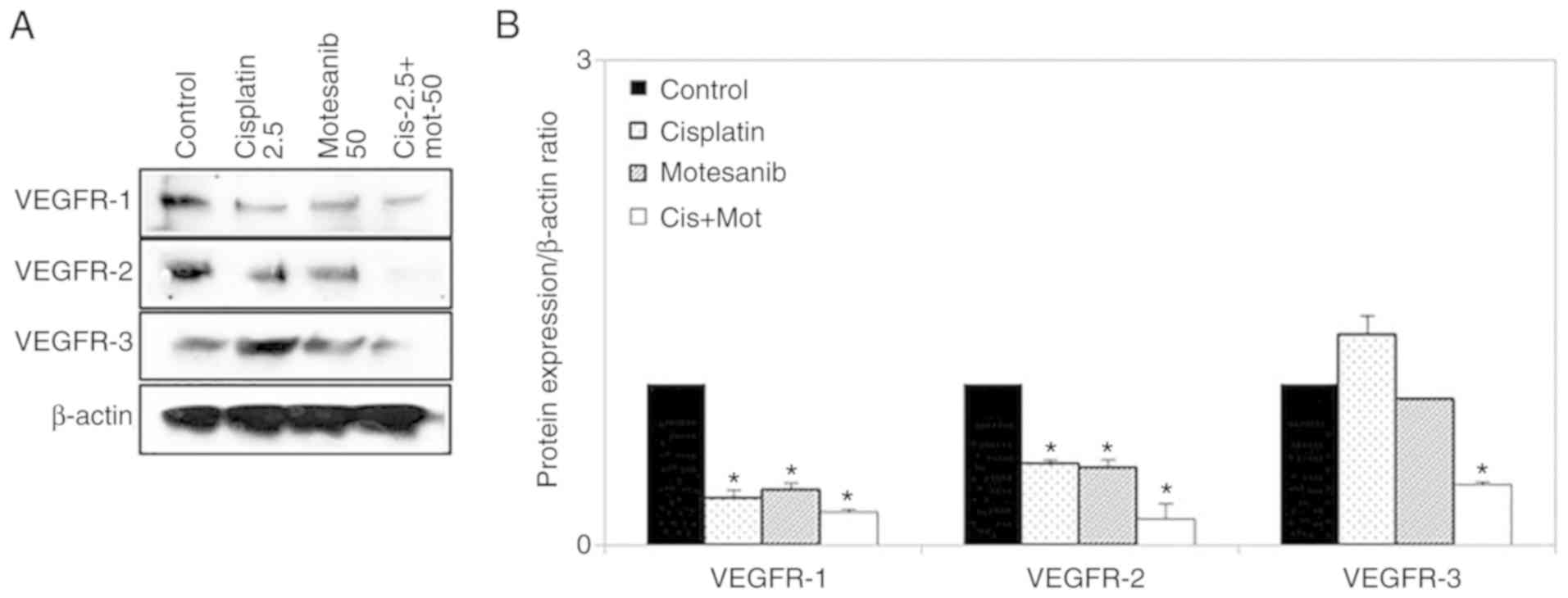
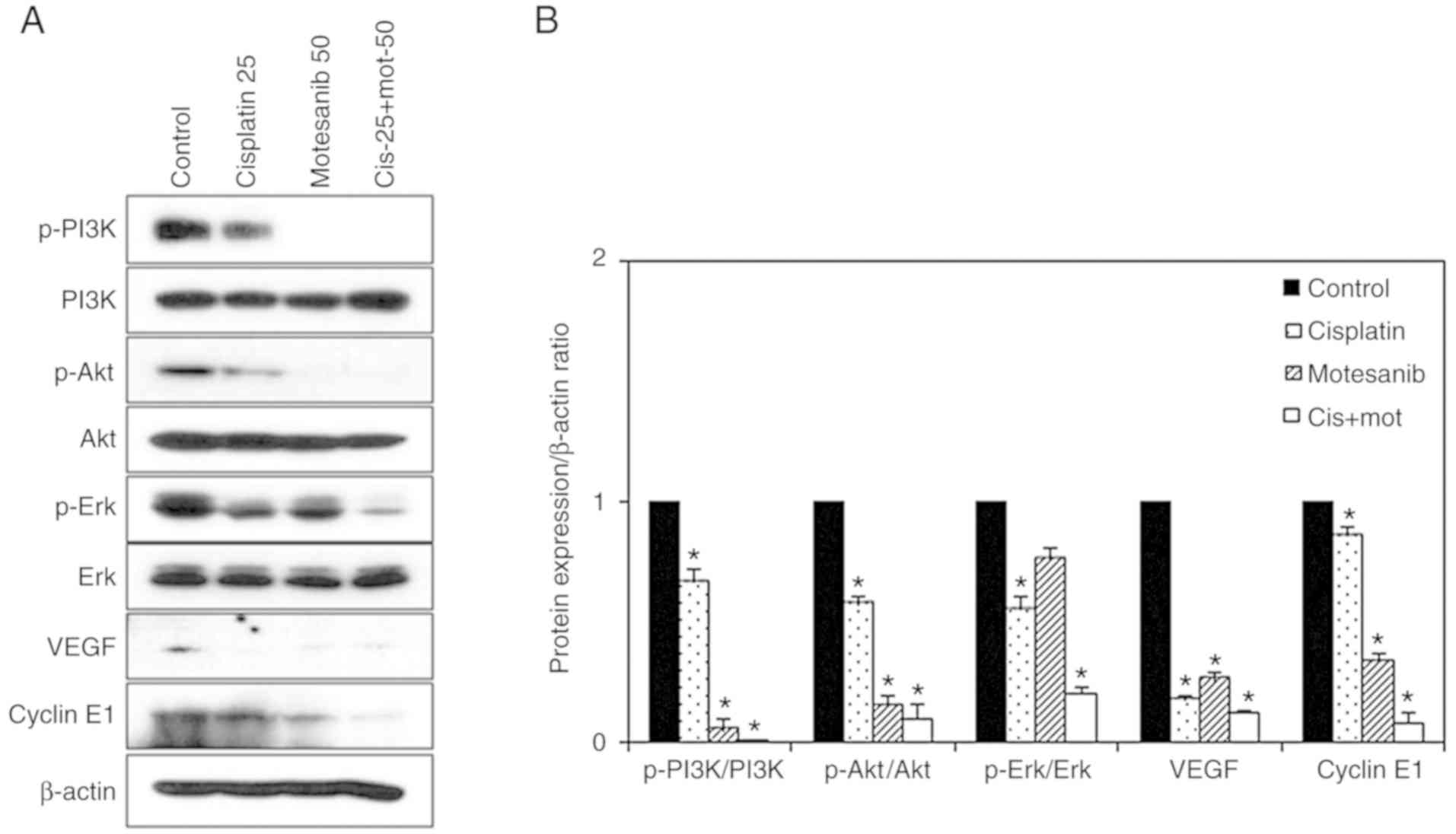
|
1
|
Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor
A, Jemal A and Bray F: Bladder cancer incidence and motality: A
Global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol. 71:96–108. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kamat AM, Hahn NM, Efstathiou JA, Lerner
SP, Malmström PU, Choi W, Guo CC, Lotan Y and Kassouf W: Bladder
cancer. Lancet. 388:2796–2810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Godwin JL, Hoffman-Censits J and Plimack
E: Recent developments in the treatment of advanced bladder cancer.
Urol Oncol. 36:109–114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
McHugh LA, Kriajevska M, Mellon JK and
Griffiths TR: Combined treatment of bladder cancer cell lines with
lapatinib and varying chemotherapy regimens-evidence of
schedule-dependent synergy. Urology. 69:390–394. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dasari S and Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in
cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol.
740:364–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao Y and Adjei AA: Targeting
angiogenesis in cancer therapy: Moving beyond vascular endothelial
growth factor. Oncologist. 20:660–673. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fus ŁP and Górnicka B: Role of
angiogenesis in urothelial bladder carcinoma. Cent Eurpean J Urol.
69:258–263. 2016.
|
|
8
|
Bellmunt J, Hussain M and Dinney CP: Novel
approaches with targeted therapies in bladder cancer therapy of
bladder cancer by blockade of the epidermal growth factor receptor
family. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 46 (Suppl 46):S85–S104. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Coxon A, Bush T, Saffran D, Kaufman S,
Belmontes B, Rex K, Hughes P, Caenepeel S, Rottman JB, Tasker A, et
al: Broad antitumor activity in breast cancer xenografts by
motesanib, a highly selective, oral inhibitor of vascular
endothelial growth factor, platelet-derived growth factor, and Kit
receptors. Clin Cancer Res. 15:110–118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Yang X, Su LJ and Flaig TW:
Pazopanib synergizes with docetaxel in the treatment of bladder
cancer cells. Urology. 78:233.e7–233.e13. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Black PC, Agarwal PK and Dinney CP:
Targeted therapies in bladder cancer-an update. Urol Oncol.
25:433–438. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jordan EJ and Iyer G: Targeted therapy in
advanced bladder cancer: What have we learned? Urol Clin North Am.
42:253–262. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Polverino A, Coxon A, Starnes C, Diaz Z,
DeMelfi T, Wang L, Bready J, Estrada J, Cattley R, Kaufman S, et
al: AMG 706, an oral, multikinase inhibitor that selectively
targets vascular endothelial growth factor, platelet-derived growth
factor, and kit receptors, potently inhibits angiogenesis and
induces regression in tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 66:8715–8721.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rosen LS, Kurzrock R, Mulay M, Van Vugt A,
Purdom M, Ng C, Silverman J, Koutsoukos A, Sun YN, Bass MB, et al:
Safety, pharmacokinetics, and efficacy of AMG 706, an oral
multikinase inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. J
Clin Oncol. 25:2369–2376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Coxon A, Bready J, Kaufman S, Estrada J,
Osgood T, Canon J, Wang L, Radinsky R, Kendall R, Hughes P, et al:
Anti-tumor activity of motesanib in a medullary thyroid cancer
model. J Endocrinol Invest. 35:181–190. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Coxon A, Ziegler B, Kaufman S, Xu M, Wang
H, Weishuhn D, Schmidt J, Sweet H, Starnes C, Saffran D and
Polverino A: Antitumor activity of motesanib alone and in
combination with cisplatin or docetaxel in multiple human
non-small-cell lung cancer xenograft models. Mol Cancer. 11:702012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tebbutt N, Kotasek D, Burris HA,
Schwartzberg LS, Hurwitz H, Stephenson J, Warner DJ, Chen L, Hsu CP
and Goldstein D: Motesanib with or without panitumumab plus FOLFIRI
or FOLFOX for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 75:993–1004. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu JF, Claret L, Sutjandra L, Kuchimanchi
M, Melara R, Bruno R and Sun YN: Population
pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling for the time course of
tumor shrinkage by motesanib in thyroid cancer patients. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 66:1151–1158. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schilder RJ, Sill MW, Lankes HA, Gold MA,
Mannel RS, Modesitt SC, Hanjani P, Bonebrake AJ, Sood AK, Godwin
AK, et al: A phase II evaluation of motesanib (AMG 706) in the
treatment of persistent or recurrent ovarian, fallopian tube and
primary peritoneal carcinomas: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study.
Gynecol Oncol. 129:86–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Byun SS, Kim SW, Choi H, Lee C and Lee E:
Augmentation of cisplatin sensitivity in cisplatin-resistant human
bladder cancer cells by modulating glutathione concentrations and
glutathione-related enzyme activities. BJU Int. 95:1086–1090. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yeo EJ, Ryu JH, Chun YS, Cho YS, Jang IJ,
Cho H, Kim J, Kim MS and Park JW: YC-1 induces S cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis by activating checkpoint kinases. Cancer Res.
66:6345–6352. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Carmeliet P: VEGF as a key mediator of
angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology. 69 (Suppl 3):S4–S10. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Appelmann I, Liersch R, Kessler T, Mesters
RM and Berdel WE: Angiogenesis inhibition in cancer therapy:
Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF) and their receptors: Biological functions and
role in malignancy. Recent Results Cancer Res. 180:51–81. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kaya TT, Altun A, Turgut NH, Ataseven H
and Koyluoglu G: Effects of a multikinase inhibitor motesanib (AMG
706) alone and combined with the selective DuP-697 COX-2 inhibitor
on colorectal cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17:1103–1110.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Elfiky AA and Rosenberg JE: Targeting
angiogenesis in bladder cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 11:244–249. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang F, Li HM, Wang HP, Ma JL, Chen XF,
Wei F, Yi MY and Huang Q: siRNA-mediated knockdown of VEGF-A,
VEGF-C and VEGFR-3 suppresses the growth and metastasis of mouse
bladder carcinoma in vivo. Exp Ther Med. 1:899–904. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu CL, Ping SY, Yu CP and Yu DS: Tyrosine
kinase receptor inhibitor-targeted combined chemotherapy for
metastatic bladder cancer. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 28:194–203. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Van Kessel KE, Zuiverloon TC, Alberts AR,
Boormans JL and Zwarthoff EC: Targeted therapies in bladder cancer:
An overview of in vivo research. Nat Rev Urol. 12:681–694. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Madka V, Zhang Y, Li Q, Mohammed A,
Sindhwani P, Lightfoot S, Wu XR, Kopelovich L and Rao CV:
P53-stabilizing agent CP-31398 prevents growth and invasion of
urothelial cancer of the bladder in transgenic UPII-SV40T mice.
Neoplasia. 15:966–974. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim SH, Ho JN, Jin H, Lee SC, Lee SE, Hong
SK, Lee JW, Lee ES and Byun SS: Upregulated expression of BCL2,
MCM7, and CCNE1 indicate cisplatin-resistance in the set of two
human bladder cancer cell lines: T24 cisplatin sensitive and T24R2
cisplatin resistant bladder cancer cell lines. Investig Clin Urol.
57:63–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bartholomeusz C and Gonzalez-Angulo AM:
Targeting the PI3K signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 16:121–130. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sathe A and Nawroth R: Targeting the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in bladder cancer. methods Mol Biol.
1655:335–350. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dienstmann R, Rodon J, Serra V and
Tabernero J: Picking the point of inhibition: A comparative review
of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:1021–1031.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fayard ETL, Baudry A and Hemmings BA:
Protein kinase B/Akt at a glance. J Cell Sci. 118:5675–5678. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|