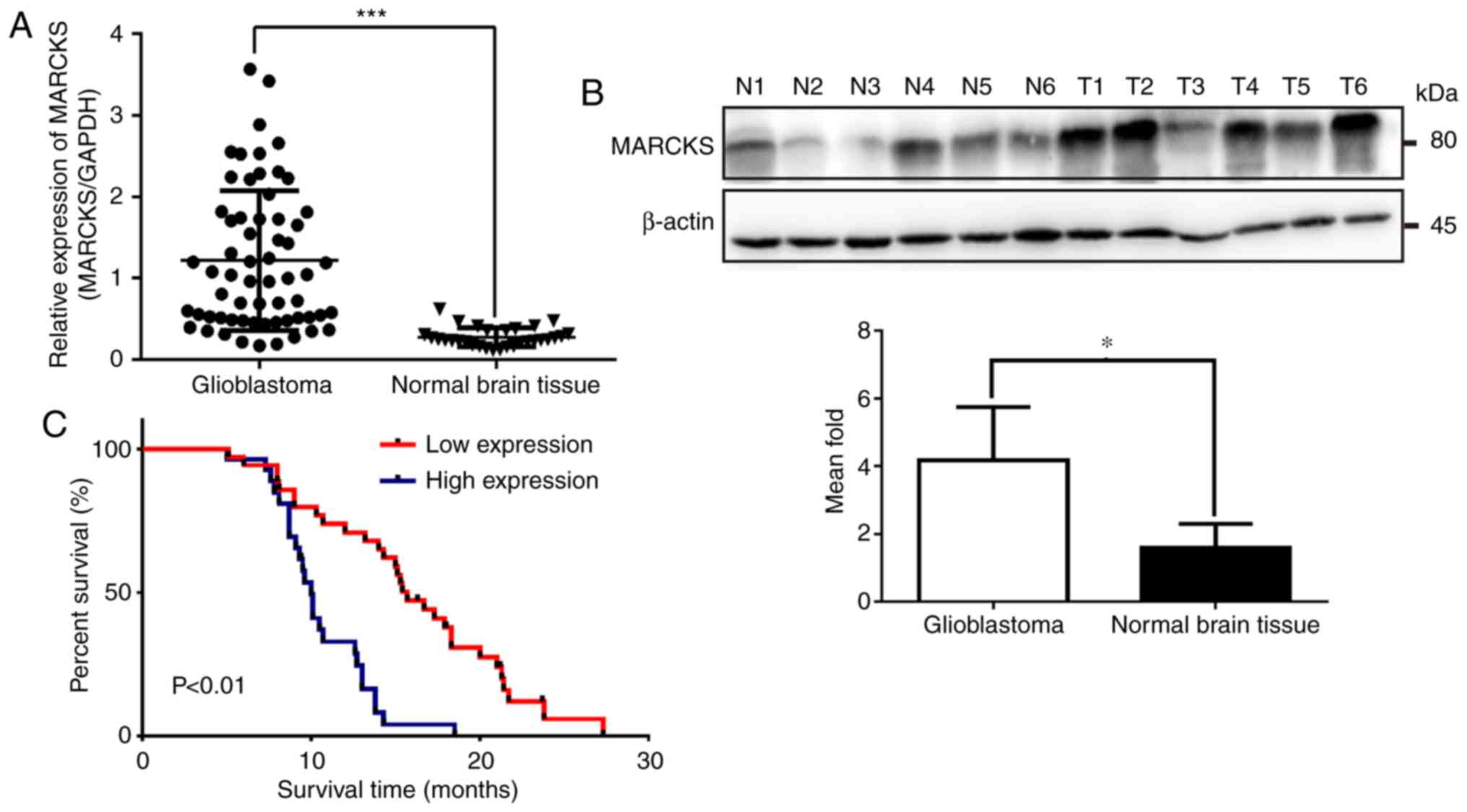
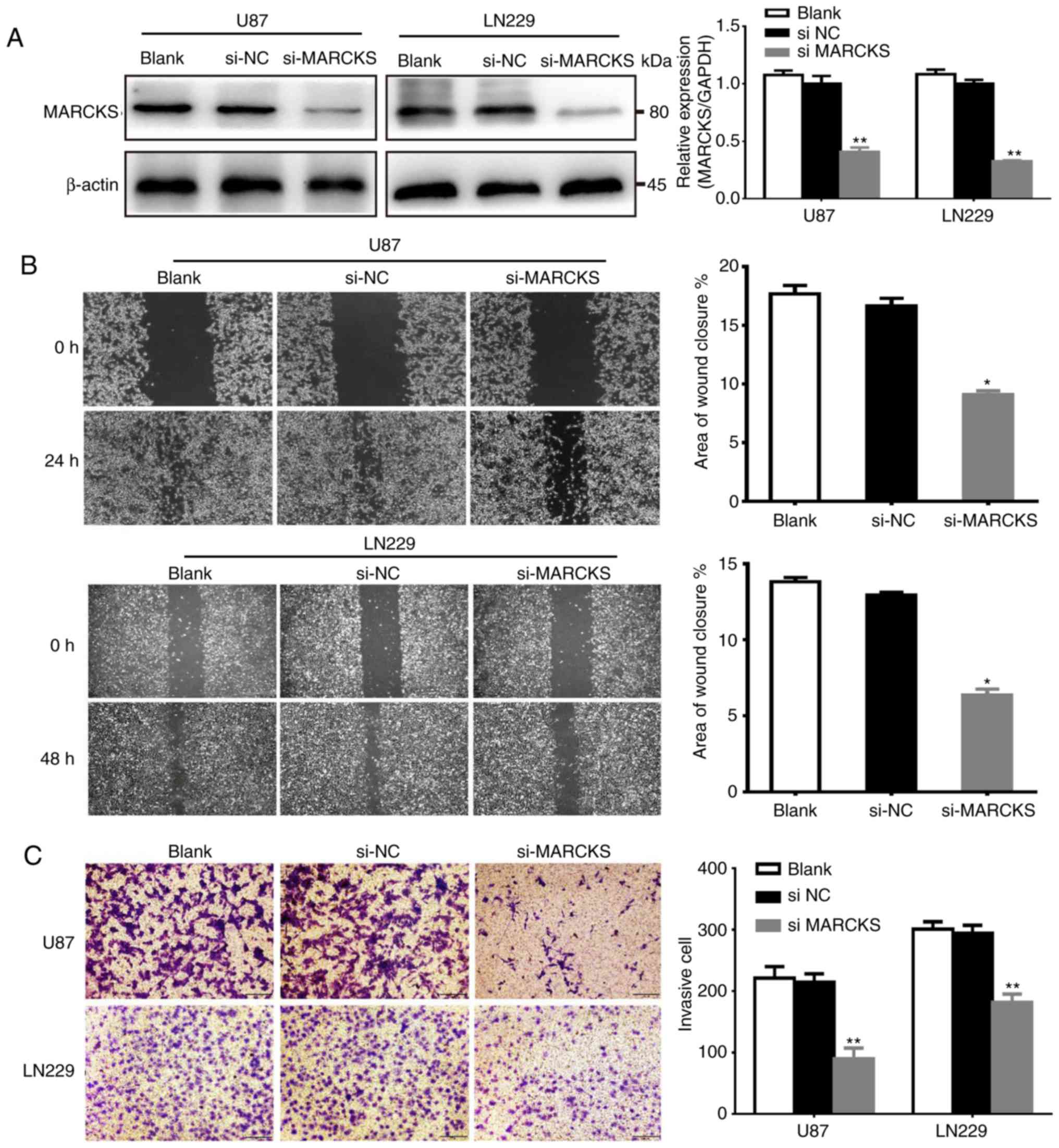
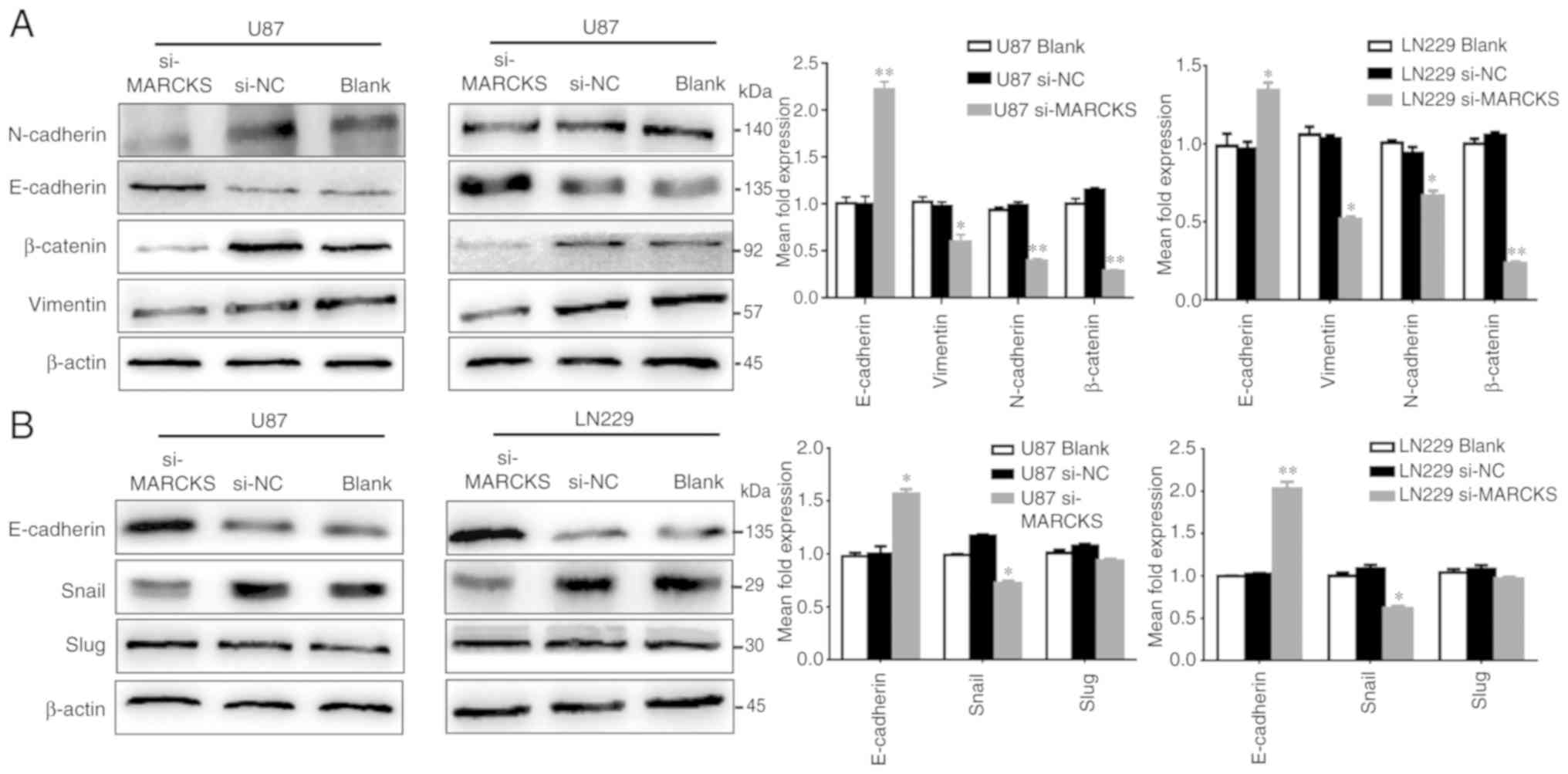
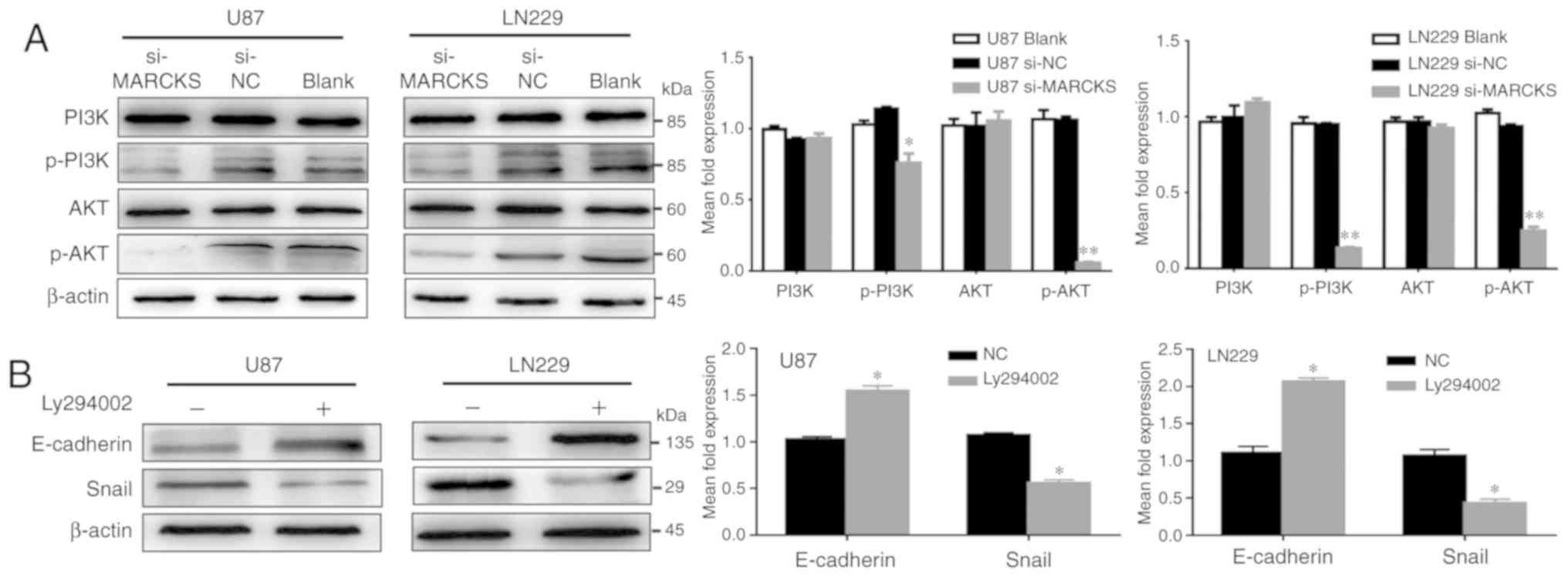
|
1
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 World Health Organization
classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary.
Acta Neuropathol. 131:803–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Demuth T and Berens ME: Molecular
mechanisms of glioma cell migration and invasion. J Neurooncol.
70:217–28. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Albert KA, Nairn AC and Greengard P: The
87-kDa protein, a major specific substrate for protein kinase C:
Purification from bovine brain and characterization. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 84:7046–7050. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Arbuzova A, Schmitz AA and Vergères G:
Cross-talk unfolded: MARCKS proteins. Biochem J. 362:1–12. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Caroni P: New EMBO members' review: Actin
cytoskeleton regulation through modulation of PI(4,5)P(2) rafts.
EMBO J. 20:4332–4336. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hanada S, Kakehashi A, Nishiyama N, Wei M,
Yamano S, Chung K, Komatsu H, Inoue H, Suehiro S and Wanibuchi H:
Myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate as a prognostic
biomarker in human primary lung squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer
Biomark. 13:289–298. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rombouts K, Carloni V, Mello T, Omenetti
S, Galastri S, Madiai S, Galli A and Pinzani M: Myristoylated
Alanine-Rich protein Kinase C Substrate (MARCKS) expression
modulates the metastatic phenotype in human and murine colon
carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett. 333:244–252. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Techasen A, Loilome W, Namwat N, Takahashi
E, Sugihara E, Puapairoj A, Miwa M, Saya H and Yongvanit P:
Myristoylated alanine-rich C kinase substrate phosphorylation
promotes cholangiocarcinoma cell migration and metastasis via the
protein kinase C-dependent pathway. Cancer Sci. 101:658–665. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang Y, Chen Y, Saha MN, Chen J, Evans K,
Qiu L, Reece D, Chen GA and Chang H: Targeting phospho-MARCKS
overcomes drug-resistance and induces antitumor activity in
preclinical models of multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 29:715–726. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang Z, Xu S, Jin P, Yang X, Li X, Wan D,
Zhang T, Long S, Wei X, Chen G, et al: MARCKS contributes to
stromal cancer-associated fibroblast activation and facilitates
ovarian cancer metastasis. Oncotarget. 7:37649–37663.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jarboe JS, Anderson JC, Duarte CW, Mehta
T, Nowsheen S, Hicks PH, Whitley AC, Rohrbach TD, McCubrey RO, Chiu
S, et al: MARCKS regulates growth and radiation sensitivity and is
a novel prognostic factor for glioma. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3030–3041. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Micallef J, Taccone M, Mukherjee J, Croul
S, Busby J, Moran MF and Guha A: Epidermal growth factor receptor
variant III-induced glioma invasion is mediated through
myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate
overexpression. Cancer Res. 69:7548–7556. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiang W, Qi ST, Liu YW, Li HZ, Zhou Q, Yi
GZ, Chen ZY and Yan L: RNA interference of PC4 and SFRS1
interacting protein 1 inhibits invasion and migration of U87 glioma
cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 36:802–806. 2016.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yi GZ, Liu YW, Xiang W, Wang H, Chen ZY,
Xie SD and Qi ST: Akt and β-catenin contribute to TMZ resistance
and EMT of MGMT negative malignant glioma cell line. J Neurol Sci.
367:101–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bolós V, Peinado H, Pérez-Moreno MA, Fraga
MF, Esteller M and Cano A: The transcription factor Slug represses
E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transitions: A comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. J Cell
Sci. 116:499–511. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moreno-Bueno G, Portillo F and Cano A:
Transcriptional regulation of cell polarity in EMT and cancer.
Oncogene. 27:6958–6969. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peinado H, Ballestar E, Esteller M and
Cano A: Snail mediates E-cadherin repression by the recruitment of
the Sin3A/histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)/HDAC2 complex. Mol Cell
Biol. 24:306–319. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang KJ, Wang DS, Zhang SY, Jiao XL, Li
CW, Wang XS, Yu QC and Cui HN: The E-cadherin repressor slug and
progression of human extrahepatic hilar cholangiocarcinoma. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 29:882010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lau MT and Leung PC: The PI3K/Akt/mTOR
signaling pathway mediates insulin-like growth factor 1-induced
E-cadherin down-regulation and cell proliferation in ovarian cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 326:191–198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jeon YK, Kim CK, Hwang KR, Park HY, Koh J,
Chung DH, Lee CW and Ha GH: Pellino-1 promotes lung carcinogenesis
via the stabilization of Slug and Snail through K63-mediated
polyubiquitination. Cell Death Differ. 24:469–480. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Manai M, Thomassin-Piana J, Gamoudi A,
Finetti P, Lopez M, Eghozzi R, Ayadi S, Lamine OB, Manai M, Rahal
K, et al: MARCKS protein overexpression in inflammatory breast
cancer. Oncotarget. 8:6246–6257. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu H, Su P, Zhi L and Zhao K: miR-34c-3p
acts as a tumor suppressor gene in osteosarcoma by targeting
MARCKS. Mol Med Red. 15:1204–1210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Song J, Wang Q, Luo Y, Yuan P, Tang C, Hui
Y and Wang Z: miR-34c-3p inhibits cell proliferation, migration and
invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting MARCKS. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:12728–12737. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li T, Li D, Sha J, Sun P and Huang Y:
MicroRNA-21 directly targets MARCKS and promotes apoptosis
resistance and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 383:280–285. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Grunert S, Jechlinger M and Beug H:
Diverse cellular and molecular mechanisms contribute to epithelial
plasticity and metastasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 4:657–665. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Christofori G: New signals from the
invasive front. Nature. 441:444–450. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Batlle E, Sancho E, Francí C, Domínguez D,
Monfar M, Baulida J and García De Herreros A: The transcription
factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in
epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2:84–89. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takkunen M, Grenman R, Hukkanen M,
Korhonen M, Garcia de Herreros A and Virtanen I: Snail-dependent
and -independent epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous
carcinoma cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 54:1263–1275. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses
HL and Arteaga CL: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is
required for transforming growth factor beta-mediated epithelial to
mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem.
275:36803–36810. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma NX, Sun W, Wu J, Liu SL, Weng L, Liu
YQ, Pu WX, Wu TT, Ding XL, Huang NG, et al: Compound wumei powder
inhibits the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer via
Cox-2/PGE2-PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2017:30394502017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu WB, Xiao N and Liu XJ: Dietary
flavonoid tangeretin induces reprogramming of epithelial to
mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells by targeting the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 15:433–440.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Z, Zhang TB, Jia DH, Sun WQ, Wang CL,
Gu AZ and Yang XM: Genipin inhibits the growth of human bladder
cancer cells via inactivation of PI3K/Akt signaling. Oncol Lett.
15:2619–2624. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|