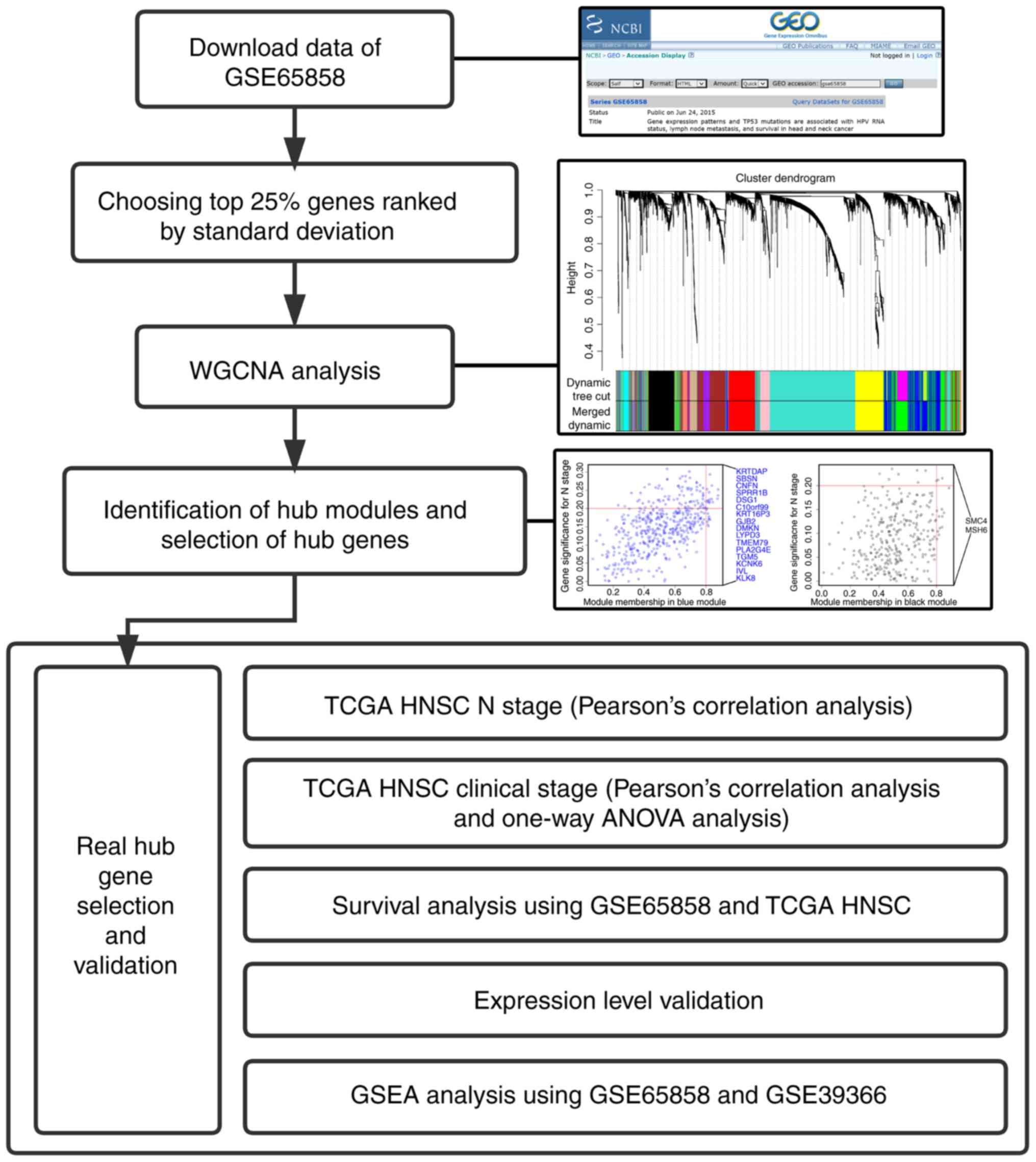
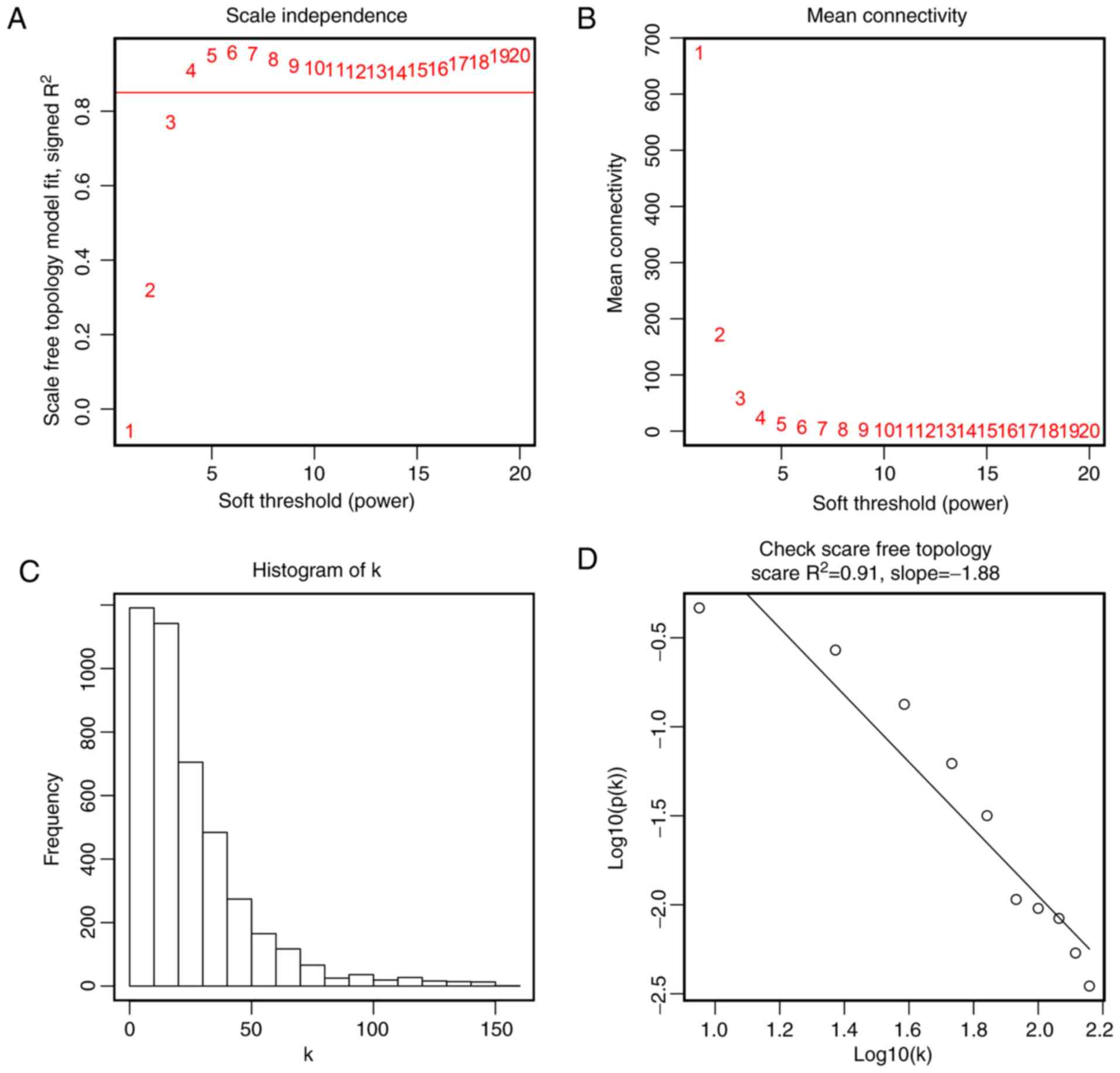
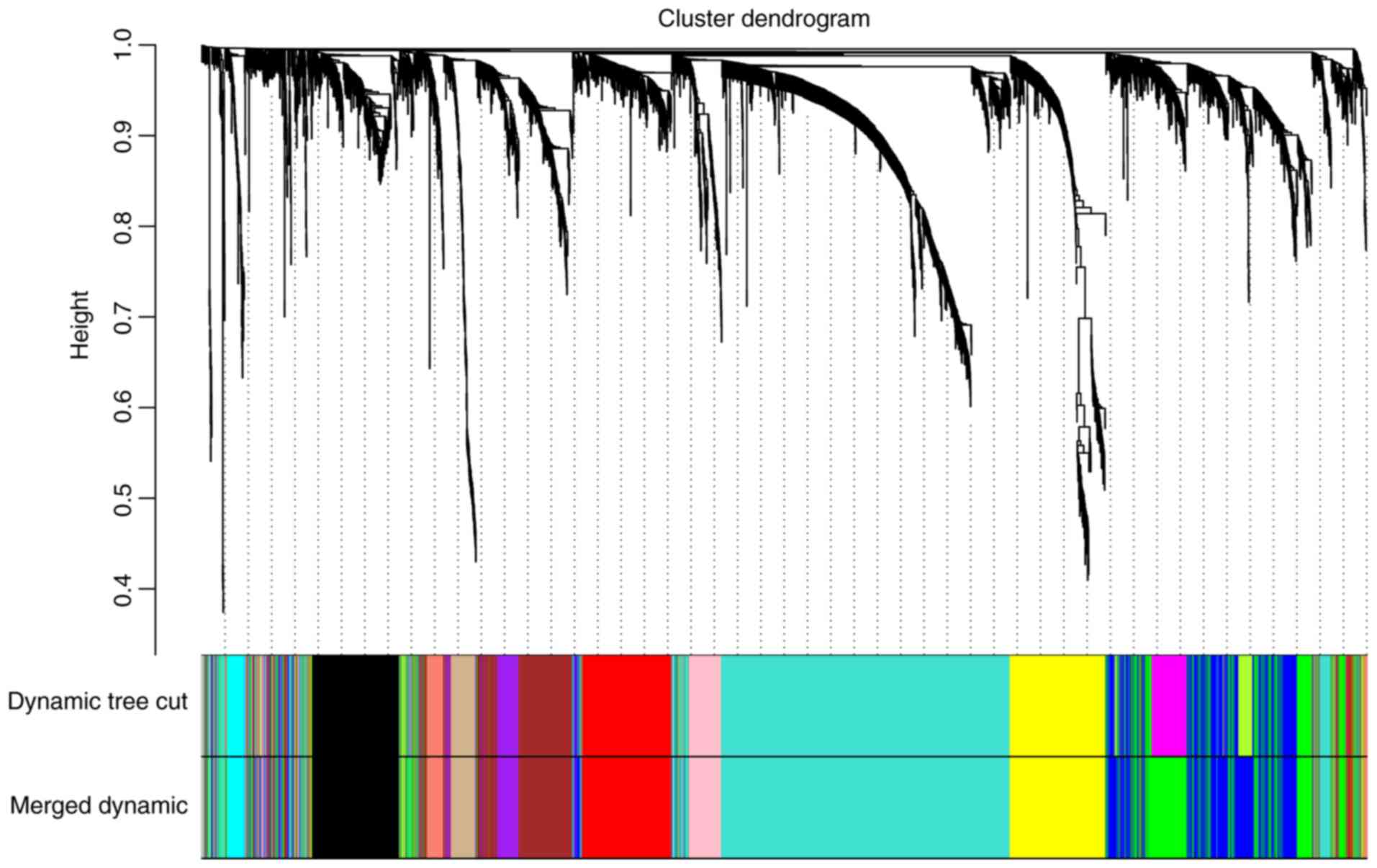
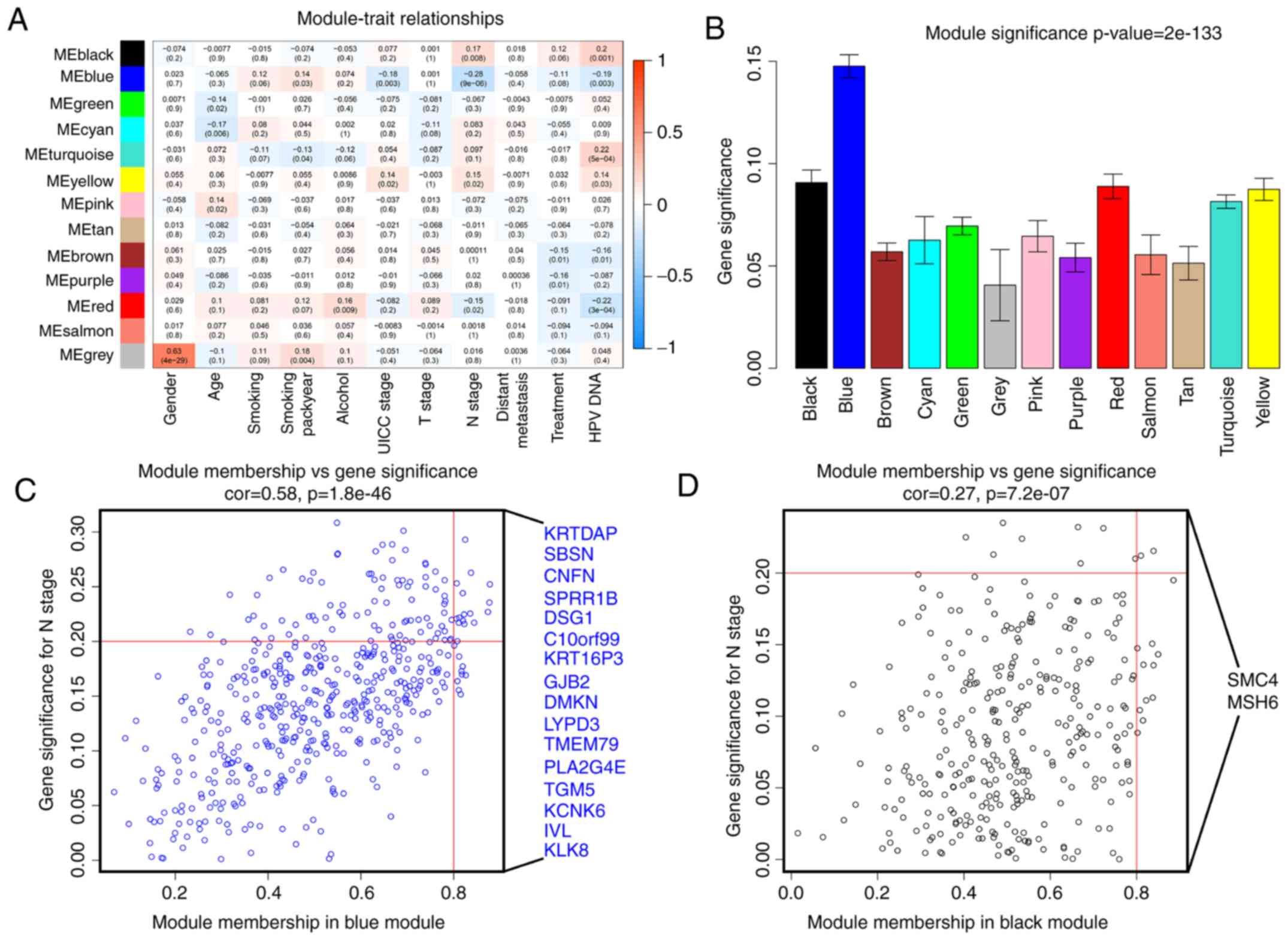
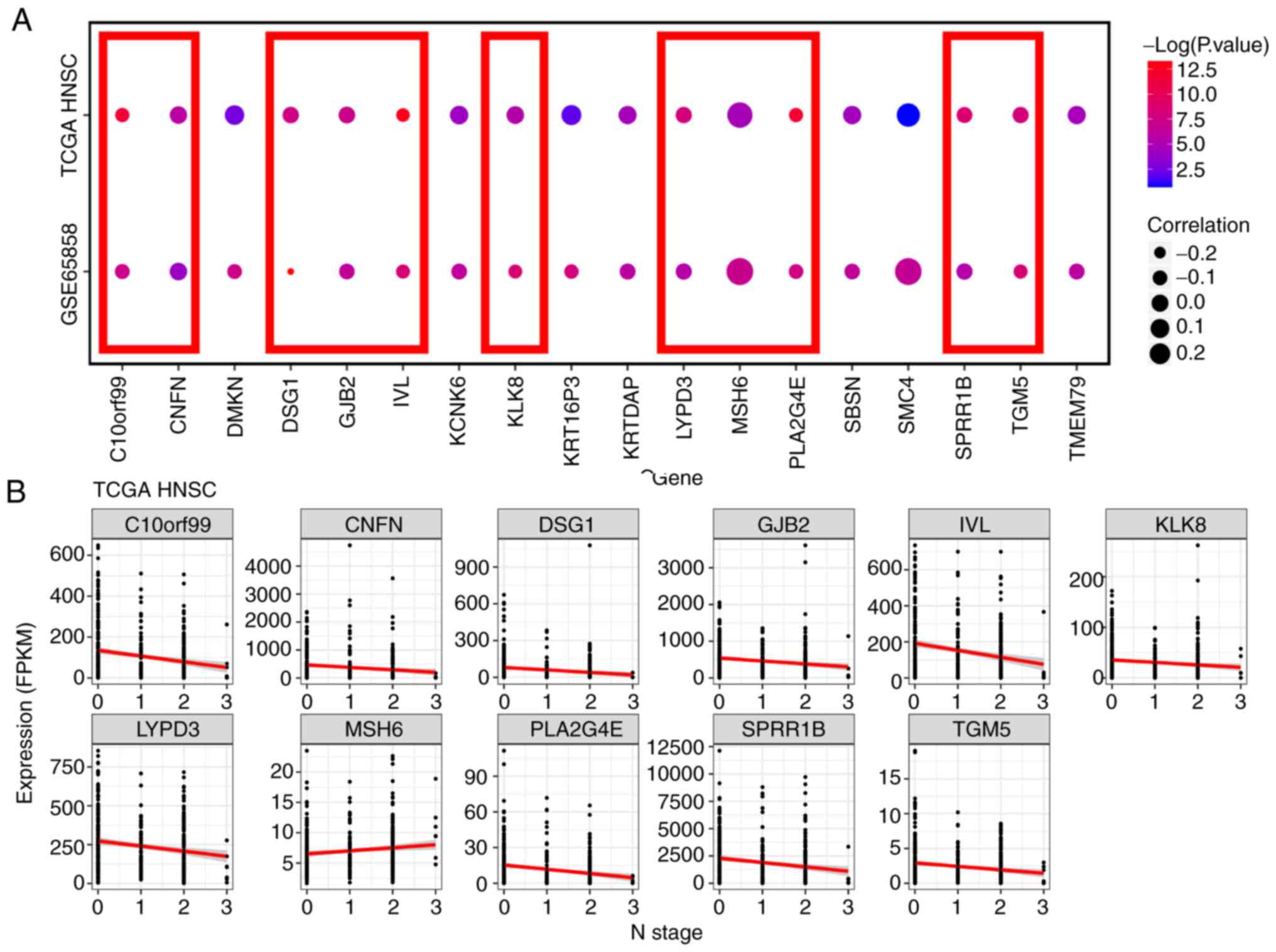
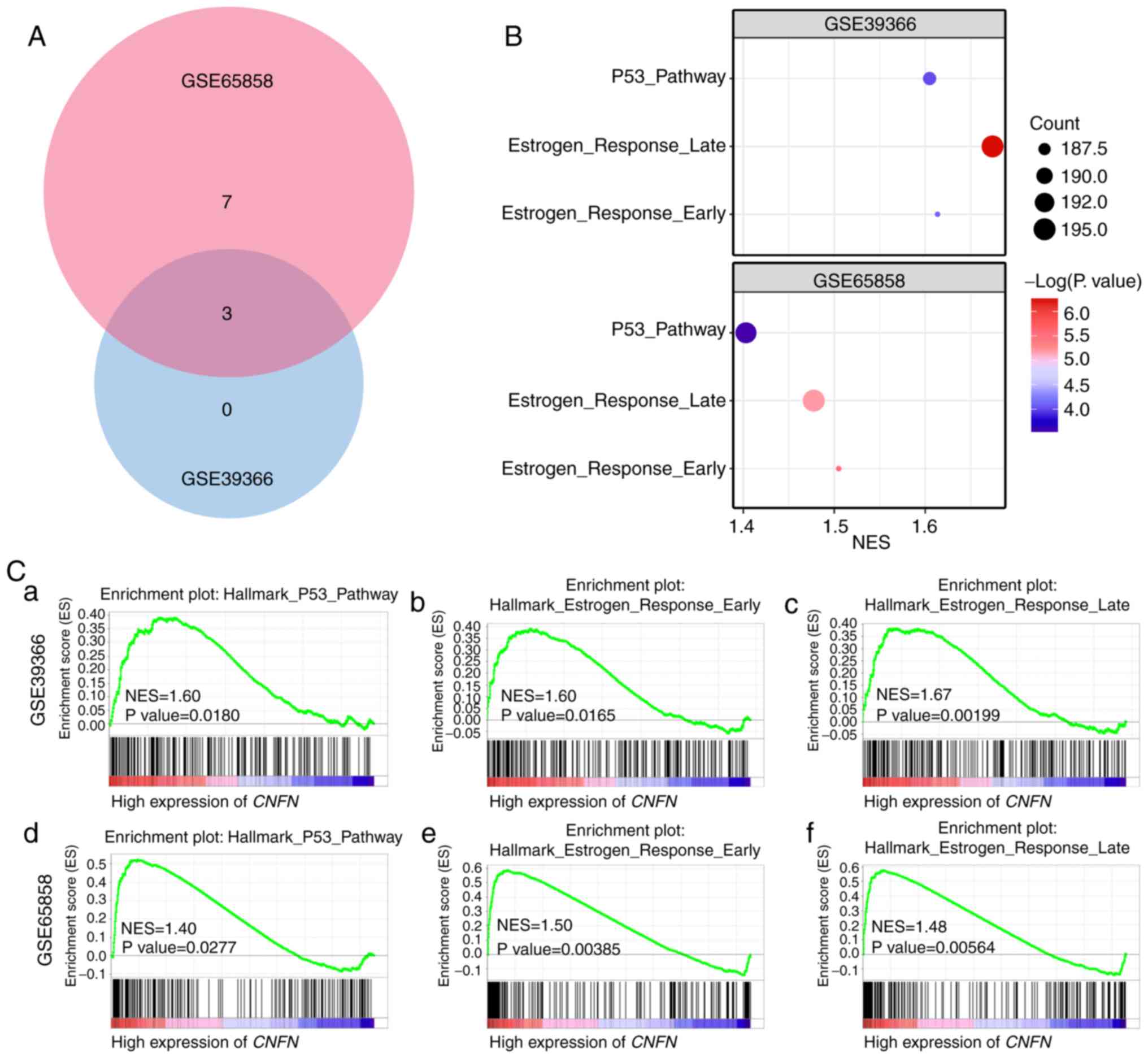
|
1
|
Leemans CR, Snijders PJF and Brakenhoff
RH: The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 18:269–282. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shield KD, Ferlay J, Jemal A,
Sankaranarayanan R, Chaturvedi AK, Bray F and Soerjomataram I: The
global incidence of lip, oral cavity, and pharyngeal cancers by
subsite in 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:51–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Denaro N, Russi EG and Merlano MC: Pros
and cons of the new edition of TNM classification of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology. 95:202–210. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chi AC, Day TA and Neville BW: Oral cavity
and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma-An update. CA Cancer J
Clin. 65:401–421. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Steuer CE, El-Deiry M, Parks JR, Higgins
KA and Saba NF: An update on larynx cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
67:31–50. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pereira ER, Kedrin D, Seano G, Gautier O,
Meijer EFJ, Jones D, Chin SM, Kitahara S, Bouta EM, Chang J, et al:
Lymph node metastases can invade local blood vessels, exit the
node, and colonize distant organs in mice. Science. 359:1403–1407.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ozsolak F, Platt AR, Jones DR,
Reifenberger JG, Sass LE, McInerney P, Thompson JF, Bowers J,
Jarosz M and Milos PM: Direct RNA sequencing. Nature. 461:814–818.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Keck MK, Zuo Z, Khattri A, Stricker TP,
Brown CD, Imanguli M, Rieke D, Endhardt K, Fang P, Brägelmann J, et
al: Integrative analysis of head and neck cancer identifies two
biologically distinct HPV and three non-HPV subtypes. Clin Cancer
Res. 21:870–881. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Walter V, Yin X, Wilkerson MD, Cabanski
CR, Zhao N, Du Y, Ang MK, Hayward MC, Salazar AH, Hoadley KA, et
al: Molecular subtypes in head and neck cancer exhibit distinct
patterns of chromosomal gain and loss of canonical cancer genes.
PLoS One. 8:e568232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peri S, Izumchenko E, Schubert AD, Slifker
MJ, Ruth K, Serebriiskii IG, Guo T, Burtness BA, Mehra R, Ross EA,
et al: NSD1- and NSD2-damaging mutations define a subset of
laryngeal tumors with favorable prognosis. Nat Commun. 8:17722017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tartour E, Mosseri V, Jouffroy T, Deneux
L, Jaulerry C, Brunin F, Fridman WH and Rodriguez J: Serum soluble
interleukin-2 receptor concentrations as an independent prognostic
marker in head and neck cancer. Lancet. 357:1263–1264. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin MC, Chien PH, Wu HY, Chen ST, Juan HF,
Lou PJ and Huang MC: C1GALT1 predicts poor prognosis and is a
potential therapeutic target in head and neck cancer. Oncogene.
37:5780–5793. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Rettig EM, Bishop JA, Agrawal N, Chung CH,
Sharma R, Zamuner F, Li RJ, Koch WM, Califano JA, Guo T, et al:
HEY1 is expressed independent of NOTCH1 and is associated with poor
prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol.
82:168–175. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan L, Shu B, Chen L, Qian K, Wang Y,
Qian G, Zhu Y, Cao X, Xie C, Xiao Y and Wang X: Overexpression of
COL3A1 confers a poor prognosis in human bladder cancer identified
by co-expression analysis. Oncotarget. 8:70508–70520. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou Z, Cheng Y, Jiang Y, Liu S, Zhang M,
Liu J and Zhao Q: Ten hub genes associated with progression and
prognosis of pancreatic carcinoma identified by co-expression
analysis. Int J Biol Sci. 14:124–136. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu X, Hu AX, Zhao JL and Chen FL:
Identification of key gene modules in human osteosarcoma by
co-expression analysis weighted gene co-expression network analysis
(WGCNA). J Cell Biochem. 118:3953–3959. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang X, Feng H, Li Z, Li D, Liu S, Huang
H and Li M: Application of weighted gene co-expression network
analysis to identify key modules and hub genes in oral squamous
cell carcinoma tumorigenesis. Onco Targets Ther. 11:6001–6021.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li XT: Identification of key genes for
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma using weighted co-expression
network analysis. Oncol Lett. 11:3327–3331. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wichmann G, Rosolowski M, Krohn K, Kreuz
M, Boehm A, Reiche A, Scharrer U, Halama D, Bertolini J, Bauer U,
et al: The role of HPV RNA transcription, immune response-related
gene expression and disruptive TP53 mutations in diagnostic and
prognostic profiling of head and neck cancer. Int J Cancer.
137:2846–2857. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: Affy-analysis of affymetrix genechip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou Z, Liu S, Zhang M, Zhou R, Liu J,
Chang Y and Zhao Q: Overexpression of topoisomerase 2-alpha confers
a poor prognosis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma identified by
co-expression analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 62:2790–2800. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mason MJ, Fan G, Plath K, Zhou Q and
Horvath S: Signed weighted gene co-expression network analysis of
transcriptional regulation in murine embryonic stem cells. BMC
Genomics. 10:3272009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan L, Chen L, Qian K, Wang G, Lu M, Qian
G, Cao X, Jiang W, Xiao Y and Wang X: A novel correlation between
ATP5A1 gene expression and progression of human clear cell renal
cell carcinoma identified by co-expression analysis. Oncol Rep.
39:525–536. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Botia JA, Vandrovcova J, Forabosco P,
Guelfi S, D'Sa K; United Kingdom Brain Expression Consortium, ;
Hardy J, Lewis CM, Ryten M and Weale ME: An additional k-means
clustering step improves the biological features of WGCNA gene
co-expression networks. BMC Syst Biol. 11:472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Foroushani A, Agrahari R, Docking R, Chang
L, Duns G, Hudoba M, Karsan A and Zare H: Large-scale gene network
analysis reveals the significance of extracellular matrix pathway
and homeobox genes in acute myeloid leukemia: An introduction to
the Pigengene package and its applications. BMC Med Genomics.
10:162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Forabosco P, Ramasamy A, Trabzuni D,
Walker R, Smith C, Bras J, Levine AP, Hardy J, Pocock JM, Guerreiro
R, et al: Insights into TREM2 biology by network analysis of human
brain gene expression data. Neurobiol Aging. 34:2699–2714. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Subramanian A, Kuehn H, Gould J, Tamayo P
and Mesirov JP: GSEA-P: A desktop application for gene set
enrichment analysis. Bioinformatics. 23:3251–3253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lydiatt WM, Patel SG, O'Sullivan B,
Brandwein MS, Ridge JA, Migliacci JC, Loomis AM and Shah JP: Head
and neck cancers-major changes in the American joint committee on
cancer eighth edition cancer staging manual. CA Cancer J Clin.
67:122–137. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ferris RL, Lotze MT, Leong SP, Hoon DS and
Morton DL: Lymphatics, lymph nodes and the immune system: Barriers
and gateways for cancer spread. Clin Exp Metastasis. 29:729–736.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kawada K and Taketo MM: Significance and
mechanism of lymph node metastasis in cancer progression. Cancer
Res. 71:1214–1218. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saksena MA, Saokar A and Harisinghani MG:
Lymphotropic nanoparticle enhanced MR imaging (LNMRI) technique for
lymph node imaging. Eur J Radiol. 58:367–374. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Grobner SN, Worst BC, Weischenfeldt J,
Buchhalter I, Kleinheinz K, Rudneva VA, Johann PD, Balasubramanian
GP, Segura-Wang M, Brabetz S, et al: The landscape of genomic
alterations across childhood cancers. Nature. 555:321–327. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang QL, Chen X, Zhang MH, Shen QH and Qin
ZM: Identification of hub genes and pathways associated with
retinoblastoma based on co-expression network analysis. Genet Mol
Res. 14:16151–16161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou R and Man Y: Integrated analysis of
DNA methylation profiles and gene expression profiles to identify
genes associated with pilocytic astrocytomas. Mol Med Rep.
13:3491–3497. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu J, Jing L and Tu X: Weighted gene
co-expression network analysis identifies specific modules and hub
genes related to coronary artery disease. BMC Cardiovasc Disord.
16:542016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Huang C, Huang BB, Niu JM, Yu Y, Qin XY,
Yang YL, Xiao TX, Chen J, Ren LR and Zhang JV: Global mRNA and long
non-coding RNA expression in the placenta and white adipose tissue
of mice fed a high-fat diet during pregnancy. Cell Physiol Biochem.
50:2260–2271. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Michibata H, Chiba H, Wakimoto K, Seishima
M, Kawasaki S, Okubo K, Mitsui H, Torii H and Imai Y:
Identification and characterization of a novel component of the
cornified envelope, cornifelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
318:803–813. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sun X, Kim A, Nakatani M, Shen Y and Liu
L: Distinctive molecular responses to ultraviolet radiation between
keratinocytes and melanocytes. Exp Dermatol. 25:708–713. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang B, Chen MY, Shen YJ, Zhuo XB, Gao P,
Zhou FS, Liang B, Zu J, Zhang Q and Suleman S: A large-scale,
exome-wide association study of han chinese women identifies three
novel loci predisposing to breast cancer. Cancer Res. 78:3087–3097.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Till JE, Yoon C, Kim BJ, Roby K, Addai P,
Jonokuchi E, Tang LH, Yoon SS and Ryeom S: Oncogenic KRAS and p53
loss drive gastric tumorigenesis in mice that can be attenuated by
E-Cadherin expression. Cancer Res. 77:5349–5359. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Turrell FK, Kerr EM, Gao M, Thorpe H,
Doherty GJ, Cridge J, Shorthouse D, Speed A, Samarajiwa S, Hall BA,
et al: Lung tumors with distinct p53 mutations respond similarly to
p53 targeted therapy but exhibit genotype-specific statin
sensitivity. Genes Dev. 31:1339–1353. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sanchez-Vega F, Mina M, Armenia J, Chatila
WK, Luna A, La KC, Dimitriadoy S, Liu DL, Kantheti HS, Saghafinia
S, et al: Oncogenic signaling pathways in the cancer genome atlas.
Cell. 173:321–337. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Venkatanarayan A, Raulji P, Norton W,
Chakravarti D, Coarfa C, Su X, Sandur SK, Ramirez MS, Lee J,
Kingsley CV, et al: IAPP-driven metabolic reprogramming induces
regression of p53-deficient tumours in vivo. Nature. 517:626–630.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen SH, Forrester W and Lahav G:
Schedule-dependent interaction between anticancer treatments.
Science. 351:1204–1208. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wade M, Li YC and Wahl GM: MDM2, MDMX and
p53 in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:83–96.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dow LE, O'Rourke KP, Simon J,
Tschaharganeh DF, van Es JH, Clevers H and Lowe SW: Apc restoration
promotes cellular differentiation and reestablishes crypt
homeostasis in colorectal cancer. Cell. 161:1539–1552. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Furth N and Aylon Y: The LATS1 and LATS2
tumor suppressors: Beyond the Hippo pathway. Cell Death Differ.
24:1488–1501. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kundu N, Brekman A, Kim JY, Xiao G, Gao C
and Bargonetti J: Estrogen-activated MDM2 disrupts mammary tissue
architecture through a p53-independent pathway. Oncotarget.
8:47916–47930. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zwijsen RM, Wientjens E, Klompmaker R, van
der Sman J, Bernards R and Michalides RJ: CDK-independent
activation of estrogen receptor by cyclin D1. Cell. 88:405–415.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hurtado A, Holmes KA, Geistlinger TR,
Hutcheson IR, Nicholson RI, Brown M, Jiang J, Howat WJ, Ali S and
Carroll JS: Regulation of ERBB2 by oestrogen receptor-PAX2
determines response to tamoxifen. Nature. 456:663–666. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hsu PY, Hsu HK, Lan X, Juan L, Yan PS,
Labanowska J, Heerema N, Hsiao TH, Chiu YC, Chen Y, et al:
Amplification of distant estrogen response elements deregulates
target genes associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer.
Cancer Cell. 24:197–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|