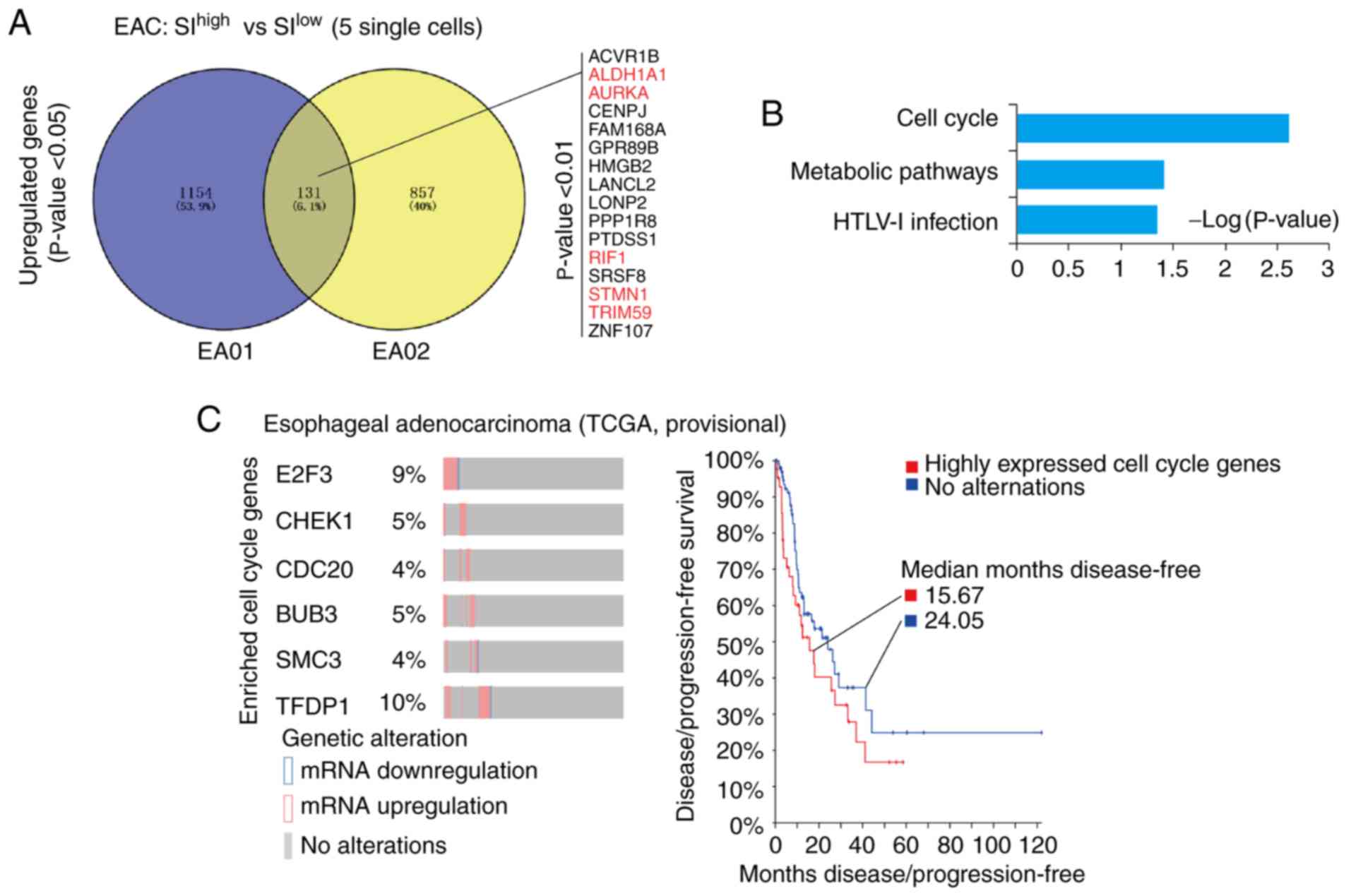
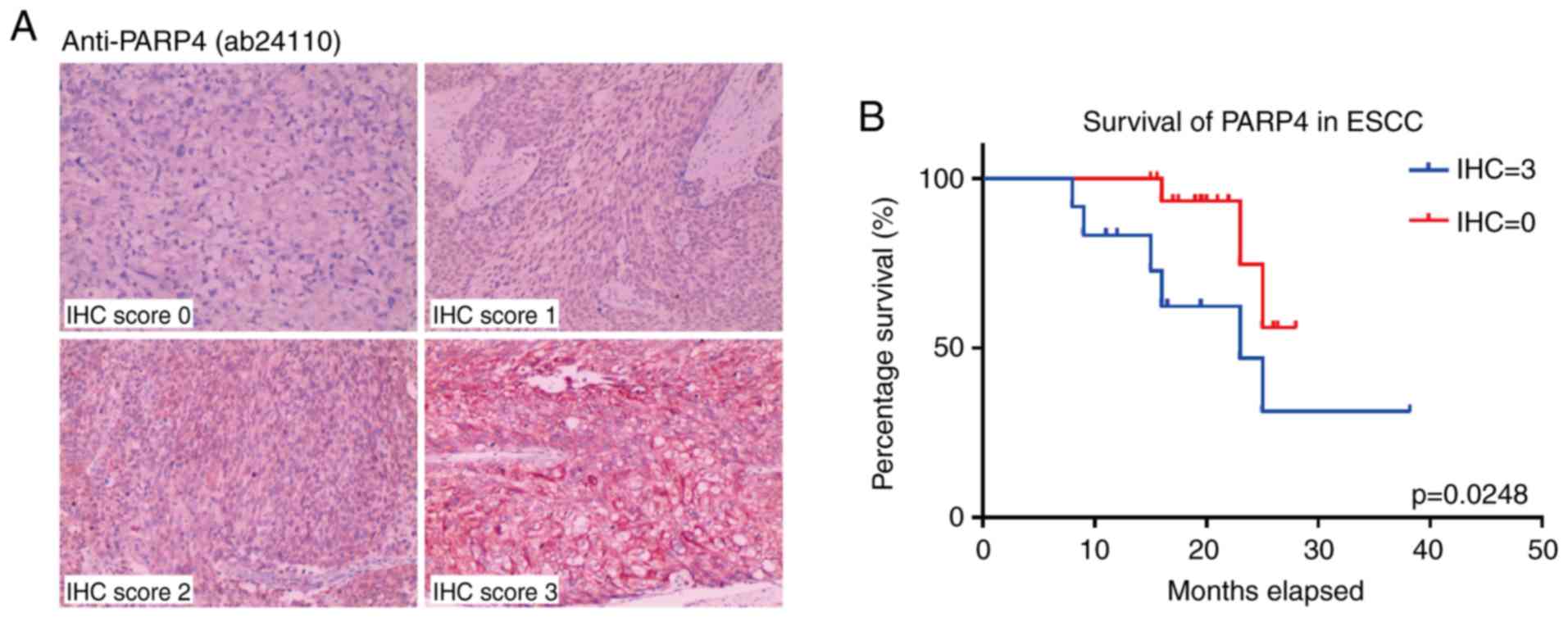
|
1
|
Wong DJ, Segal E and Chang HY: Stemness,
cancer and cancer stem cells. Cell Cycle. 7:3622–3624. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Monteiro J and Fodde R: Cancer stemness
and metastasis: Therapeutic consequences and perspectives. Eur J
Cancer. 46:1198–1203. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Khosrotehrani K and Roy E: Tell me about
your stemness. I'll give your cancer risk! Cell Death Differ.
24:6–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ghisolfi L, Keates AC, Hu X, Lee DK and Li
CJ: Ionizing radiation induces stemness in cancer cells. PLoS One.
7:e436282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu X, Ghisolfi L, Keates AC, Zhang J,
Xiang S and Lee DK: Induction of cancer cell stemness by
chemotherapy. Cell Cycle. 11:2691–2698. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Z, Duan Q, Zhao H, Liu T, Wu H, Shen
Q, Wang C and Yin T: Gemcitabine treatment promotes pancreatic
cancer stemness through the Nox/ROS/NF-kappaB/STAT3 signaling
cascade. Cancer Lett. 382:53–63. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu L, Yang L, Yan W, Zhai J, Pizzo DP,
Chu P, Chin AR, Shen M, Dong C, Ruan X, et al: Chemotherapy induces
breast cancer stemness in association with dysregulated
monocytosis. Clin Cancer Res. 24:2370–2382. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Rogoff HA, Keates S, Gao Y,
Murikipudi S, Mikule K, Leggett D, Li W, Pardee AB and Li CJ:
Suppression of cancer relapse and metastasis by inhibiting cancer
stemness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:1839–1844. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang ZM, Chen Y and Luo ML: Targeting
stemness: Implications for precision medicine in breast cancer. Adv
Exp Med Biol. 1026:147–169. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fodde R and Brabletz T: Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling in cancer stemness and malignant behavior. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 19:150–158. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang X, Lou Y, Wang H, Zheng X, Dong Q,
Sun J and Han B: Wnt signaling regulates the stemness of lung
cancer stem cells and its inhibitors exert anticancer effect on
lung cancer SPC-A1 cells. Med Oncol. 32:952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jin L, Vu T, Yuan G and Datta PK: STRAP
promotes stemness of human colorectal cancer via epigenetic
regulation of the NOTCH pathway. Cancer Res. 77:5464–5478. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu T, Li Z, Yang Y, Ji W, Yu Y, Niu X,
Zeng Q, Xia W and Lu S: The Hippo/YAP1 pathway interacts with FGFR1
signaling to maintain stemness in lung cancer. Cancer Lett.
423:36–46. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yun Z and Lin Q: Hypoxia and regulation of
cancer cell stemness. Adv Exp Med Biol. 772:41–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu X, Li F, Huang Q, Zhang Z, Zhou L,
Deng Y, Zhou M, Fleenor DE, Wang H, Kastan MB and Li CY:
Self-inflicted DNA double-strand breaks sustain tumorigenicity and
stemness of cancer cells. Cell Res. 27:764–783. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Carné Trécesson S, Souazé F, Basseville A,
Bernard AC, Pécot J, Lopez J, Bessou M, Sarosiek KA, Letai A,
Barillé-Nion S, et al: BCL-XL directly modulates RAS
signalling to favour cancer cell stemness. Nat Commun. 8:11232017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sottoriva A, Spiteri I, Piccirillo SG,
Touloumis A, Collins VP, Marioni JC, Curtis C, Watts C and Tavaré
S: Intratumor heterogeneity in human glioblastoma reflects cancer
evolutionary dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:4009–4014. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li H, Courtois ET, Sengupta D, Tan Y, Chen
KH, Goh JJL, Kong SL, Chua C, Hon LK, Tan WS, et al: Reference
component analysis of single-cell transcriptomes elucidates
cellular heterogeneity in human colorectal tumors. Nat Genet.
49:708–718. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Morgan M, Anders S, Lawrence M, Aboyoun P,
Pages H and Gentleman R: ShortRead: A bioconductor package for
input, quality assessment and exploration of high-throughput
sequence data. Bioinformatics. 25:2607–2608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bolger AM, Lohse M and Usadel B:
Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data.
Bioinformatics. 30:2114–2120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Trapnell C, Cacchiarelli D, Grimsby J,
Pokharel P, Li S, Morse M, Lennon NJ, Livak KJ, Mikkelsen TS and
Rinn JL: The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are
revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells. Nat
Biotechnol. 32:381–386. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G,
Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL and Pachter L:
Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with tophat and cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 7:562–578. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dalerba P, Cho RW and Clarke MF: Cancer
stem cells: Models and concepts. Annu Rev Med. 58:267–284. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu H, Yu J, Li Y, Hou Q, Zhou R, Zhang N,
Jing Z, Jiang M, Li Z, Hua Y, et al: Single-cell RNA sequencing
reveals diverse intratumoral heterogeneities and gene signatures of
two types of esophageal cancers. Cancer Lett. 438:133–143. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kulsum S, Sudheendra HV, Pandian R,
Ravindra DR, Siddappa G, R N, Chevour P, Ramachandran B, Sagar M,
Jayaprakash A, et al: Cancer stem cell mediated acquired
chemoresistance in head and neck cancer can be abrogated by
aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 A1 inhibition. Mol Carcinog. 56:694–711.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Wang L, Cui W, Yuan X, Lin L, Cao
Q, Wang N, Li Y, Guo W, Zhang X, et al: Targeting ALDH1A1 by
disulfiram/copper complex inhibits non-small cell lung cancer
recurrence driven by ALDH-positive cancer stem cells. Oncotarget.
7:58516–58530. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meng E, Mitra A, Tripathi K, Finan MA,
Scalici J, McClellan S, Madeira da Silva L, Reed E, Shevde LA,
Palle K, et al: ALDH1A1 maintains ovarian cancer stem cell-like
properties by altered regulation of cell cycle checkpoint and DNA
repair network signaling. PLoS One. 9:e1071422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thomas ML, de Antueno R, Coyle KM, Sultan
M, Cruickshank BM, Giacomantonio MA, Giacomantonio CA, Duncan R and
Marcato P: Citral reduces breast tumor growth by inhibiting the
cancer stem cell marker ALDH1A3. Mol Oncol. 10:1485–1496. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang L, Ren Y, Yu X, Qian F, Bian BS, Xiao
HL, Wang WG, Xu SL, Yang J, Cui W, et al: ALDH1A1 defines invasive
cancer stem-like cells and predicts poor prognosis in patients with
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 27:775–783. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen C, Song G, Xiang J, Zhang H, Zhao S
and Zhan Y: AURKA promotes cancer metastasis by regulating
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell properties
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
486:514–520. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eterno V, Zambelli A, Villani L, Tuscano
A, Manera S, Spitaleri A, Pavesi L and Amato A: AurkA controls
self-renewal of breast cancer-initiating cells promoting wnt3a
stabilization through suppression of miR-128. Sci Rep. 6:284362016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang N, Wang C, Wang Z, Zona S, Lin SX,
Wang X, Yan M, Zheng FM, Li SS, Xu B, et al: FOXM1 recruits nuclear
aurora kinase A to participate in a positive feedback loop
essential for the self-renewal of breast cancer stem cells.
Oncogene. 36:3428–3440. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zheng F, Yue C, Li G, He B, Cheng W, Wang
X, Yan M, Long Z, Qiu W, Yuan Z, et al: Nuclear AURKA acquires
kinase-independent transactivating function to enhance breast
cancer stem cell phenotype. Nat Commun. 7:101802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
GursesCila HE, Acar M, Barut FB, Gunduz M,
Grenman R and Gunduz E: Investigation of the expression of RIF1
gene on head and neck, pancreatic and brain cancer and cancer stem
cells. Clin Invest Med. 39:275002016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li P, Ma X, Adams IR and Yuan P: A tight
control of Rif1 by Oct4 and Smad3 is critical for mouse
embryonic stem cell stability. Cell Death Dis. 6:e15882015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mei Y, Peng C, Liu YB, Wang J and Zhou HH:
Silencing RIF1 decreases cell growth, migration and increases
cisplatin sensitivity of human cervical cancer cells. Oncotarget.
8:107044–107051. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li M, Yang J, Zhou W, Ren Y, Wang X, Chen
H, Zhang J, Chen J, Sun Y, Cui L, et al: Activation of an
AKT/FOXM1/STMN1 pathway drives resistance to tyrosine kinase
inhibitors in lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 117:974–983. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Obayashi S, Horiguchi J, Higuchi T,
Katayama A, Handa T, Altan B, Bai T, Bao P, Bao H, Yokobori T, et
al: Stathmin1 expression is associated with aggressive phenotypes
and cancer stem cell marker expression in breast cancer patients.
Int J Oncol. 51:781–790. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sang Y, Li Y, Song L, Alvarez AA, Zhang W,
Lv D, Tang J, Liu F, Chang Z, Hatakeyama S, et al: TRIM59 promotes
gliomagenesis by inhibiting TC45 dephosphorylation of STAT3. Cancer
Res. 78:1792–1804. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhou Z, Ji Z, Wang Y, Li J, Cao H, Zhu HH
and Gao WQ: TRIM59 is up-regulated in gastric tumors, promoting
ubiquitination and degradation of p53. Gastroenterology.
147:1043–1054. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Malta TM, Sokolov A, Gentles AJ,
Burzykowski T, Poisson L, Weinstein JN, Kamińska B, Huelsken J,
Omberg L, Gevaert O, et al: Machine learning identifies stemness
features associated with oncogenic dedifferentiation. Cell.
173:338–354.e15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: EMT, CSCs, and
drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:611–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Guiu J, Bergen DJ, De Pater E, Islam AB,
Ayllon V, Gama-Norton L, Ruiz-Herguido C, González J, López-Bigas
N, Menendez P, et al: Identification of Cdca7 as a novel Notch
transcriptional target involved in hematopoietic stem cell
emergence. J Exp Med. 211:2411–2423. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Imai T, Oue N, Sentani K, Sakamoto N,
Uraoka N, Egi H, Hinoi T, Ohdan H, Yoshida K, Yasui W, et al: KIF11
is required for spheroid formation by oesophageal and colorectal
cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 37:47–55. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiang M, Zhuang H, Xia R, Gan L, Wu Y, Ma
J, Sun Y and Zhuang Z: KIF11 is required for proliferation and
self-renewal of docetaxel resistant triple negative breast cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 8:92106–92118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Venere M, Horbinski C, Crish JF, Jin X,
Vasanji A, Major J, Burrows AC, Chang C, Prokop J, Wu Q, et al: The
mitotic kinesin KIF11 is a driver of invasion, proliferation, and
self- renewal in glioblastoma. Sci Transl Med. 7:304ra1432015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Augustin I, Dewi DL, Hundshammer J,
Erdmann G, Kerr G and Boutros M: Autocrine wnt regulates the
survival and genomic stability of embryonic stem cells. Sci Signal.
10:eaah68292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Augustin I, Dewi DL, Hundshammer J, Rempel
E, Brunk F and Boutros M: Immune cell recruitment in teratomas is
impaired by increased wnt secretion. Stem Cell Res. 17:607–615.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ren M and Cowell JK: Constitutive notch
pathway activation in murine ZMYM2-FGFR1-induced T-cell lymphomas
associated with atypical myeloproliferative disease. Blood.
117:6837–6847. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ren M, Qin H, Wu Q, Savage NM, George TI
and Cowell JK: Development of ZMYM2-FGFR1 driven AML in human CD34+
cells in immunocompromised mice. Int J Cancer. 139:836–840. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rubben A and Araujo A: Cancer
heterogeneity: Converting a limitation into a source of biologic
information. J Transl Med. 15:1902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mills CC, Kolb EA and Sampson VB: Recent
advances of cell-cycle inhibitor therapies for pediatric cancer.
Cancer Res. 77:6489–6498. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lord CJ and Ashworth A: PARP inhibitors:
Synthetic lethality in the clinic. Science. 355:1152–1158. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Weaver AN, Cooper TS, Rodriguez M,
Trummell HQ, Bonner JA, Rosenthal EL and Yang ES: DNA double strand
break repair defect and sensitivity to poly ADP-ribose polymerase
(PARP) inhibition in human papillomavirus 16-positive head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget. 6:26995–277007. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nasuno T, Mimaki S, Okamoto M, Esumi H and
Tsuchihara K: Effect of a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor
against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Sci.
105:202–210. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wurster S, Hennes F, Parplys AC, Seelbach
JI, Mansour WY, Zielinski A, Petersen C, Clauditz TS, Münscher A,
Friedl AA and Borgmann K: PARP1 inhibition radiosensitizes HNSCC
cells deficient in homologous recombination by disabling the DNA
replication fork elongation response. Oncotarget. 7:9732–9741.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ramalingam SS, Blais N, Mazieres J, Reck
M, Jones CM, Juhasz E, Urban L, Orlov S, Barlesi F, Kio E, et al:
Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II study of veliparib in
combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel for advanced/metastatic
non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 23:1937–1944. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhan L, Qin Q, Lu J, Liu J, Zhu H, Yang X,
Zhang C, Xu L, Liu Z, Cai J, et al: Novel poly (ADP-ribose)
polymerase inhibitor, AZD2281, enhances radiosensitivity of both
normoxic and hypoxic esophageal squamous cancer cells. Dis
Esophagus. 29:215–223. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yasukawa M, Fujihara H, Fujimori H,
Kawaguchi K, Yamada H, Nakayama R, Yamamoto N, Kishi Y, Hamada Y
and Masutani M: Synergetic effects of PARP inhibitor AZD2281 and
cisplatin in oral squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Int
J Mol Sci. 17:2722016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|