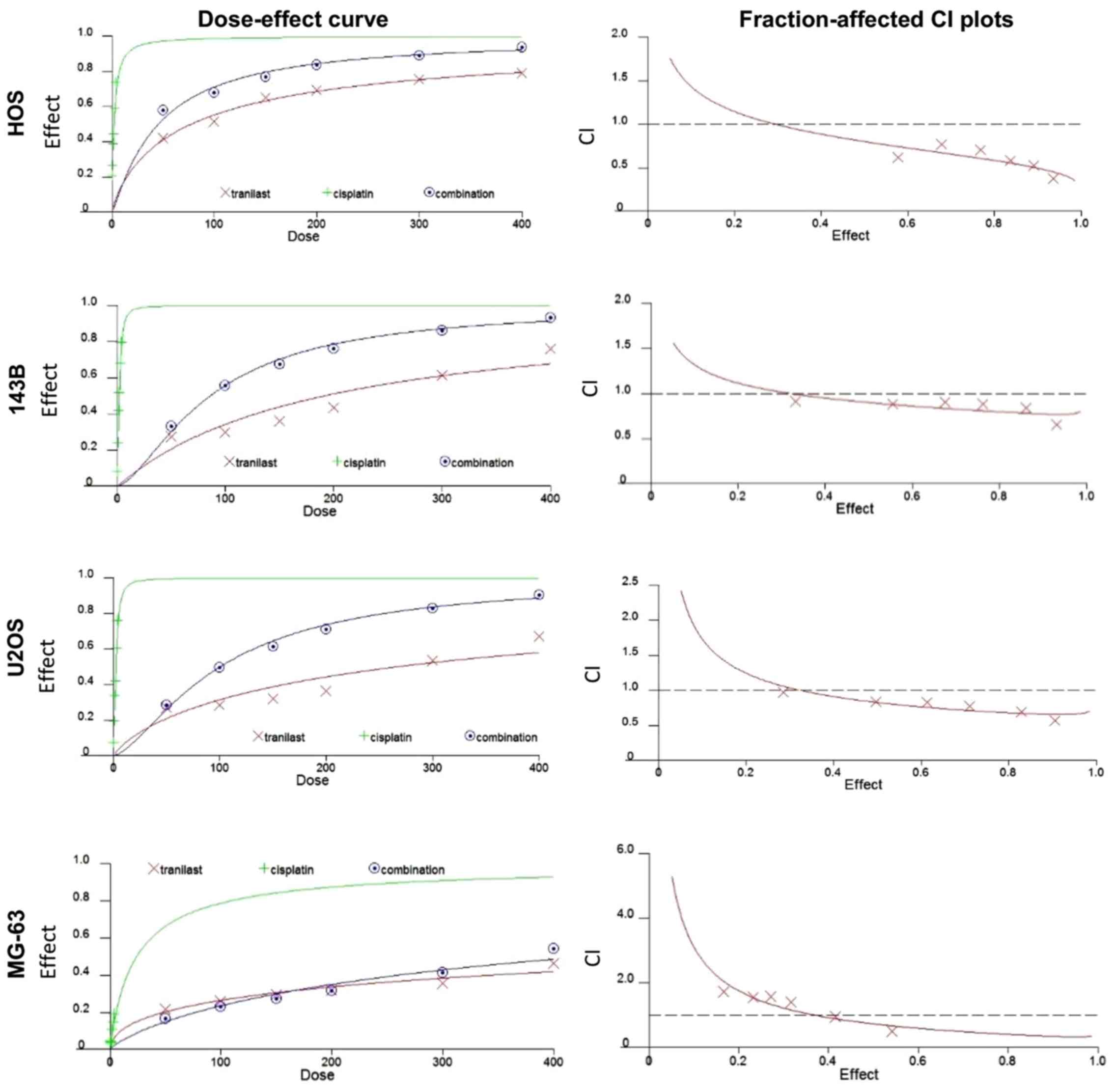
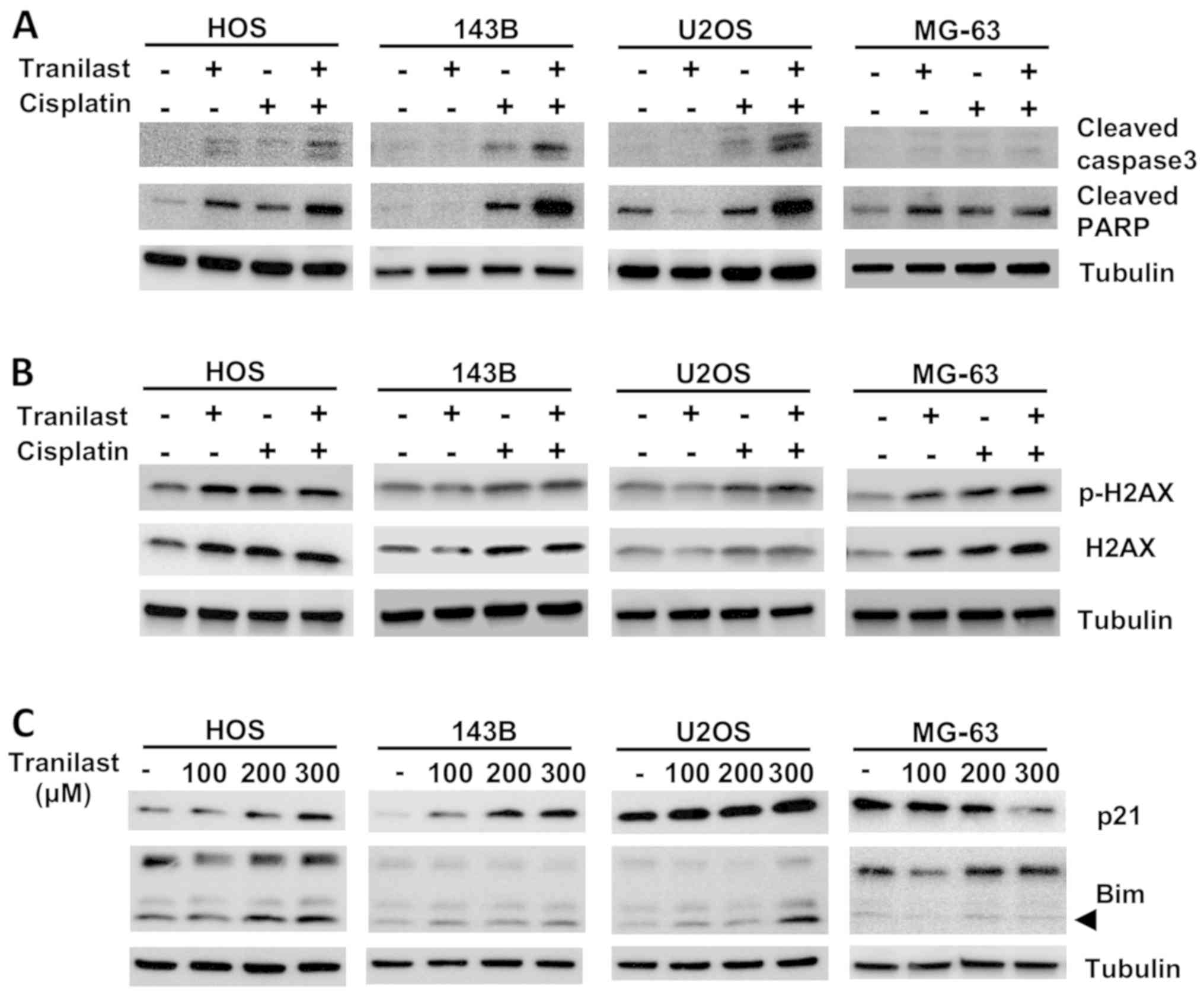
|
1
|
Darakhshan S and Pour AB: Tranilast: A
review of its therapeutic applications. Pharmacol Res. 91:15–28.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ward MR, Sasahara T, Agrotis A, Dilley RJ,
Jennings GL and Bobik A: Inhibitory effects of tranilast on
expression of transforming growth factor-beta isoforms and
receptors in injured arteries. Atherosclerosis. 137:267–275. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Phan TV, Ke K, Sul OJ, Park YK, Kim KK,
Cho YS, Chung HT and Choi HS: Protection against
ovariectomy-induced bone loss by tranilast. PLoS One. 9:e955852014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holmes DR Jr, Savage M, LaBlanche JM, Grip
L, Serruys PW, Fitzgerald P, Fischman D, Goldberg S, Brinker JA,
Zeiher AM, et al: Results of prevention of REStenosis with
tranilast and its outcomes (PRESTO) trial. Circulation.
106:1243–1250. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang Y, Jiang H, Chen Y, Wang X, Yang Y,
Tao J, Deng X, Liang G, Zhang H, Jiang W and Zhou R: Tranilast
directly targets NLRP3 to treat inflammasome-driven diseases. EMBO
Mol Med. 10:e86892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tokuyama H, Kelly DJ, Cox A, Zhang Y, Thai
K, Nikolic-Paterson DJ and Gilbert RE: Tranilast ameliorates
experimental mesangial proliferative glomerulonephritis. Nephron
Exp Nephrol. 109:e1–e7. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Darakhshan S, Bidmeshkipour A, Mansouri K,
Saeid HM and Ghanbari A: The effects of tamoxifen in combination
with tranilast on CXCL12-CXCR4 axis and invasion in breast cancer
cell lines. Iran J Pharm Res. 13:683–693. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Subramaniam V, Ace O, Prud'homme GJ and
Jothy S: Tranilast treatment decreases cell growth, migration and
inhibits colony formation of human breast cancer cells. Exp Mol
Pathol. 90:116–122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Izumi K, Mizokami A, Li YQ, Narimoto K,
Sugimoto K, Kadono Y, Kitagawa Y, Konaka H, Koh E, Keller ET and
Namiki M: Tranilast inhibits hormone refractory prostate cancer
cell proliferation and suppresses transforming growth factor
beta1-associated osteoblastic changes. Prostate. 69:1222–1234.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kaneda M, Obara H, Suzuki K, Takeuchi O,
Takizawa A, Osaku M, Matsubara H and Kitagawa Y: Evaluation of
suppressive effects of tranilast on the invasion/metastasis
mechanism in a murine pancreatic cancer cell line. Pancreas.
46:567–574. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yatsunami J, Aoki S, Fukuno Y, Kikuchi Y,
Kawashima M and Hayashi SI: Antiangiogenic and antitumor effects of
tranilast on mouse lung carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 17:1151–1156.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yashiro M, Murahashi K, Matsuoka T,
Nakazawa K, Tanaka H, Osaka H, Koyama T, Ohira M and Chung KH:
Tranilast (N-3,4-dimethoxycinamoyl anthranilic acid): A novel
inhibitor of invasion-stimulating interaction between gastric
cancer cells and orthotopic fibroblasts. Anticancer Res.
23:3899–3904. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meazza C and Scanagatta P: Metastatic
osteosarcoma: A challenging multidisciplinary treatment. Expert Rev
Anticancer Ther. 16:543–556. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chandar N, Billig B, McMaster J and Novak
J: Inactivation of p53 gene in human and murine osteosarcoma cells.
Br J Cancer. 65:208–214. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ganjavi H, Gee M, Narendran A, Parkinson
N, Krishnamoorthy M, Freedman MH and Malkin D: Adenovirus-mediated
p53 gene therapy in osteosarcoma cell lines: Sensitization to
cisplatin and doxorubicin. Cancer Gene Ther. 13:415–419. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Allan LA and Fried M: p53-dependent
apoptosis or growth arrest induced by different forms of radiation
in U2OS cells: p21WAF1/CIP1 repression in UV induced apoptosis.
Oncogene. 18:5403–5412. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakamura S, Nagano S, Nagao H, Ishidou Y,
Yokouchi M, Abematsu M, Yamamoto T, Komiya S and Setoguchi T:
Arsenic trioxide prevents osteosarcoma growth by inhibition of GLI
transcription via DNA damage accumulation. PLoS One. 8:e694662013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takahashi K, Setoguchi T, Tsuru A, Saitoh
Y, Nagano S, Ishidou Y, Maeda S, Furukawa T and Komiya S:
Inhibition of casein kinase 2 prevents growth of human
osteosarcoma. Oncol Rep. 37:1141–1147. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Isaji M, Miyata H, Ajisawa Y, Takehana Y
and Yoshimura N: Tranilast inhibits the proliferation, chemotaxis
and tube formation of human microvascular endothelial cells in
vitro and angiogenesis in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 122:1061–1066.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Suzawa H, Kikuchi S, Arai N and Koda A:
The mechanism involved in the inhibitory action of tranilast on
collagen biosynthesis of keloid fibroblasts. Jpn J Pharmacol.
60:91–96. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Subramaniam V, Chakrabarti R, Prud'homme
GJ and Jothy S: Tranilast inhibits cell proliferation and migration
and promotes apoptosis in murine breast cancer. Anticancer Drugs.
21:351–361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shapiro GI and Harper JW: Anticancer drug
targets: Cell cycle and checkpoint control. J Clin Invest.
104:1645–1653. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Siddik ZH: Cisplatin: Mode of cytotoxic
action and molecular basis of resistance. Oncogene. 22:7265–7279.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goto A, Kanda H, Ishikawa Y, Matsumoto S,
Kawaguchi N, Machinami R, Kato Y and Kitagawa T: Association of
loss of heterozygosity at the p53 locus with chemoresistance in
osteosarcomas. Jpn J Cancer Res. 89:539–547. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jaffe N: Historical perspective on the
introduction and use of chemotherapy for the treatment of
osteosarcoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 804:1–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sabisz M and Skladanowski A: Modulation of
cellular response to anticancer treatment by caffeine: Inhibition
of cell cycle checkpoints, DNA repair and more. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 9:325–336. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu Y, Li C, Li H, Li M and Shu X:
Resveratrol-mediated reversal of tumor multi-drug resistance. Curr
Drug Metab. 15:703–710. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rogosnitzky M, Danks R and Kardash E:
Therapeutic potential of tranilast, an anti-allergy drug, in
proliferative disorders. Anticancer Res. 32:2471–2478.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Murahashi K, Yashiro M, Inoue T, Nishimura
S, Matsuoka T, Sawada T, Sowa M and Hirakawa-Ys Chung K: Tranilast
and cisplatin as an experimental combination therapy for scirrhous
gastric cancer. Int J Oncol. 13:1235–1240. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mitsuno M, Kitajima Y, Ohtaka K, Kai K,
Hashiguchi K, Nakamura J, Hiraki M, Noshiro H and Miyazaki K:
Tranilast strongly sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to
gemcitabine via decreasing protein expression of ribonucleotide
reductase 1. Int J Oncol. 36:341–349. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Darakhshan S, Bidmeshkipour A, Khazaei M,
Rabzia A and Ghanbari A: Synergistic effects of tamoxifen and
tranilast on VEGF and MMP-9 regulation in cultured human breast
cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:6869–6874. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kusama H, Kikuchi S, Tazawa S, Katsuno K,
Baba Y, Zhai YL, Nikaido T and Fujii S: Tranilast inhibits the
proliferation of human coronary smooth muscle cell through the
activation of p21waf1. Atherosclerosis. 143:307–313. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fox E, Levin K, Zhu Y, Segers B, Balamuth
N, Womer R, Bagatell R and Balis F: Pantoprazole, an inhibitor of
the organic cation transporter 2, does not ameliorate
cisplatin-related ototoxicity or nephrotoxicity in children and
adolescents with newly diagnosed osteosarcoma treated with
methotrexate, doxorubicin, and cisplatin. Oncologist. 23:762–e779.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|