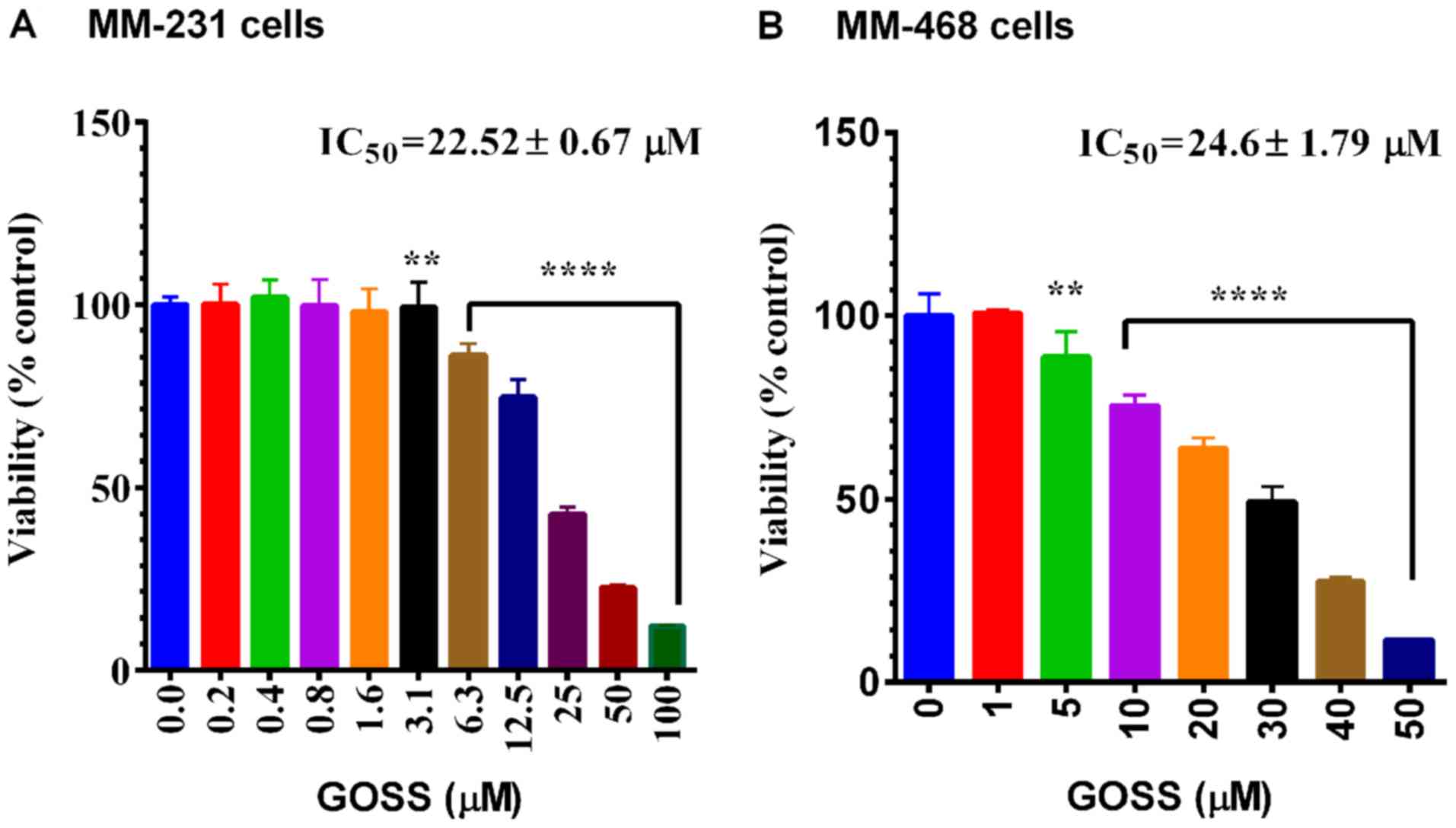
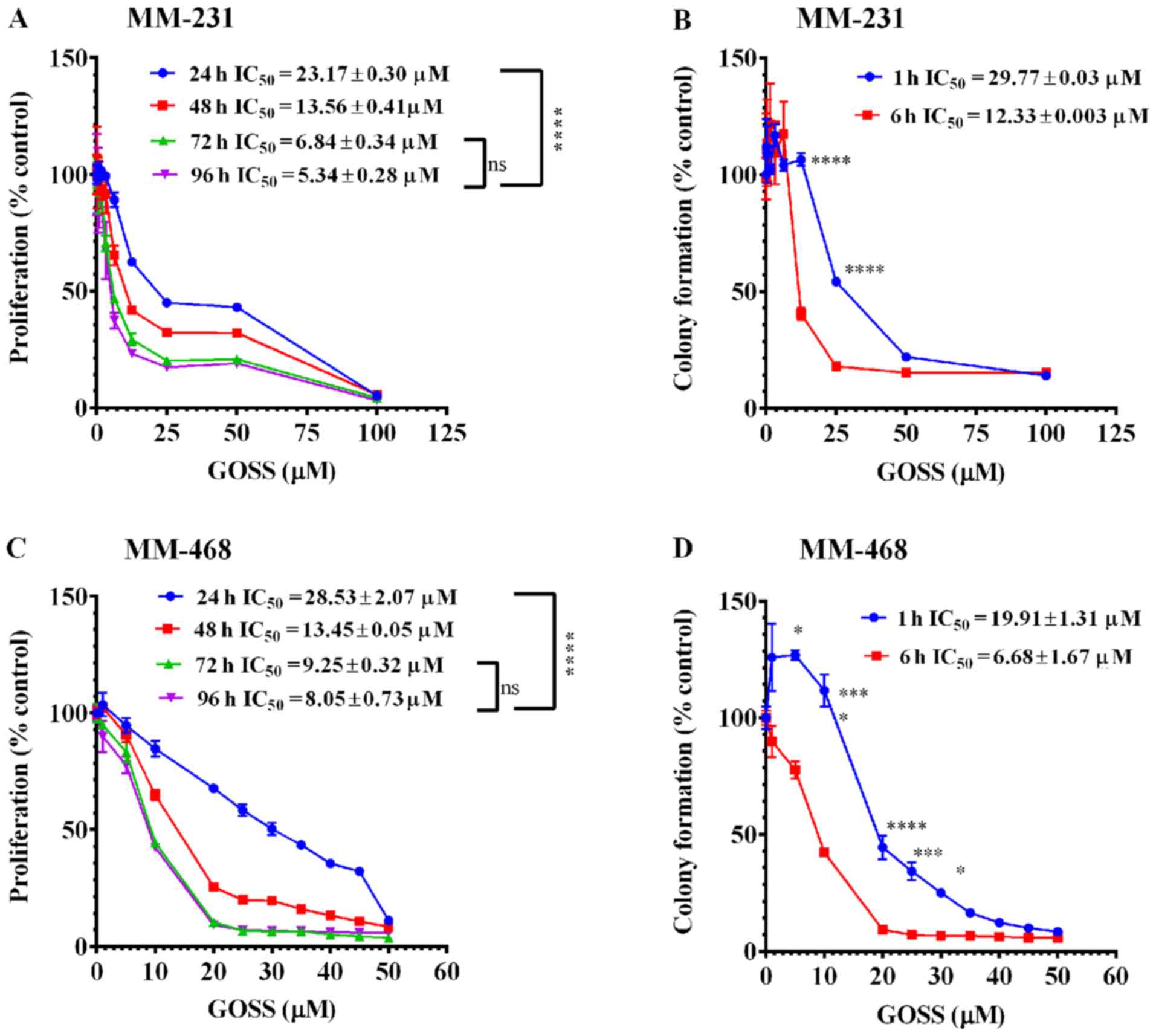
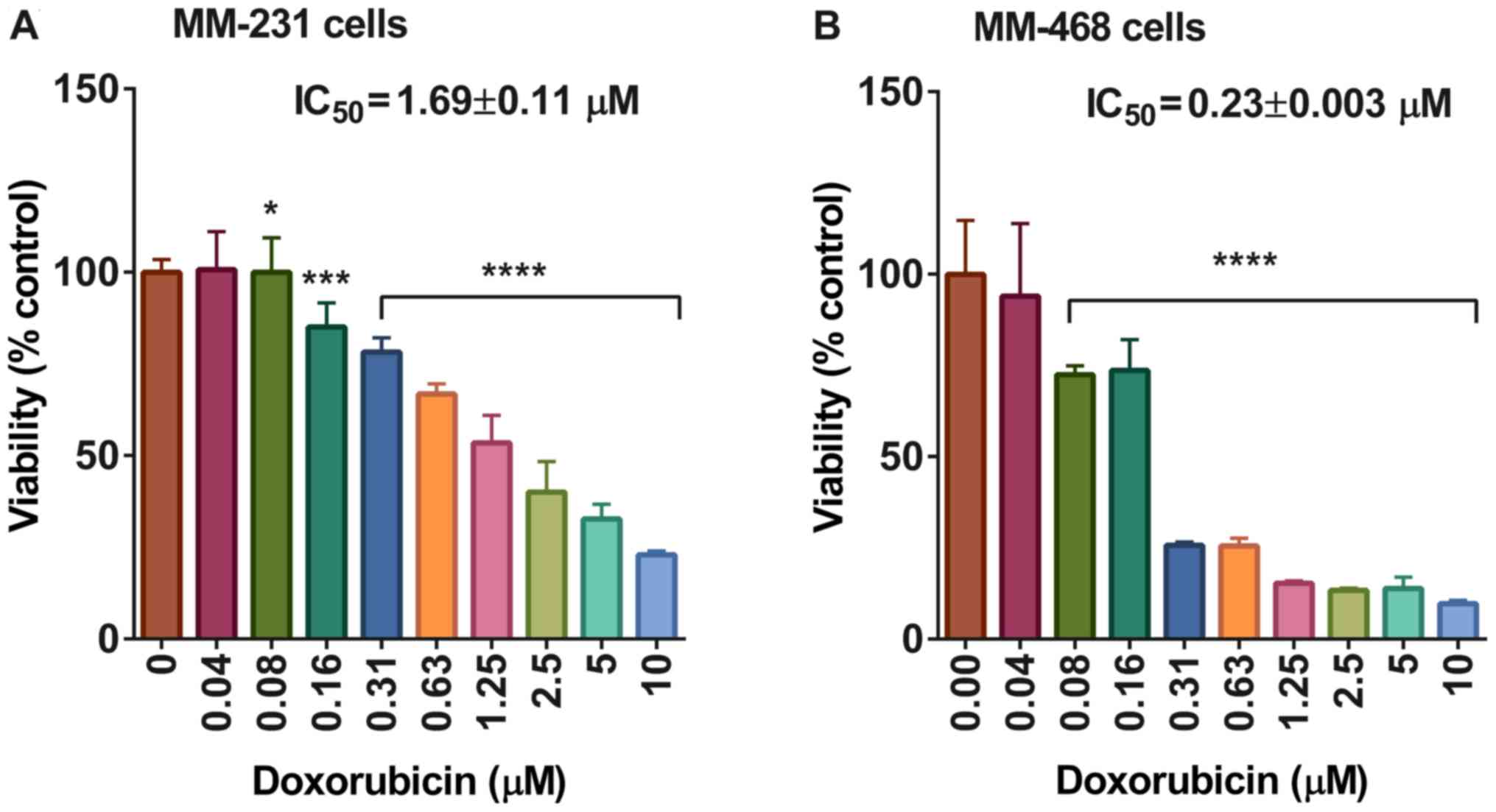
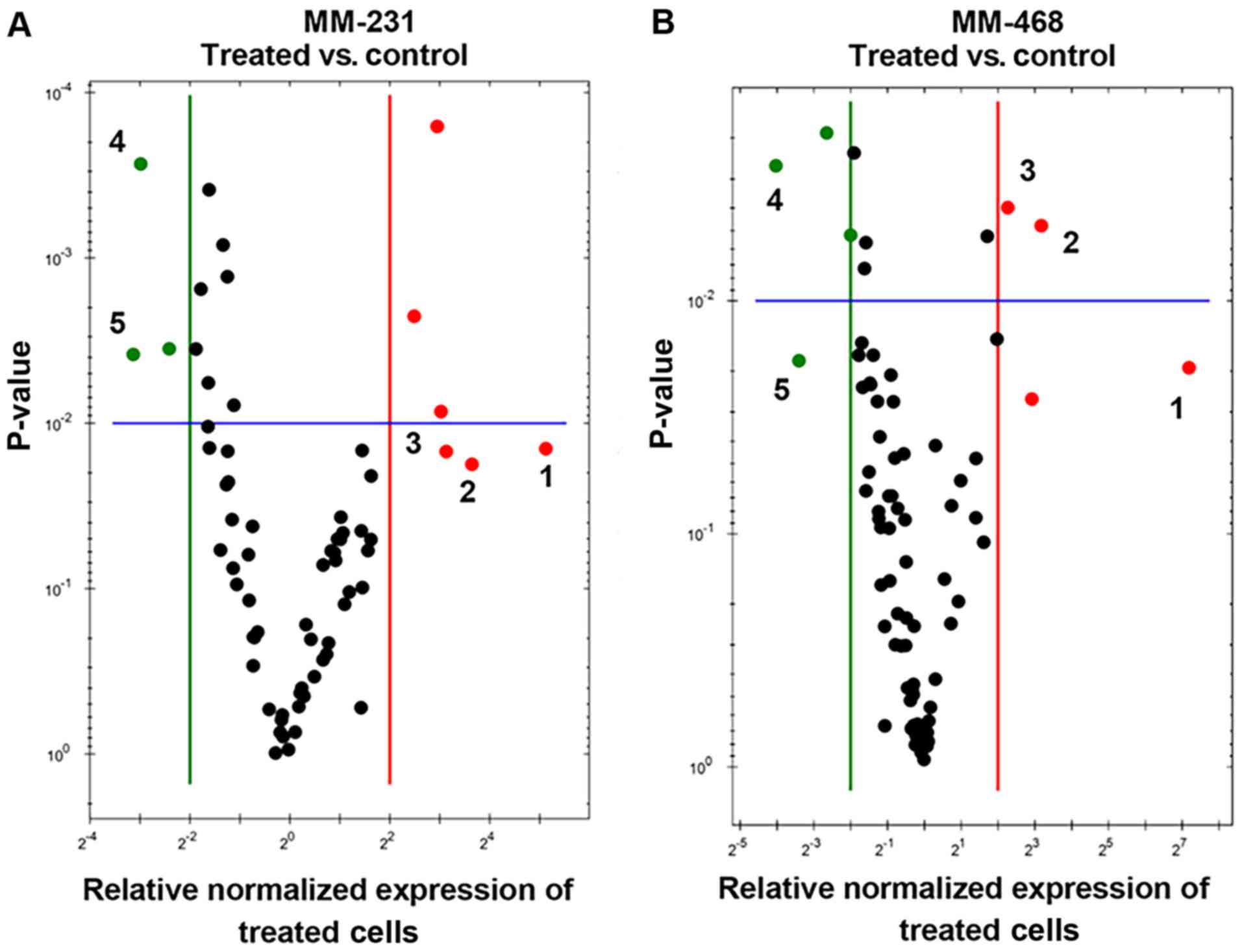
|
1
|
Al-Romaih K, Sadikovic B, Yoshimoto M,
Wang Y, Zielenska M and Squire JA: Decitabine-induced demethylation
of 5′ CpG island in GADD45A leads to apoptosis in osteosarcoma
cells. Neoplasia. 10:471–480. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Albain KS, Unger JM, Crowley JJ, Coltman
CA Jr and Hershman DL: Racial disparities in cancer survival among
randomized clinical trials patients of the Southwest oncology
group. J Natl Cancer Inst. 101:984–992. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alderson MR, Smith CA, Tough TW,
Davis-Smith T, Armitage RJ, Falk B, Roux E, Baker E, Sutherland GR
and Din WS: Molecular and biological characterization of human
4-1BB and its ligand. Eur J Immunol. 24:2219–2227. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schulze-Osthoff K, Ferrari D, Los M,
Wesselborg S and Peter ME: Apoptosis signaling by death receptors.
Eur J Biochem. 254:439–459. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mishra AP, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad M,
Pezzani R, Kobarfard F, Sharifi-Rad J and Nigam M: Programmed cell
death, from a cancer perspective: An overview. Mol Diagn Ther.
22:281–295. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wali JA, Masters SL and Thomas HE: Linking
metabolic abnormalities to apoptotic pathways in Beta cells in type
2 diabetes. Cells. 2:266–283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M,
Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B and Reed JC: Tumor
suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in
vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 9:1799–1805. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kang MH and Reynolds CP: Bcl-2 inhibitors:
Targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:1126–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fulda S: Targeting inhibitor of apoptosis
proteins (IAPs) for cancer therapy. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
8:533–539. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mannhold R, Fulda S and Carosati E: IAP
antagonists: Promising candidates for cancer therapy. Drug Discov
Today. 15:210–219. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
DeSantis CE, Fedewa SA, Goding Sauer A,
Kramer JL, Smith RA and Jemal A: Breast cancer statistics, 2015:
Convergence of incidence rates between black and white women. CA
Cancer J Clin. 66:31–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anders CK and Carey LA: Biology,
metastatic patterns, and treatment of patients with triple-negative
breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 9 (Suppl 2):S73–S81. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Beaumont T and Leadbeater M: Treatment and
care of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Nurs Stand.
25:49–56. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fernández Y, Cueva J, Palomo AG, Ramos M,
de Juan A, Calvo L, García-Mata J, García-Teijido P, Peláez I and
García-Estévez L: Novel therapeutic approaches to the treatment of
metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 36:33–42. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu P, Kumar IS, Brown S, Kannappan V,
Tawari PE, Tang JZ, Jiang W, Armesilla AL, Darling JL and Wang W:
Disulfiram targets cancer stem-like cells and reverses resistance
and cross-resistance in acquired paclitaxel-resistant
triple-negative breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 109:1876–1885.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Craig DW, O'Shaughnessy JA, Kiefer JA,
Aldrich J, Sinari S, Moses TM, Wong S, Dinh J, Christoforides A,
Blum JL, et al: Genome and transcriptome sequencing in prospective
metastatic triple-negative breast cancer uncovers therapeutic
vulnerabilities. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:104–116. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cao H, Sethumadhavan K and Bland JM:
Isolation of cottonseed extracts that affect human cancer cell
growth. Sci Rep. 8:104582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He Z, Zhang H and Olk DC: Chemical
composition of defatted cottonseed and soy meal products. PLoS One.
10:e01299332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sharifi-Rad M, Fokou PVT, Sharopov F,
Martorell M, Ademiluyi AO, Rajkovic J, Salehi B, Martins N, Iriti M
and Sharifi-Rad J: Antiulcer agents: From plant extracts to
phytochemicals in healing promotion. Molecules. 23(pii): E17512018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin TS, Schinazi RF, Zhu J, Birks E,
Carbone R, Si Y, Wu K, Huang L and Prusoff WH: Anti-HIV-1 activity
and cellular pharmacology of various analogs of gossypol. Biochem
Pharmacol. 46:251–255. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Janero DR and Burghardt B: Protection of
rat myocardial phospholipid against peroxidative injury through
superoxide-(xanthine oxidase)-dependent, iron-promoted fenton
chemistry by the male contraceptive gossypol. Biochem Pharmacol.
37:3335–3342. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu S, Kulp SK, Sugimoto Y, Jiang J, Chang
HL, Dowd MK, Wan P and Lin YC: The (−)-enantiomer of gossypol
possesses higher anticancer potency than racemic gossypol in human
breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 22:33–38. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Moon DO, Kim MO, Lee JD and Kim GY:
Gossypol suppresses NF-kappaB activity and NF-kappaB-related gene
expression in human leukemia U937 cells. Cancer Lett. 264:192–200.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Voss V, Senft C, Lang V, Ronellenfitsch
MW, Steinbach JP, Seifert V and Kögel D: The pan-Bcl-2 inhibitor
(−)-gossypol triggers autophagic cell death in malignant glioma.
Mol Cancer Res. 8:1002–1016. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang M, Liu H, Guo R, Ling Y, Wu X, Li B,
Roller PP, Wang S and Yang D: Molecular mechanism of
gossypol-induced cell growth inhibition and cell death of HT-29
human colon carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 66:93–103. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pang X, Wu Y, Wu Y, Lu B, Chen J, Wang J,
Yi Z, Qu W and Liu M: (−)-Gossypol suppresses the growth of human
prostate cancer xenografts via modulating VEGF signaling-mediated
angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:795–805. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Flack MR, Pyle RG, Mullen NM, Lorenzo B,
Wu YW, Knazek RA, Nisula BC and Reidenberg MM: Oral gossypol in the
treatment of metastatic adrenal cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
76:1019–1024. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moon DO, Choi YH, Moon SK, Kim WJ and Kim
GY: Gossypol decreases tumor necrosis factor-α-induced
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression via suppression of
NF-κB activity. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:999–1005. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gilbert NE, O'Reilly JE, Chang CJ, Lin YC
and Brueggemeier RW: Antiproliferative activity of gossypol and
gossypolone on human breast cancer cells. Life Sci. 57:61–67. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu YF, Chang CJ, Brueggemeier RW and Lin
YC: Gossypol inhibits basal and estrogen-stimulated DNA synthesis
in human breast carcinoma cells. Life Sci. 53:Pl433–Pl438. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ye W, Chang HL, Wang LS, Huang YW, Shu S,
Sugimoto Y, Dowd MK, Wan PJ and Lin YC: Induction of apoptosis by
(−)-gossypol-enriched cottonseed oil in human breast cancer cells.
Int J Mol Med. 26:113–119. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lin J, Wu Y, Yang D and Zhao Y: Induction
of apoptosis and antitumor effects of a small molecule inhibitor of
Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl, gossypol acetate, in multiple myeloma in
vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep. 30:731–738. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sadahira K, Sagawa M, Nakazato T, Uchida
H, Ikeda Y, Okamoto S, Nakajima H and Kizaki M: Gossypol induces
apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells by inhibition of interleukin-6
signaling and Bcl-2/Mcl-1 pathway. Int J Oncol. 45:2278–2286. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baoleri X, Dong C, Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Lu X,
Xie P and Li Y: Combination of L-gossypol and low-concentration
doxorubicin induces apoptosis in human synovial sarcoma cells. Mol
Med Rep. 12:5924–5932. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Benvenuto M, Mattera R, Masuelli L,
Taffera G, Andracchio O, Tresoldi I, Lido P, Giganti MG, Godos J,
Modesti A and Bei R: (±)-Gossypol induces apoptosis and autophagy
in head and neck carcinoma cell lines and inhibits the growth of
transplanted salivary gland cancer cells in BALB/c mice. Int J Food
Sci Nutr. 68:298–312. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao GX, Xu LH, Pan H, Lin QR, Huang MY,
Cai JY, Ouyang DY and He XH: The BH3-mimetic gossypol and
noncytotoxic doses of valproic acid induce apoptosis by suppressing
cyclin-A2/Akt/FOXO3a signaling. Oncotarget. 6:38952–38966. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang M, Liu H, Tian Z, Griffith BN, Ji M
and Li QQ: Gossypol induces apoptosis in human PC-3 prostate cancer
cells by modulating caspase-dependent and caspase-independent cell
death pathways. Life Sci. 80:767–774. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Volate SR, Kawasaki BT, Hurt EM, Milner
JA, Kim YS, White J and Farrar WL: Gossypol induces apoptosis by
activating p53 in prostate cancer cells and prostate
tumor-initiating cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:461–470. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu MD, Li LY, Li PH, You T, Wang FH, Sun
WJ and Zheng ZQ: Gossypol induces cell death by activating
apoptosis and autophagy in HT-29 cells. Mol Med Rep. 16:2128–2132.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jin L, Chen Y, Mu X, Lian Q, Deng H and Ge
R: Phosphoproteomic analysis of gossypol-induced apoptosis in
ovarian cancer cell line, HOC1a. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1234822014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang J, Jin L, Li X and Deng H, Chen Y,
Lian Q, Ge R and Deng H: Gossypol induces apoptosis in ovarian
cancer cells through oxidative stress. Mol Biosyst. 9:1489–1497.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xin J, Zhan YH, Xia LM, Zhu HW, Nie YZ,
Liang JM and Tian J: ApoG2 as the most potent gossypol derivatives
inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis on gastric cancer cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 67:88–95. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheng W, Zhao YQ, Li YM and Yang DJ:
Effects of gossypol acetate on apoptosis in primary cultured cells
from patients with lymphoid leukemia and its synergy with
dexamethasone. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 20:229–234.
2012.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Balakrishnan K, Wierda WG, Keating MJ and
Gandhi V: Gossypol, a BH3 mimetic, induces apoptosis in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood. 112:1971–1980. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tang J, Wang Z, Chen L, Huang G and Hu X:
Gossypol acetate induced apoptosis of pituitary tumor cells by
targeting the BCL-2 via the upregulated microRNA miR-15a. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 8:9079–9085. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Karaca B, Atmaca H, Uzunoglu S, Karabulut
B, Sanli UA and Uslu R: Enhancement of taxane-induced cytotoxicity
and apoptosis by gossypol in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7. J
BUON. 14:479–485. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yoshida R, Niki M, Jyotaki M, Sanematsu K,
Shigemura N and Ninomiya Y: Modulation of sweet responses of taste
receptor cells. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 24:226–231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tate CR, Rhodes LV, Segar HC, Driver JL,
Pounder FN, Burow ME and Collins-Burow BM: Targeting
triple-negative breast cancer cells with the histone deacetylase
inhibitor panobinostat. Breast Cancer Res. 14:R792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Messeha SS, Zarmouh NO, Mendonca P,
Alwagdani H, Kolta MG and Soliman KFA: The inhibitory effects of
plumbagin on the NF-κB pathway and CCL2 release in racially
different triple-negative breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
13:e02011162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Citalingam K, Abas F, Lajis NH, Othman I
and Naidu R: Anti-proliferative effect and induction of apoptosis
in androgen-independent human prostate cancer cells by
1,5-bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4-pentadiene-3-one. Molecules.
20:3406–3430. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chougule MB, Patel AR, Jackson T and Singh
M: Antitumor activity of noscapine in combination with doxorubicin
in triple negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 6:e177332011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Plati J, Bucur O and Khosravi-Far R:
Dysregulation of apoptotic signaling in cancer: Molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Cell Biochem.
104:1124–1149. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kretschmer C, Sterner-Kock A, Siedentopf
F, Schoenegg W, Schlag PM and Kemmner W: Identification of early
molecular markers for breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 10:152011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ma XJ, Salunga R, Tuggle JT, Gaudet J,
Enright E, McQuary P, Payette T, Pistone M, Stecker K, Zhang BM, et
al: Gene expression profiles of human breast cancer progression.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:5974–5979. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Van Poznak C, Seidman AD, Reidenberg MM,
Moasser MM, Sklarin N, Van Zee K, Borgen P, Gollub M, Bacotti D,
Yao TJ, et al: Oral gossypol in the treatment of patients with
refractory metastatic breast cancer: A phase I/II clinical trial.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 66:239–248. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:872011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhan Q: Gadd45a, a p53- and
BRCA1-regulated stress protein, in cellular response to DNA damage.
Mutat Res. 569:133–143. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tront JS, Willis A, Huang Y, Hoffman B and
Liebermann DA: Gadd45a levels in human breast cancer are hormone
receptor dependent. J Transl Med. 11:1312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Desjardins S, Ouellette G, Labrie Y,
Simard J; INHERIT BRCAs, ; Durocher F: Analysis of GADD45A sequence
variations in French Canadian families with high risk of breast
cancer. J Hum Genet. 53:490–498. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Takekawa M and Saito H: A family of
stress-inducible GADD45-like proteins mediate activation of the
stress-responsive MTK1/MEKK4 MAPKKK. Cell. 95:521–530. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Harkin DP, Bean JM, Miklos D, Song YH,
Truong VB, Englert C, Christians FC, Ellisen LW, Maheswaran S,
Oliner JD and Haber DA: Induction of GADD45 and JNK/SAPK-dependent
apoptosis following inducible expression of BRCA1. Cell.
97:575–586. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yasuda M, Theodorakis P, Subramanian T and
Chinnadurai G: Adenovirus E1B-19K/BCL-2 interacting protein BNIP3
contains a BH3 domain and a mitochondrial targeting sequence. J
Biol Chem. 273:12415–12421. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bandyopadhyay S, Zhan R, Wang Y, Pai SK,
Hirota S, Hosobe S, Takano Y, Saito K, Furuta E, Iiizumi M, et al:
Mechanism of apoptosis induced by the inhibition of fatty acid
synthase in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:5934–5940. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Vande Velde C, Cizeau J, Dubik D, Alimonti
J, Brown T, Israels S, Hakem R and Greenberg AH: BNIP3 and genetic
control of necrosis-like cell death through the mitochondrial
permeability transition pore. Mol Cell Biol. 20:5454–5468. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Khan A, Aljarbou AN, Aldebasi YH, Faisal
SM and Khan MA: Resveratrol suppresses the proliferation of breast
cancer cells by inhibiting fatty acid synthase signaling pathway.
Cancer Epidemiol. 38:765–772. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Silva JC, Ferreira-Strixino J, Fontana LC,
Paula LM, Raniero L, Martin AA and Canevari RA:
Apoptosis-associated genes related to photodynamic therapy in
breast carcinomas. Lasers Med Sci. 29:1429–1436. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ruddle NH: Tumor necrosis factor
(TNF-alpha) and lymphotoxin (TNF-beta). Curr Opin Immunol.
4:327–332. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Rath PC and Aggarwal BB: TNF-induced
signaling in apoptosis. J Clin Immunol. 19:350–364. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Robbs BK, Lucena PI and Viola JP: The
transcription factor NFAT1 induces apoptosis through cooperation
with Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway and upregulation of TNF-α expression.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1833:2016–2028. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Balkwill F: TNF-alpha in promotion and
progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:409–416. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Szlosarek PW and Balkwill FR: Tumour
necrosis factor alpha: A potential target for the therapy of solid
tumours. Lancet Oncol. 4:565–573. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Balkwill F: Tumor necrosis factor or tumor
promoting factor? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13:135–141. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Luo JL, Maeda S, Hsu LC, Yagita H and
Karin M: Inhibition of NF-kappaB in cancer cells converts
inflammation-induced tumor growth mediated by TNFalpha to
TRAIL-mediated tumor regression. Cancer Cell. 6:297–305. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hassan M, Watari H, AbuAlmaaty A, Ohba Y
and Sakuragi N: Apoptosis and molecular targeting therapy in
cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014:1508452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Hahne M, Kataoka T, Schröter M, Hofmann K,
Irmler M, Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Bornand T, Holler N, French LE,
et al: APRIL, a new ligand of the tumor necrosis factor family,
stimulates tumor cell growth. J Exp Med. 188:1185–1190. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Schwarz H, Valbracht J, Tuckwell J, von
Kempis J and Lotz M: ILA, the human 4-1BB homologue, is inducible
in lymphoid and other cell lineages. Blood. 85:1043–1052.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bellarosa D, Bressan A, Bigioni M, Parlani
M, Maggi CA and Binaschi M: SAHA/Vorinostat induces the expression
of the CD137 receptor/ligand system and enhances apoptosis mediated
by soluble CD137 receptor in a human breast cancer cell line. Int J
Oncol. 41:1486–1494. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hingorani P, Dickman P, Garcia-Filion P,
White-Collins A, Kolb EA and Azorsa DO: BIRC5 expression is a poor
prognostic marker in ewing sarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 60:35–40.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Jha K, Shukla M and Pandey M: Survivin
expression and targeting in breast cancer. Surg Oncol. 21:125–131.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Shin S, Sung BJ, Cho YS, Kim HJ, Ha NC,
Hwang JI, Chung CW, Jung YK and Oh BH: An anti-apoptotic protein
human survivin is a direct inhibitor of caspase-3 and −7.
Biochemistry. 40:1117–1123. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ghaffari K, Hashemi M, Ebrahimi E and
Shirkoohi R: BIRC5 genomic copy number variation in early-onset
breast cancer. Iran Biomed J. 20:241–245. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Mahlamäki EH, Bärlund M, Tanner M,
Gorunova L, Höglund M, Karhu R and Kallioniemi A: Frequent
amplification of 8q24, 11q, 17q, and 20q-specific genes in
pancreatic cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 35:353–358. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Baykara O, Bakir B, Buyru N, Kaynak K and
Dalay N: Amplification of chromosome 8 genes in lung cancer. J
Cancer. 6:270–275. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Gunaldi M, Isiksacan N, Kocoglu H,
Okuturlar Y, Gunaldi O, Topcu TO and Karabulut M: The value of
serum survivin level in early diagnosis of cancer. J Cancer Res
Ther. 14:570–573. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kato J, Kuwabara Y, Mitani M, Shinoda N,
Sato A, Toyama T, Mitsui A, Nishiwaki T, Moriyama S, Kudo J and
Fujii Y: Expression of survivin in esophageal cancer: Correlation
with the prognosis and response to chemotherapy. Int J Cancer.
95:92–95. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Coumar MS, Tsai FY, Kanwar JR, Sarvagalla
S and Cheung CH: Treat cancers by targeting survivin: Just a dream
or future reality? Cancer Treat Rev. 39:802–811. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Gu J, Ren L, Wang X, Qu C and Zhang Y:
Expression of livin, survivin, and caspase-3 in prostatic cancer
and their clinical significance. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:14034–14039. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wu B, Yao H, Wang S and Xu R: DAPK1
modulates a curcumin-induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis by
regulating STAT3, NF-κB, and caspase-3 activation. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 434:75–80. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Yoo HJ, Byun HJ, Kim BR, Lee KH, Park SY
and Rho SB: DAPk1 inhibits NF-κB activation through TNF-α and
INF-γ-induced apoptosis. Cell Signal. 24:1471–1477. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Pozniak CD, Radinovic S, Yang A, McKeon F,
Kaplan DR and Miller FD: An anti-apoptotic role for the p53 family
member, p73, during developmental neuron death. Science.
289:304–306. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Melino G, De Laurenzi V and Vousden KH:
p73: Friend or foe in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:605–615.
2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Huang L, Li A, Liao G, Yang F, Yang J,
Chen X and Jiang X: Curcumol triggers apoptosis of p53 mutant
triple-negative human breast cancer MDA-MB 231 cells via activation
of p73 and PUMA. Oncol Lett. 14:1080–1088. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Yamamoto T, Oda K, Kubota T, Miyazaki K,
Takenouti Y, Nimura Y, Hamaguchi M and Matsuda S: Expression of p73
gene, cell proliferation and apoptosis in breast cancer:
Immunohistochemical and clinicopathological study. Oncol Rep.
9:729–735. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yu XJ, Fang F and Xie J: Relationship
between TP73 polymorphism (G4C14-A4T14) and cancer risk: A
meta-analysis based on literatures. Gene. 484:42–46. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Jung JH, Chae YS, Moon JH, Kang BW, Kim
JG, Sohn SK, Park JY, Lee MH and Park HY: TNF superfamily gene
polymorphism as prognostic factor in early breast cancer. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 136:685–694. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Jarvis WD, Turner AJ, Povirk LF, Traylor
RS and Grant S: Induction of apoptotic DNA fragmentation and cell
death in HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cells by
pharmacological inhibitors of protein kinase C. Cancer Res.
54:1707–1714. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wang Y and Rao PN: Effect of gossypol on
DNA synthesis and cell cycle progression of mammalian cells in
vitro. Cancer Res. 44:35–38. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Kitada S, Leone M, Sareth S, Zhai D, Reed
JC and Pellecchia M: Discovery, characterization, and
structure-activity relationships studies of proapoptotic
polyphenols targeting B-cell lymphocyte/leukemia-2 proteins. J Med
Chem. 46:4259–4264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Oliver CL, Miranda MB, Shangary S, Land S,
Wang S and Johnson DE: (−)-Gossypol acts directly on the
mitochondria to overcome Bcl-2- and Bcl-X(L)-mediated apoptosis
resistance. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:23–31. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Lei X, Chen Y, Du G, Yu W, Wang X, Qu H,
Xia B, He H, Mao J, Zong W, et al: Gossypol induces
Bax/Bak-independent activation of apoptosis and cytochrome c
release via a conformational change in Bcl-2. FASEB J.
20:2147–2149. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|