|
1
|
Hughes MF: Arsenic toxicity and potential
mechanisms of action. Toxicol Lett. 133:1–16. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
IARC, . Arsenic and inorganic arsenic
compounds. http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/latest_classif.phpWorld
Health Organization. 1-121:41–94. 2012.
|
|
3
|
Lee-Feldstein A: Cumulative exposure to
arsenic and its relationship to respiratory cancer among copper
smelter employees. J Occup Med. 28:296–302. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tseng WP: Effects and dose-response
relationships of skin cancer and blackfoot disease with arsenic.
Environ Health Perspect. 19:109–119. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cebrian ME, Albores A, Aguilar M and
Blakely E: Chronic arsenic poisoning in the north of Mexico. Hum
Toxicol. 2:121–133. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chiou HY, Chiou ST, Hsu YH, Chou YL, Tseng
CH, Wei ML and Chen CJ: Incidence of transitional cell carcinoma
and arsenic in drinking water: A follow-up study of 8,102 residents
in an arseniasis-endemic area in northeastern Taiwan. Am J
Epidemiol. 153:411–418. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hopenhayn-Rich C, Biggs ML, Fuchs A,
Bergoglio R, Tello EE, Nicolli H and Smith AH: Bladder cancer
mortality associated with arsenic in drinking water in Argentina.
Epidemiology. 7:117–124. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Smith AH, Goycolea M, Haque R and Biggs
ML: Marked increase in bladder and lung cancer mortality in a
region of Northern Chile due to arsenic in drinking water. Am J
Epidemiol. 147:660–669. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen CJ, Chuang YC, You SL, Lin TM and Wu
HY: A retrospective study on malignant neoplasms of bladder, lung
and liver in blackfoot disease endemic area in Taiwan. Br J Cancer.
53:399–405. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tokar EJ, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Ward JM,
Lunn R, Sams RL II and Waalkes MP: Cancer in experimental animals
exposed to arsenic and arsenic compounds. Crit Rev Toxicol.
40:912–927. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wei M, Wanibuchi H, Morimura K, Iwai S,
Yoshida K, Endo G, Nakae D and Fukushima S: Carcinogenicity of
dimethylarsinic acid in male F344 rats and genetic alterations in
induced urinary bladder tumors. Carcinogenesis. 23:1387–1397. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cohen SM, Ohnishi T, Arnold LL and Le XC:
Arsenic-induced bladder cancer in an animal model. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 222:258–263. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Arnold LL, Eldan M, Nyska A, van Gemert M
and Cohen SM: Dimethylarsinic acid: Results of chronic
toxicity/oncogenicity studies in F344 rats and in B6C3F1 mice.
Toxicology. 223:82–100. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yokohira M, Arnold LL, Pennington KL,
Suzuki S, Kakiuchi-Kiyota S, Herbin-Davis K, Thomas DJ and Cohen
SM: Effect of sodium arsenite dose administered in the drinking
water on the urinary bladder epithelium of female arsenic (+3
oxidation state) methyltransferase knockout mice. Toxicol Sci.
121:257–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arnold LL, Suzuki S, Yokohira M,
Kakiuchi-Kiyota S, Pennington KL and Cohen SM: Time course of
urothelial changes in rats and mice orally administered arsenite.
Toxicol Pathol. 42:855–862. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dai YC, Wang SC, Haque MM, Lin WH, Lin LC,
Chen CH and Liu YW: The interaction of arsenic and
N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine on urothelial carcinogenesis
in mice. PLoS One. 12:e01862142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Su PF, Hu YJ, Ho IC, Cheng YM and Lee TC:
Distinct gene expression profiles in immortalized human urothelial
cells exposed to inorganic arsenite and its methylated trivalent
metabolites. Environ Health Perspect. 114:394–403. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Medeiros M, Zheng X, Novak P, Wnek SM,
Chyan V, Escudero-Lourdes C and Gandolfi AJ: Global gene expression
changes in human urothelial cells exposed to low-level
monomethylarsonous acid. Toxicology. 291:102–112. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Boivin GP, Bottomley MA, Schimi PA, Goss L
and Grobe N: Physiologic, behavioral, and histologic responses to
various euthanasia methods in C57BL/6NTac male mice. J Am Assoc Lab
Anim Sci. 56:69–78. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Leary S, Underwood W, Anthony R, Cartner
S, Corey D, Grandin T, Greenacre C, Gwaltney-Brant S, MaCrackin MA,
Meyer R, et al: AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals.
2013.edition.
|
|
21
|
Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG; National centre for the replacement refinement and
reduction of animals in research, : Animal research: Reporting in
vivo experiments-the ARRIVE guidelines. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
31:991–993. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weng L, Dai H, Zhan Y, He Y, Stepaniants
SB and Bassett DE: Rosetta error model for gene expression
analysis. Bioinformatics. 22:1111–1121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shen CH, Wang ST, Wang SC, Lin SM, Lin LC,
Dia YC and Liu YW: Ketamine-induced bladder dysfunction is
associated with extracellular matrix accumulation and impairment of
clacium signaling in a mouse model. Mol Med Rep. 19:2716–2728.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dodmane PR, Arnold LL, Muirhead DE, Suzuki
S, Yokohira M, Pennington KL, Dave BJ, Lu X, Le XC and Cohen SM:
Characterization of intracellular inclusions in the urothelium of
mice exposed to inorganic arsenic. Toxicol Sci. 137:36–46. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gai JW, Qin W, Liu M, Wang HF, Zhang M, Li
M, Zhou WH, Ma QT, Liu GM, Song WH, et al: Expression profile of
hydrogen sulfide and its synthases correlates with tumor stage and
grade in urothelial cell carcinoma of bladder. Urol Oncol.
34:166.e15–e20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xue G, Lu CJ, Pan SJ, Zhang YL, Miao H,
Shan S, Zhu XT and Zhang Y: DNA hypomethylation of CBS promoter
induced by folate deficiency is a potential noninvasive circulating
biomarker for colorectal adenocarcinomas. Oncotarget.
8:51387–51401. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li C, Cui Y, Liu LF, Ren WB, Li QQ, Zhou
X, Li YL, Li Y, Bai XY and Zu XB: High expression of long noncoding
RNA MALAT1 indicates a poor prognosis and promotes clinical
progression and metastasis in bladder cancer. Clin Genitourin
Cancer. 15:570–576. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang C, Mao ZP, Wang L, Wu GH, Zhang FH,
Wang DY and Shi JL: Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes
cholangiocarcinoma cell proliferation and invasion by activating
PI3K/Akt pathway. Neoplasma. 64:725–731. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mirza A, Basso A, Black S, Malkowski M,
Kwee L, Pachter JA, Lachowicz JE, Wang Y and Liu S: RNA
interference targeting of A1 receptor-overexpressing breast
carcinoma cells leads to diminished rates of cell proliferation and
induction of apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:1355–1360. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dastjerdi MN, Rarani MZ, Valiani A and
Mahmoudieh M: The effect of adenosine A1 receptor agonist and
antagonist on p53 and caspase 3, 8, and 9 expression and apoptosis
rate in MCF-7 breast cancer cell line. Res Pharm Sci. 11:303–310.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wissmann C, Wild PJ, Kaiser S, Roepcke S,
Stoehr R, Woenckhaus M, Kristiansen G, Hsieh JC, Hofstaedter F,
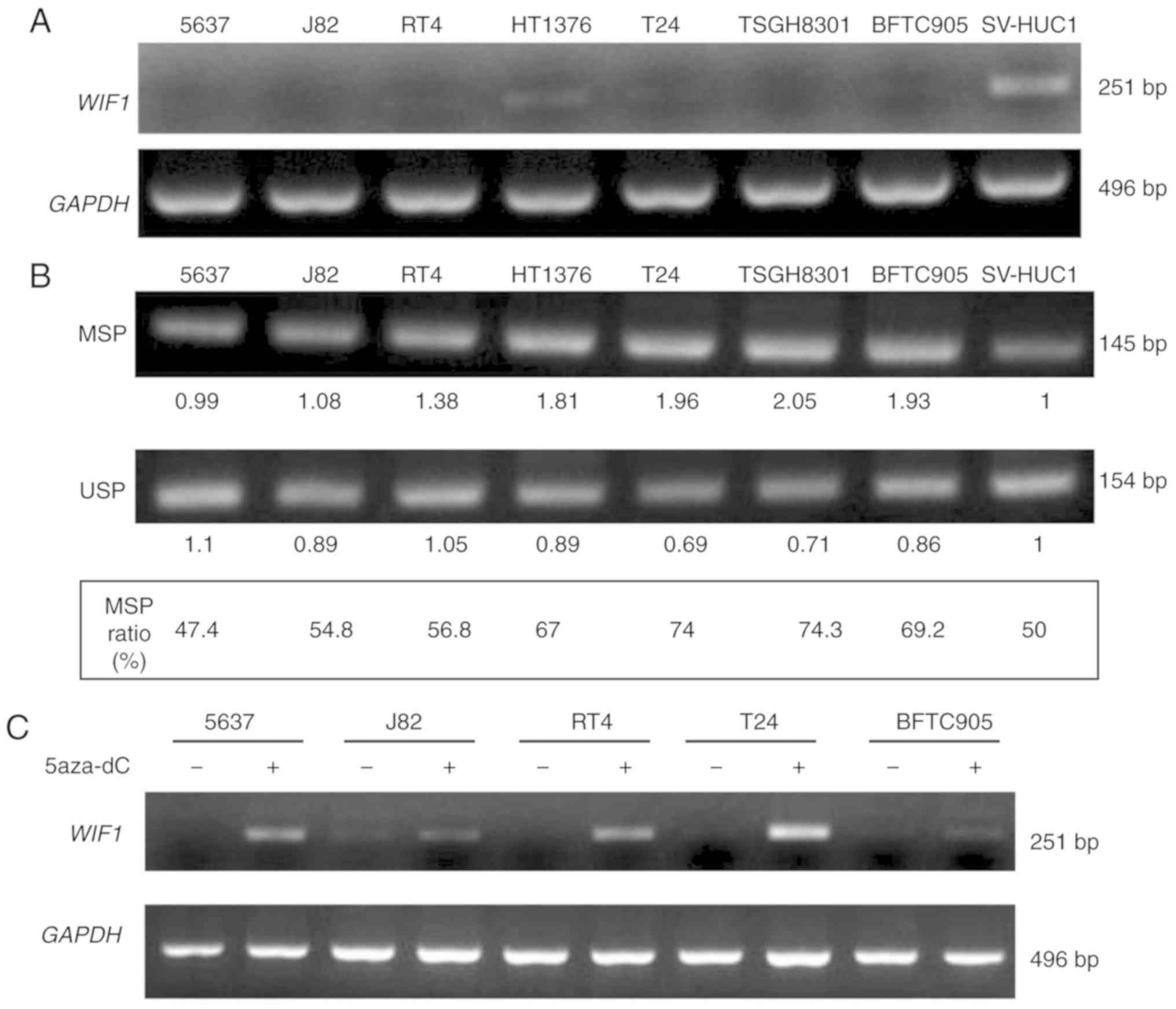
Hartmann A, et al: WIF1, a component of the Wnt pathway, is
down-regulated in prostate, breast, lung, and bladder cancer. J
Pathol. 201:204–212. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Urakami S, Shiina H, Enokida H, Kawakami
T, Tokizane T, Ogishima T, Tanaka Y, Li LC, Ribeiro-Filho LA,
Terashima M, et al: Epigenetic inactivation of Wnt inhibitory
factor-1 plays an important role in bladder cancer through aberrant
canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res.
12:383–391. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu P, Shen JK, Hornicek FJ, Liu F and
Duan Z: Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF1) methylation and its
association with clinical prognosis in patients with
chondrosarcoma. Sci Rep. 7:15802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Guo H, Zhou S, Tan L, Wu X, Wu Z and Ran
R: Clinicopathological significance of WIF1 hypermethylation in
NSCLC, a meta-analysis and literature review. Oncotarget.
8:2550–2557. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Watanabe T and Hirano S: Metabolism of
arsenic and its toxicological relevance. Arch Toxicol. 87:969–979.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Styblo M, Del Razo LM, Vega L, Germolec
DR, LeCluyse EL, Hamilton GA, Reed W, Wang C, Cullen WR and Thomas
DJ: Comparative toxicity of trivalent and pentavalent inorganic and
methylated arsenicals in rat and human cells. Arch Toxicol.
74:289–299. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wanibuchi H, Salim EI, Kinoshita A, Shen
J, Wei M, Morimura K, Yoshida K, Kuroda K, Endo G and Fukushima S:
Understanding arsenic carcinogenicity by the use of animal models.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 198:366–376. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cui X, Wakai T, Shirai Y, Hatakeyama K and
Hirano S: Chronic oral exposure to inorganic arsenate interferes
with methylation status of p16INK4a and RASSF1A and induces lung
cancer in A/J mice. Toxicol Sci. 91:372–381. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kawano Y and Kypta R: Secreted antagonists
of the Wnt signalling pathway. J Cell Sci. 116:2627–2634. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Duchartre Y, Kim YM and Kahn M: The Wnt
signaling pathway in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 99:141–149.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Niehrs C: The complex world of WNT
receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:767–779. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang X, Wang H, Bu R, Fei X, Zhao C and
Song Y: Methylation and aberrant expression of the Wnt antagonist
secreted Frizzled-related protein 1 in bladder cancer. Oncol Lett.
4:334–338. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jhee KH and Kruger WD: The role of
cystathionine beta-synthase in homocysteine metabolism. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 7:813–822. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lan B, Zhang J, Zhang P, Zhang W, Yang S,
Lu D, Li W and Dai Q: Metformin suppresses CRC growth by inducing
apoptosis via ADORA1. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 22:248–257. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Baris D, Waddell R, Beane Freeman LE,
Schwenn M, Colt JS, Ayotte JD, Ward MH, Nuckols J, Schned A,
Jackson B, et al: Elevated bladder cancer in northern New England:
The role of drinking water and arsenic. J Natl Cancer Inst.
108(pii): djw0992016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Saint-Jacques N, Parker L, Brown P and
Dummer TJ: Arsenic in drinking water and urinary tract cancers: A
systematic review of 30 years of epidemiological evidence. Environ
Health. 13:442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chuang JJ, Dai YC, Lin YL, Chen YY, Lin
WH, Chan HL and Liu YW: Downregulation of glutathione S-transferase
M1 protein in N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine-induced mouse
bladder carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 279:322–330. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Engel LS, Taioli E, Pfeiffer R,
Garcia-Closas M, Marcus PM, Lan Q, Boffetta P, Vineis P, Autrup H,
Bell DA, et al: Pooled analysis and meta-analysis of glutathione
S-transferase M1 and bladder cancer: A HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol.
156:95–109. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Williams PD, Lee JK and Theodorescu D:
Molecular credentialing of rodent bladder carcinogenesis models.
Neoplasia. 10:838–846. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Juan YS, Lee YL, Long CY, Wong JH, Jang
MY, Lu JH, Wu WJ, Huang YS, Chang WC and Chuang SM: Translocation
of NF-κB and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 are enhanced by
ketamine-induced ulcerative cystitis in rat bladder. Am J Pathol.
185:2269–2285. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Shen CH, Wang SC, Wang ST, Lin SM, Wu JD,
Lin CT and Liu YW: Evaluation of urinary bladder fibrogenesis in a
mouse model of long-term ketamine injection. Mol Med Rep.
14:1880–1890. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|