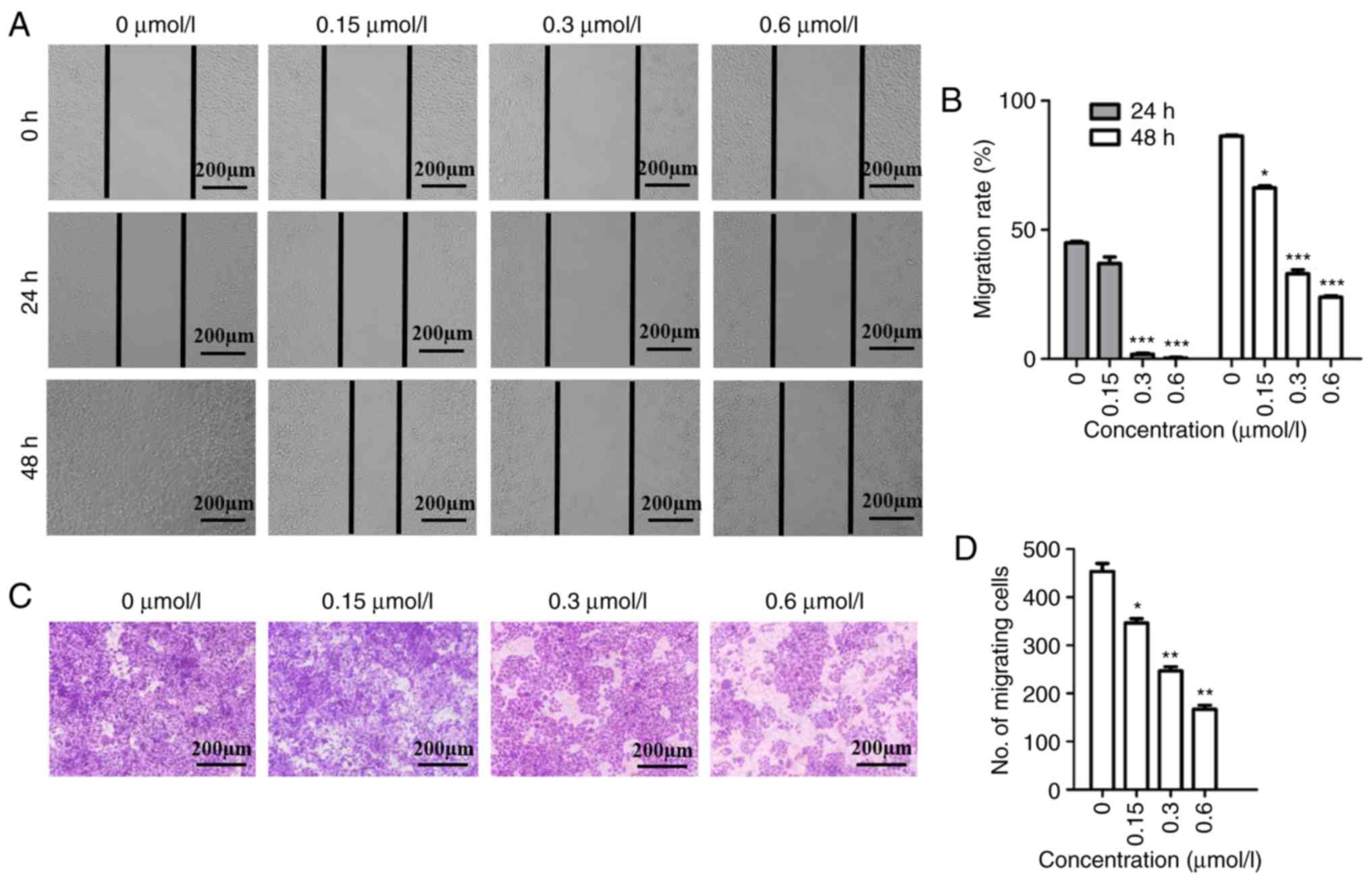
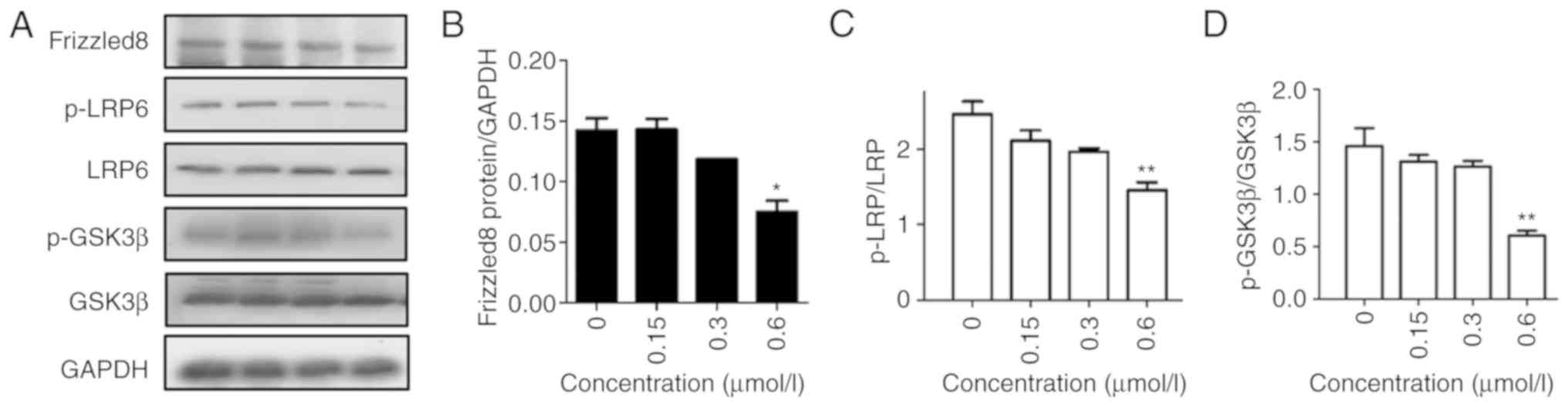
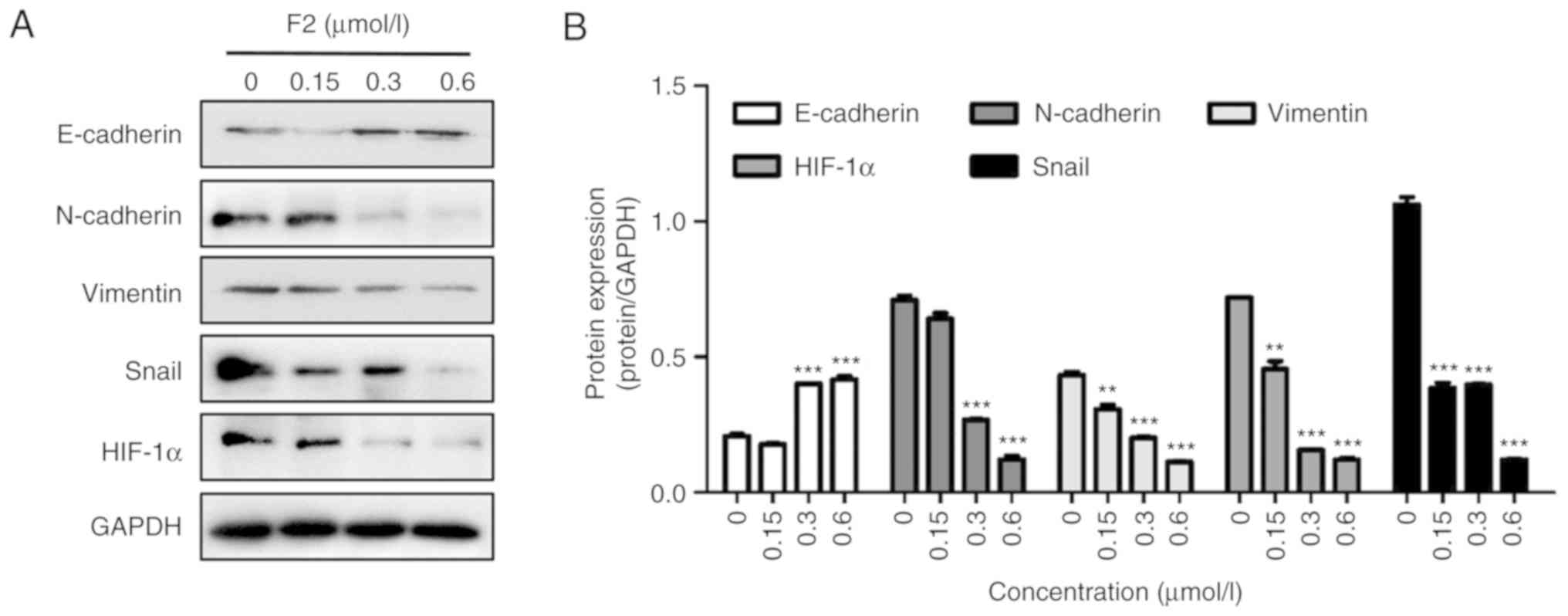
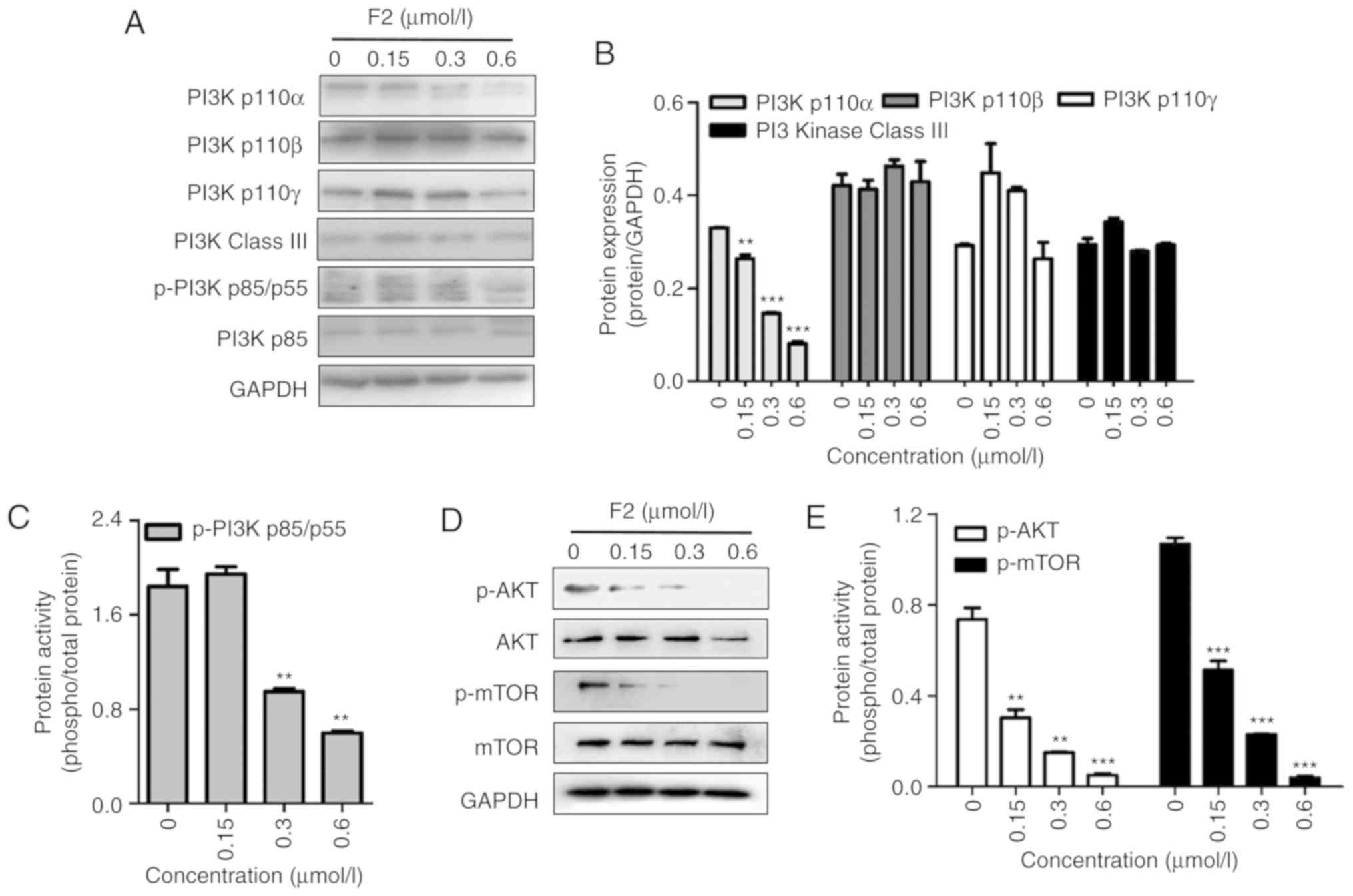
|
1
|
Marth C, Landoni F, Mahner S, McCormack M,
Gonzalez-Martin A and Colombo N; ESMO Guidelines Committee, :
Cervical cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 28 (Suppl):iv72–iv83. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fomenko Y, Cialkowska-Rysz A, Muravlyova
L, Sirota V and Sapar B: Assessment of direct results of cervical
cancer combined treatment. Georgian Med News. 21–24.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang L, Qian H, Sha M, Luan Z, Lin M,
Yuan D, Li X, Huang J and Ye L: Downregulation of HOTAIR expression
mediated anti-metastatic effect of artesunate on cervical cancer by
inhibiting COX-2 expression. PLoS One. 11:e01648382016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chu SC, Yu CC, Hsu LS, Chen KS, Su MY and
Chen PN: Berberine reverses epithelial-tomesenchymal transition and
inhibits metastasis and tumor-induced angiogenesis in human
cervical cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 86:609–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: New insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Z, He S, Guo P, Guo X and Zheng J:
Microrna-1297 inhibits metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition by targeting aeg-1 in cervical cancer. Oncol Rep.
38:3121–3129. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sathyanarayanan A, Chandrasekaran KS and
Karunagaran D: Microrna-145 modulates epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and suppresses proliferation, migration and invasion by
targeting sip1 in human cervical cancer cells. Cell Oncol (Dordr).
40:119–131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qi X, Zhang L and Lu X: New insights into
the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Trend Pharmacol
Sci. 37:246–248. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Franco-Chuaire ML, Magda Carolina SC and
Chuaire-Noack L: Epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT):
Principles and clinical impact in cancer therapy. Invest Clin.
54:186–205. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Wen M, Kwon Y, Xu Y, Liu Y, Zhang
P, He X, Wang Q, Huang Y, Jen KY, et al: CUL4A induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes cancer metastasis by
regulating ZEB1 expression. Cancer Res. 74:520–531. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li HQ and Ke Y: Mechanism of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Chin Pharmacol Bull.
33:1342–1344. 2017.
|
|
12
|
Wheelock MJ, Shintani Y, Maeda M, Fukumoto
Y and Johnson KR: Cadherin switching. J Cell Sci. 121:727–735.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gos M, Miloszewska J and Przybyszewska M:
Epithelial- mesenchymal transition in cancer progression. Postepy
Biochem. 55:121–128. 2009.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sethi S, Macoska J, Chen W and Sarkar FH:
Molecular signature of epithelialmesenchymal transition (EMT) in
human prostate cancer bone metastasis. Am J Transl Res. 3:90–99.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li W, Li S, Deng L, Yang S, Li M, Long S,
Chen S, Lin F and Xiao L: Decreased MT1-MMP in gastric cancer
suppressed cell migration and invasion via regulating MMPs and EMT.
Tumor Biol. 36:6883–6889. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hugo HJ, Kokkinos MI, Blick T, Ackland ML,
Thompson EW and Newgreen DF: Defining the E-cadherin repressor
interactome in epithelial mesenchymal transition: The PM C42 model
as a case study. Cells Tissues Organs. 193:23–40. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nguyen PT, Kudo Y, Yoshida M, Iizuka S,
Ogawa I and Takata T: N-cadherin expression is correlated with
metastasis of spindle cell carcinoma of head and neck region. J
Oral Pathol Med. 40:77–82. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu Y and Zhou BP:
TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and
invasion. Br J Cancer. 102:639–644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang YL, Liu HF, Shi XJ and Wang Y:
Antiproliferative activity of Farnesol in HeLa cervical cancer
cells is mediated via apoptosis induction, loss of mitochondrial
membrane protential and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J Buon.
23:752–757. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dai B, Yang T, Ma Y, Ma N, Shi X, Zhang D,
Zhang J and Zhang Y: HMQ-T-F2 exert antitumour effects by
upregulation of Axin in human cervical HeLa cells. J Cell Mol Med.
22:2955–2959. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Beavon IR: The E-cadherin-catenin complex
in tumour metastasis: Structure, function and regulation. Eur J
Cancer. 36:1607–1620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bahnson A, Athanassiou C, Koebler D, Qian
L, Shun T, Shields D, Yu H, Wang H, Goff J, Cheng T, et al:
Automated measurement of cell motility and proliferation. BMC Cell
Biol. 6:192005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yan J, Zhang Y, Ren C, Shi W and Chen L:
Involvement of nuclear protein C23 in activation of EGFR signaling
in cervical cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:905–910. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yee GP, de Souza P and Khachigian LM:
Current and potential treatments for cervical cancer. Curr Cancer
Drug Targets. 13:205–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sánchez-Tilló E, de Barrios O, Siles L,
Cuatrecasas M, Castells A and Postigo A: β-catenin/TCF4 complex
induces the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-activator
ZEB1 to regulate tumor invasiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:19204–19209. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Solanas G, Porta-de-la-Riva M, Agustí C,
Casagolda D, Sánchez-Aguilera F, Larriba MJ, Pons F, Peiró S,
Escrivà M, Muñoz A, et al: E-cadherin controls beta-catenin and
NF-kappaB transcriptional activity in mesenchymal gene expression.
J Cell Sci. 121:2224–2234. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qureshi R, Arora H and Rizvi MA: EMT in
cervical cancer: Itsrole in tumour progression and response to
therapy. Cancer Lett. 356:321–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kwon YJ, Ye DJ, Baek HS and Chun YJ:
7,12-Dimethylbenz[α]anthracene increases cell proliferation and
invasion through induction of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and EMT
process. Environ Toxicol. 33:729–742. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Höckel M and Vaupel P: Tumor hypoxia:
Definitions and current clinical, biologic, and molecular aspects.
J Natl Cancer. 93:266–276. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bos R, van der Groep P, Greijer AE,
Shvarts A, Meijer S, Pinedo HM, Semenza GL, van Diest PJ and van
der Wall E: Levels of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha independently
predict prognosis in patients with lymph node negative breast
carcinoma. Cancer. 97:1573–1581. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Birner P, Schindl M, Obermair A,
Breitenecker G and Oberhuber G: Expression of hypoxia-inducible
factor 1alpha in epithelial ovarian tumors: Its impact on prognosis
and on response to chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1661–1668.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Song IS, Wang AG, Yoon SY, Kim JM, Kim JH,
Lee DS and Kim NS: Regulation of glucose metabolism-related genes
and VEGF by HIF-1alpha and HIF-1beta, but not HIF-2alpha, in
gastric cancer. Exp Mol Med. 41:51–58. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Porta C, Paglino C and Mosca A: Targeting
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in cancer. Front Oncol. 4:642014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bachelder RE, Yoon SO, Franci C, de
Herreros AG and Mercurio AM: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is an
endogenous inhibitor of Snail transcription: Implications for the
epithelial to mensenchymal transition. J Cell Biol. 168:29–33.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|