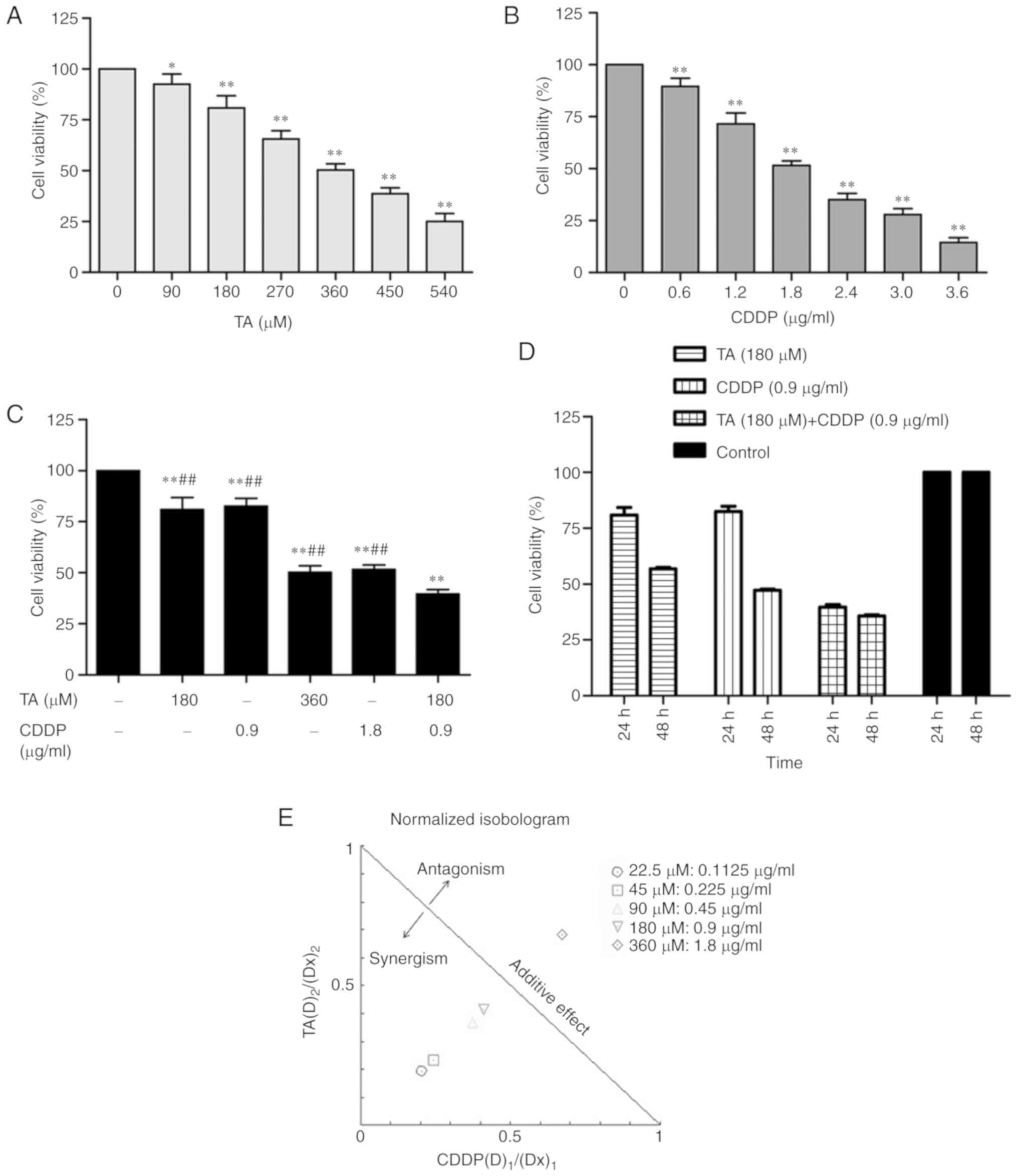
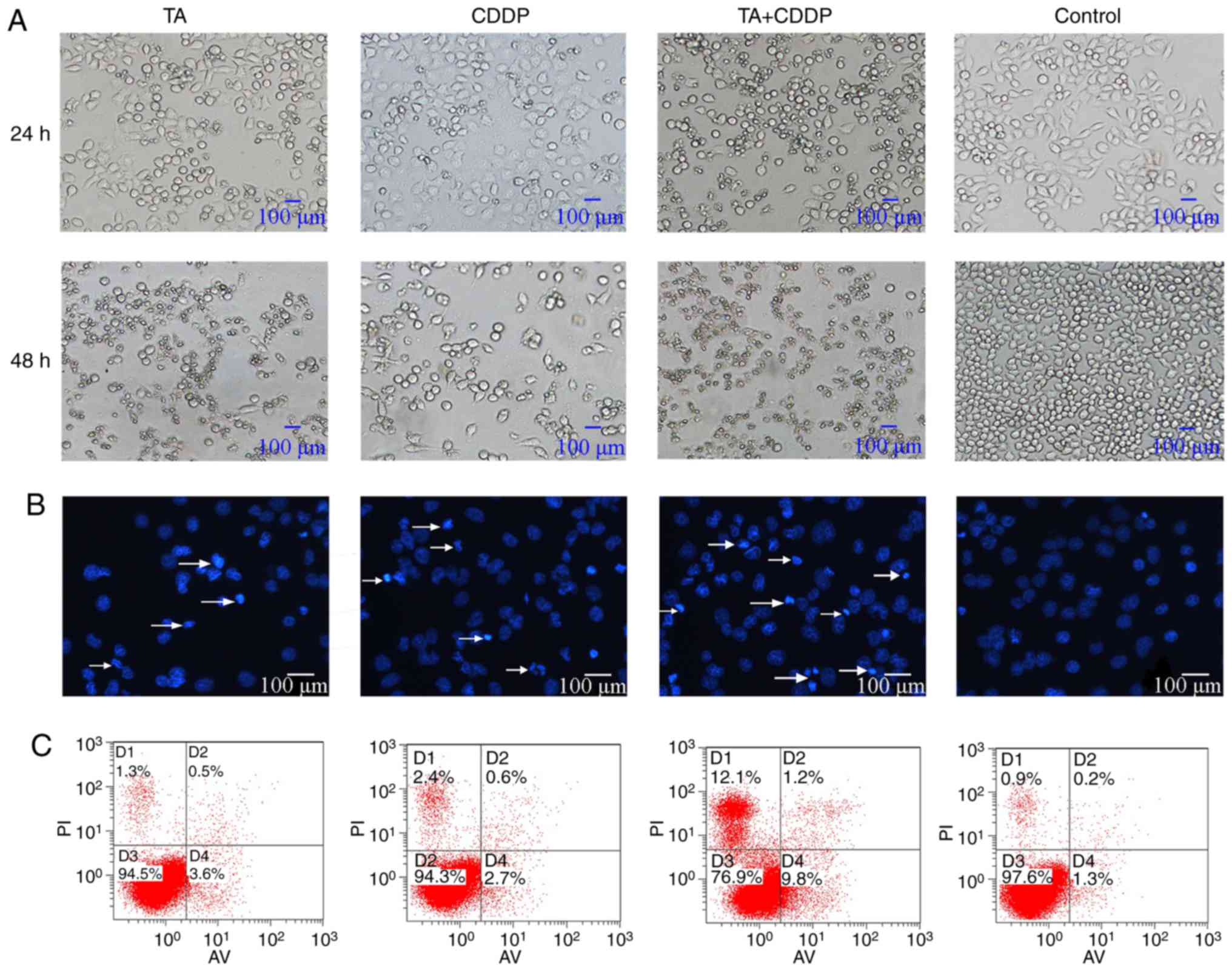
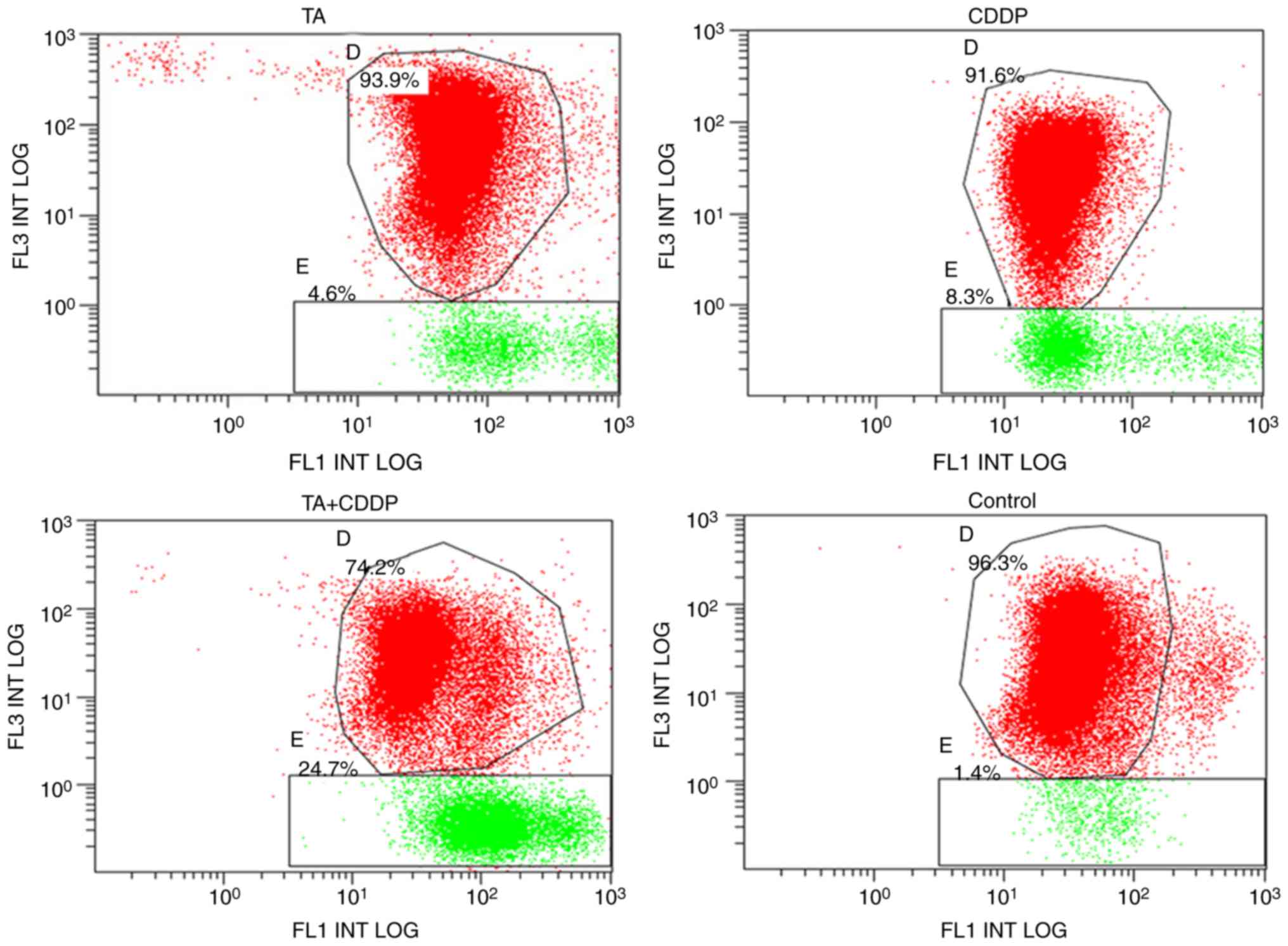
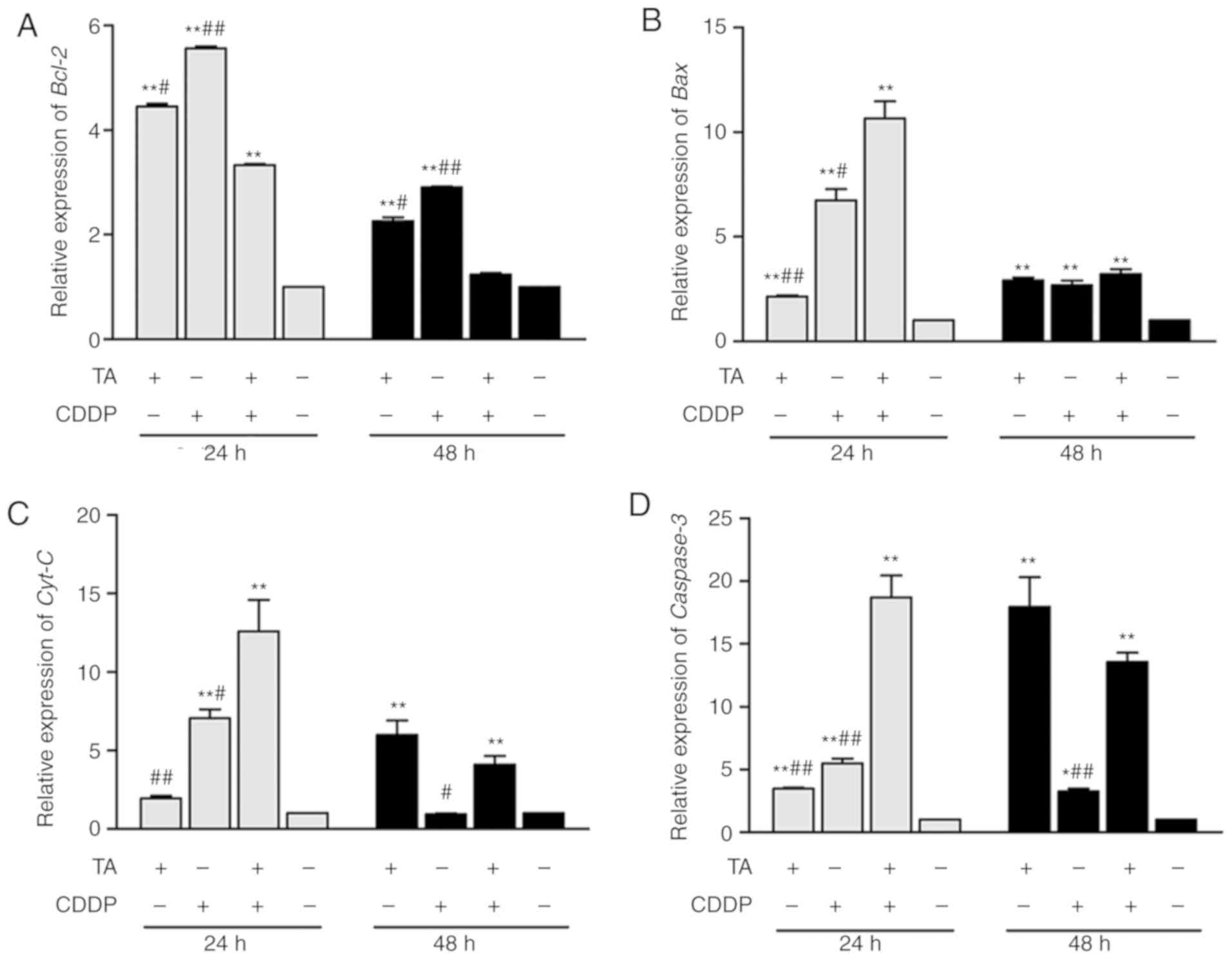
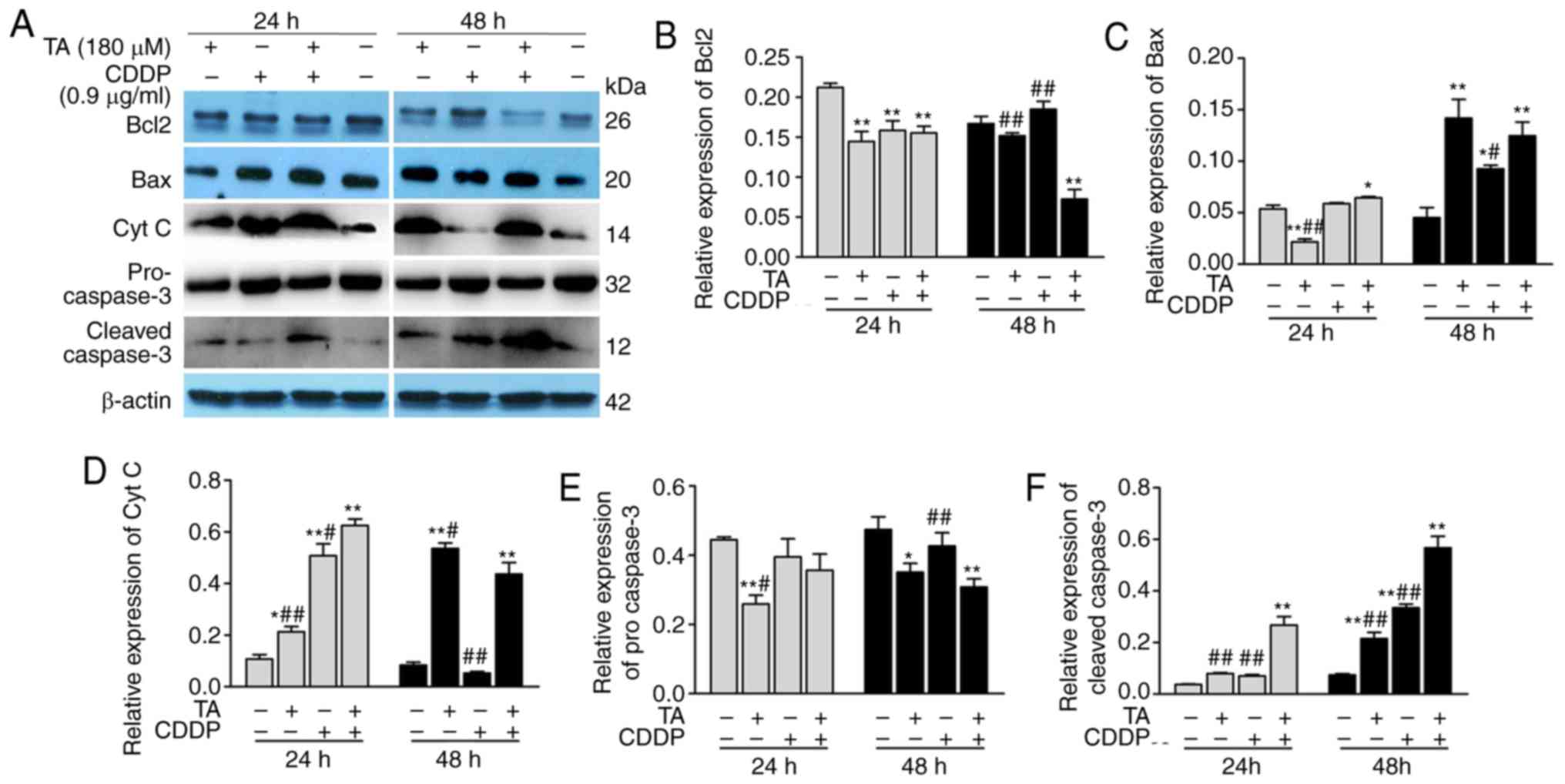
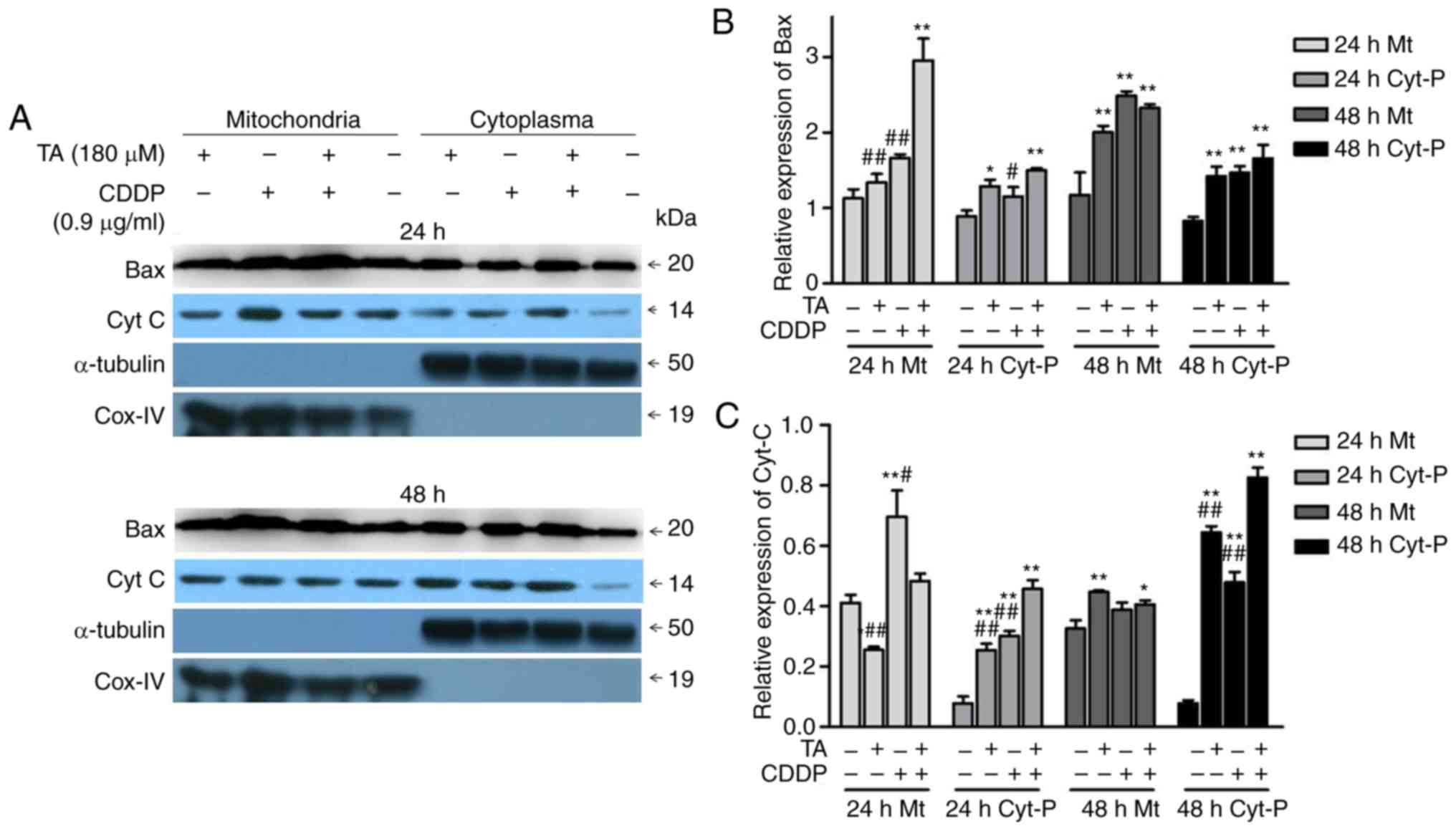
|
1
|
Ferrin G, Aguilar-Melero P,
Rodriguez-Peralvarez M, Montero-Alvarez JL and de la Mata M:
Biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnostic and therapeutic
utility. Hepat Med. 7:1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Proença de Moraes T, Massignan B,
Figueiredo AE, Barretti P, Olandoski M, Kirk A and Pecoits-Filho R:
Systemic lupus erythematous and clinical outcomes in peritoneal
dialysis. Lupus. 24:290–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao H, Dong H, Li G and Jin H: Combined
treatment with acetazolamide and cisplatin enhances
chemosensitivity in laryngeal carcinoma Hep-2 cells. Oncol Lett.
15:9299–9306. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peng F, Zhang H, Du Y and Tan P: Cetuximab
enhances cisplatin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated
apoptosis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells by inhibiting
expression of TXNDC5. Mol Med Rep. 17:4767–4776. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hoch MA, Cousins K, Nartey R, Riley K and
Hartranft M: Two cases of combination therapy with cetuximab,
paclitaxel, and cisplatin for advanced head and neck cancer. J
Oncol Pharm Pract. 24:553–554. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen X, Gao X, Li H, Gu Y and Wang J:
TIMP-3 increases the chemosensitivity of laryngeal carcinoma to
cisplatin via facilitating mitochondria-dependent apoptosis. Oncol
Res. 27:73–80. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Manohar S and Leung N: Cisplatin
nephrotoxicity: A review of the literature. J Nephrol. 31:15–25.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Paken J, Govender CD, Pillay M and Sewram
V: Cisplatin-associated ototoxicity: A review for the health
professional. J Toxicol. 2016:18093942016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Barabas K, Milner R, Lurie D and Adin C:
Cisplatin: A review of toxicities and therapeutic applications. Vet
Comp Oncol. 6:1–18. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Palmieri A, Iapichino A, Cura F, Scapoli
L, Carinci F, Mandrone M and Martinelli M: Pre-treatment with
berberine enhances effect of 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin in HEP2
laryngeal cancer cell line. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 32 (Suppl
1):S167–S177. 2018.
|
|
14
|
Matoba T, Ijichi K, Yanagi T, Kabaya K,
Kawakita D, Beppu S, Torii J and Murakami S: Chemo-selection with
docetaxel, cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (TPF) regimen followed by
radiation therapy or surgery for pharyngeal and laryngeal
carcinoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 47:1031–1037. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lohitesh K, Chowdhury R and Mukherjee S:
Resistance a major hindrance to chemotherapy in hepatocellular
carcinoma: An insight. Cancer Cell Int. 18:442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ryu SH and Chung YH: How to overcome
multidrug resistance in chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma. Liver Int. 30:496–498. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun Y, Zhang T, Wang B, Li H and Li P:
Tannic acid, an inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase,
sensitizes ovarian carcinoma cells to cisplatin. Anticancer Drugs.
23:979–990. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Booth BW, Inskeep BD, Shah H, Park JP, Hay
EJ and Burg KJ: Tannic Acid preferentially targets estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer. Int J Breast Cancer.
2013:3696092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tikoo K, Sane MS and Gupta C: Tannic acid
ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and potentiates its
anticancer activity: Potential role of tannins in cancer
chemotherapy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 251:191–200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cass CA and Burg KJ: Tannic acid
cross-linked collagen scaffolds and their anticancer potential in a
tissue engineered breast implant. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.
23:281–298. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen KS, Hsiao YC, Kuo DY, Chou MC, Chu
SC, Hsieh YS and Lin TH: Tannic acid-induced apoptosis and
-enhanced sensitivity to arsenic trioxide in human leukemia HL-60
cells. Leuk Res. 33:297–307. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cosan D, Soyocak A, Basaran A, Degirmenci
I and Gunes HV: The effects of resveratrol and tannic acid on
apoptosis in colon adenocarcinoma cell line. Saudi Med J.
30:191–195. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Darvin P, Baeg SJ, Joung YH, Sp N, Kang
DY, Byun HJ, Park JU and Yang YM: Tannic acid inhibits the
Jak2/STAT3 pathway and induces G1/S arrest and mitochondrial
apoptosis in YD-38 gingival cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
47:1111–1120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Darvin P, Joung YH, Kang DY, Sp N, Byun
HJ, Hwang TS, Sasidharakurup H, Lee CH, Cho KH, Park KD, et al:
Tannic acid inhibits EGFR/STAT1/3 and enhances p38/STAT1 signalling
axis in breast cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 21:720–734. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kamei H, Koide T, Hashimoto Y, Kojima T
and Hasegawa M: Tumor cell growth suppression by tannic acid.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 14:135–138. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karakurt S and Adali O: Tannic acid
inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion of prostate cancer and
modulates drug metabolizing and antioxidant enzymes. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 16:781–789. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Majed F, Rashid S, Khan AQ, Nafees S, Ali
N, Ali R, Khan R, Hasan SK, Mehdi SJ and Sultana S: Tannic acid
mitigates the DMBA/croton oil-induced skin cancer progression in
mice. Mol Cell Biochem. 399:217–228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nagesh PKB, Hatami E, Chowdhury P, Kashyap
VK, Khan S, Hafeez BB, Chauhan SC, Jaggi M and Yallapu MM: Tannic
acid induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in
prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 10:E682018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Naus PJ, Henson R, Bleeker G, Wehbe H,
Meng F and Patel T: Tannic acid synergizes the cytotoxicity of
chemotherapeutic drugs in human cholangiocarcinoma by modulating
drug efflux pathways. J Hepatol. 46:222–229. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ngobili TA, Shah H, Park JP, Kwist KW,
Inskeep B, Burg KJ and Booth BW: Remodeling of tannic acid
crosslinked collagen type I induces apoptosis in ER+
breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 35:1285–1290. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nie F, Liang Y, Jiang B, Li X, Xun H, He
W, Lau HT and Ma X: Apoptotic effect of tannic acid on fatty acid
synthase over-expressed human breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol.
37:2137–2143. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Chen D, Han DM, Cheng YH, Dai C,
Wu XJ, Che FY and Heng XY: Tannic acid mediated induction of
apoptosis in human glioma Hs 683 cells. Oncol Lett. 15:6845–6850.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Loewe S: The problem of synergism and
antagonism of combined drugs. Arzneimittelforschung. 3:285–290.
1953.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Estaquier J, Vallette F, Vayssiere JL and
Mignotte B: The mitochondrial pathways of apoptosis. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 942:157–183. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zielińska-Przyjemska M, Kaczmarek M,
Krajka-Kuźniak V, Łuczak M and Baer-Dubowska W: The effect of
resveratrol, its naturally occurring derivatives and tannic acid on
the induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in rat C6 and
human T98G glioma cell lines. Toxicol In Vitro. 43:69–75. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|