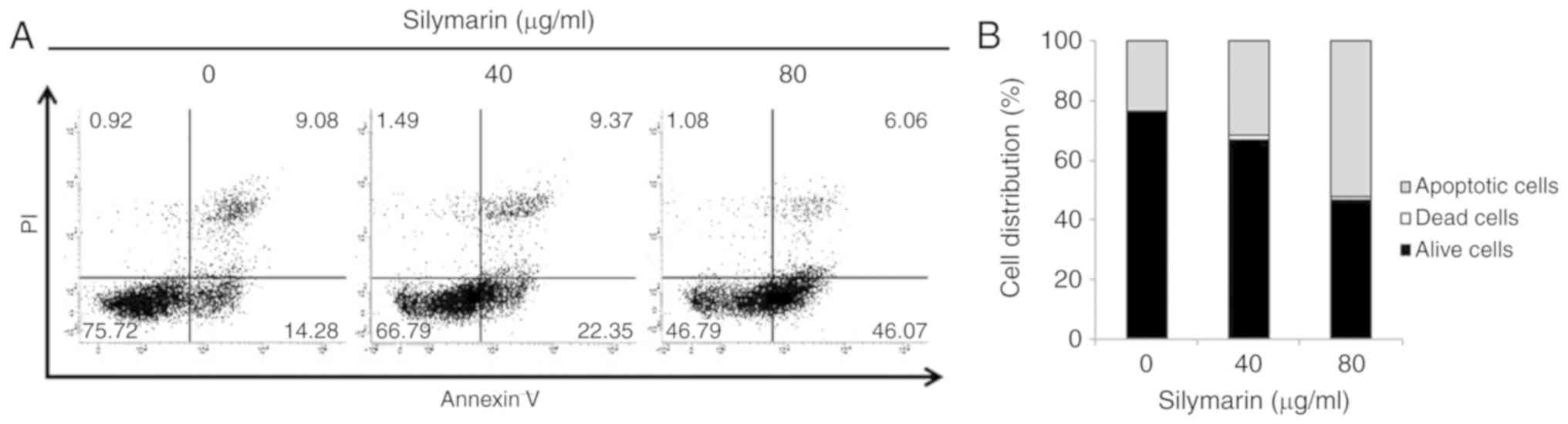
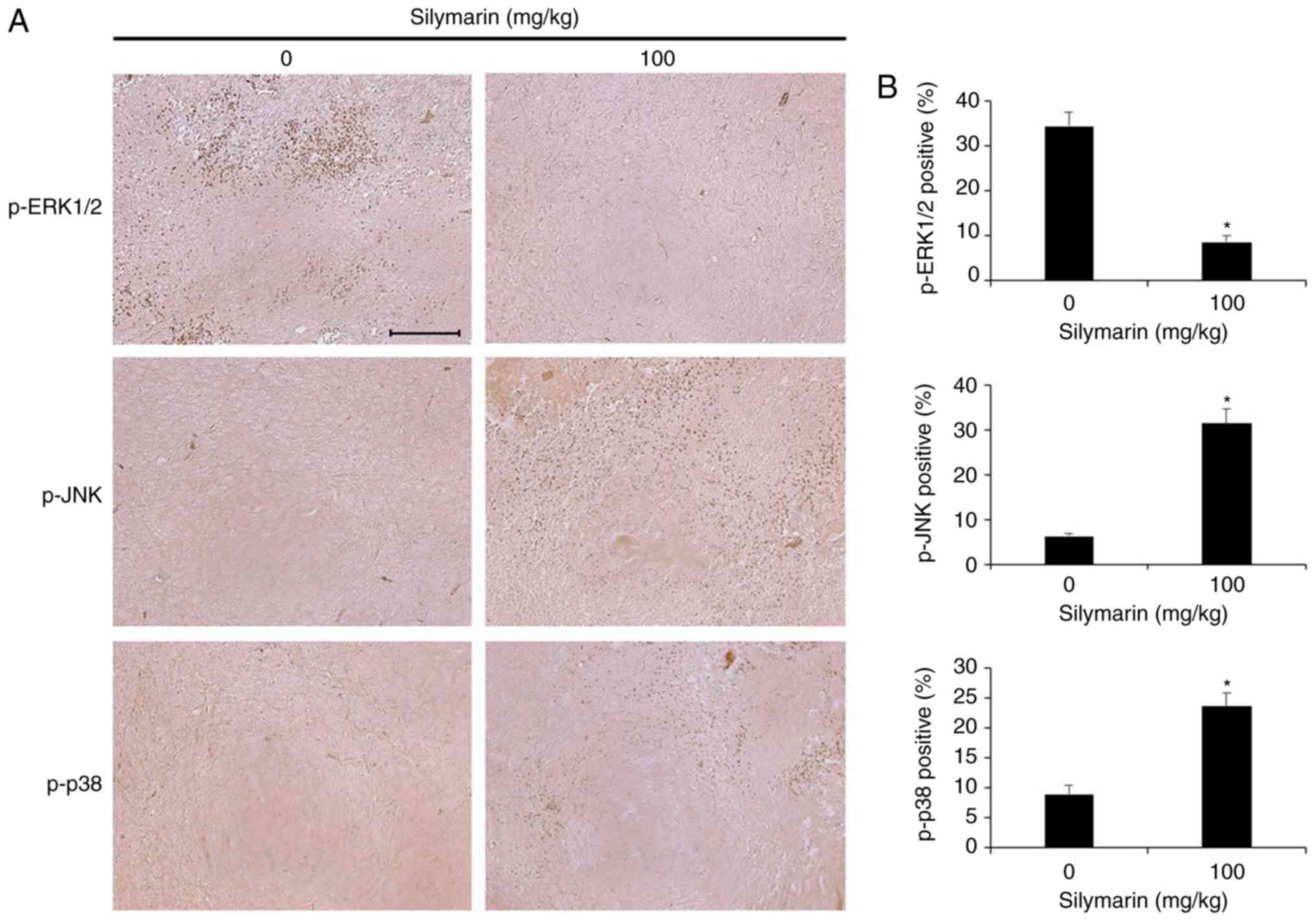
|
1
|
Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ and Lee ES:
Prediction of cancer incidence and mortality in Korea, 2019. Cancer
Res Treat. 51:431–437. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Won YJ, Sung J, Jung KW, Kong HJ, Park S,
Shin HR, Park EC, Ahn YO, Hwang IK, Lee DH, et al: Nationwide
cancer incidence in Korea, 2003–2005. Cancer Res Treat. 41:122–131.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jung KW, Won YJ, Kong HJ, Oh CM, Lee DH
and Lee JS: Cancer statistics in Korea: Incidence, mortality,
survival, and prevalence in 2011. Cancer Res Treat. 46:109–123.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jemal A, Center MM, DeSantis C and Ward
EM: Global patterns of cancer incidence and mortality rates and
trends. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1893–1907. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Forman D and Burley VJ: Gastric cancer:
Global pattern of the disease and an overview of environmental risk
factors. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 20:633–649. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee MS, Cha EY, Thuong PT, Kim JY, Ahn MS
and Sul JY: Down-regulation of human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2/neu oncogene by corosolic acid induces cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in NCI-N87 human gastric cancer cells. Biol Pharm
Bull. 33:931–937. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li N, Fan LL, Sun GP, Wan XA, Wang ZG, Wu
Q and Wang H: Paeonol inhibits tumor growth in gastric cancer in
vitro and in vivo. World J Gastroenterol. 16:4483–4490. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang L, Hou YH, Wu K, Zhai JS and Lin N:
Proteomic analysis reveals molecular biological details in
varioliform gastritis without helicobacter pylori infection. World
J Gastroenterol. 16:3664–3673. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Seeram NP: Berry fruits for cancer
prevention: Current status and future prospects. J Agric Food Chem.
56:630–635. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
An IJ, Kwon JK, Lee JS, Park HS, Kim DC,
Choi BJ, Lee KM, Park YJ and Jung JY: Induction of apoptosis in
human cancer cells with compositae extracts. J Korean Soc Food Sci
Nutr. 41:584–590. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kwon MJ and Nam TJ: A polysaccharide of
the marine alga capsosiphon fulvescens induces apoptosis in AGS
gastric cancer cells via an IGF-IR-mediated PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell
Biol Int. 31:768–775. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schuier M, Sies H, Illek B and Fischer H:
Cocoa-related flavonoids inhibit CFTR-mediated chloride transport
across T84 human colon epithelia. J Nutr. 135:2320–2325. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Murakami A, Ashida H and Terao J:
Multitargeted cancer prevention by quercetin. Cancer Lett.
269:315–325. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren W, Qiao Z, Wang H, Zhu L and Zhang L:
Flavonoids: Promising anticancer agents. Med Res Rev. 23:519–534.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hackett ES, Twedt DC and Gustafson DL:
Milk thistle and its derivative compounds: A review of
opportunities for treatment of liver disease. J Vet Intern Med.
27:10–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen CH, Huang TS, Wong CH, Hong CL, Tsai
YH, Liang CC, Lu FJ and Chang WH: Synergistic anti-cancer effect of
baicalein and silymarin on human hepatoma HepG2 Cells. Food Chem
Toxicol. 47:638–644. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ramasamy K and Agarwal R: Multitargeted
therapy of cancer by silymarin. Cancer Lett. 269:352–362. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Surai PF: Silymarin as a natural
antioxidant: An overview of the current evidence and perspectives.
Antioxidants (Basel). 4:204–247. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Katiyar SK: Silymarin and skin cancer
prevention: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and immunomodulatory
effects (Review). Int J Oncol. 26:169–176. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Féher J and Lengyel G: Silymarin in the
prevention and treatment of liver diseases and primary liver
cancer. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 13:210–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Eo HJ, Park GH and Jeong JB: Inhibition of
Wnt signaling by silymarin in human colorectal cancer cells. Biomol
Ther (Seoul). 24:380–386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hajighasemlou S, Farajollahi M, Alebouyeh
M, Rastegar H, Manazi MT, Mirmoghtadaei M, Moayedi B, Ahmadzadeh M,
Kazemi M, Parvizpour F and Gharibzadeh S: Study of the effect of
silymarin on viability of breast cancer cell lines. Adv Breast
Cancer Res. 3:100–105. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu T, Liu W, Guo W and Zhu X: Silymarin
suppressed lung cancer growth in mice via inhibiting
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 81:460–467.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deep G, Singh RP, Agarwal C, Kroll DJ and
Agarwal R: Silymarin and silibinin cause G1 and G2-M cell cycle
arrest via distinct circuitries in human prostate cancer PC3 cells:
A comparison of flavanone silibinin with flavanolignan mixture
silymarin. Oncogene. 25:1053–1069. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hsu HF, Houng JY, Kuo CF, Tsao N and Wu
YC: Glossogin, a novel phenylpropanoid from glossogyne tenuifolia,
induced apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol.
46:3785–3791. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kaufmann T, Strasser A and Jost PJ: Fas
death receptor signalling: Roles of Bid and XIAP. Cell Death
Differ. 19:42–50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tummers B and Green DR: Caspase-8:
Regulating life and death. Immunol Rev. 277:76–89. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim D and Chung J: Akt: Versatile mediator
of cell survival and beyond. J Biochem Mol Biol. 35:106–115.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Burz C, Berindan-Neagoe I, Balacescu O and
Irimie A: Apoptosis in cancer: Key molecular signaling pathways and
therapy targets. Acta Oncol. 48:811–821. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Soldani C and Scovassi AI: Poly
(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: An update.
Apoptosis. 7:321–328. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Pathological roles of
MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1802:396–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ramakrishnan G, Lo Muzio L, Elinos-Báez
CM, Jagan S, Augustine TA, Kamaraj S, Anandakumar P and Devaki T:
Silymarin inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in hepatic
cancer cells. Cell Prolif. 42:229–240. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhong X, Zhu Y, Lu Q, Zhang J, Ge Z and
Zheng S: Silymarin causes caspases activation and apoptosis in K562
leukemia cells through inactivation of Akt pathway. Toxicology.
227:211–216. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fan L, Ma Y, Liu Y, Zheng D and Huang G:
Silymarin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in ovarian cancer
cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 743:79–88. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vaid M, Prasad R, Sun Q and Katiyar SK:
Silymarin targets β-catenin signaling in blocking
migration/invasion of human melanoma cells. PLoS One. 6:e230002011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Danial NN and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death:
Critical control points. Cell. 116:205–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Halicka HD, Bedner E and Darzynkiewicz Z:
Segregation of RNA and separate packaging of DNA and RNA in
apoptotic bodies during apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 260:248–256. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Katiyar SK, Roy AM and Baliga MS:
Silymarin induces apoptosis primarily through a p53-dependent
pathway involving Bcl-2/Bax, cytochrome c release, and caspase
activation. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:207–216. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vaid M, Singh T, Prasad R and Katiyar SK:
Silymarin inhibits melanoma cell growth both in vitro and in vivo
by targeting cell cycle regulators, angiogenic biomarkers and
induction of apoptosis. Mol Carcinog. 54:1328–1339. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yan C, Yahua WU, Wang Z, Yin C and Yin M:
Inhibitory effect of silymarin on human osteosarcoma Saos-2 cells
and its mechanism. Chin Pharmacol Bull. 32:966–969. 2016.(In
Chinese).
|
|
43
|
Huang Q, Wu LJ, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Li
LH and Ikejima T: Silymarin augments human cervical cancer HeLa
cell apoptosis via P38/JNK MAPK pathways in serum-free medium. J
Asian Nat Prod Res. 7:701–709. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Won DH, Kim LH, Jang B, Yang IH, Kwon HJ,
Jin B, Oh SH, Kang JH, Hong SD, Shin JA and Cho SD: In vitro and in
vivo anti-cancer activity of silymarin on oral cancer. Tumor Biol.
40:10104283187761702018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Singh RP, Tyagi AK, Zhao J and Agarwal R:
Silymarin inhibits growth and causes regression of established skin
tumors in SENCAR mice via modulation of mitogen-activated protein
kinases and induction of apoptosis. Carcinogenesis. 23:499–510.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|