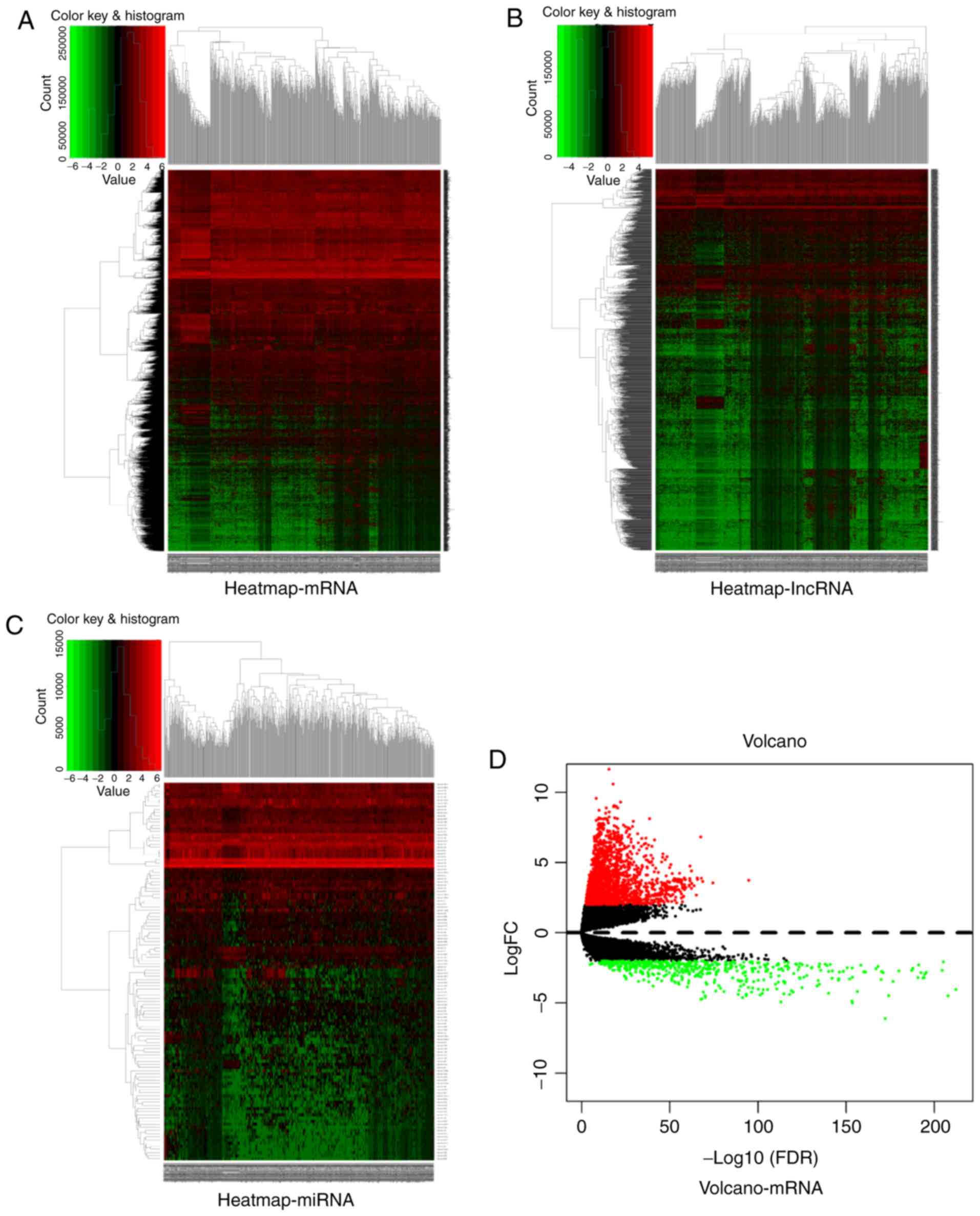
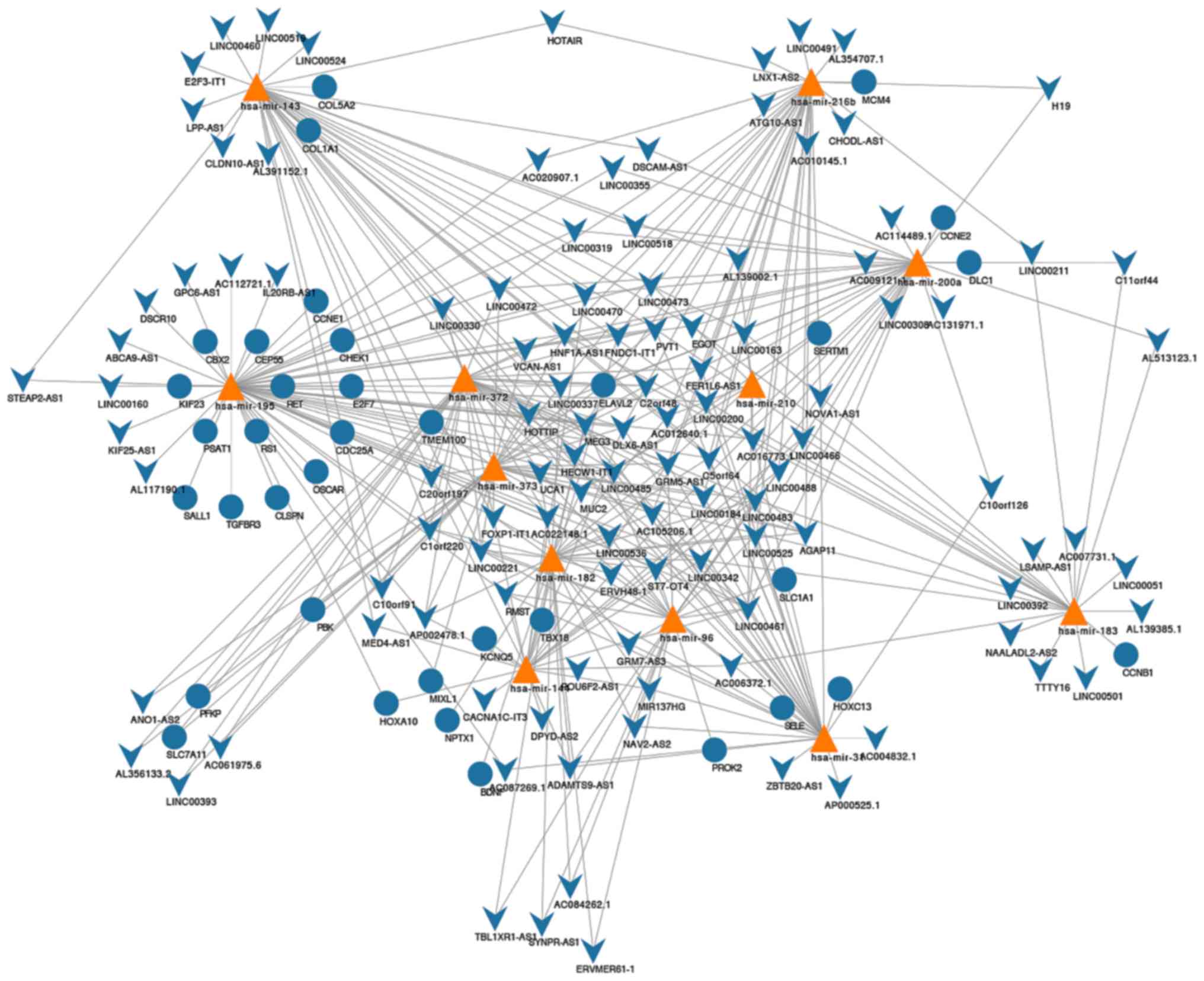
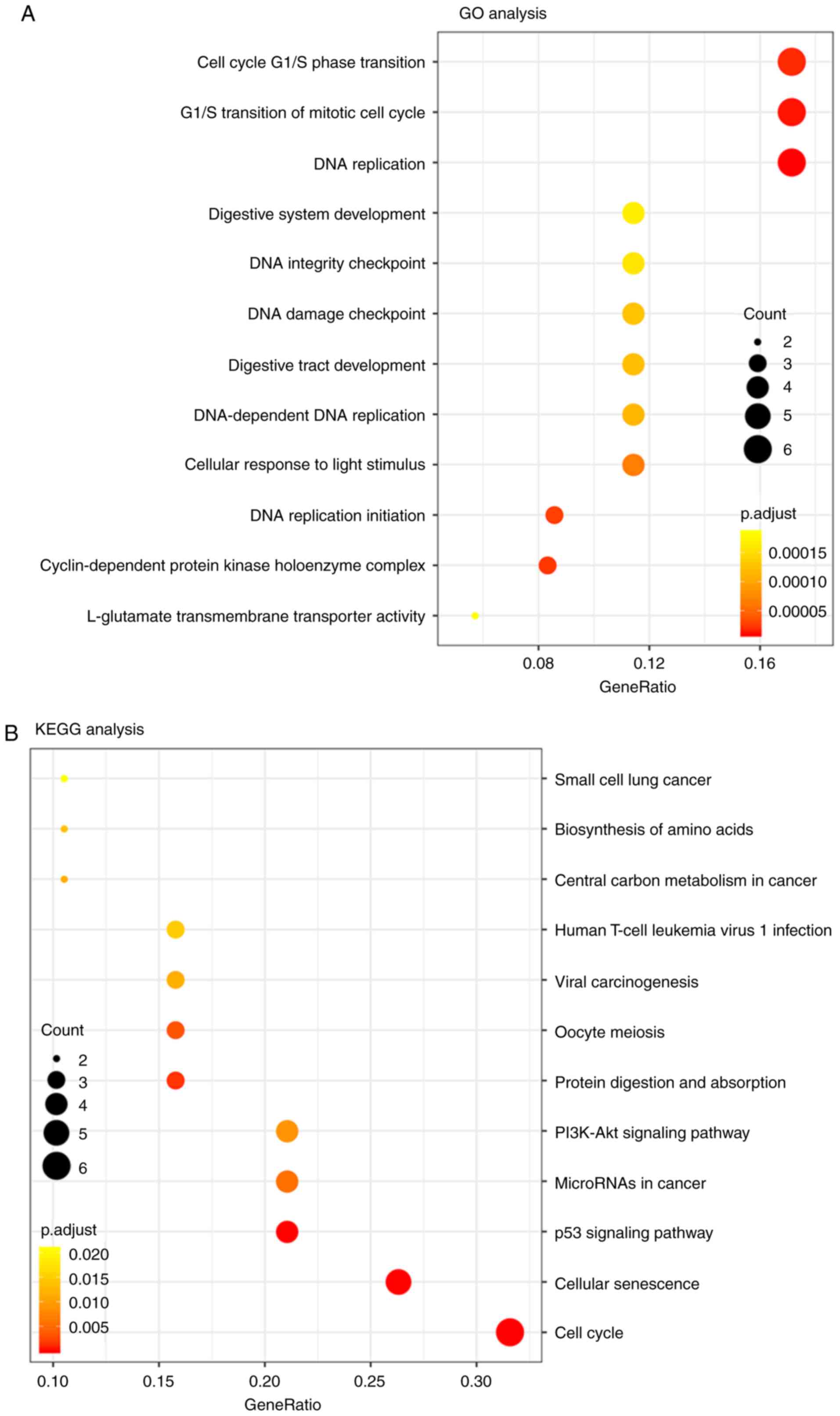
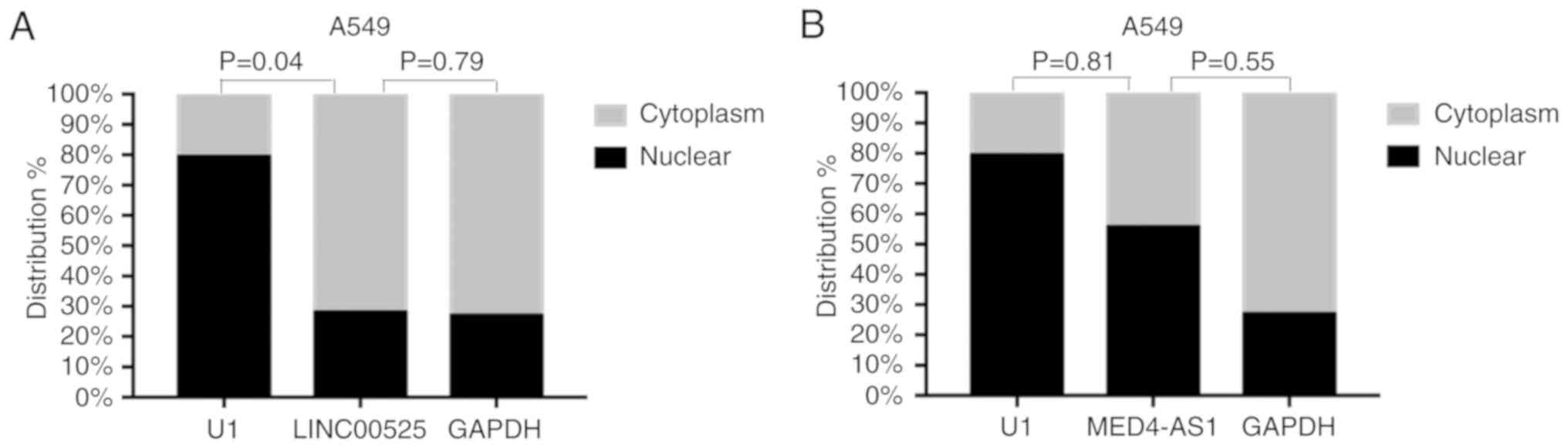
|
1
|
Hirsch FR, Scagliotti GV, Mulshine JL,
Kwon R, Curran WJ Jr, Wu YL and Paz-Ares L: Lung cancer: Current
therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet. 389:299–311. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kris MG, Gaspar LE, Chaft JE, Kennedy EB,
Azzoli CG, Ellis PM, Lin SH, Pass HI, Seth R, Shepherd FA, et al:
Adjuvant systemic therapy and adjuvant radiation therapy for stage
I to IIIA completely resected non-small-cell lung cancers: American
society of clinical oncology/cancer care ontario clinical practice
guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 35:2960–2974. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moghissi K and Dixon K: Image-guided
surgery and therapy for lung cancer: A critical review. Future
Oncol. 13:2383–2394. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nagasaka M and Gadgeel SM: Role of
chemotherapy and targeted therapy in early-stage non-small cell
lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 18:63–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oak CH, Wilson D, Lee HJ, Lim HJ and Park
EK: Potential molecular approaches for the early diagnosis of lung
cancer (review). Mol Med Rep. 6:931–936. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jarroux J, Morillon A and Pinskaya M:
History, discovery, and classification of lncRNAs. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1008:1–46. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun W, Shi Y, Wang Z, Zhang J, Cai H,
Zhang J and Huang D: Interaction of long-chain non-coding RNAs and
important signaling pathways on human cancers (Review). Int J
Oncol. 53:2343–2355. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang N, Wang X, Xie X, Liao Y, Liu N, Liu
J, Miao N, Shen J and Peng T: lncRNA DANCR promotes tumor
progression and cancer stemness features in osteosarcoma by
upregulating AXL via miR-33a-5p inhibition. Cancer Lett. 405:46–55.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Osielska MA and Jagodzinski PP: Long
non-coding RNA as potential biomarkers in non-small-cell lung
cancer: What do we know so far? Biomed Pharmacother. 101:322–333.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qiu L, Tang Q, Li G and Chen K: Long
non-coding RNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic targets: Recent
insights into hepatocellular carcinoma. Life Sci. 191:273–282.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vecera M, Sana J, Lipina R, Smrcka M and
Slaby O: Long non-coding RNAs in gliomas: From molecular pathology
to diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic Targets. Int J Mol Sci.
19(pii): E27542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu YH, Tu JR, Zhao TT, Xie SG and Tang SB:
Overexpression of lncRNA EGFRAS1 is associated with a poor
prognosis and promotes chemotherapy resistance in nonsmall cell
lung cancer. Int J Oncol. 54:295–305. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chang L, Xu W, Zhang Y and Gong F: Long
non-coding RNA-NEF targets glucose transportation to inhibit the
proliferation of non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Lett.
17:2795–2801. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen ZP, Wei JC, Wang Q, Yang P, Li WL, He
F, Chen HC, Hu H, Zhong JB and Cao J: Long noncoding RNA 00152
functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate NRP1 expression
by sponging with miRNA206 in colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol.
53:1227–1236. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chan JJ and Tay Y: Noncoding RNA:RNA
regulatory networks in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii): E13102018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang YC, Wu YP, Chen DN, Chen SH, Li XD,
Sun XL, Wei Y, Ning X and Xue XY: Building a competing endogenous
RNA network to find potential long non-coding RNA biomarkers for
pheochromocytoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 51:2916–2924. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Han L, Zhou L, Wang L and Zhang
LM: Prediction of candidate RNA signatures for recurrent ovarian
cancer prognosis by the construction of an integrated competing
endogenous RNA network. Oncol Rep. 40:2659–2673. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan Y, Yu J, Liu H, Guo S, Zhang Y, Ye Y,
Xu L and Ming L: Construction of a long non-coding RNA-associated
ceRNA network reveals potential prognostic lncRNA biomarkers in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 214:2031–2038. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Loewen G, Jayawickramarajah J, Zhuo Y and
Shan B: Functions of lncRNA HOTAIR in lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol.
7:902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gutschner T, Hammerle M, Eissmann M, Hsu
J, Kim Y, Hung G, Revenko A, Arun G, Stentrup M, Gross M, et al:
The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the metastasis
phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 73:1180–1189. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lou X, Li J, Yu D, Wei YQ, Feng S and Sun
JJ: Comprehensive analysis of five long noncoding RNAs expression
as competing endogenous RNAs in regulating hepatoma carcinoma.
Cancer Med. 8:5735–5749. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gene Ontology Consortium: The gene
ontology (GO) project in 2006. Nucleic Acids Res. 34((Database
Issue)): D322–D326. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Detterbeck FC, Boffa DJ, Kim AW and Tanoue
LT: The eighth edition lung cancer stage classification. Chest.
151:193–203. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KG and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, Zhang S, Zou X,
Wang N, Zhang L, Tang J, Chen J, Wei K, et al: Cancer survival in
China, 2003–2005: A population-based study. Int J Cancer.
136:1921–1930. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kimmelman AC and White E: Autophagy and
tumor metabolism. Cell Metab. 25:1037–1043. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Domschke P, Trucu D, Gerisch A and
Chaplain MAJ: Structured models of cell migration incorporating
molecular binding processes. J Math Biol. 75:1517–1561. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Franci G, Manfroni G, Cannalire R,
Felicetti T, Tabarrini O, Salvato A, Barreca ML, Altucci L and
Cecchetti V: Tumour cell population growth inhibition and cell
death induction of functionalized 6-aminoquinolone derivatives.
Cell Prolif. 48:705–717. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li C, Miao R, Zhang J, Qu K and Liu C:
Long non-coding RNA KCNQ1OT1 mediates the growth of hepatocellular
carcinoma by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-504.
Int J Oncol. Mar 12–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
31
|
Mou K, Liu B, Ding M, Mu X, Han D, Zhou Y
and Wang LJ: lncRNA-ATB functions as a competing endogenous RNA to
promote YAP1 by sponging miR-590-5p in malignant melanoma. Int J
Oncol. 53:1094–1104. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu SP, Wang JY, Wang XG and Zhao JP: Long
intergenic non-protein coding RNA 00858 functions as a competing
endogenous RNA for miR-422a to facilitate the cell growth in
non-small cell lung cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 9:475–486. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shang M, Wang X, Zhang Y, Gao Z, Wang T
and Liu R: LincRNA-ROR promotes metastasis and invasion of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-145/FSCN1.
Onco Targets Ther. 11:639–649. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rui X, Xu Y, Huang Y, Ji L and Jiang X:
lncRNA DLG1-AS1 promotes cell proliferation by competitively
binding with miR-107 and up-regulating ZHX1 expression in cervical
cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:1792–1803. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jiao D, Li Z, Zhu M, Wang Y, Wu G and Han
X: LncRNA MALAT1 promotes tumor growth and metastasis by targeting
miR-124/foxq1 in bladder transitional cell carcinoma (BTCC). Am J
Cancer Res. 8:748–760. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shen X, Bai H, Zhu H, Yan Q, Yang Y, Yu W,
Shi Q, Wang J, Li J and Chen L: Long non-coding RNA MEG3 functions
as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HOXA11 expression by
sponging miR-181a in multiple myeloma. Cell Physiol Biochem.
49:87–100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu J, Li H, Zheng B, Sun L, Yuan Y and
Xing C: Competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) regulation network of
lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA in colorectal carcinogenesis. Dig Dis Sci.
64:1868–1877. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang Z, Lei W, Hu HB, Zhang H and Zhu Y:
H19 promotes non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) development through
STAT3 signaling via sponging miR-17. J Cell Physiol. 233:6768–6776.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jiang C, Yang Y, Yang Y, Guo L, Huang J,
Liu X, Wu C and Zou J: Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) hOTAIR affects
tumorigenesis and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by
upregulating miR-613. Oncol Res. 26:725–734. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wu JL, Meng FM and Li HJ: High expression
of lncRNA MEG3 participates in non-small cell lung cancer by
regulating microRNA-7-5p. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:5938–5945.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Nie W, Ge HJ, Yang XQ, Sun X, Huang H, Tao
X, Chen WS and Li B: LncRNA-UCA1 exerts oncogenic functions in
non-small cell lung cancer by targeting miR-193a-3p. Cancer Lett.
371:99–106. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chang N, Ahn SH, Kong DS, Lee HW and Nam
DH: The role of STAT3 in glioblastoma progression through dual
influences on tumor cells and the immune microenvironment. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 451:53–65. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang H, Yan L, Sun K, Sun X, Zhang X, Cai
K and Song T: lncRNA BCAR4 increases viability, invasion, and
migration of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting
glioma-associated oncogene 2 (GLI2). Oncol Res. 27:359–369. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li C, Wan L, Liu Z, Xu G, Wang S, Su Z,
Zhang Y, Zhang C, Liu X, Lei Z and Zhang HT: Long non-coding RNA
XIST promotes TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by
regulating miR-367/141-ZEB2 axis in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Cancer Lett. 418:185–195. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu L, Ni J and He X: Upregulation of the
long noncoding RNA SNHG3 promotes lung adenocarcinoma
proliferation. Dis Markers. 2018:57367162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zeng H, Wang J, Chen T, Zhang K, Chen J,
Wang L, Li H, Tuluhong D, Li J and Wang S: Downregulation of long
non-coding RNA Opa interacting protein 5-antisense RNA 1 inhibits
breast cancer progression by targeting sex-determining region Y-box
2 by microRNA-129-5p upregulation. Cancer Sci. 110:289–302.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Renganathan A and Felley-Bosco E: Long
noncoding RNAs in cancer and therapeutic potential. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1008:199–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu Z, Liu A, Nan A, Cheng Y, Yang T, Dai
X, Chen L, Li X, Jia Y, Zhang N and Jiang Y: The linc00152 controls
cell cycle progression by regulating CCND1 in 16HBE cells
malignantly transformed by cigarette smoke extract. Toxicol Sci.
167:496–508. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Saito S, Espinoza-Mercado F, Liu H, Sata
N, Cui X and Soukiasian HJ: Current status of research and
treatment for non-small cell lung cancer in never-smoking females.
Cancer Biol Ther. 18:359–368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|