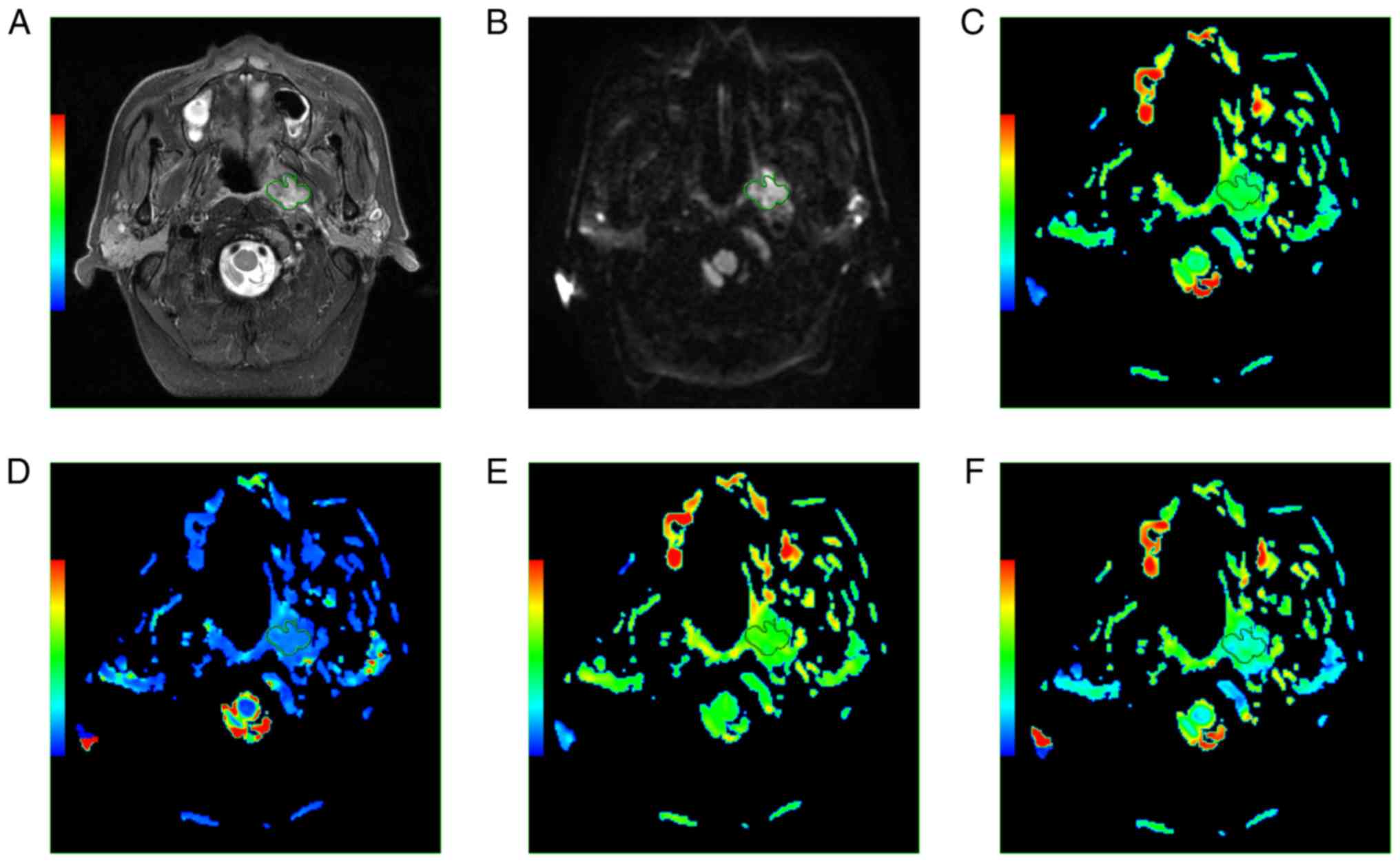
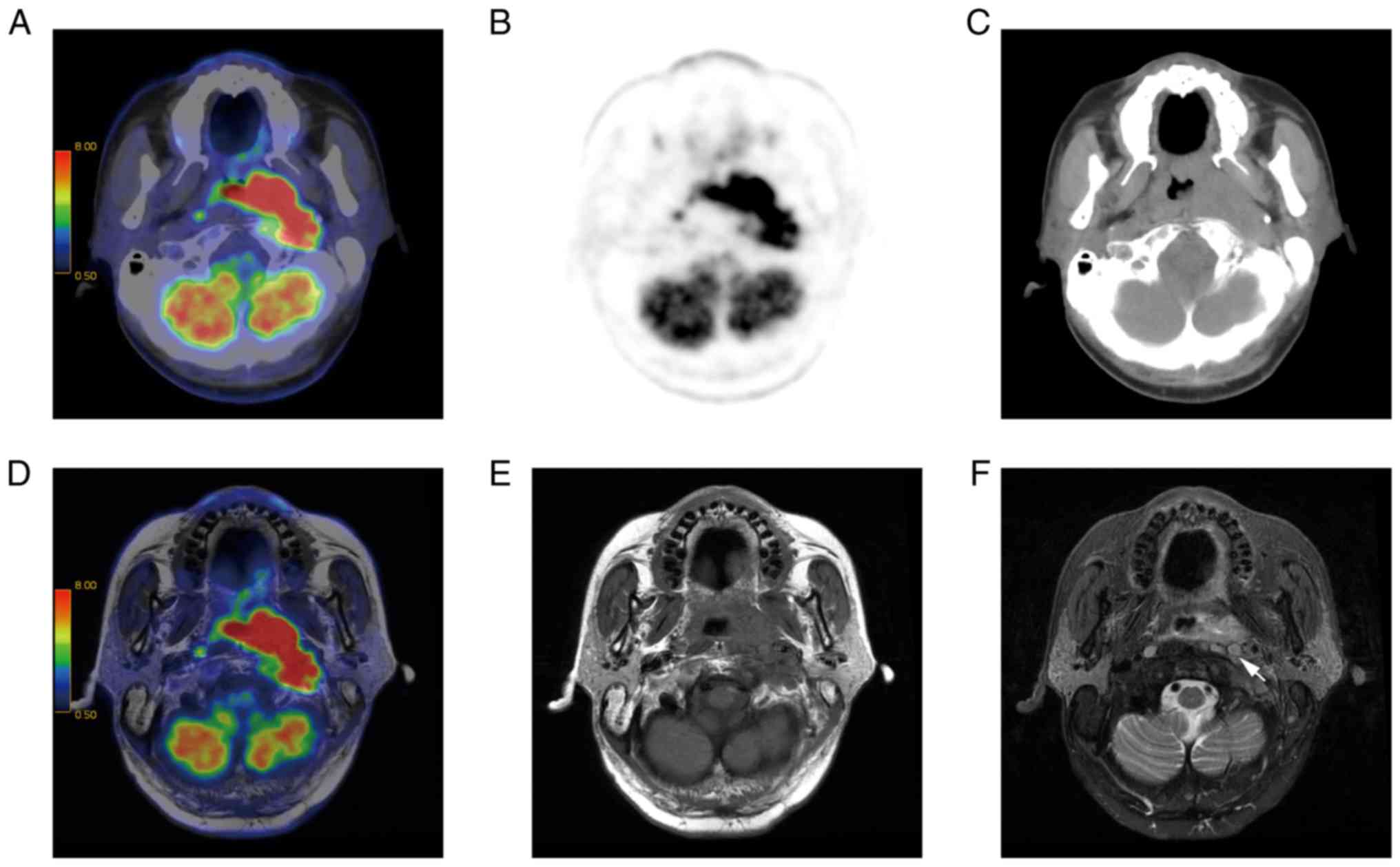
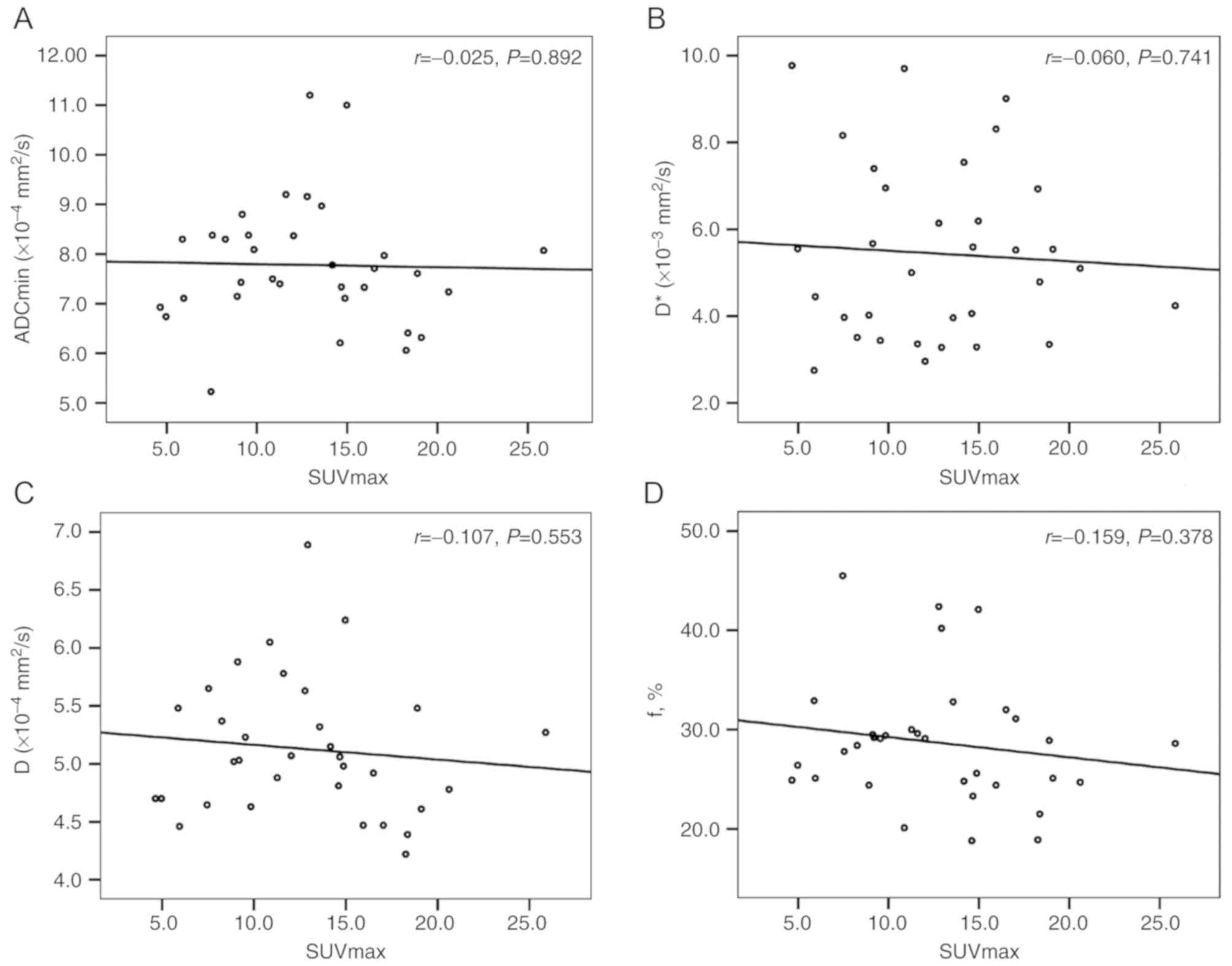
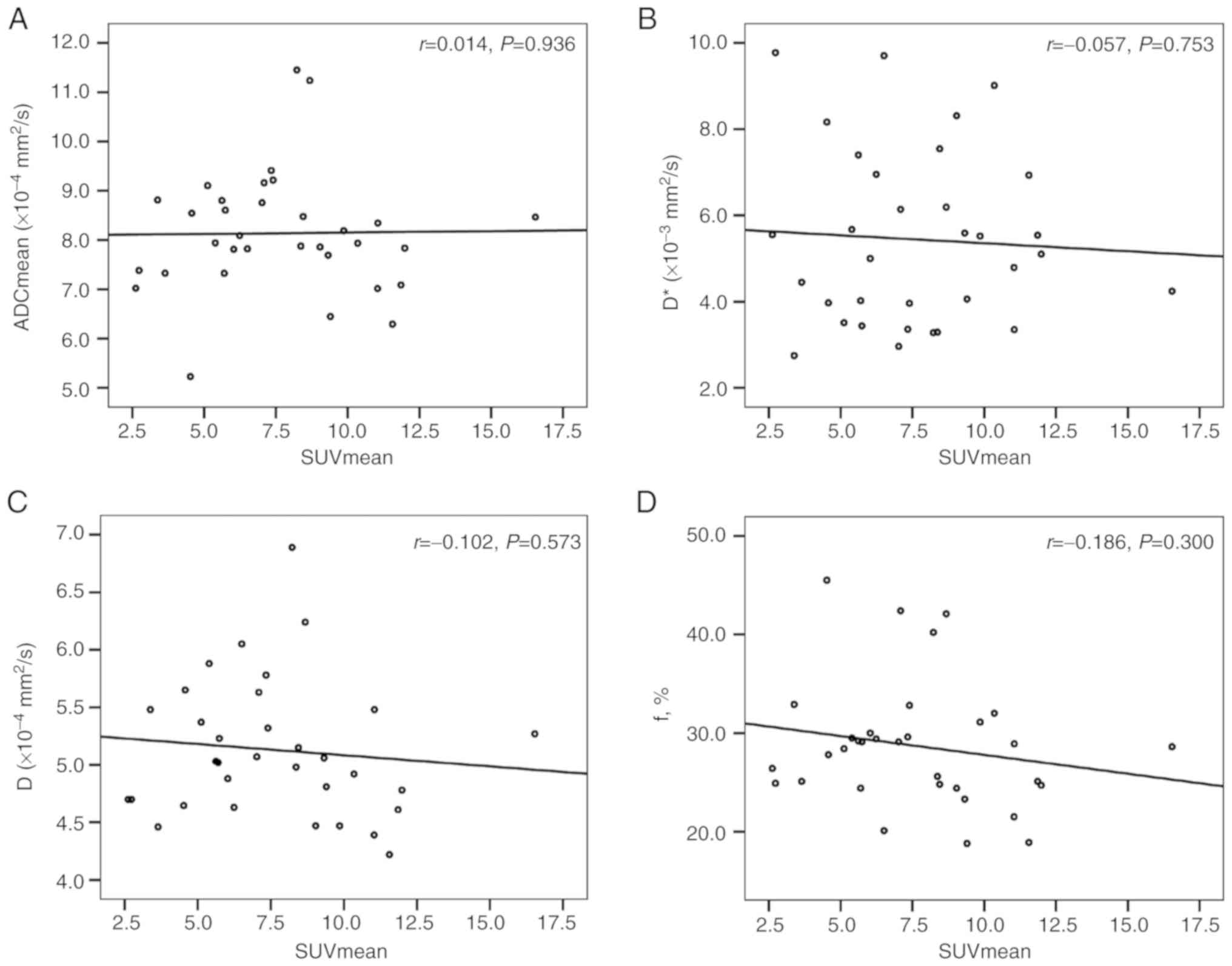
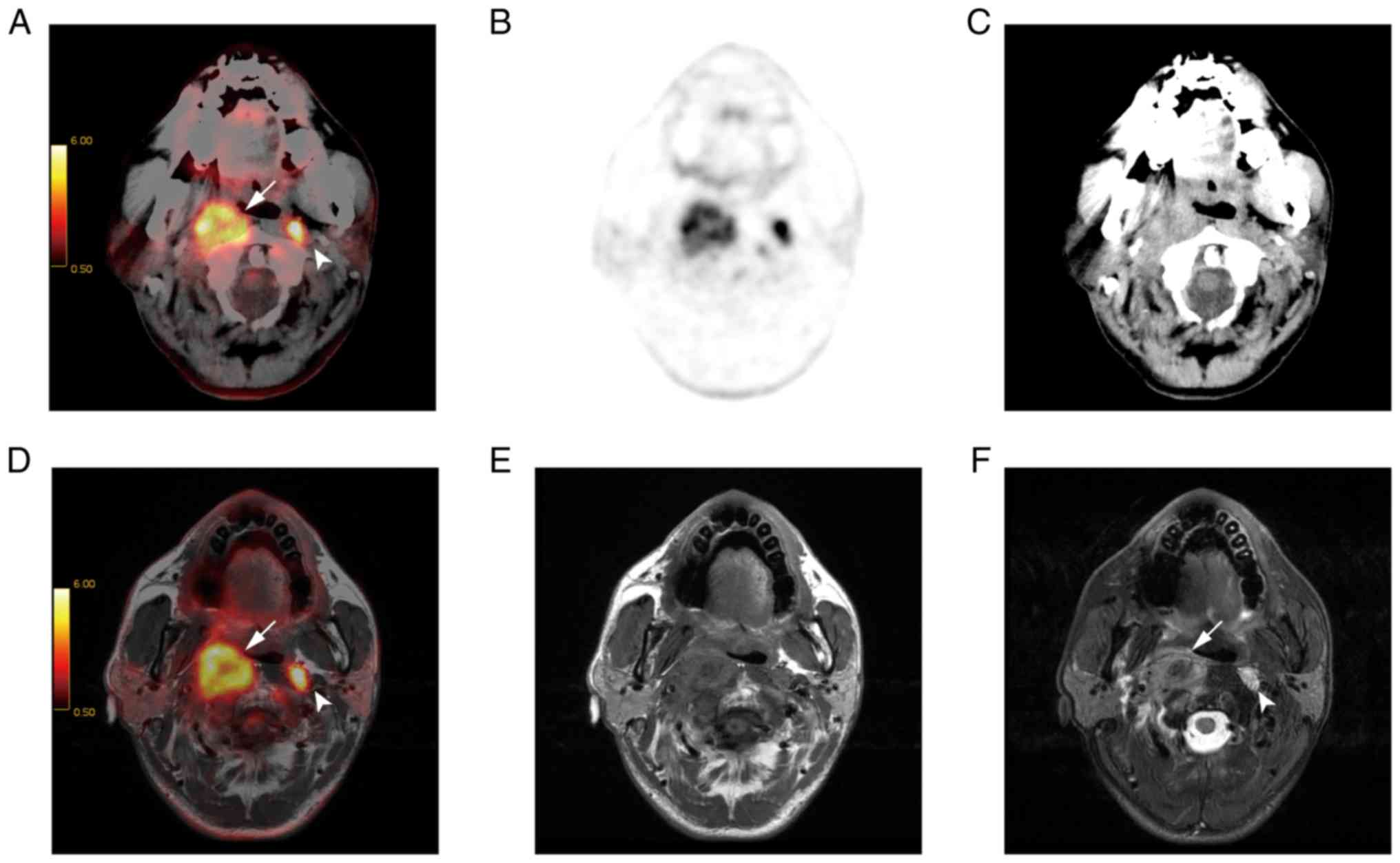
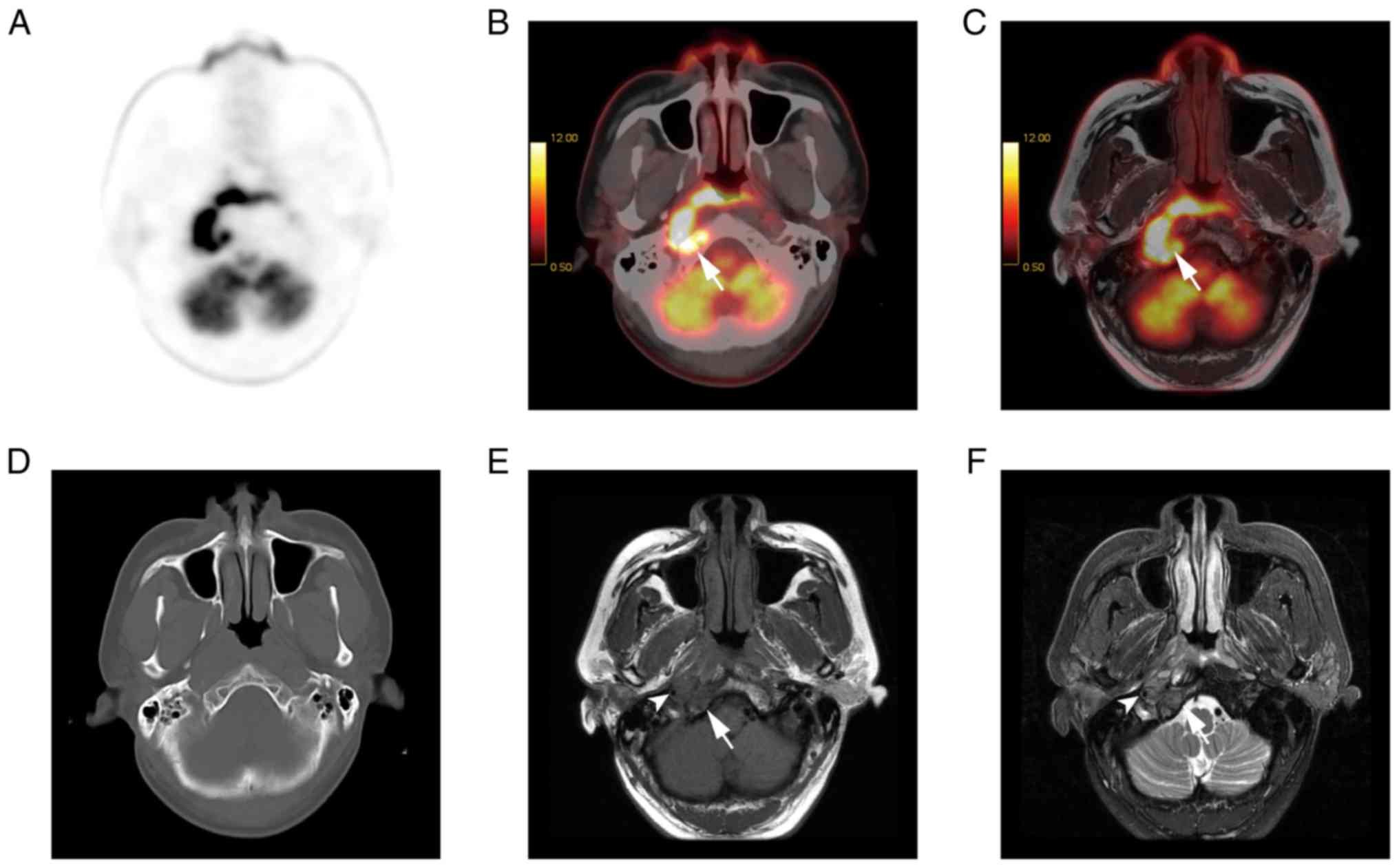
|
1
|
Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP and Chan ATC:
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 387:1012–1024. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee AW, Ma BB, Ng WT and Chan AT:
Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Current practice and future
perspective. J Clin Oncol. 33:3356–3364. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chang KP, Tsang NM, Liao CT, Hsu CL, Chung
MJ, Lo CW, Chan SC, Ng SH, Wang HM and Yen TC: Prognostic
significance of 18F-FDG PET parameters and plasma
Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in patients with nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. J Nucl Med. 53:21–28. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang Z, Shi Q, Zhang Y, Pan H, Yao Z, Hu
S, Shi W, Zhu B, Zhang Y and Hu C: Pretreatment 18F-FDG
uptake heterogeneity can predict survival in patients with locally
advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma-a retrospective study. Radiat
Oncol. 10:42015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vellayappan BA, Soon YY, Earnest A, Zhang
Q, Koh WY, Tham IW and Lee KM: Accuracy of
18F-flurodeoxyglucose-positron emission
tomography/computed tomography in the staging of newly diagnosed
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Radiol Oncol. 48:331–338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chua ML, Ong SC, Wee JT, Ng DC, Gao F, Tan
TW, Fong KW, Chua ET, Khoo JB and Low JS: Comparison of 4
modalities for distant metastasis staging in endemic nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Head Neck. 31:346–354. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chang MC, Chen JH, Liang JA, Yang KT,
Cheng KY and Kao CH: Accuracy of whole-body FDG-PET and FDG-PET/CT
in M staging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Eur J Radiol. 82:366–373. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Varoquaux A, Rager O, Lovblad KO,
Masterson K, Dulguerov P, Ratib O, Becker CD and Becker M:
Functional imaging of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with
diffusion-weighted MRI and FDG PET/CT: Quantitative analysis of ADC
and SUV. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 40:842–852. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Regier M, Derlin T, Schwarz D, Laqmani A,
Henes FO, Groth M, Buhk JH, Kooijman H and Adam G: Diffusion
weighted MRI and 18F-FDG PET/CT in non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC): Does the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC)
correlate with tracer uptake (SUV). Eur J Radiol. 81:2913–2918.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baba S, Isoda T, Maruoka Y, Kitamura Y,
Sasaki M, Yoshida T and Honda H: Diagnostic and prognostic value of
pretreatment SUV in 18F-FDG/PET in breast cancer:
Comparison with apparent diffusion coefficient from
diffusion-weighted MR imaging. J Nucl Med. 55:736–742. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nakajo M, Kajiya Y, Kaneko T, Kaneko Y,
Takasaki T, Tani A, Ueno M, Koriyama C and Nakajo M: FDG PET/CT and
diffusion-weighted imaging for breast cancer: Prognostic value of
maximum standardized uptake values and apparent diffusion
coefficient values of the primary lesion. Eur J Nucl Med Mol
Imagin. 37:2011–2020. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kitajima K, Yamano T, Fukushima K, Miyoshi
Y and Hirota S, Kawanaka Y, Miya M, Doi H, Yamakado K and Hirota S:
Correlation of the SUVmax of FDG-PET and ADC values of
diffusion-weighted MR imaging with pathologic prognostic factors in
breast carcinoma. Eur J Radiol. 85:943–949. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wong CS, Gong N, Chu YC, Anthony MP, Chan
Q, Lee HF, Chu KM and Khong PL: Correlation of measurements from
diffusion weighted MR imaging and FDG PET/CT in GIST patients: ADC
versus SUV. Eur J Radiol. 81:2122–2126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brandmaier P, Purz S, Bremicker K, Höckel
M, Barthel H, Kluge R, Kahn T, Sabri O and Stumpp P: Simultaneous
[18F]FDG-PET/MRI: Correlation of apparent diffusion
coefficient (ADC) and standardized uptake value (SUV) in primary
and recurrent cervical cancer. PLoS One. 10:e01416842015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu X, Korkola P, Pertovaara H, Eskola H,
Järvenpää R and Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL: No correlation between
glucose metabolism and apparent diffusion coefficient in diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma: A PET/CT and DW-MRI study. Eur J Radiol.
79:e117–e121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Giraudo C, Karanikas G, Weber M, Raderer
M, Jaeger U, Simonitsch-Klupp I and Mayerhoefer ME: Correlation
between glycolytic activity on [18F]-FDG-PET and cell density on
diffusion-weighted MRI in lymphoma at staging. J Magn Reson
Imaging. 47:1217–1226. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fruehwald-Pallamar J, Czerny C,
Mayerhoefer ME, Halpern BS, Eder-Czembirek C, Brunner M, Schuetz M,
Weber M, Fruehwald L and Herneth AM: Functional imaging in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma: Correlation of PET/CT and
diffusion-weighted imaging at 3 tesla. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
38:1009–1019. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakajo M, Nakajo M, Kajiya Y, Tani A,
Kamiyama T, Yonekura R, Fukukura Y, Matsuzaki T, Nishimoto K,
Nomoto M and Koriyama C: FDG PET/CT and diffusion-weighted imaging
of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Comparison of prognostic
significance between primary tumor standardized uptake value and
apparent diffusion coefficient. Clin Nucl Med. 37:475–480. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Choi SH, Paeng JC, Sohn CH, Pagsisihan JR,
Kim YJ, Kim KG, Jang JY, Yun TJ, Kim JH, Han MH and Chang KH:
Correlation of 18F-FDG uptake with apparent diffusion
coefficient ratio measured on standard and high b value diffusion
MRI in head and neck cancer. J Nucl Med. 52:1056–1062. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dixon WT: Separation of diffusion and
perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging: A modest
proposal with tremendous potential. Radiology. 168:566–567. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Aubin
ML, Vignaud J and Laval-Jeantet M: Separation of diffusion and
perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology.
168:497–505. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier
P, Cabanis E and Laval-Jeantet M: MR imaging of intravoxel
incoherent motions: Application to diffusion and perfusion in
neurologic disorders. Radiology. 161:401–407. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu C, Liang C, Liu Z, Zhang S and Huang
B: Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in evaluation of breast
lesions: Comparison with conventional DWI. Eur J Radiol.
82:e782–e789. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang SX, Jia QJ, Zhang ZP, Liang CH, Chen
WB, Qiu QH and Li H: Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI: Emerging
applications for nasopharyngeal carcinoma at the primary site. Eur
Radiol. 24:1998–2004. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jia QJ, Zhang SX, Chen WB, Liang L, Zhou
ZG, Qiu QH, Liu ZY, Zeng QX and Liang CH: Initial experience of
correlating parameters of intravoxel incoherent motion and dynamic
contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging at 3.0 T in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 24:3076–3087. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lai V, Li X, Lee VH, Lam KO, Fong DY,
Huang B, Chan Q and Khong PL: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Comparison
of diffusion and perfusion characteristics between different tumour
stages using intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Eur Radiol.
24:176–183. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu XP, Hou J, Li FP, Wang H, Hu PS, Bi F
and Wang W: Intravoxel incoherent motion diffusion weighted
magnetic resonance imaging for differentiation between
nasopharyngeal carcinoma and lymphoma at the primary site. J Comput
Assist Tomogr. 40:413–418. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xiao-Ping Y, Jing H, Fei-ping L, Yin H,
Qiang L, Lanlan W and Wei W: Intravoxel incoherent motion MRI for
predicting early response to induction chemotherapy and
chemoradiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Magn
Reson Imaging. 43:1179–1190. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiao Y, Pan J, Chen Y, Chen Y, He Z and
Zheng X: Intravoxel incoherent motion-magnetic resonance imaging as
an early predictor of treatment response to neoadjuvant
chemotherapy in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e9732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Queiroz MA and Huellner MW: PET/MR in
cancers of the head and neck. Semin Nucl Med. 45:248–265. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Spick C, Herrmann K and Czernin J:
18F-FDG PET/CT and PET/MRI perform equally well in
cancer: Evidence from studies on more than 2,300 patients. J Nucl
Med. 57:420–430. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Queiroz MA, Hüllner M, Kuhn F, Huber G,
Meerwein C, Kollias S, von Schulthess G and Veit-Haibach P: PET/MRI
and PET/CT in follow-up of head and neck cancer patients. Eur J
Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 41:1066–1075. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kuhn FP, Hüllner M, Mader CE, Kastrinidis
N, Huber GF, von Schulthess GK, Kollias S and Veit-Haibach P:
Contrast-enhanced PET/MR imaging versus contrast-enhanced PET/CT in
head and neck cancer: How much MR information is needed. J Nucl
Med. 55:551–558. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kubiessa K, Purz S, Gawlitza M, Kühn A,
Fuchs J, Steinhoff KG, Boehm A, Sabri O, Kluge R, Kahn T and Stumpp
P: Initial clinical results of simultaneous 18F-FDG
PET/MRI in comparison to 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with
head and neck cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 41:639–648. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Partovi S, Kohan A, Vercher-Conejero JL,
Rubbert C, Margevicius S, Schluchter MD, Gaeta C, Faulhaber P and
Robbin MR: Qualitative and quantitative performance of
18F-FDG-PET/MRI versus 18F-FDG-PET/CT in
patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
35:1970–1975. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Varoquaux A, Rager O, Poncet A, Delattre
BM, Ratib O, Becker CD, Dulguerov P, Dulguerov N, Zaidi H and
Becker M: Detection and quantification of focal uptake in head and
neck tumours: 18F-FDG PET/MR versus PET/CT. Eur J Nucl
Med Mol Imaging. 41:462–475. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Covello M, Cavaliere C, Aiello M, Cianelli
MS, Mesolella M, Iorio B, Rossi A and Nicolai E: Simultaneous
PET/MR head-neck cancer imaging: Preliminary clinical experience
and multiparametric evaluation. Eur J Radiol. 84:1269–1276. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schaarschmidt BM, Heusch P, Buchbender C,
Ruhlmann M, Bergmann C, Ruhlmann V, Schlamann M, Antoch G, Forsting
M and Wetter A: Locoregional tumour evaluation of squamous cell
carcinoma in the head and neck area: A comparison between MRI,
PET/CT and integrated PET/MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
43:92–102. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chan SC, Yeh CH, Yen TC, Ng SH, Chang JT,
Lin CY, Yen-Ming T, Fan KH, Huang BS, Hsu CL, et al: Clinical
utility of simultaneous whole-body 18F-FDG PET/MRI as a single-step
imaging modality in the staging of primary nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 45:1297–1308. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cao C, Yang P, Xu Y, Niu T, Hu Q and Chen
X: Feasibility of multiparametric imaging with PET/MR in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A pilot study. Oral Oncol. 93:91–95.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene F and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual7th. Springer; New
York, NY: 2010
|
|
42
|
Prakash P, Kalra MK, Digumarthy SR, Hsieh
J, Pien H, Singh S, Gilman MD and Shepard JA: Radiation dose
reduction with chest computed tomography using adaptive statistical
iterative reconstruction technique: Initial experience. J Comput
Assist Tomogr. 34:40–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rodrigues RS, Bozza FA, Christian PE,
Hoffman JM, Butterfield RI, Christensen CR, Heilbrun M, Wiggins RH
3rd, Hunt JP, Bentz BG, et al: Comparison of whole-body PET/CT,
dedicated high-resolution head and neck PET/CT, and
contrast-enhanced CT in preoperative staging of clinically M0
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Nucl Med.
50:1205–1213. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Abdel Khalek Abdel Razek A and King A: MRI
and CT of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 198:11–18.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Le Bihan D, Turner R and MacFall JR:
Effects of intravoxel incoherent motions (IVIM) in steady-state
free precession (SSFP) imaging: Application to molecular diffusion
imaging. Magn Reson Med. 10:324–337. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
King AD, Vlantis AC, Bhatia KS, Zee BC,
Woo JK, Tse GM, Chan AT and Ahuja AT: Primary nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: Diagnostic accuracy of MR imaging versus that of
endoscopy and endoscopic biopsy. Radiology. 258:531–537. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen YK, Su CT, Ding HJ, Chi KH, Liang JA,
Shen YY, Chen LK, Yeh CL, Liao AC and Kao CH: Clinical usefulness
of fused PET/CT compared with PET alone or CT alone in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Anticancer Res. 26:1471–1477.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ng SH, Chan SC, Yen TC, Chang JT, Liao CT,
Ko SF, Liu FY, Chin SC, Fan KH and Hsu CL: Staging of untreated
nasopharyngeal carcinoma with PET/CT: Comparison with conventional
imaging work-up. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 36:12–22. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Mohandas A, Marcus C, Kang H, Truong MT
and Subramaniam RM: FDG PET/CT in the management of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 203:W146–W157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Le Bihan D and Turner R: The capillary
network: A link between IVIM and classical perfusion. Magn Reson
Med. 27:171–178. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|