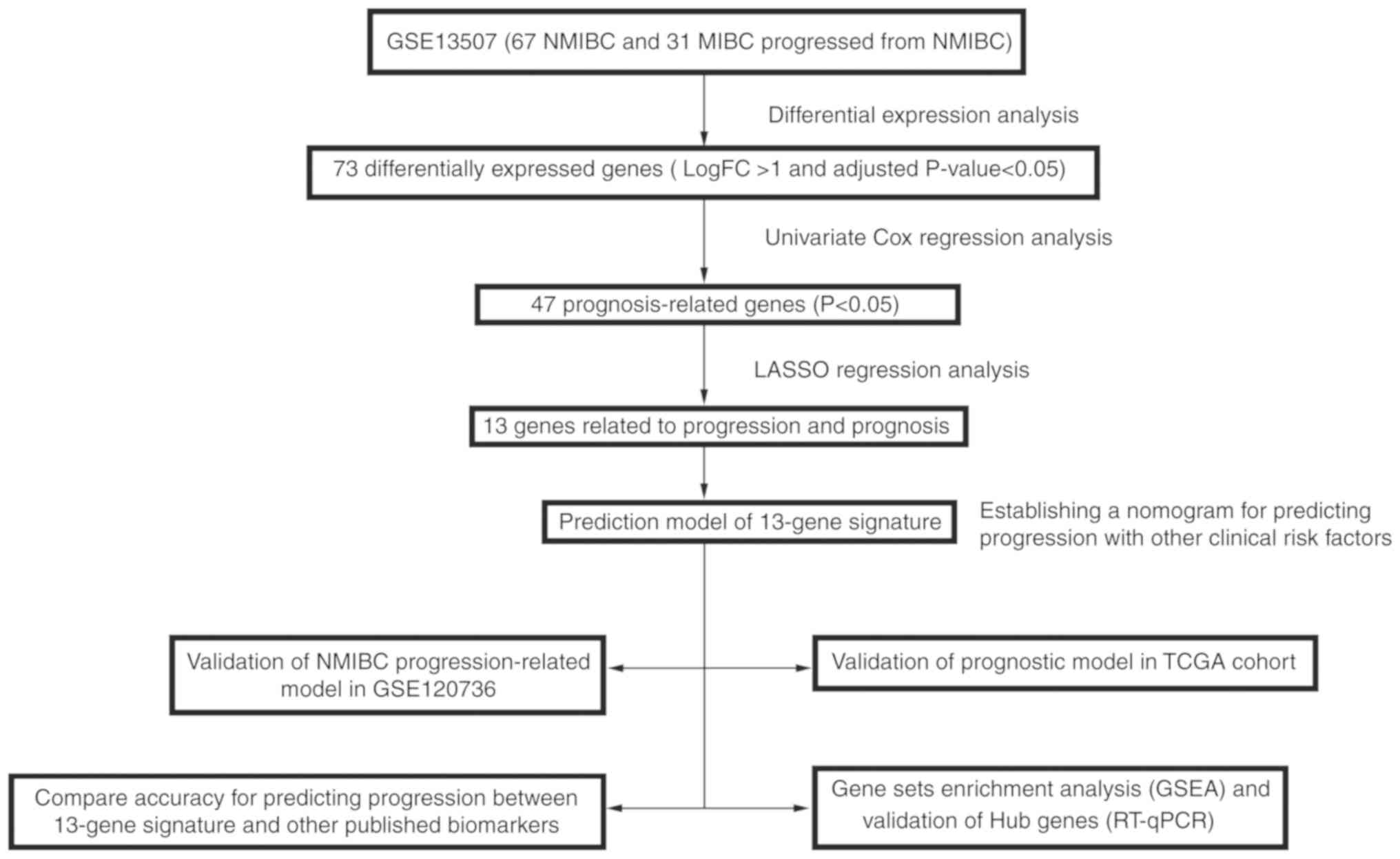
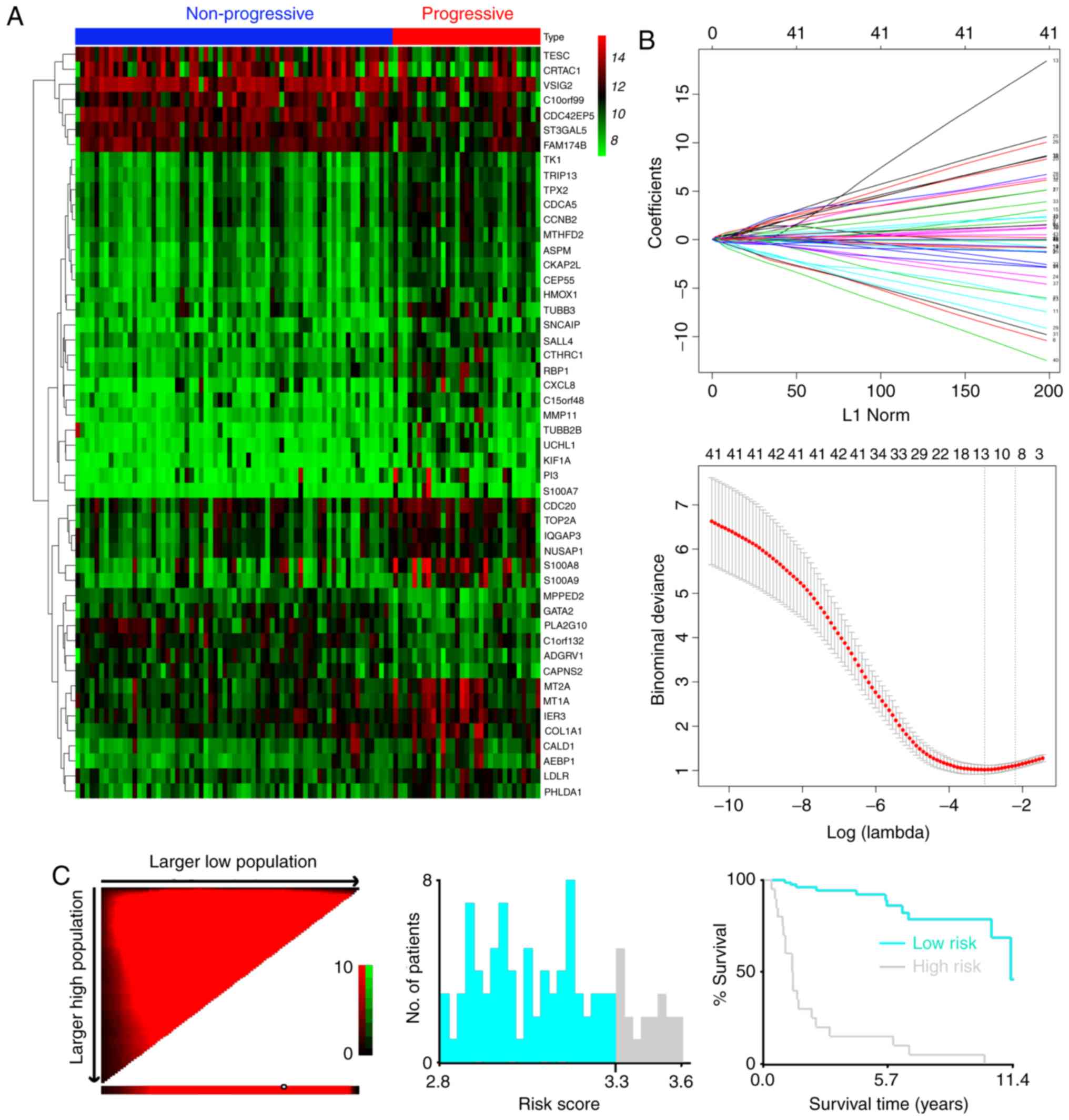
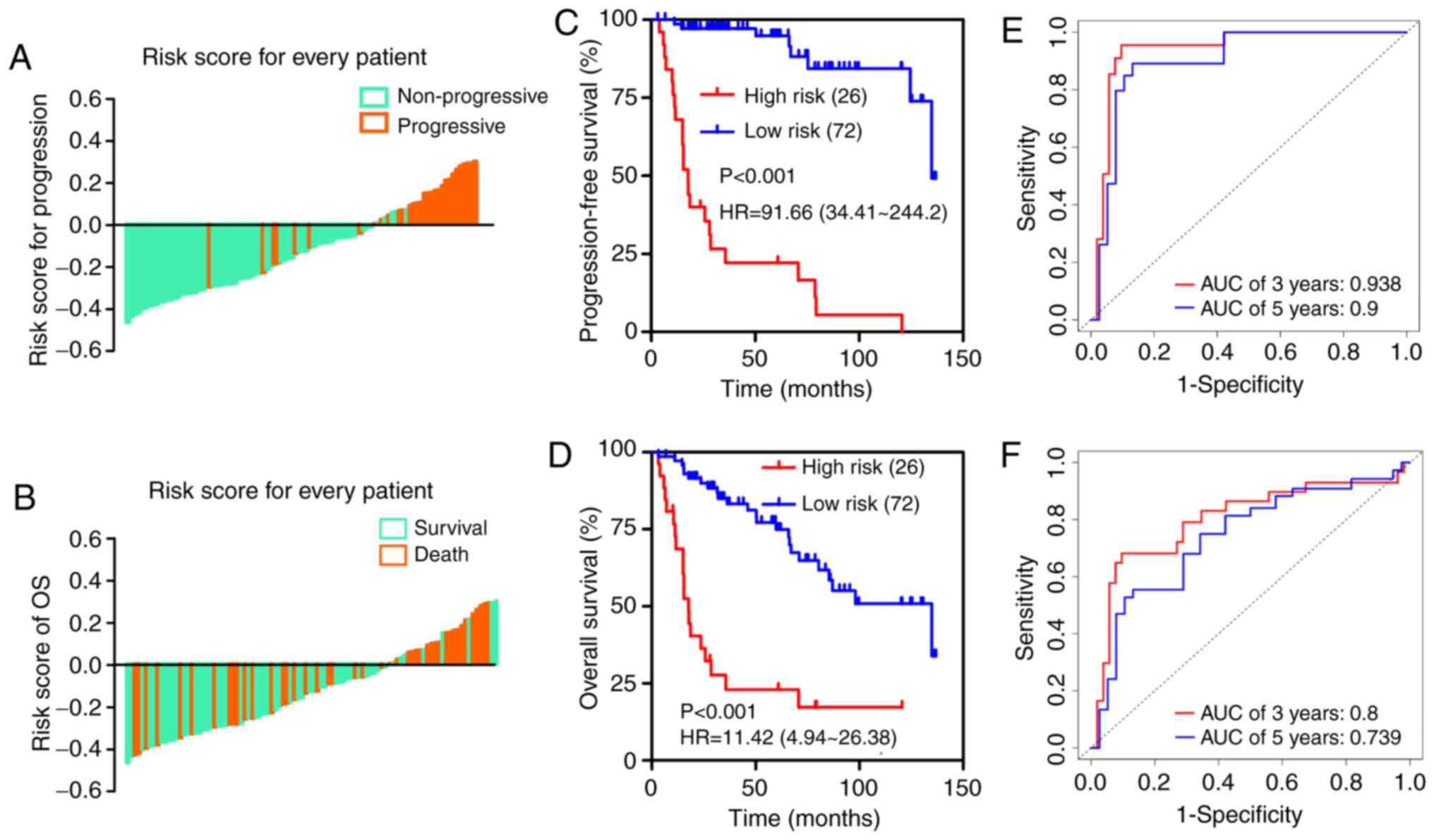
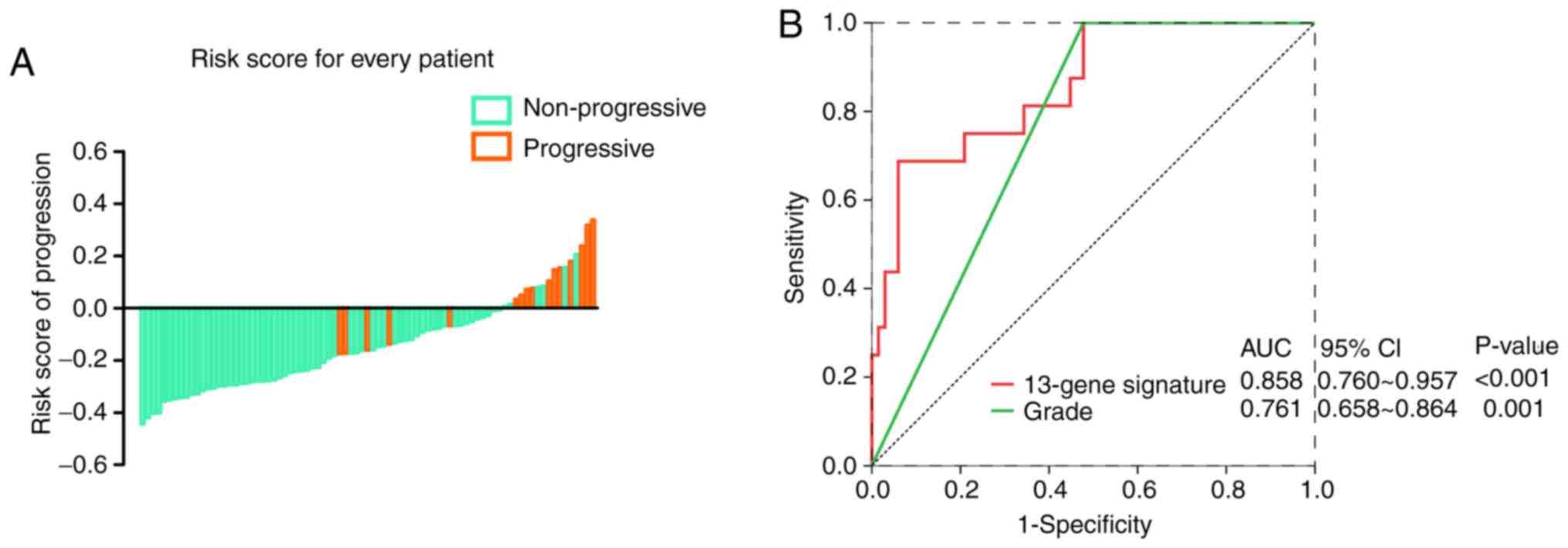
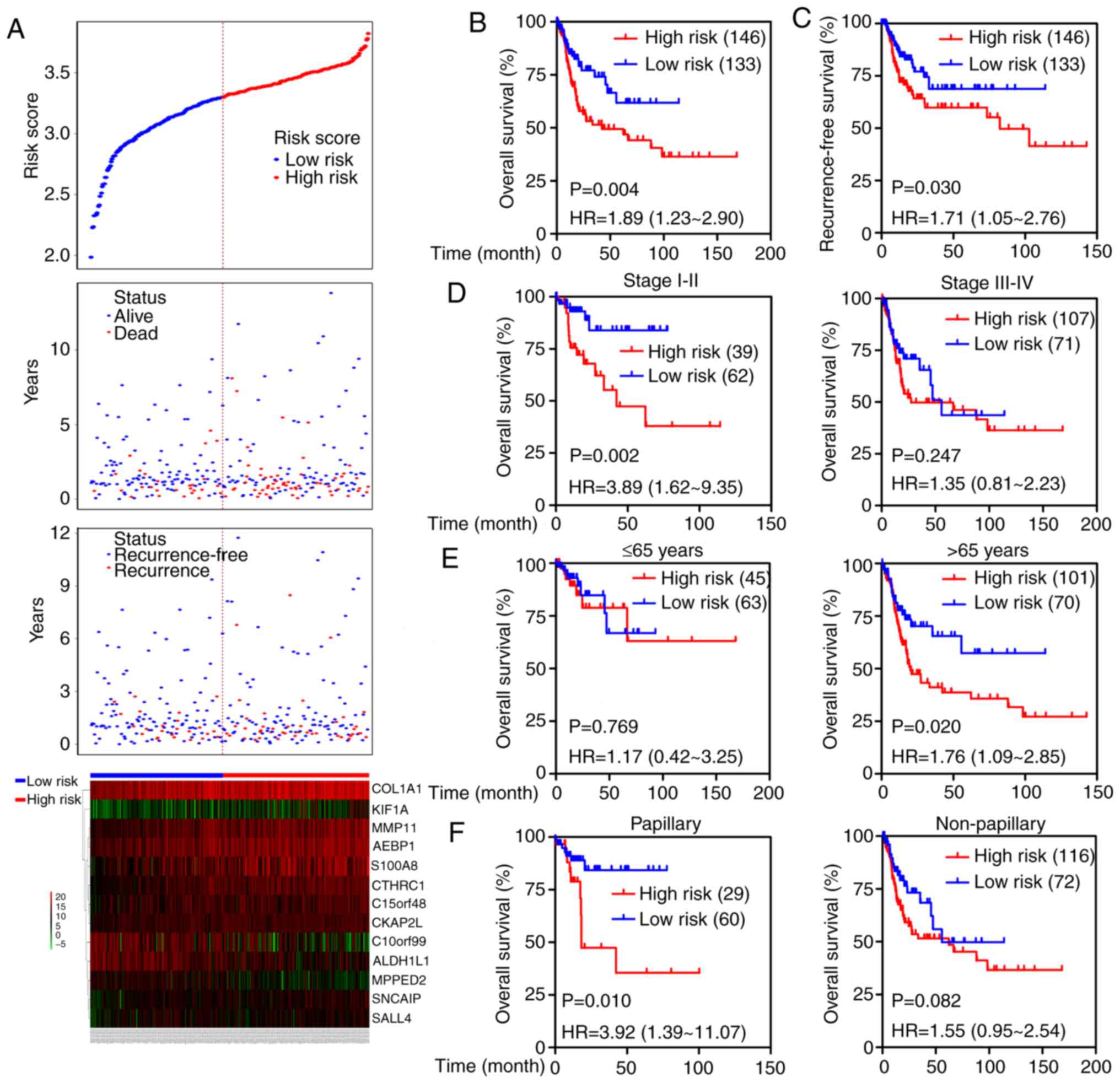
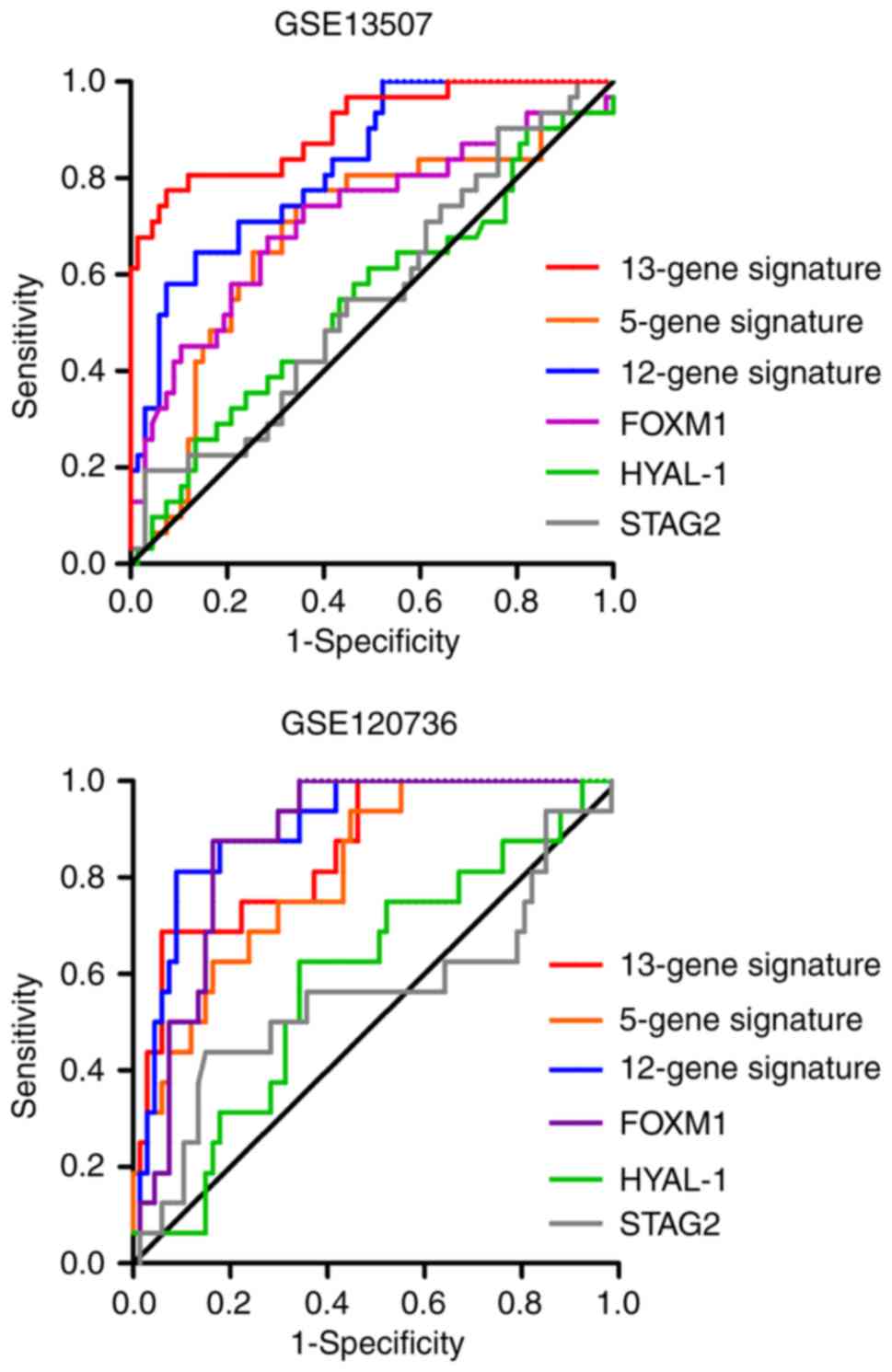
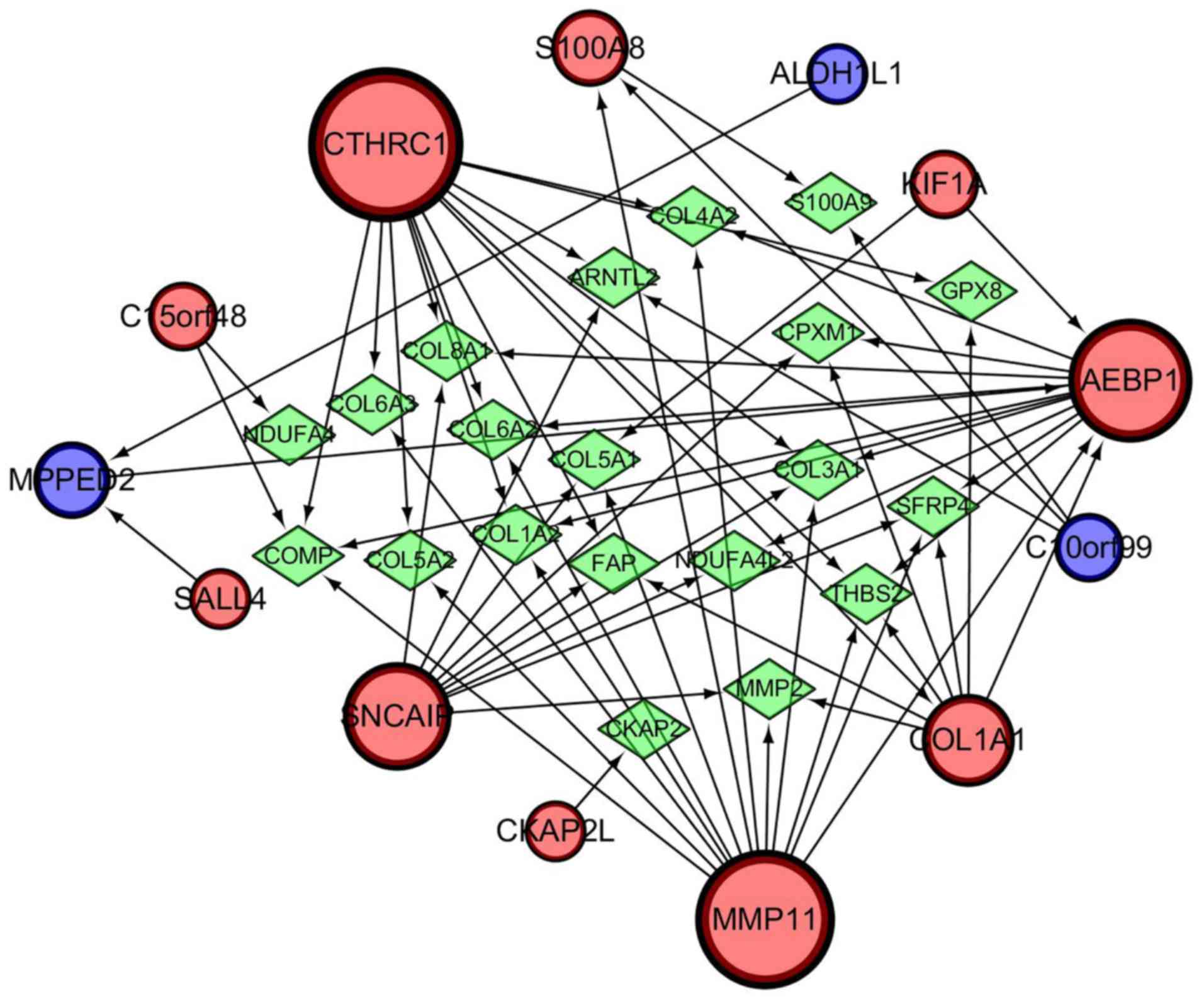
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Burger M, van der Aa MN, van Oers JM,
Brinkmann A, van der Kwast TH, Steyerberg EC, Stoehr R, Kirkels WJ,
Denzinger S, Wild PJ, et al: Prediction of progression of
non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer by WHO 1973 and 2004 grading and
by FGFR3 mutation status: A prospective study. Eur Urol.
54:835–843. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lamm D, Persad R, Brausi M, Buckley R,
Witjes JA, Palou J, Böhle A, Kamat AM, Colombel M and Soloway M:
Defining progression in nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer: It is
time for a new, standard definition. J Urol. 191:20–27. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sylvester RJ, van der Meijden AP,
Oosterlinck W, Witjes JA, Bouffioux C, Denis L, Newling DW and
Kurth K: Predicting recurrence and progression in individual
patients with stage Ta T1 bladder cancer using EORTC risk tables: A
combined analysis of 2596 patients from seven EORTC trials. Eur
Urol. 49:466–465. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Le Goux C, Vacher S, Pignot G, Sibony M,
Barry Delongchamps N, Terris B, Piaggio E, Zerbib M, Damotte D and
Bieche I: mRNA Expression levels of genes involved in antitumor
immunity: Identification of a 3-gene signature associated with
prognosis of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Oncoimmunology.
6:e13583302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sanchez-Carbayo M, Socci ND, Lozano J,
Saint F and Cordon-Cardo C: Defining molecular profiles of poor
outcome in patients with invasive bladder cancer using
oligonucleotide microarrays. J Clin Oncol. 24:778–789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang L, Taylor J, Eustace A, Irlam JJ,
Denley H, Hoskin PJ, Alsner J, Buffa FM, Harris AL, Choudhury A and
West CML: A gene signature for selecting benefit from hypoxia
modification of radiotherapy for high-risk bladder cancer patients.
Clin Cancer Res. 23:4761–4768. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JS, Leem SH, Lee SY, Kim SC, Park ES,
Kim SB, Kim SK, Kim YJ, Kim WJ and Chu IS: Expression signature of
E2F1 and its associated genes predict superficial to invasive
progression of bladder tumors. J Clin Oncol. 28:2660–2667. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: Affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Warde-Farley D, Donaldson SL, Comes O,
Zuberi K, Badrawi R, Chao P, Franz M, Grouios C, Kazi F, Lopes CT,
et al: The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network
integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38:W214–W220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yin H, Yang X, Gu W, Liu Y, Li X, Huang X,
Zhu X, Tao Y, Gou X and He W: HMGB1-mediated autophagy attenuates
gemcitabine-induced apoptosis in bladder cancer cells involving JNK
and ERK activation. Oncotarget. 8:71642–71656. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
van der Heijden AG, Mengual L, Lozano JJ,
Ingelmo-Torres M, Ribal MJ, Fernández PL, Oosterwijk E, Schalken
JA, Alcaraz A and Witjes JA: A five-gene expression signature to
predict progression in T1G3 bladder cancer. Eur J Cancer.
64:127–136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dyrskjøt L, Reinert T, Algaba F,
Christensen E, Nieboer D, Hermann GG, Mogensen K, Beukers W,
Marquez M, Segersten U, et al: Prognostic impact of a 12-gene
progression score in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A
prospective multicentre validation study. Eur Urol. 72:461–469.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rinaldetti S, Wirtz R, Worst TS, Hartmann
A, Breyer J, Dyrskjot L and Erben P: FOXM1 predicts disease
progression in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 144:1701–1709. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kramer MW, Golshani R, Merseburger AS,
Knapp J, Garcia A, Hennenlotter J, Duncan RC, Soloway MS, Jorda M,
Kuczyk MA, et al: HYAL-1 hyaluronidase: A potential prognostic
indicator for progression to muscle invasion and recurrence in
bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 57:86–93. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lelo A, Prip F, Harris BT, Solomon D,
Berry DL, Chaldekas K, Kumar A, Simko J, Jensen JB, Bhattacharyya
P, et al: STAG2 is a biomarker for prediction of recurrence and
progression in papillary non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 24:4145–4153. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Simon R and Altman DG: Statistical aspects
of prognostic factor studies in oncology. Br J Cancer. 69:979–985.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hedegaard J, Lamy P, Nordentoft I, Algaba
F, Høyer S, Ulhøi BP, Vang S, Reinert T, Hermann GG, Mogensen K, et
al: Comprehensive transcriptional analysis of early-stage
urothelial carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 30:27–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dyrskjøt L, Reinert T, Novoradovsky A,
Zuiverloon TC, Beukers W, Zwarthoff E, Malats N, Real FX, Segersten
U, Malmström PU, et al: Analysis of molecular intra-patient
variation and delineation of a prognostic 12-gene signature in
non-muscle invasive bladder cancer; technology transfer from
microarrays to PCR. Br J Cancer. 107:1392–1398. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai J, Yang L, Wang J, Xiao Y and Ruan Q:
Prognostic value of FOXM1 in patients with malignant solid tumor: A
meta-analysis and system review. Dis Markers. 2015:3524782015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang X, Shi Y, Yan J and Fan H:
Downregulation of FoxM1 inhibits cell growth and migration and
invasion in bladder cancer cells. Am J Transl Res. 10:629–638.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Breyer J, Wirtz RM, Erben P, Rinaldetti S,
Worst TS, Stoehr R, Eckstein M, Sikic D, Denzinger S, Burger M, et
al: FOXM1 overexpression is associated with adverse outcome and
predicts response to intravesical instillation therapy in stage pT1
non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. BJU Int. 123:187–196. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Diakos CI, Charles KA, McMillan DC and
Clarke SJ: Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness.
Lancet Oncol. 15:e493–e503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mbeutcha A, Shariat SF, Rieken M, Rink M,
Xylinas E, Seitz C, Lucca I, Mathieu R, Rouprêt M, Briganti A, et
al: Prognostic significance of markers of systemic inflammatory
response in patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Urol
Oncol. 34:483.e17–483.e24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kharaishvili G, Cizkova M, Bouchalova K,
Mgebrishvili G, Kolar Z and Bouchal J: Collagen triple helix repeat
containing 1 protein, periostin and versican in primary and
metastatic breast cancer: An immunohistochemical study. J Clin
Pathol. 64:977–982. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu G, Sengupta PK, Jamal B, Yang HY,
Bouchie MP, Lindner V, Varelas X and Kukuruzinska MA:
N-glycosylation induces the CTHRC1 protein and drives oral cancer
cell migration. J Biol Chem. 288:20217–20227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miller P, Kidwell KM, Thomas D, Sabel M,
Rae JM, Hayes DF, Hudson BI, El-Ashry D and Lippman ME: Elevated
S100A8 protein expression in breast cancer cells and breast tumor
stroma is prognostic of poor disease outcome. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 166:85–94. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim SK, Kim EJ, Leem SH, Ha YS, Kim YJ and
Kim WJ: Identification of S100A8-correlated genes for prediction of
disease progression in non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. BMC
Cancer. 10:212010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bansal N, Gupta A, Sankhwar SN and Mahdi
AA: Low- and high-grade bladder cancer appraisal via serum-based
proteomics approach. Clin Chim Acta. 436:97–103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nicklas AP, Kramer MW, Serth J,
Hennenlotter J, Hupe MC, Reimer DU, Stenzl A, Merseburger AS,
Kuczyk MA and von Klot CJ: Calgranulin A (S100A8) immunostaining: A
future candidate for risk assessment in patients with
non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). Adv Ther. 35:2054–2068.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li WM, Wei YC, Huang CN, Ke HL, Li CC, Yeh
HC, Chang LL, Huang CH, Li CF and Wu WJ: Matrix
metalloproteinase-11 as a marker of metastasis and predictor of
poor survival in urothelial carcinomas. J Surg Oncol. 113:700–707.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu SX, Huang J, Liu ZW, Chen HG, Guo P,
Cai QQ, Zheng JJ, Qin HD, Zheng ZS, Chen X, et al: A
genomic-clinicopathologic nomogram for the preoperative prediction
of lymph node metastasis in bladder cancer. EBioMedicine. 31:54–65.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|