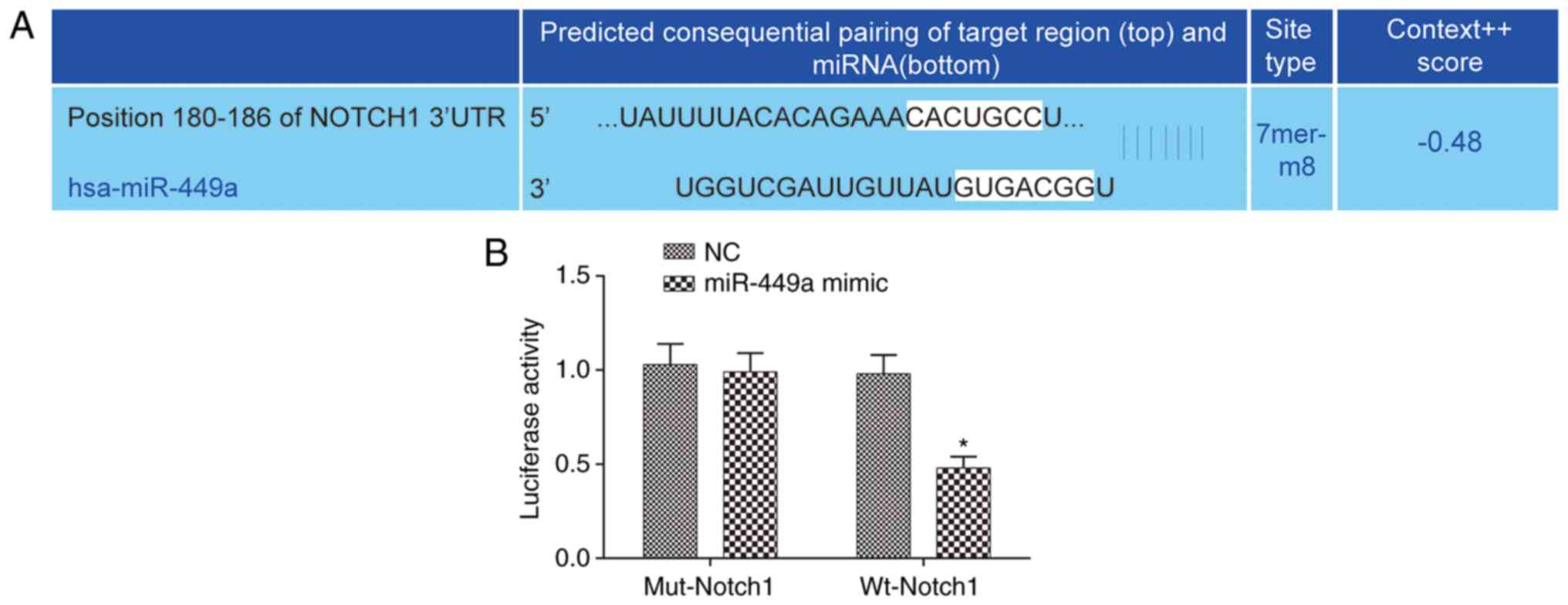
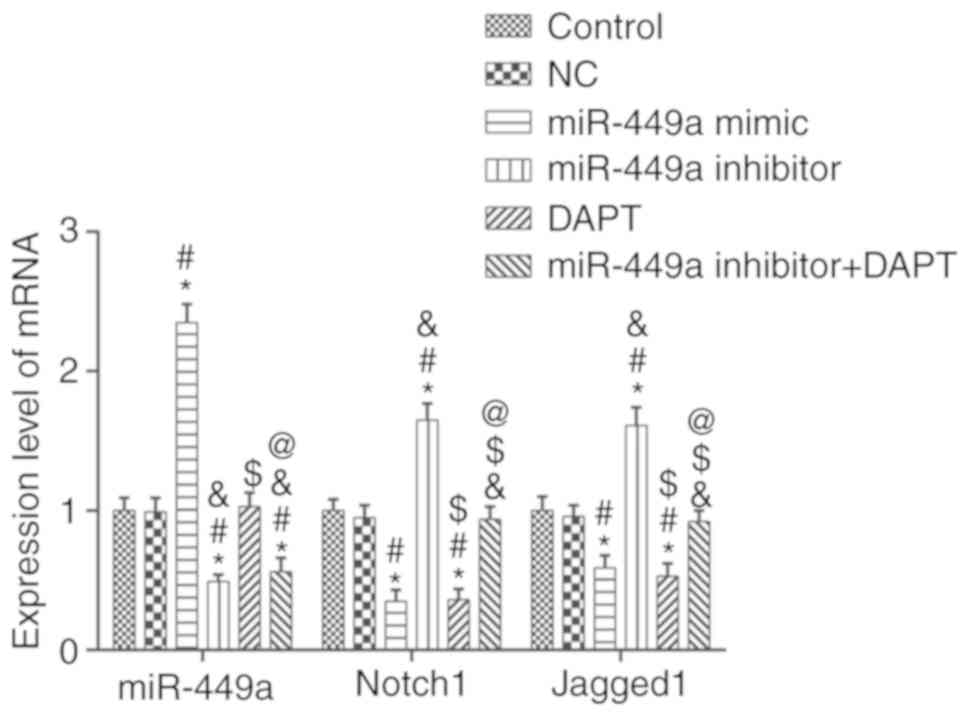
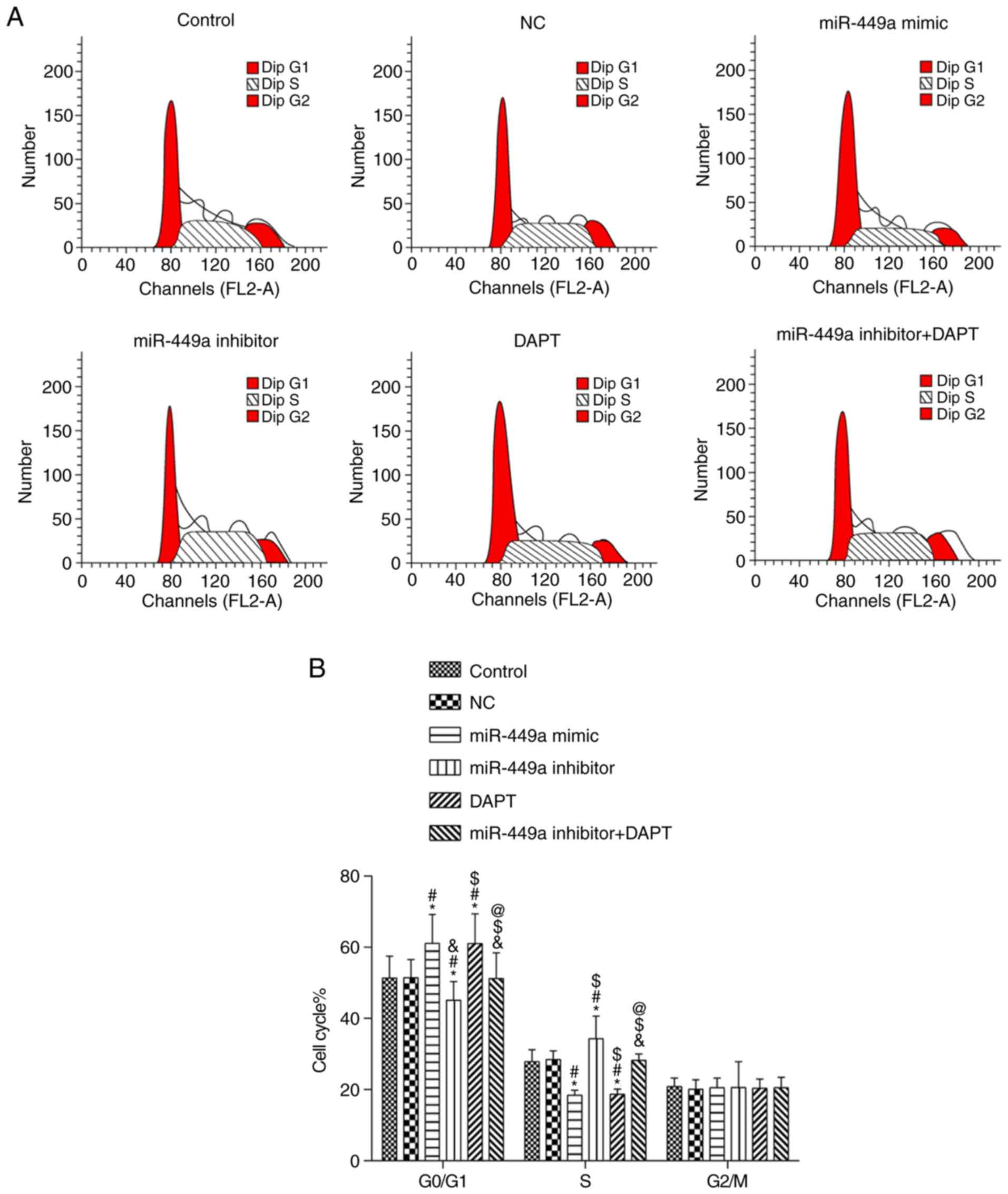
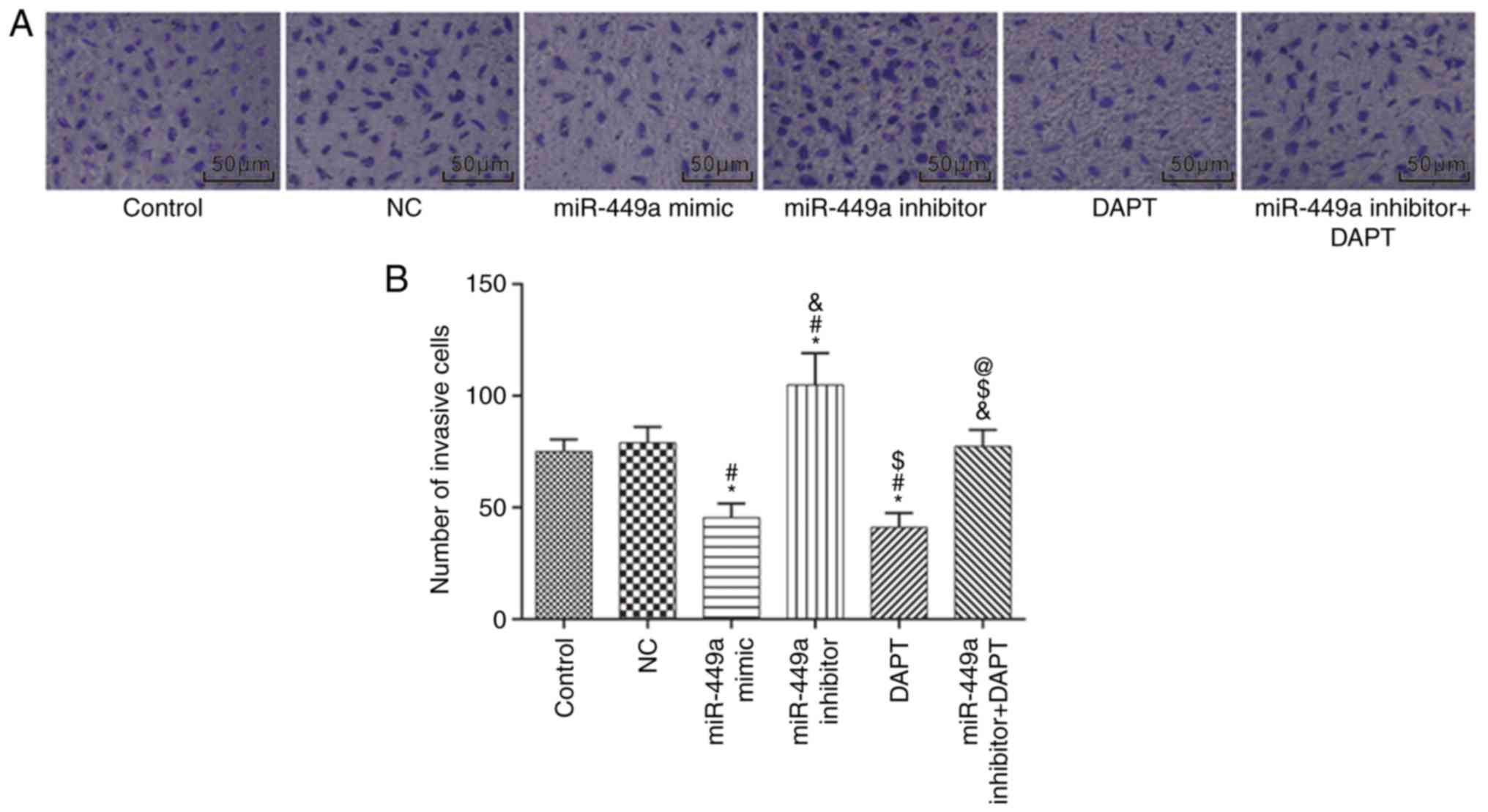
|
1
|
Li Z, Huang X, Xu J, Su Q, Zhao J and Ma
J: miR-449 overexpression inhibits papillary thyroid carcinoma cell
growth by targeting RET kinase-β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J
Oncol. 49:1629–1637. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu D, Liu J, Chen J, He H, Ma H and Lv X:
miR-449a suppresses tumor growth, migration, and invasion in
non-small cell lung cancer by targeting a HMGB1-Mediated NF-κB
signaling pathway. Oncol Res. 27:227–235. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang YL, Li XB, Hou YX, Fang NZ, You JC
and Zhou QH: The lncRNA XIST exhibits oncogenic properties via
regulation of miR-449a and Bcl-2 in human non-small cell lung. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 38:371–381. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ji C, Xu Q, Guo L, Wang X, Ren Y, Zhang H,
Zhu W, Ming Z, Yuan Y, Ren X, et al: eEF-2 Kinase-targeted miR-449b
confers radiation sensitivity to cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
418:64–74. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang H, Cai Y, Zheng L, Zhang Z, Lin X
and Jiang N: Long noncoding RNA NEAT1 regulate papillary thyroid
cancer progression by modulating miR-129-5p/KLK7 expression. J Cell
Physiol. 233:6638–6648. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Geraldo MV, Fuziwara CS, Friguglieti CU,
Costa RB, Kulcsar MA, Yamashita AS and Kimura ET: MicroRNAs
miR-146-5p and let-7f as prognostic tools for aggressive papillary
thyroid carcinoma: A case report. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol.
56:552–557. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bou Kheir T, Futoma-Kazmierczak E,
Jacobsen A, Krogh A, Bardram L, Hother C, Grønbaek K, Federspiel B,
Lund AH and Friis-Hansen L: miR-449 inhibits cell proliferation and
is down-regulated in gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 10:292011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim HJ, Kim MJ, Kim A, Jung CW, Park S,
Koh JS and Myung JK: The role of notch1 signaling in anaplastic
thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Res Treat. 49:509–517. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cao YW, Wan GX, Sun JP, Cui XB, Hu JM,
Liang WH, Zheng YQ, Li WQ and Li F: Implications of the
Notch1-Snail/Slug-epithelial to mesenchymal transition axis for
lymph node metastasis in infiltrating ductal carcinoma. Kaohsiung J
Med Sci. 31:70–76. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gopalakrishnan N, Sivasithamparam ND and
Devaraj H: Synergistic association of Notch and NFκB signaling and
role of Notch signaling in modulating epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Biochimie. 107:310–318.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Li Y, Kong D and Sarkar FH: The
role of Notch signaling pathway in epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) during development and tumor aggressiveness. Curr
Drug Targets. 11:745–751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bao B, Wang Z, Ali S, Kong D, Li Y, Ahmad
A, Banerjee S, Azmi AS, Miele L and Sarkar FH: Notch-1 induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition consistent with cancer stem cell
phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 307:26–36. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hu KF, Kong XY, Zhong MC, Wan HY, Lin N
and Pei XH: Brucine inhibits bone metastasis of breast cancer cells
by suppressing Jagged1/Notch1 signaling pathways. Chin J Integr
Med. 23:110–116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Q, Cao X, Tao G, Zhou F, Zhao P, Shen
Y and Chen X: Effects of FOXJ2 on TGF-beta1-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition through Notch signaling pathway
in non-small lung cancer. Cell Biol Int. 41:79–83. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bi YL, Min M, Shen W and Liu Y: Numb/Notch
signaling pathway modulation enhances human pancreatic cancer cell
radiosensitivity. Tumour Biol. 37:15145–15155. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheng J, Wu Q, Lv R, Huang L, Xu B, Wang
X, Chen A and He F: MicroRNA-449a inhibition protects H9C2 cells
against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury by targeting the
Notch-1 signaling pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:2587–2600.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak K and Schmittgen T: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu J, Li C, Liu C, Zhao S, Wang Y and Fu
Z: Expressions of miRNAs in papillary thyroid carcinoma and their
associations with the clinical characteristics of PTC. Cancer
Biomark. 18:87–94. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo W, Huang B, Li Z, Li H, Sun L, Zhang
Q, Qiu X and Wang E: MicroRNA-449a is downregulated in non-small
cell lung cancer and inhibits migration and invasion by targeting
c-Met. PLoS One. 8:e647592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang X, Wang HL, Liang HW, Liang L, Wen
DY, Zhang R, Chen G and Wei DM: Clinical significance of
microRNA-449a in hepatocellular carcinoma with microarray data
mining together with initial bioinformatics analysis. Exp Ther Med.
15:3247–3258. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li F, Liang J and Bai L: MicroRNA-449a
functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer by the
epigenetic regulation of ATDC expression. Biomed Pharmacother.
103:782–789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aster JC, Pear WS and Blacklow SC: The
varied roles of notch in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 12:245–275. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rong C, Feng Y and Ye Z: Notch is a
critical regulator in cervical cancer by regulating Numb splicing.
Oncol Lett. 13:2465–2470. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang X, Duan B and Zhou X: Long non-coding
RNA FOXD2-AS1 functions as a tumor promoter in colorectal cancer by
regulating EMT and Notch signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 21:3586–3591. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou Y, An Q, Guo RX, Qiao YH, Li LX,
Zhang XY and Zhao XL: miR424-5p functions as an anti-oncogene in
cervical cancer cell growth by targeting KDM5B via the Notch
signaling pathway. Life Sci. 171:9–15. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shen Q, Cohen B, Zheng W, Rahbar R, Martin
B, Murakami K, Lamorte S, Thompson P, Berman H, Zúñiga-Pflücker JC,
et al: Notch shapes the innate immunophenotype in breast cancer.
Cancer Discov. 7:1320–1335. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li C, Liu S, Yan R, Han N, Wong KK and Li
L: CD54-NOTCH1 axis controls tumor initiation and cancer stem cell
functions in human prostate cancer. Theranostics. 7:67–80. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cai H, Yao J, An Y, Chen X, Chen W, Wu D,
Luo B, Yang Y, Jiang Y, Sun D and He X: LncRNA HOTAIR acts a
competing endogenous RNA to control the expression of notch3 via
sponging miR-613 in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 8:32905–32917.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jung CW, Kong JS, Seol H, Park S, Koh JS,
Lee SS, Kim MJ, Choi IJ and Myung JK: Expression of activated
Notch1 and Hey1 in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Histopathology.
70:301–308. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun J, Shi R, Zhao S, Li X, Lu S, Bu H, Ma
X and Su C: E2F8, a direct target of miR-144, promotes papillary
thyroid cancer progression via regulating cell cycle. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 36:402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|