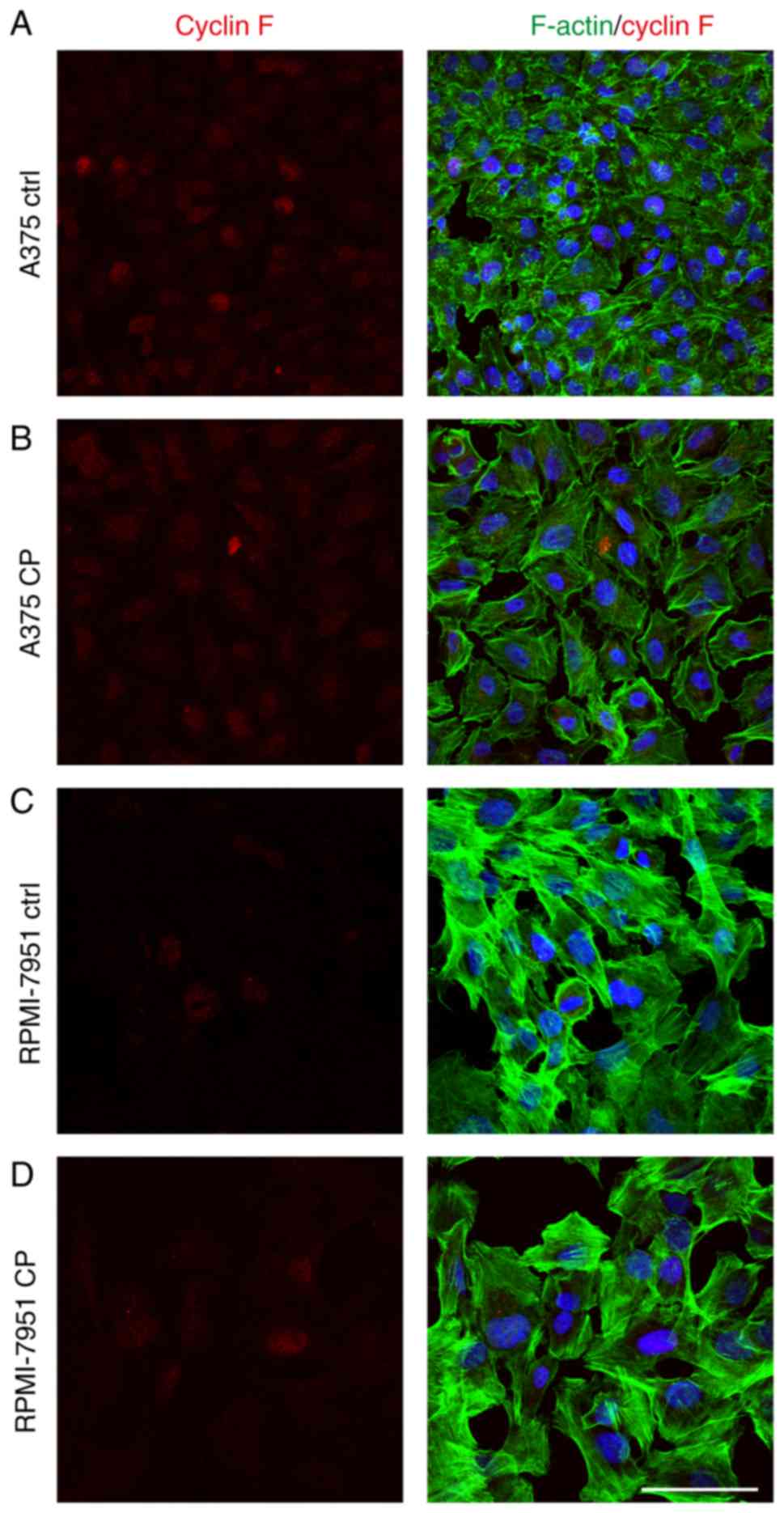
|
1
|
Maverakis E, Cornelius LA, Bowen GM, Phan
T, Patel FB, Fitzmaurice S, He Y, Burrall B, Duong C, Kloxin AM, et
al: Metastatic melanoma-a review of current and future treatment
options. Acta Dermato Venereol. 95:516–524. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fatkhutdinov N, Sproesser K, Krepler C,
Liu Q, Brafford PA, Herlyn M, Aird KM and Zhang R: Targeting RRM2
and mutant BRAF is a novel combinatorial strategy for melanoma. Mol
Cancer Res. 14:767–775. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rahman MA, Amin AR, Wang D, Koenig L,
Nannapaneni S, Chen Z, Wang Z, Sica G, Deng X, Chen ZG and Shin DM:
RRM2 regulates Bcl-2 in head and neck and lung cancers: A potential
target for cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 19:3416–3428. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang L, Meng L, Wang XW, Ma GY and Chen
JH: Expression of RRM1 and RRM2 as a novel prognostic marker in
advanced non-small cell lung cancer receiving chemotherapy. Tumor
Biol. 35:1899–1906. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bamford S, Dawson E, Forbes S, Clements J,
Pettett R, Dogan A, Flanagan A, Teague J, Futreal PA, Stratton MR
and Wooster R: The COSMIC (catalogue of somatic mutations in
cancer) database and website. Br J Cancer. 91:355–358. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Żuryń A, Krajewski A,
Klimaszewska-Wiśniewska A, Grzanka A and Grzanka D: Expression of
cyclin B1, D1 and K in non-small cell lung cancer H1299 cells
following treatment with sulforaphane. Oncol Rep. 41:1313–1323.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Levine AJ: p53, the cellular gatekeeper
for growth and division. Cell. 88:323–331. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lowe SW, Ruley HE, Jacks T and Housman DE:
p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer
agents. Cell. 74:957–967. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
D'Angiolella V, Donato V, Forrester FM,
Jeong YT, Pellacani C, Kudo Y, Saraf A, Florens L, Washburn MP and
Pagano M: Cyclin F-mediated degradation of ribonucleotide reductase
M2 controls genome integrity and DNA repair. Cell. 149:1023–1034.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shao J, Zhou B, Chu B and Yen Y:
Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors and future drug design. Curr
Cancer Drug Targets. 6:409–431. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Su YF, Wu TF, Ko JL, Tsai HT, Tee YT,
Chien MH, Chou CH, Lin WL, Low HY, Chou MY, et al: The expression
of ribonucleotide reductase M2 in the carcinogenesis of uterine
cervix and its relationship with clinicopathological
characteristics and prognosis of cancer patients. PLoS One.
9:e916442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhong Z, Cao Y, Yang S and Zhang S:
Overexpression of RRM2 in gastric cancer cell promotes their
invasiveness via AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway. Pharmazie.
71:280–284. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fu J, Qiu H, Cai M, Pan Y, Cao Y, Liu L,
Yun J and Zhang CZ: Low cyclin F expression in hepatocellular
carcinoma associates with poor differentiation and unfavorable
prognosis. Cancer Sci. 104:508–515. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deshmukh RS, Sharma S and Das S: Cyclin
F-dependent degradation of RBPJ inhibits
IDH1R132H-mediated tumorigenesis. Cancer Res.
78:6386–6398. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li J, D'Angiolella V, Seeley ES, Kim S,
Kobayashi T, Fu W, Campos EI, Pagano M and Dynlacht BD: USP33
regulates centrosome biogenesis via deubiquitination of the
centriolar protein CP110. Nature. 495:255–259. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Denu RA, Shabbir M, Nihal M, Singh CK,
Longley BJ, Burkard ME and Ahmad N: Centriole overduplication is
the predominant mechanism leading to centrosome amplification in
melanoma. Mol Cancer Res. 16:517–527. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Donaldson KL, Goolsby GL and Wahl AF:
Cytotoxicity of the anticancer agents cisplatin and taxol during
cell proliferation and the cell cycle. Int J Cancer. 57:847–855.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Perego P, Giarola M, Righetti SC, Supino
R, Caserini C, Delia D, Pierotti MA, Miyashita T, Reed JC and
Zunino F: Association between cisplatin resistance and mutation of
p53 gene and reduced bax expression in ovarian carcinoma cell
systems. Cancer Res. 56:556–562. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hawkins DS, Demers GW and Galloway DA:
Inactivation of p53 enhances sensitivity to multiple
chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer Res. 56:892–898. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He Z, Hu X, Liu W, Dorrance A, Garzon R,
Houghton PJ and Shen C: P53 suppresses ribonucleotide reductase via
inhibiting mTORC1. Oncotarget. 8:41422–41431. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kollareddy M, Dimitrova E, Vallabhaneni
KC, Chan A, Le T, Chauhan KM, Carrero ZI, Ramakrishnan G, Watabe K,
Haupt Y, et al: Regulation of nucleotide metabolism by mutant p53
contributes to its gain-of-function activities. Nat Commun.
6:73892015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klein DK, Hoffmann S, Ahlskog JK, O'Hanlon
K, Quaas M, Larsen BD, Rolland B, Rösner HI, Walter D, Kousholt AN,
et al: Cyclin F suppresses B-Myb activity to promote cell cycle
checkpoint control. Nat Commun. 6:58002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mavrommati I, Faedda R, Galasso G, Li J,
Burdova K, Fischer R, Kessler BM, Carrero ZI, Guardavaccaro D,
Pagano M and D'Angiolella V: β-TrCP- and casein kinase II-mediated
degradation of cyclin F controls timely mitotic progression. Cell
Rep. 24:3404–3412. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen T, You Y, Jiang H and Wang ZZ:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT): A biological process in
the development, stem cell differentiation, and tumorigenesis. J
Cell Physiol. 232:3261–3272. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Phi LTH, Sari IN, Yang YG, Lee SH, Jun N,
Kim KS, Lee YK and Kwon HY: Cancer stem cells (CSCs) in drug
resistance and their therapeutic implications in cancer treatment.
Stem Cells Int. 2018:54169232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu Y, So C, Lam HM, Fung MC and Tsang SY:
Apoptosis reversal promotes cancer stem cell-like cell formation.
Neoplasia. 20:295–303. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Loh YH, Wu Q, Chew JL, Vega VB, Zhang W,
Chen X, Bourque G, George J, Leong B, Liu J, et al: The Oct4 and
Nanog transcription network regulates pluripotency in mouse
embryonic stem cells. Nat Genet. 38:431–440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li SJ, Huang J, Zhou XD, Zhang WB, Lai YT
and Che GW: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
Oct-4 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 8:1587–1600.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Comisso E, Scarola M, Rosso M, Piazza S,
Marzinotto S, Ciani Y, Orsaria M, Mariuzzi L, Schneider C,
Schoeftner S and Benetti R: OCT4 controls mitotic stability and
inactivates the RB tumor suppressor pathway to enhance ovarian
cancer aggressiveness. Oncogene. 36:4253–4266. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chiou SH, Wang ML, Chou YT, Chen CJ, Hong
CF, Hsieh WJ, Chang HT, Chen YS, Lin TW, Hsu HS and Wu CW:
Coexpression of Oct4 and nanog enhances malignancy in lung
adenocarcinoma by inducing cancer stem cell-like properties and
epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation. Cancer Res.
70:10433–10444. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Borrull A, Ghislin S, Deshayes F, Lauriol
J, Alcaide-Loridan C and Middendorp S: Nanog and Oct4
overexpression increases motility and transmigration of melanoma
cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:1145–1154. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pan D, Chen Y, Du Y, Ren Z, Li X and Hu B:
Methylation of promoter of RBL1 enhances the radioresistance of
three dimensional cultured carcinoma cells. Oncotarget.
8:4422–4435. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang YM, Wu FJ, Du L, Li GY, Takahashi K,
Xue Y and Xue CH: Effects of polysaccharides from abalone (Haliotis
discus hannai Ino) on HepG2 cell proliferation. Int J Biol
Macromol. 66:354–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Choudhury R, Bonacci T, Wang X, Truong A,
Arceci A, Zhang Y, Mills CA, Kernan JL, Liu P and Emanuele MJ: The
E3 ubiquitin ligase SCF(Cyclin F) transmits AKT signaling to the
cell-cycle machinery. Cell Rep. 20:3212–3222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Choudhury R, Bonacci T, Arceci A, Lahiri
D, Mills CA, Kernan JL, Branigan TB, DeCaprio JA, Burke DJ and
Emanuele MJ: APC/C and SCF (cyclin F) constitute a reciprocal
feedback circuit controlling s-phase entry. Cell Rep. 16:3359–3372.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Walter D, Hoffmann S, Komseli ES,
Rappsilber J, Gorgoulis V and Sørensen CS: SCF(Cyclin F)-dependent
degradation of CDC6 suppresses DNA re-replication. Nat Commun.
7:105302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dankert JF, Rona G, Clijsters L, Geter P,
Skaar JR, Bermudez-Hernandez K, Sassani E, Fenyö D, Ueberheide B,
Schneider R and Pagano M: Cyclin F-mediated degradation of SLBP
limits H2A.X accumulation and apoptosis upon genotoxic stress in
G2. Mol Cell. 64:507–519. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gagat M, Krajewski A, Grzanka D and
Grzanka A: Potential role of cyclin F mRNA expression in the
survival of skin melanoma patients: Comprehensive analysis of the
pathways altered due to cyclin F upregulation. Oncol Rep.
40:123–144. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|