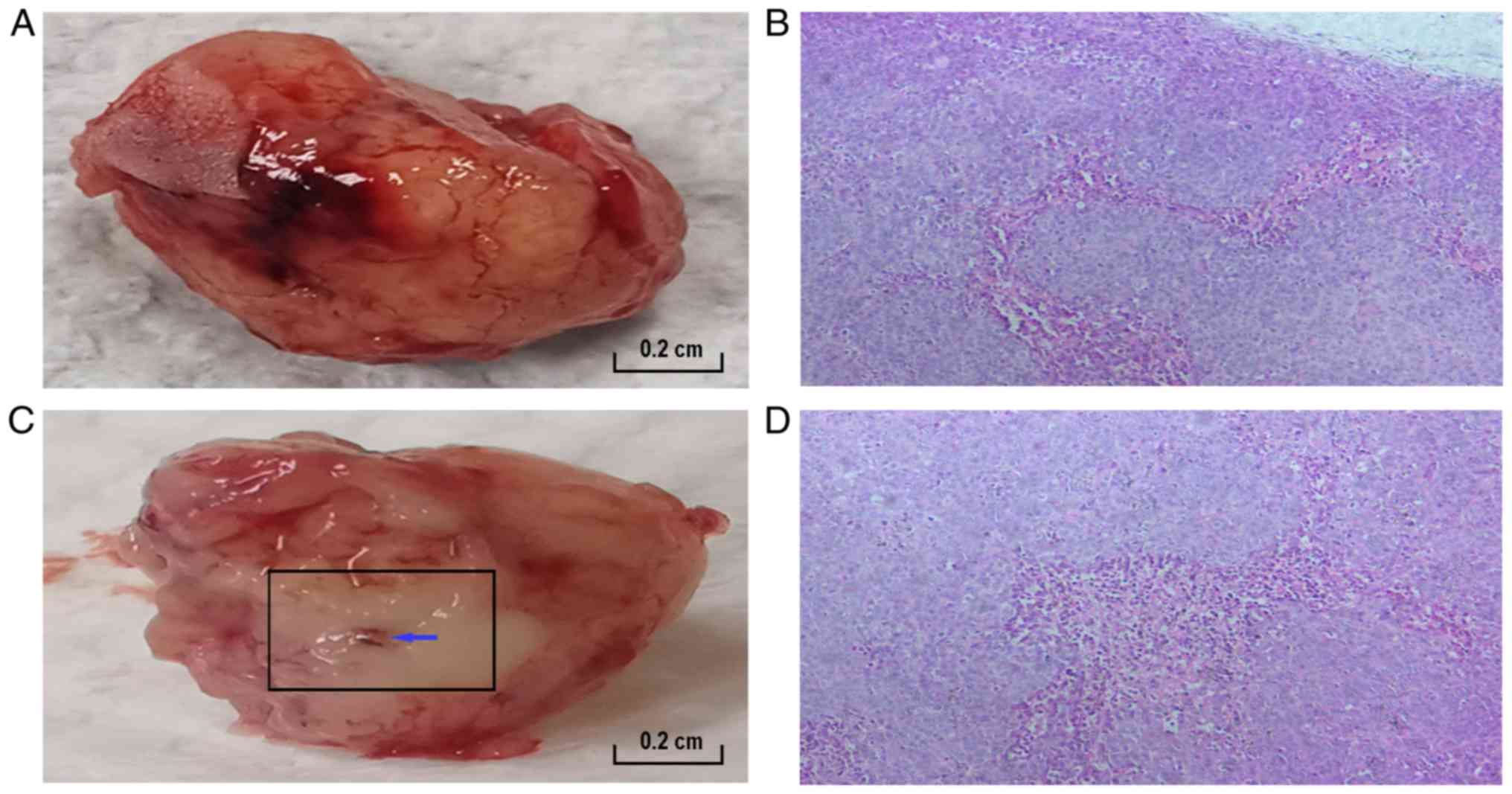
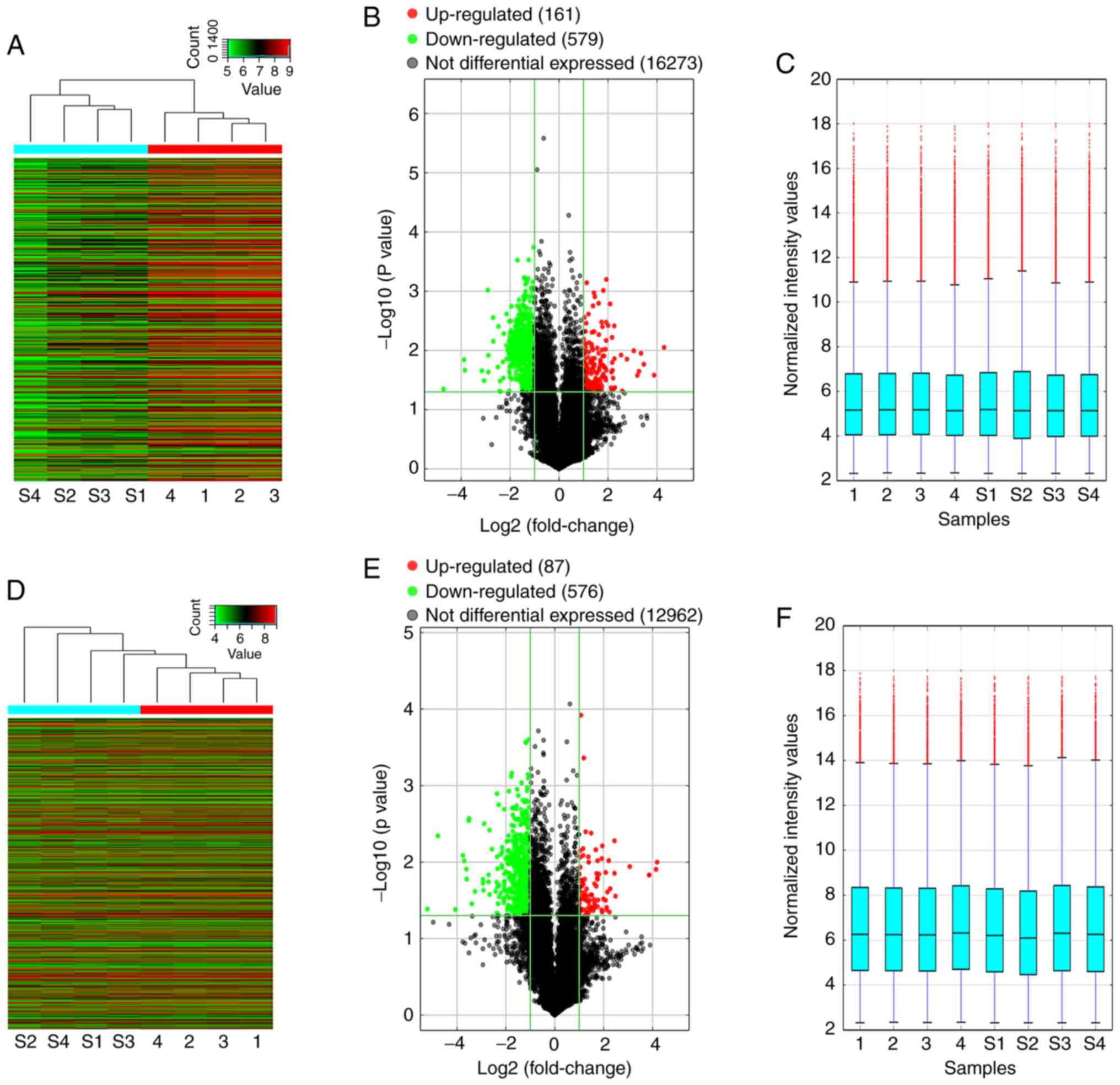
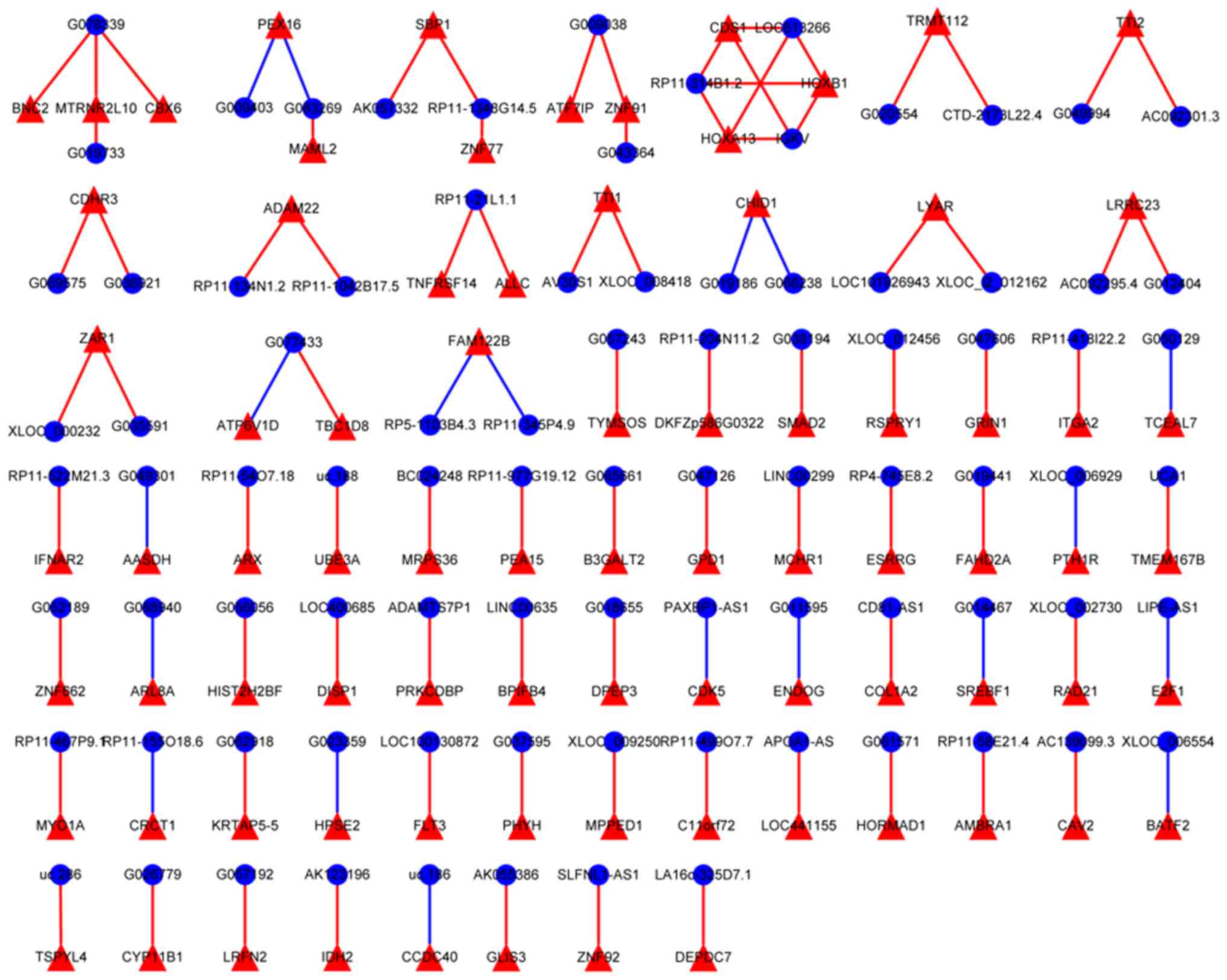
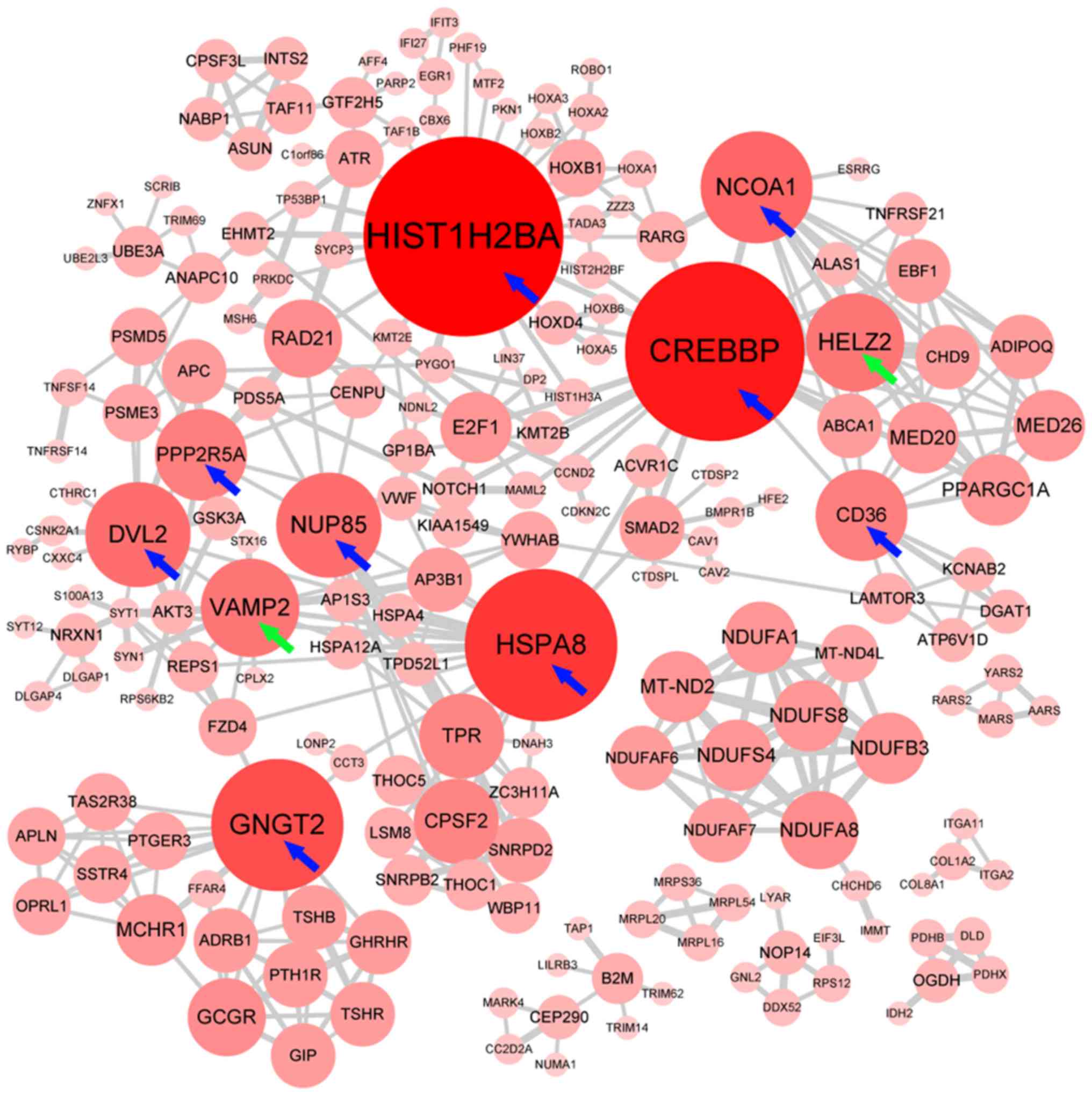
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kremer N, Walther AE and Tiao GM:
Management of hepatoblastoma: An update. Curr Opin Pediatr.
26:362–369. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Qiao GL, Li L, Cheng W, Ge J, Zhang Z and
Wei Y: Predictors of survival after resection of children with
hepatoblastoma: A single Asian center experience. Eur J Surg Oncol.
40:1533–1539. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu B, Zhou L, Huang G, Zhong Z, Jiang C,
Shan Q, Xu M, Kuang M and Xie X: First experience of
ultrasound-guided percutaneous ablation for recurrent
hepatoblastoma after liver resection in children. Sci Rep.
5:168052015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Agarwala S, Gupta A, Bansal D, Vora T,
Prasad M, Arora B, Kapoor G, Chinnaswamy G, Radhakrishnan V, Laskar
S, et al: Management of hepatoblastoma: ICMR consensus document.
Indian J Pediatr. 84:456–464. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meyers RL, Tiao G, de Ville de Goyet J,
Superina R and Aronson DC: Hepatoblastoma state of the art:
Pre-treatment extent of disease, surgical resection guidelines and
the role of liver transplantation. Curr Opin Pediatr. 26:29–36.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sumazin P, Chen Y, Treviño LR, Sarabia SF,
Hampton OA, Patel K, Mistretta TA, Zorman B, Thompson P, Heczey A,
et al: Genomic analysis of hepatoblastoma identifies distinct
molecular and prognostic subgroups. Hepatology. 65:104–121. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heimbach JK, Kulik LM, Finn RS, Sirlin CB,
Abecassis MM, Roberts LR, Zhu AX, Murad MH and Marrero JA: AASLD
guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 67:358–380. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
European Association For The Study Of The
Liver: European Organisation For Research And Treatment Of Cancer:
EASL-EORTC clinical practice guidelines: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 56:908–943. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Korean Liver Cancer Study Group (KLCSG);
National Cancer Center, Korea (NCC), . 2014 KLCSG-NCC Korea
practice guideline for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gut Liver. 9:267–317. 2015.
|
|
11
|
Clavien PA, Lesurtel M, Bossuyt PM, Gores
GJ, Langer B and Perrier A; OLT for HCC Consensus Group, :
Recommendations for liver transplantation for hepatocellular
carcinoma: An international consensus conference report. Lancet
Oncol. 13:e11–e22. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bruix J and Sherman M; American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, : Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Vitale A, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Giannini
EG, Vibert E, Sieghart W, Van Poucke S and Pawlik TM: Personalized
treatment of patients with very early hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Hepatol. 66:412–423. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver. Electronic address, . easloffice@easloffice.eu; European
Association for the Study of the Liver: EASL clinical practice
guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol.
69:182–236. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xu XL, Liu XD, Liang M and Luo BM:
Radiofrequency ablation versus hepatic resection for small
hepatocellular carcinoma: Systematic review of randomized
controlled trials with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.
Radiology. 287:461–472. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
N'Kontchou G, Mahamoudi A, Aout M,
Ganne-Carrié N, Grando V, Coderc E, Vicaut E, Trinchet JC, Sellier
N, Beaugrand M and Seror O: Radiofrequency ablation of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Long-term results and prognostic factors
in 235 Western patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 50:1475–1483.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, Rolle E,
Solbiati L, Tinelli C and Rossi S: Sustained complete response and
complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early
hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Is resection still the
treatment of choice? Hepatology. 47:82–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jiang K, Chen J, Liu Y, Liu J, Liu A, Dong
J and Huang Z: Heat-irrigate effect' of radiofrequency ablation on
relevant regional hepatocyte in living swine liver-initial study on
pathology. Cell Biochem Biophys. 72:37–41. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kang TW, Lim HK and Cha DI: Aggressive
tumor recurrence after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 23:95–101. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Yevich S, Calandri M, Gravel G, Fresneau
B, Brugières L, Valteau-Couanet D, Branchereau S, Chardot C, Aerts
I, de Baere T, et al: Reiterative radiofrequency ablation in the
management of pediatric patients with hepatoblastoma metastases to
the lung, liver, or bone. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 42:41–47.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Spizzo R, Almeida MI, Colombatti A and
Calin GA: Long non-coding RNAs and cancer: A new frontier of
translational research? Oncogene. 31:4577–4587. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
St Laurent G, Wahlestedt C and Kapranov P:
The Landscape of long noncoding RNA classification. Trends Genet.
31:239–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Devaux Y, Zangrando J, Schroen B, Creemers
EE, Pedrazzini T, Chang CP, Dorn GW II, Thum T and Heymans S;
Cardiolinc network, : Long noncoding RNAs in cardiac development
and ageing. Nat Rev Cardiol. 12:415–425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Huo X, Han S, Wu G, Latchoumanin O, Zhou
G, Hebbard L, George J and Qiao L: Dysregulated long noncoding RNAs
(lncRNAs) in hepatocellular carcinoma: Implications for
tumorigenesis, disease progression, and liver cancer stem cells.
Mol Cancer. 16:1652017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Li H, An J, Wu M, Zheng Q, Gui X, Li T, Pu
H and Lu D: LncRNA HOTAIR promotes human liver cancer stem cell
malignant growth through downregulation of SETD2. Oncotarget.
6:27847–27864. 2015.
|
|
28
|
Dong R, Liu GB, Liu BH, Chen G, Li K,
Zheng S and Dong KR: Targeting long non-coding RNA-TUG1 inhibits
tumor growth and angiogenesis in hepatoblastoma. Cell Death Dis.
7:e22782016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Musa A, Ghoraie LS, Zhang SD, Glazko G,
Yli-Harja O, Dehmer M, Haibe-Kains B and Emmert-Streib F: A review
of connectivity map and computational approaches in
pharmacogenomics. Brief Bioinform. 19:506–523. 2018.
|
|
30
|
Lamb J: The connectivity map: A new tool
for biomedical research. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:54–60. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Brum AM, van de Peppel J, Nguyen L, Aliev
A, Schreuders-Koedam M, Gajadien T, van der Leije CS, van Kerkwijk
A, Eijken M, van Leeuwen JPTM and van der Eerden BCJ: Using the
connectivity map to discover compounds influencing human osteoblast
differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 233:4895–4906. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hakimé A, Hines-Peralta A, Peddi H, Atkins
MB, Sukhatme VP, Signoretti S, Regan M and Goldberg SN: Combination
of radiofrequency ablation with antiangiogenic therapy for tumor
ablation efficacy: Study in mice. Radiology. 244:464–470. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang N, Wang L, Chai ZT, Zhu ZM, Zhu XD,
Ma DN, Zhang QB, Zhao YM, Wang M, Ao JY, et al: Incomplete
radiofrequency ablation enhances invasiveness and metastasis of
residual cancer of hepatocellular carcinoma cell HCCLM3 via
activating β-catenin signaling. PLoS One. 9:e1159492014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Fischer AH, Jacobson KA, Rose J and Zeller
R: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of tissue and cell sections. CSH
Protoc. 2008:pdb.prot4986. 2008.
|
|
35
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson KF,
Subramanian A, Sihag S, Lehar J, Puigserver P, Carlsson E,
Ridderstråle M, Laurila E, et al: PGC-1alpha-responsive genes
involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately
downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet. 34:267–273. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Szklarczyk D, Morris JH, Cook H, Kuhn M,
Wyder S, Simonovic M, Santos A, Doncheva NT, Roth A, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein
association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:D362–D368. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Szklarczyk D, Santos A, von Mering C,
Jensen LJ, Bork P and Kuhn M: STITCH 5: Augmenting protein-chemical
interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44:D380–D384. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Burley SK, Berman HM, Christie C, Duarte
JM, Feng Z, Westbrook J, Young J and Zardecki C: RCSB Protein Data
Bank: Sustaining a living digital data resource that enables
breakthroughs in scientific research and biomedical education.
Protein Sci. 27:316–330. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Meng XY, Zhang HX, Mezei M and Cui M:
Molecular docking: A powerful approach for structure-based drug
discovery. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 7:146–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Clark RD, Strizhev A, Leonard JM, Blake JF
and Matthew JB: Consensus scoring for ligand/protein interactions.
J Mol Graph Model. 20:281–295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Weinberg AG and Finegold MJ: Primary
hepatic tumors of childhood. Hum Pathol. 14:512–537. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Haas JE, Feusner JH and Finegold MJ: Small
cell undifferentiated histology in hepatoblastoma may be
unfavorable. Cancer. 92:3130–3134. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Dong R, Jia D, Xue P, Cui X, Li K, Zheng
S, He X and Dong K: Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA
(lncRNA) expression in hepatoblastoma tissues. PLoS One.
9:e855992014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
46
|
Umeda Y, Matsuda H, Sadamori H, Matsukawa
H, Yagi T and Fujiwara T: A prognostic model and treatment strategy
for intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after
curative resection. World J Surg. 35:170–177. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kang TW, Lim HK, Lee MW, Kim YS, Rhim H,
Lee WJ, Gwak GY, Paik YH, Lim HY and Kim MJ: Aggressive
intrasegmental recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after
radiofrequency ablation: Risk factors and clinical significance.
Radiology. 276:274–285. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Shiozawa K, Watanabe M, Takahashi M, Wakui
N, Iida K and Sumino Y: Analysis of patients with rapid aggressive
tumor progression of hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous
radiofrequency ablation. Hepatogastroenterology. 56:1689–1695.
2009.
|
|
49
|
Dong R, Liu XQ, Zhang BB, Liu BH, Zheng S
and Dong KR: Long non-coding RNA-CRNDE: A novel regulator of tumor
growth and angiogenesis in hepatoblastoma. Oncotarget.
8:42087–42097. 2017.
|
|
50
|
Zhang Z, Liu F, Yang F and Liu Y: Kockdown
of OIP5-AS1 expression inhibits proliferation, metastasis and EMT
progress in hepatoblastoma cells through up-regulating miR-186a-5p
and down-regulating ZEB1. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:14–23. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
van Laarhoven S, van Baren R, Tamminga RY
and de Jong KP: Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of liver
tumors in children. J Pediatr Surg. 47:e7–e12. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ye J, Shu Q, Li M and Jiang TA:
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for treatment of
hepatoblastoma recurrence. Pediatr Radiol. 38:1021–1023. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Gómez FM, Patel PA, Stuart S and Roebuck
DJ: Systematic review of ablation techniques for the treatment of
malignant or aggressive benign lesions in children. Pediatr Radiol.
44:1281–1289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Tomson T, Battino D and Perucca E:
Valproic acid after five decades of use in epilepsy: Time to
reconsider the indications of a time-honoured drug. Lancet Neurol.
15:210–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Terbach N and Williams RS:
Structure-function studies for the panacea, valproic acid. Biochem
Soc Trans. 37:1126–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Tomson T, Battino D and Perucca E: The
remarkable story of valproic acid. Lancet Neurol. 15:1412016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhu W, Liang Q, Yang X, Yu Y, Shen X and
Sun G: Combination of sorafenib and Valproic acid synergistically
induces cell apoptosis and inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma growth
via down-regulating Notch3 and pAkt. Am J Cancer Res. 7:2503–2514.
2017.
|
|
58
|
Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB,
Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R and
Matthews DR: Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: A
patient-centered approach. Position statement of the American
Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the
Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 55:1577–1596. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Schneider MB, Matsuzaki H, Haorah J,
Ulrich A, Standop J, Ding XZ, Adrian TE and Pour PM: Prevention of
pancreatic cancer induction in hamsters by metformin.
Gastroenterology. 120:1263–1270. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Donadon V, Balbi M, Mas MD, Casarin P and
Zanette G: Metformin and reduced risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
in diabetic patients with chronic liver disease. Liver Int.
30:750–758. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Tseng CH: Metformin reduces ovarian cancer
risk in Taiwanese women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes
Metab Res Rev. 31:619–626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Campagnoli C, Pasanisi P, Abbà C,
Ambroggio S, Biglia N, Brucato T, Colombero R, Danese S, Donadio M,
Venturelli E, et al: Effect of different doses of metformin on
serum testosterone and insulin in non-diabetic women with breast
cancer: A randomized study. Clin Breast Cancer. 12:175–182. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Tseng CH: Metformin significantly reduces
incident prostate cancer risk in Taiwanese men with type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Eur J Cancer. 50:2831–2837. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Sehdev A, Shih YC, Vekhter B, Bissonnette
MB, Olopade OI and Polite BN: Metformin for primary colorectal
cancer prevention in patients with diabetes: A case-control study
in a US population. Cancer. 121:1071–1078. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Zhang HH, Zhang Y, Cheng YN, Gong FL, Cao
ZQ, Yu LG and Guo XL: Metformin incombination with curcumin
inhibits the growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis of hepatocellular
carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Mol Carcinog. 57:44–56. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Tsai HH, Lai HY, Chen YC, Li CF, Huang HS,
Liu HS, Tsai YS and Wang JM: Metformin promotes apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma through the CEBPD-induced autophagy
pathway. Oncotarget. 8:13832–13845. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
67
|
Modi S, Stopeck AT, Gordon MS, Mendelson
D, Solit DB, Bagatell R, Ma W, Wheler J, Rosen N, Norton L, et al:
Combination of trastuzumab and tanespimycin (17-AAG, KOS-953) is
safe and active in trastuzumab-refractory HER-2 overexpressing
breast cancer: A phase I dose-escalation study. J Clin Oncol.
25:5410–5417. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ma L, Yang D, Li Z, Zhang X and Pu L:
Co-delivery of paclitaxel and tanespimycin in lipid nanoparticles
enhanced anti-gastric-tumor effect in vitro and in vivo. Artif
Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 46:904–911. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Ghadban T, Dibbern JL, Reeh M, Miro JT,
Tsui TY, Wellner U, Izbicki JR, Güngör C and Vashist YK: HSP90 is a
promising target in gemcitabine and 5-fluorouracil resistant
pancreatic cancer. Apoptosis. 22:369–380. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Hong DS, Bowles DW, Falchook GS,
Messersmith WA, George GC, O'Bryant CL, Vo AC, Klucher K, Herbst
RS, Eckhardt SG, et al: A multicenter phase I trial of PX-866, an
oral irreversible phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor, in
patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 18:4173–4182.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Boér K: Fulvestrant in advanced breast
cancer: Evidence to date and place in therapy. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
9:465–479. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
72
|
Nathan MR and Schmid P: A review of
fulvestrant in breast cancer. Oncol Ther. 5:17–29. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
73
|
Fan XM, Tu SP, Lam SK, Wang WP, Wu J, Wong
WM, Yuen MF, Lin MC, Kung HF and Wong BC:
Five-lipoxygenase-activating protein inhibitor MK-886 induces
apoptosis in gastric cancer through upregulation of p27kip1 and
bax. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:31–37. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Huang JK, Huang CC, Lu T, Chang HT, Lin
KL, Tsai JY, Liao WC, Chien JM and Jan CR: Effect of MK-886 on Ca2+
level and viability in PC3 human prostate cancer cells. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 104:441–447. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Rioux N and Castonguay A: Inhibitors of
lipoxygenase: A new class of cancer chemopreventive agents.
Carcinogenesis. 19:1393–1400. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|