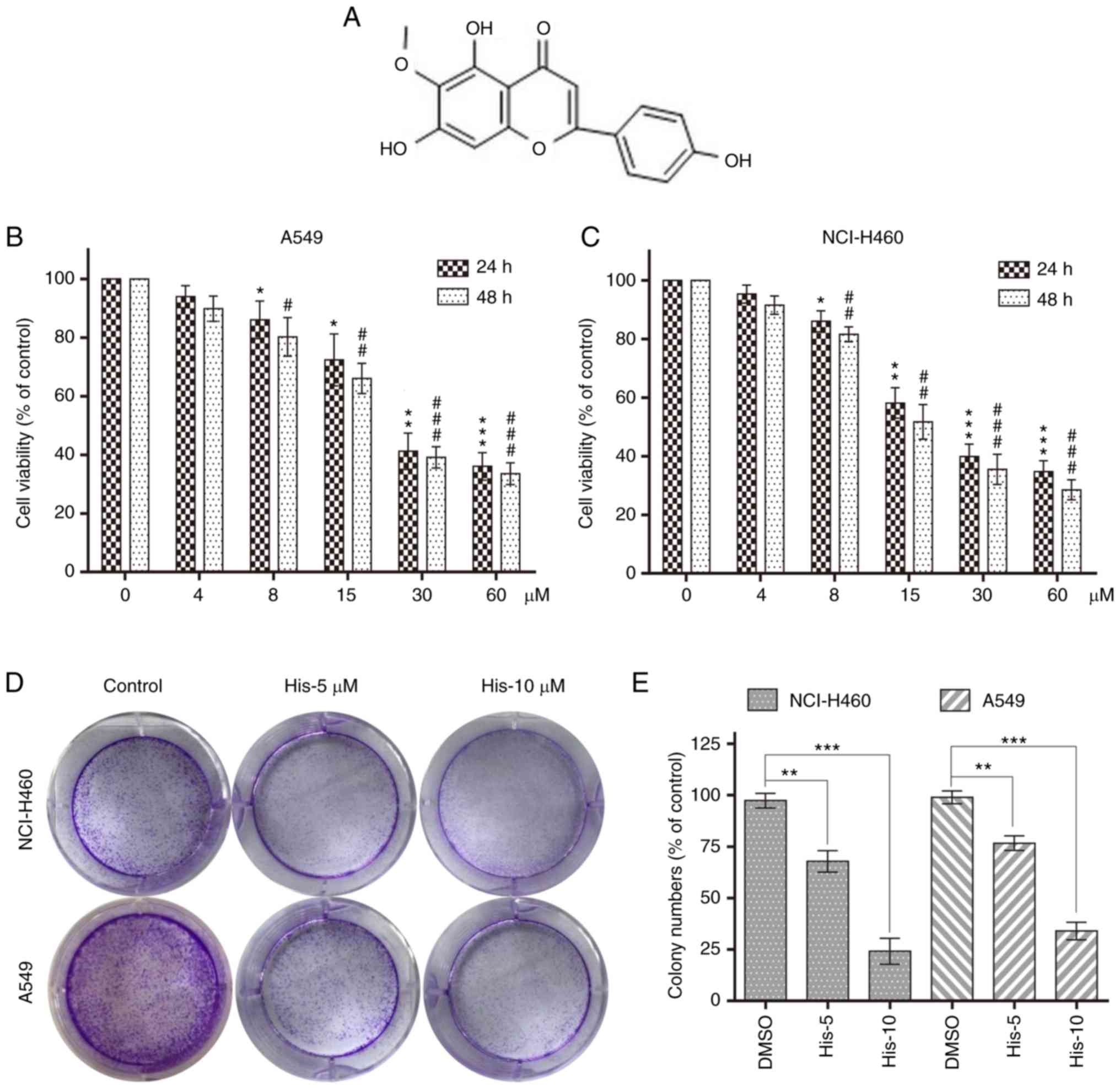
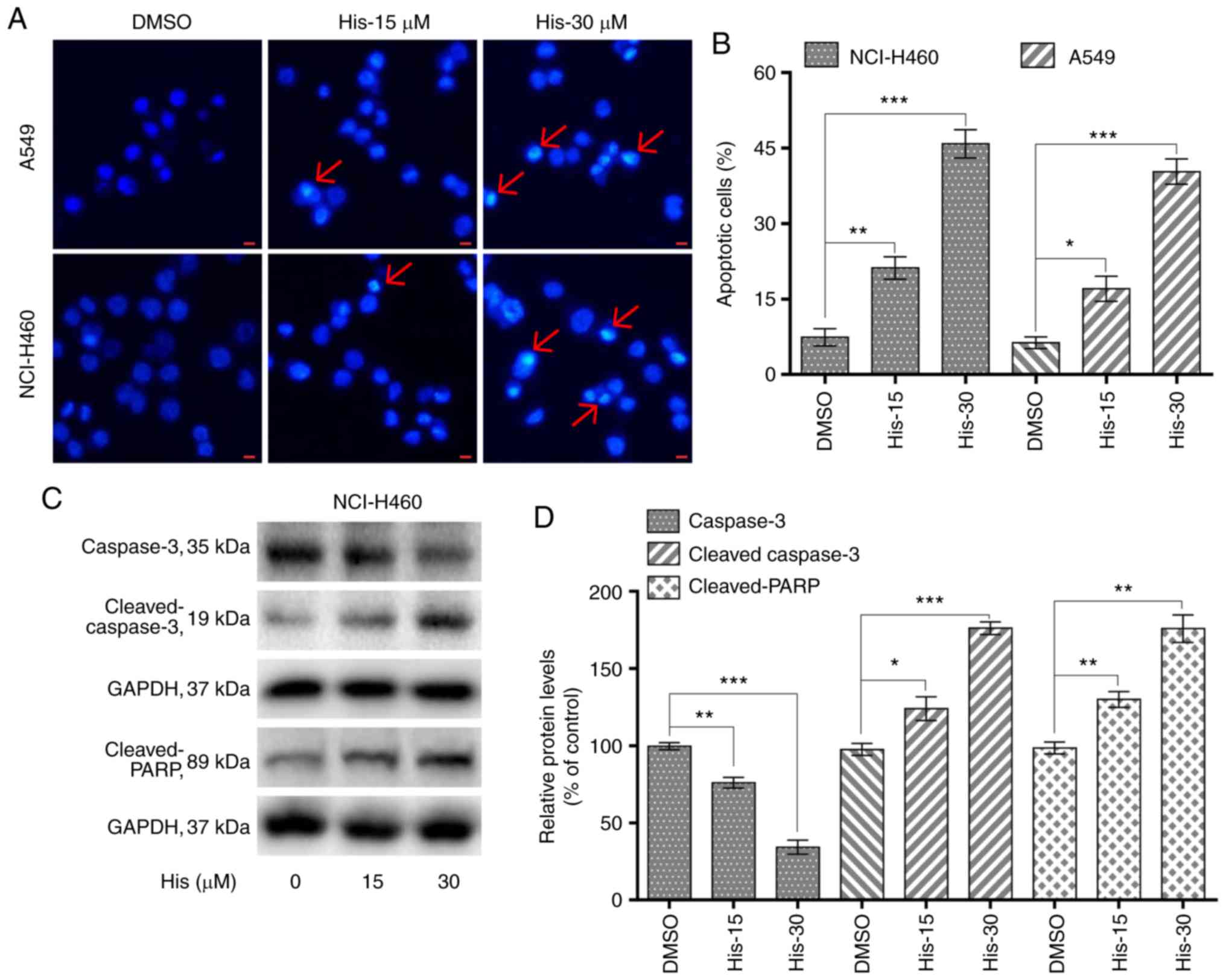
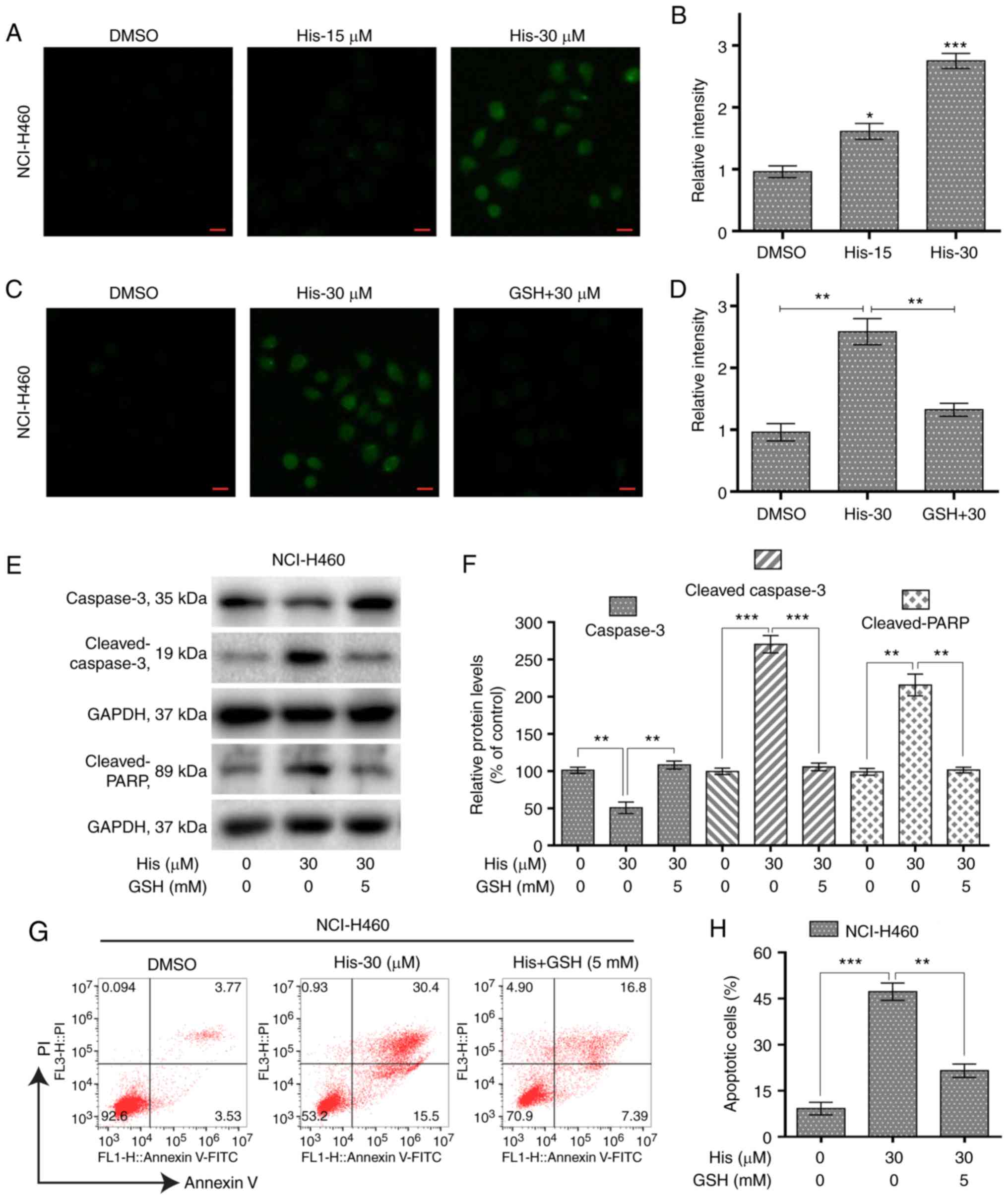
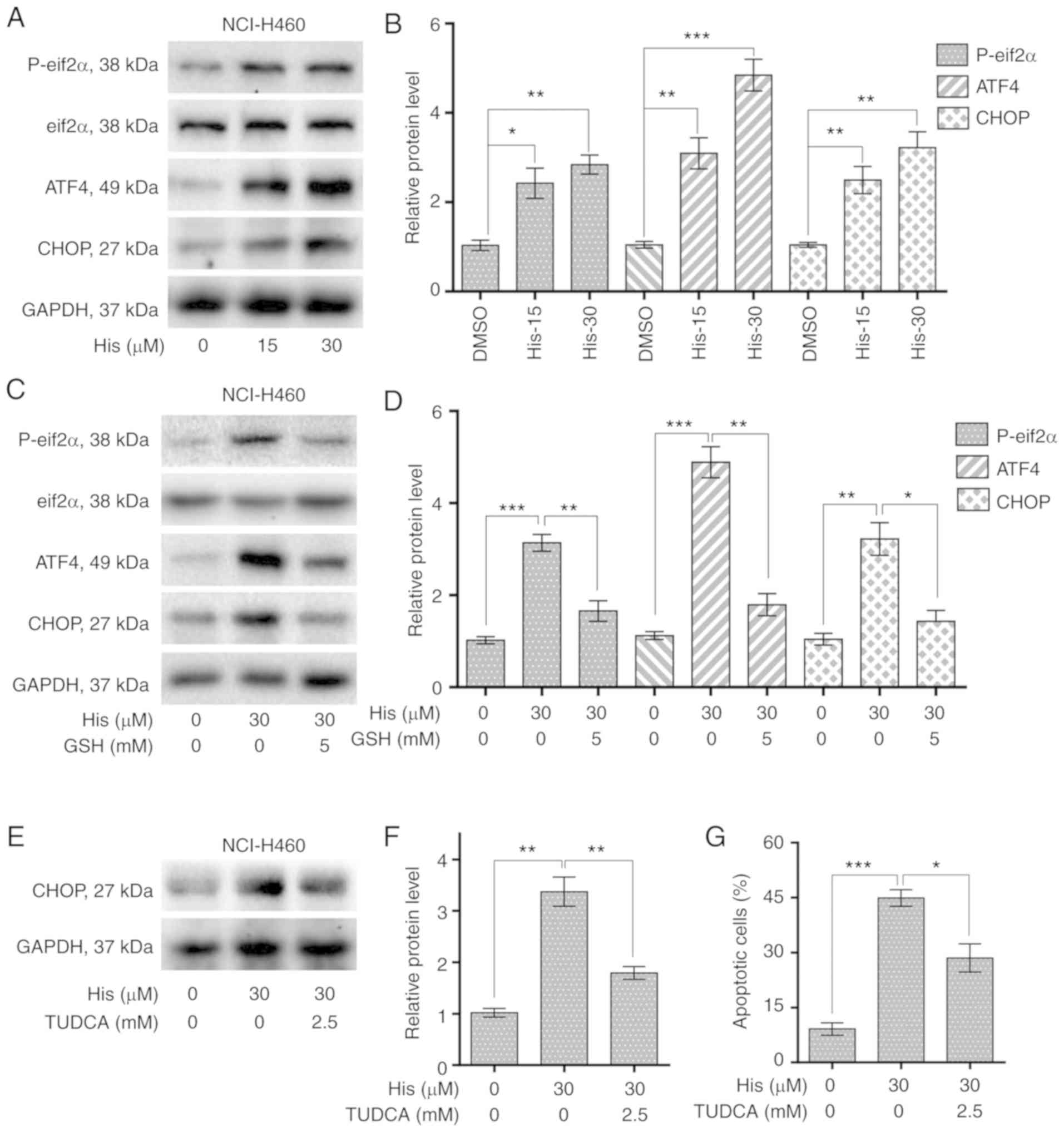
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:10–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yang F, Sui X, Chen X, Zhang L, Wang X,
Wang S and Wang J: Sublobar resection versus lobectomy in surgical
treatment of elderly patients with early-stage non-small cell lung
cancer (STEPS): Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.
Trials. 17:1912016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Shtivelman E, Hensing T, Simon GR, Dennis
PA, Otterson GA, Bueno R and Salgia R: Molecular pathways and
therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Oncotarget. 5:1392–1433. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Li S, Fan J, Liu J, Zhou J, Ren Y, Shen C
and Che G: Neoadjuvant therapy and risk of bronchopleural fistula
after lung cancer surgery: A systematic meta-analysis of 14 912
patients. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 46:534–546. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Socinski MA, Stinchcombe TE, Moore DT,
Gettinger SN, Decker RH, Petty WJ, Blackstock AW, Schwartz G,
Lankford S, Khandani A and Morris DE: Incorporating bevacizumab and
erlotinib in the combined-modality treatment of stage III
non-small-cell lung cancer: Results of a phase I/II trial. J Clin
Oncol. 30:3953–3959. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wagner KW, Alam H, Dhar SS, Giri U, Li N,
Wei Y, Giri D, Cascone T, Kim JH, Ye Y, et al: KDM2A promotes lung
tumorigenesis by epigenetically enhancing ERK1/2 signaling. J Clin
Invest. 123:5231–5246. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Bishayee A and Sethi G: Bioactive natural
products in cancer prevention and therapy: Progress and promise.
Sem Cancer Biol. 40:1–3. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xu YJ, Zhao DX, Fu CX, Cheng LQ, Wang NF,
Han LJ and Ma FS: Determination of flavonoid compounds from
Saussurea involucrata by liquid chromatography electrospray
ionisation mass spectrometry. Nat Prod Res. 23:1689–1698. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yin Y, Gong FY, Wu XX, Sun Y, Li YH, Chen
T and Xu Q: Anti-Inflammatory and immunosuppressive effect of
flavones isolated from artemisia vestita. J Ethnopharmacol.
120:1–6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhou R, Wang Z and Ma C: Hispidulin exerts
anti-osteoporotic activity in ovariectomized mice via activating
AMPK signaling pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys. 69:311–317. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yang JM, Hung CM, Fu CN, Lee JC, Huang CH,
Yang MH, Lin CL, Kao JY and Way TD: Hispidulin sensitizes human
ovarian cancer cells to TRAIL-Induced apoptosis by AMPK activation
leading to Mcl-1 block in translation. J Agric Food Chem.
58:10020–10026. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xie J, Gao H, Peng J, Han Y, Chen X, Jiang
Q and Wang C: Hispidulin prevents hypoxia-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human colon carcinoma cells.
Am J Cancer Res. 5:1047–1061. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Lee-Hilz YY, Boerboom AM, Westphal AH,
Berkel WJ, Aarts JM and Rietjens IM: Pro-Oxidant activity of
flavonoids induces EpRE-Mediated gene expression. Chem Res Toxicol.
19:1499–1505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang YG, Liu W, He X and Fei Z: Hispidulin
enhances the anti-tumor effects of temozolomide in glioblastoma by
activating AMPK. Cell Biochem Biophys. 71:701–706. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Han M, Gao H, Xie J, Yuan YP, Yuan Q, Gao
MQ, Liu KL, Chen XH, Han YT and Han ZW: Hispidulin induces ER
stress-mediated apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
in vitro and in vivo by activating AMPK signaling pathway. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 40:666–676. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu K, Gao H, Wang Q, Wang L, Zhang B, Han
Z, Chen X, Han M and Gao M: Hispidulin suppresses cell growth and
metastasis by targeting PIM1 through JAK2/STAT3 signaling in
colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:1369–1381. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Gao MQ, Gao H, Han M, Liu KL, Peng JJ and
Han YT: Hispidulin suppresses tumor growth and metastasis in renal
cell carcinoma by modulating ceramide-sphingosine 1-phosphate
rheostat. Am J Cancer Res. 7:1501–1514. 2017.
|
|
18
|
Gao H, Gao MQ, Peng JJ, Han M, Liu KL and
Han YT: Hispidulin mediates apoptosis in human renal cell carcinoma
by inducing ceramide accumulation. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
38:1618–1631. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
19
|
Scoparo C, Valdameri G, Worfel P, Guterres
FA, Martinez GR, Winnischofer SM, Di Pietro A and Rocha ME: Dual
properties of hispidulin: Antiproliferative effects on HepG2 cancer
cells and selective inhibition of ABCG2 transport activity. Mol
Cell Biochem. 409:123–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Han Y, Yang X, Zhao N, Peng J, Gao H and
Qiu X: Alpinumisoflavone induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma by modulating miR-370/PIM1 signaling. Am J Cancer
Res. 6:2755–2771. 2016.
|
|
21
|
Zinszner H, Kuroda M, Wang XZ, Batchvarova
N, Ron D, Lightfoot RT, Remotti H and Stevens JL: CHOP is
implicated in programmed cell death in response to impaired
function of the endoplasmic reticulum. Genes Dev. 12:982–995. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Launay N, Ruiz M, Grau L, Ortega FJ,
Ilieva EV, Martínez JJ, Galea E, Ferrer I, Knecht E, Pujol A and
Fourcade S: Tauroursodeoxycholic bile acid arrests axonal
degeneration by inhibiting the unfolded protein response in
X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 133:283–301. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu CY, Su KY, Lee PL, Jhan JY, Tsao PH,
Chan DC and Chen YL: Potential therapeutic role of hispidulin in
gastric cancer through induction of apoptosis via NAG-1 signaling.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:5183012013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Lin YC, Hung CM, Tsai JC, Lee JC, Chen YL,
Wei CW, Kao JY and Way TD: Hispidulin potently inhibits human
glioblastoma multiforme cells through activation of AMP-activated
protein kinase (AMPK). J Agric Food Chem. 58:9511–9517. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
He L, Wu Y, Lin L, Wang J, Wu Y, Chen Y,
Yi Z, Liu M and Pang X: Hispidulin, a small flavonoid molecule,
suppresses the angiogenesis and growth of human pancreatic cancer
by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2-mediated
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Sci. 102:219–225. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lu Z, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Hua P, Fang M, Wu
M and Liu T: Isoalantolactone induces apoptosis through reactive
oxygen species-dependent upregulation of death receptor 5 in human
esophageal cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 352:46–58. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jin C, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Hua P, Zhang X,
Song G, Sun M, Li X, Tong T and Li B: Isoalantolactone induces
intrinsic apoptosis through p53 signaling pathway in human lung
squamous carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 12:e01817312017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De
Guevara RL, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Huang P, Zhang YH, Zheng XW, Liu YJ, Zhang
H, Fang L, Zhang YW, Yang C, Islam K, Wang C and Naranmandura H:
Phenylarsine oxide (PAO) induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells via
ROS-mediated mitochondria and ER-stress dependent signaling
pathways. Metallomics. 9:1756–1764. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yang J, Wei J, Wu Y, Wang Z, Guo Y, Lee P
and Li X: Metformin induces ER stress-dependent apoptosis through
miR-708-5p/NNAT pathway in prostate cancer. Oncogensis.
193:e1582015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Maryam A, Mehmood T, Yan Q, Li Y, Khan M
and Ma T: Proscillaridin A promotes oxidative stress and ER stress,
inhibits STAT3 activation, and induces apoptosis in A549 lung
adenocarcinoma cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 11:38534092018.
|
|
32
|
Zhang L, Sang BK, Luitel K and Shay JW:
Cholesterol depletion by TASIN-1 induces apoptotic cell death
through the ER Stress/ROS/JNK signaling in colon cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 17:943–951. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ron D: Translational control in the
endoplasmic reticulum stress response. J Clin Invest.
110:1383–1388. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Scheuner D, Song B, Mcewen E, Liu C,
Laybutt R, Gillespie P, Saunders T, Bonner-Weir S and Kaufman RJ:
Translational control is required for the unfolded protein response
and in vivo glucose. Mol Cell. 7:1165–1176. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Harding HP, Zhang Y, Zeng H, Novoa I, Lu
PD, Calfon M, Sadri N, Yun C, Popko B, Paules R, et al: An
integrated stress response regulates amino acid metabolism and
resistance to oxidative stress. Mol Cell. 11:619–633. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Malhotra JD and Kaufman RJ: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and oxidative stress: A vicious cycle or a
double-edged sword? Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:2277–2294. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lee DH, Jung Jung Y, Koh D, Lim Y, Lee YH
and Shin SY: A synthetic chalcone,
2′-hydroxy-2,3,5′-trimethoxychalcone triggers unfolded protein
response-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
372:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Prasad S, Yadav VR, Ravindran J and
Aggarwal BB: ROS and CHOP are critical for dibenzylideneacetone to
sensitize tumor cells to TRAIL through induction of death receptors
and downregulation of cell survival proteins. Cancer Res.
71:538–549. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shu G, Yue L, Zhao W, Xu C, Yang J, Wang S
and Yang X: Isoliensinine, a bioactive alkaloid derived from
embryos of nelumbo nucifera, induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell
apoptosis through suppression of NF-κB signaling. J Agric Food
Chem. 63:8793–8803. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang W, Liu S, Liu K, Ji B, Wang Y and
Liu Y: Knockout of ADAM10 enhances sorafenib antitumor activity of
hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Rep.
32:1913–1922. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|