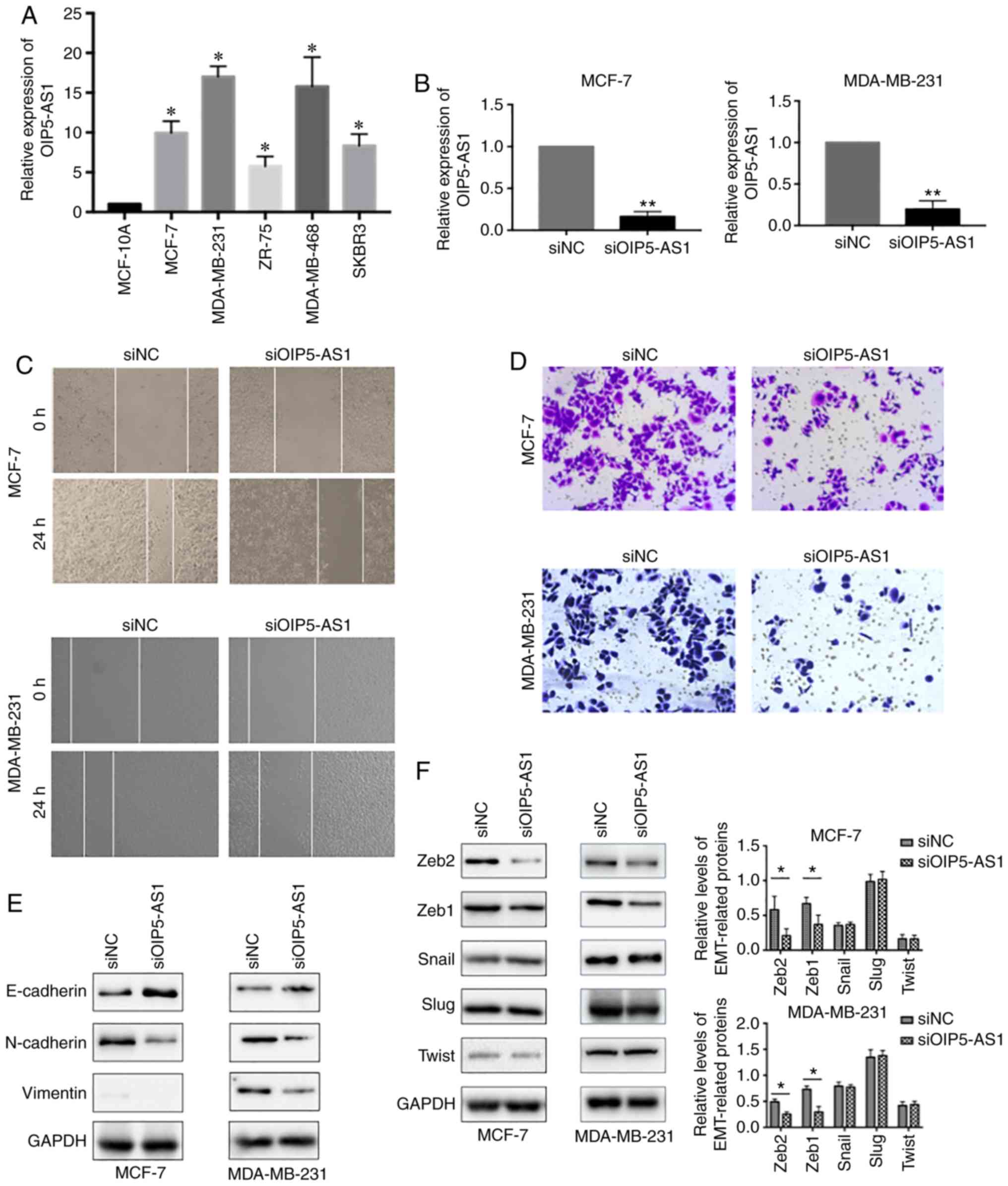
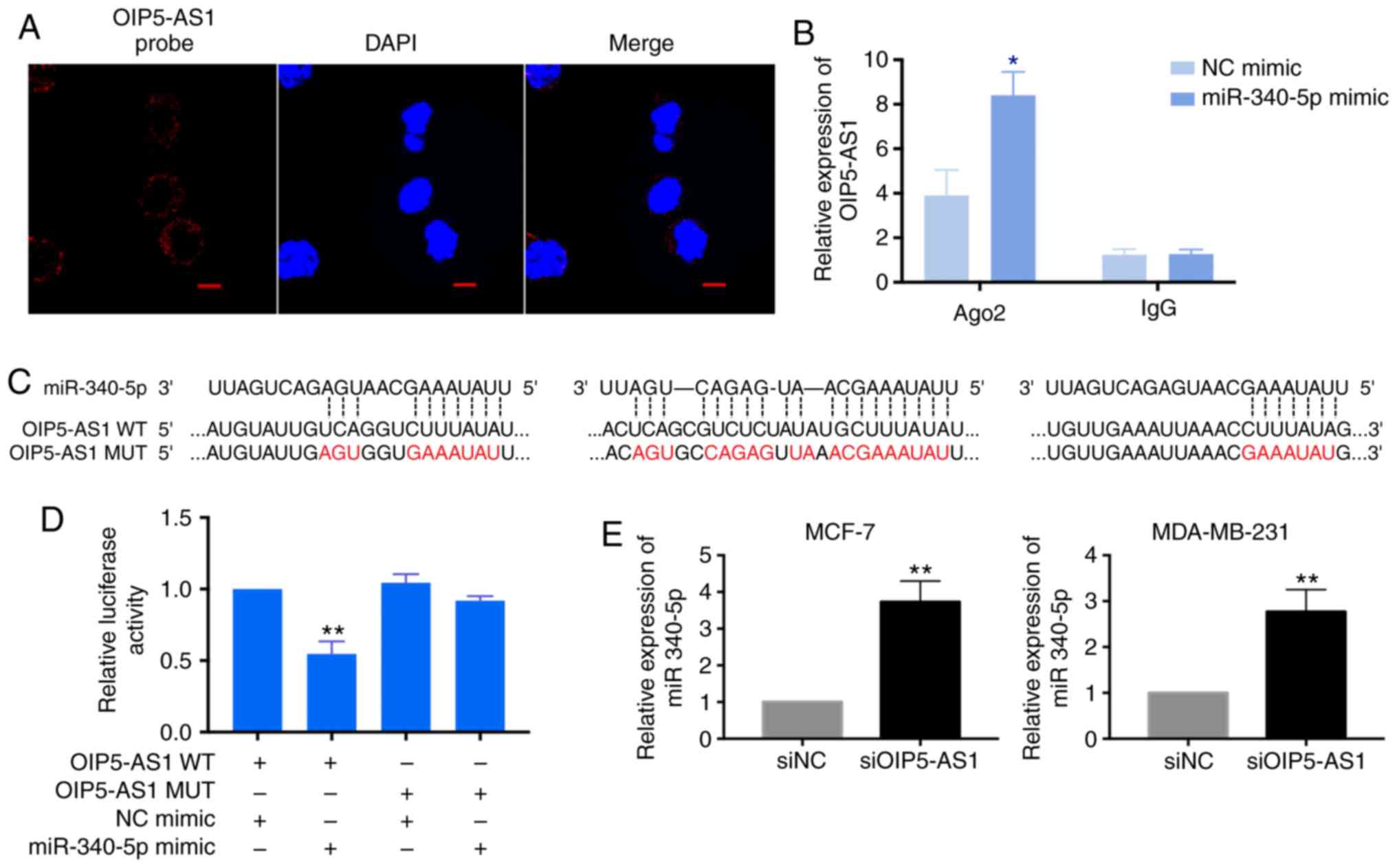
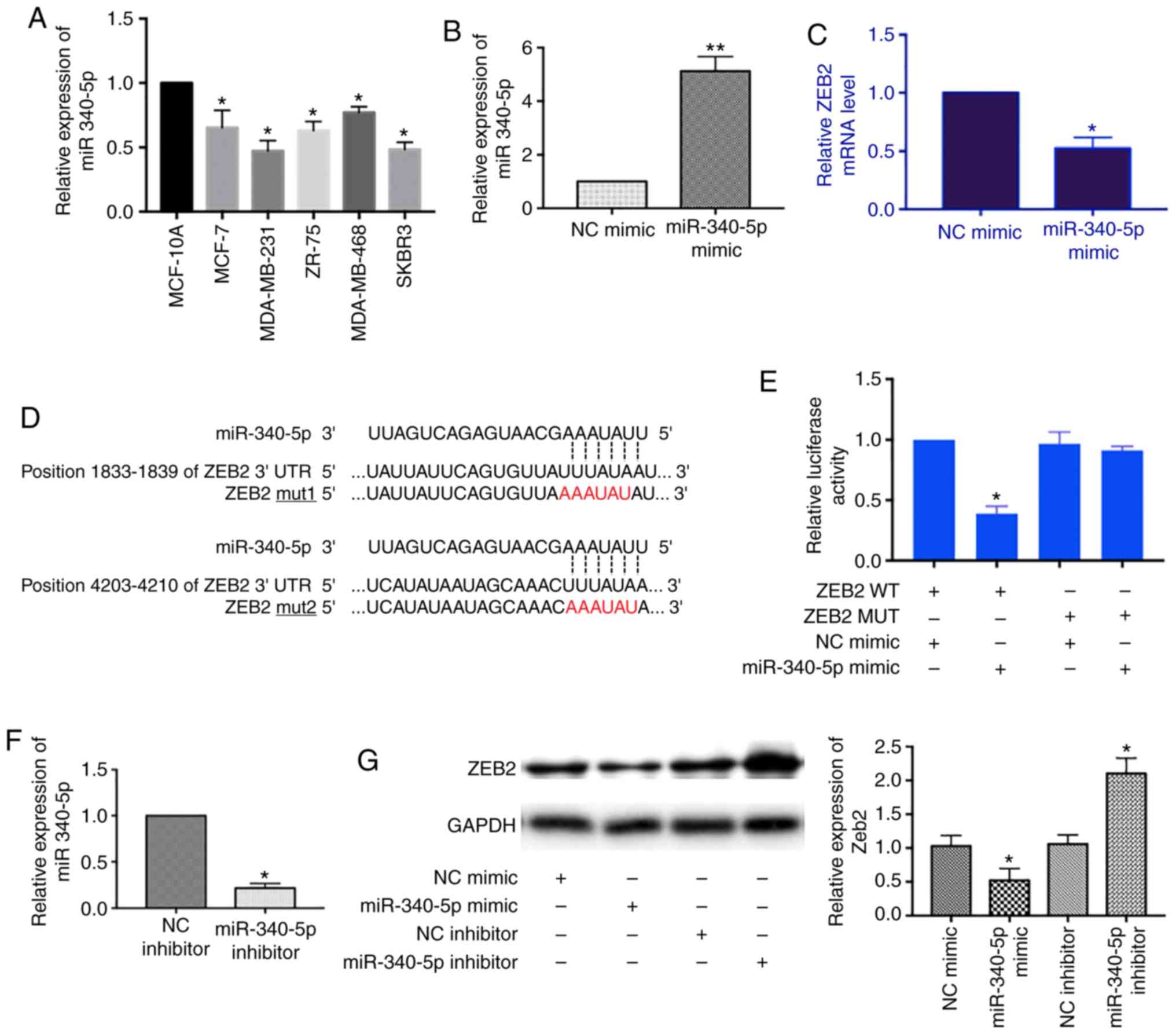
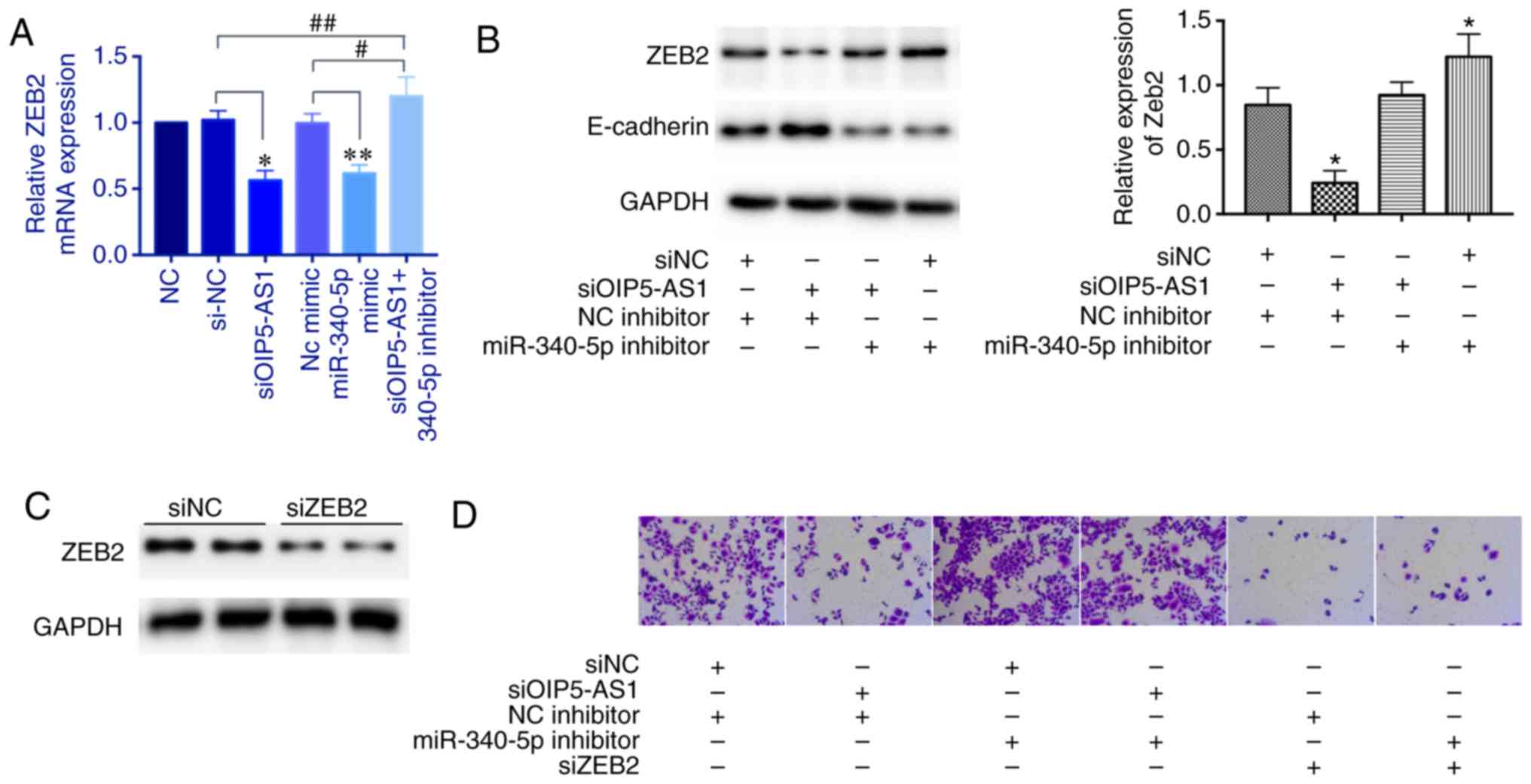
|
1
|
Li N, Deng Y, Zhou L, Tian T, Yang S, Wu
Y, Zheng Y, Zhai Z, Hao Q, Song D, et al: Global burden of breast
cancer and attributable risk factors in 195 countries and
territories, from 1990 to 2017: Results from the global burden of
disease study 2017. J Hematol Oncol. 12:1402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
DeSantis CE, Ma J, Sauer AG, Newman LA and
Jemal A: Breast cancer statistics, 2017, racial disparity in
mortality by state. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:439–448. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cardoso F, Costa A, Senkus E, Aapro M,
André F, Barrios CH, Bergh J, Bhattacharyya G, Biganzoli L, Cardoso
MJ, et al: 3rd ESO-ESMO international consensus guidelines for
advanced breast cancer (ABC 3). Ann Oncol. 28:16–33. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Malhotra GK, Zhao X, Band H and Band V:
Histological, molecular and functional subtypes of breast cancers.
Cancer Biol Ther. 10:955–960. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xiao W, Zheng S, Yang A, Zhang X, Zou Y,
Tang H and Xie X: Breast cancer subtypes and the risk of distant
metastasis at initial diagnosis: A population-based study. Cancer
Manag Res. 10:5329–5338. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kozłowski J, Kozłowska A and Kocki J:
Breast cancer metastasis-insight into selected molecular mechanisms
of the phenomenon. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 69:447–451. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chaffer CL, Juan BPS, Lim E and Weinberg
RA: EMT, cell plasticity and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
35:645–654. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee JY, Park MK, Park JH, Lee HJ, Shin DH,
Kang Y, Lee CH and Kong G: Loss of the polycomb protein Mel-18
enhances the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by ZEB1 and ZEB2
expression through the downregulation of miR-205 in breast cancer.
Oncogene. 33:1325–1335. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Evans JR, Feng FY and Chinnaiyan AM: The
bright side of dark matter: lncRNAs in cancer. J Clin Invest.
126:2775–2782. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Calle AS, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y,
Takeshita F and Ochiya T: Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in
cancer. Cancer Sci. 109:2093–2100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marchese FP, Raimondi I and Huarte M: The
multidimensional mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function. Genome
Biol. 18:2062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mendell JT: Targeting a long noncoding RNA
in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 374:2287–2289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li W, Zhai L, Wang H, Liu C, Zhang J, Chen
W and Wei Q: Downregulation of LncRNA GAS5 causes trastuzumab
resistance in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:27778–27786. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang YS, Chang CC, Lee SS, Jou YS and
Shih HM: Xist reduction in breast cancer upregulates AKT
phosphorylation via HDAC3-mediated repression of PHLPP1 expression.
Oncotarget. 7:43256–43266. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tian T, Wang M, Lin S, Guo Y, Dai Z, Liu
K, Yang P, Dai C, Zhu Y, Zheng Y, et al: The impact of lncRNA
dysregulation on clinicopathology and survival of breast cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
12:359–369. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ulitsky I, Shkumatava A, Jan CH, Sive H
and Bartel DP: Conserved function of lincRNAs in vertebrate
embryonic development despite rapid sequence evolution. Cell.
147:1537–1550. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meseure D, Alsibai KD, Nicolas A, Bieche I
and Morillon A: Long noncoding RNAs as new architects in cancer
epigenetics, prognostic biomarkers, and potential therapeutic
targets. BioMed Res Int. 2015:3202142015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Naemura M, Kuroki M, Tsunoda T, Arikawa N,
Sawata Y, Shirasawa S and Kotake Y: The long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1
is involved in the regulation of cell proliferation. Anticancer
Res. 38:77–81. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zeng H, Wang J, Chen T, Zhang K, Chen J,
Wang L, Li H, Tuluhong D, Li J and Wang S: Downregulation of long
non-coding RNA Opa interacting protein 5-antisense RNA 1 inhibits
breast cancer progression by targeting sex-determining region Y-box
2 by microRNA-129-5p upregulation. Cancer Sci. 110:289–302.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Deng J, Deng H, Liu C, Liang Y and Wang S:
Long non-coding RNA OIP5-AS1 functions as an oncogene in lung
adenocarcinoma through targeting miR-448/Bcl-2. Biomed
Pharmacother. 98:102–110. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Shi F, Xia Y and Zhao H: LncRNA
OIP5-AS1 predicts poor prognosis and regulates cell proliferation
and apoptosis in bladder cancer. J Cell Biochem. Nov 18–2018.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
25
|
Ren X, He J, Qi L, Li S, Zhang C, Duan Z,
Wang W, Tu C and Li Z: Prognostic and clinicopathologic
significance of long non-coding RNA opa-interacting protein
5-antisense RNA 1 in multiple human cancers. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 48:353–361. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen LL: Linking long noncoding RNA
localization and function. Trends Biochem Sci. 41:761–772. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rohan TE, Wang T, Weinmann S, Wang Y, Lin
J, Ginsberg M and Loudig O: A miRNA expression signature in breast
tumor tissue is associated with risk of distant metastasis. Cancer
Res. 79:1705–1713. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arunkumar G, Anand S, Raksha P,
Dhamodharan S, Rao HPS, Subbiah S, Murugan AK and Munirajan AK:
LncRNA OIP5-AS1 is overexpressed in undifferentiated oral tumors
and integrated analysis identifies as a downstream effector of
stemness-associated transcription factors. Sci Rep. 8:70182018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang MC, Ni JJ, Cui WY, Wang BY and Zhuo
W: Emerging roles of lncRNA in cancer and therapeutic
opportunities. Am J Cancer Res. 9:1354–1366. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Arun G, Diermeier S, Akerman M, Chang KC,
Wilkinson JE, Hearn S, Kim Y, MacLeod AR, Krainer AR, Norton L, et
al: Differentiation of mammary tumors and reduction in metastasis
upon Malat1 lncRNA loss. Genes Dev. 30:34–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xing Z, Lin A, Li C, Liang K, Wang S, Liu
Y, Park PK, Qin L, Wei Y, Hawke DH, et al: lncRNA directs
cooperative epigenetic regulation downstream of chemokine signals.
Cell. 159:1110–1125. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Comijn J, Berx G, Vermassen P, Verschueren
K, van Grunsven L, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, Huylebroeck D and van Roy
F: The two-handed E box binding zinc finger protein SIP1
downregulates E-cadherin and induces invasion. Mol Cell.
7:1267–1278. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Z, Liu F, Yang F and Liu Y: Kockdown
of OIP5-AS1 expression inhibits proliferation, metastasis and EMT
progress in hepatoblastoma cells through up-regulating miR-186a-5p
and down-regulating ZEB1. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:14–23. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang M, Sun X, Yang Y and Jiao W: Long
non-coding RNA OIP5-AS1 promotes proliferation of lung cancer cells
and leads to poor prognosis by targeting miR-378a-3p. Thorac
Cancer. 9:939–949. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang X, Xu X, Ge G, Zang X, Shao M, Zou
S, Zhang Y, Mao Z, Zhang J, Mao F, et al: miR-498 inhibits the
growth and metastasis of liver cancer by targeting ZEB2. Oncol Rep.
41:1638–1648. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|