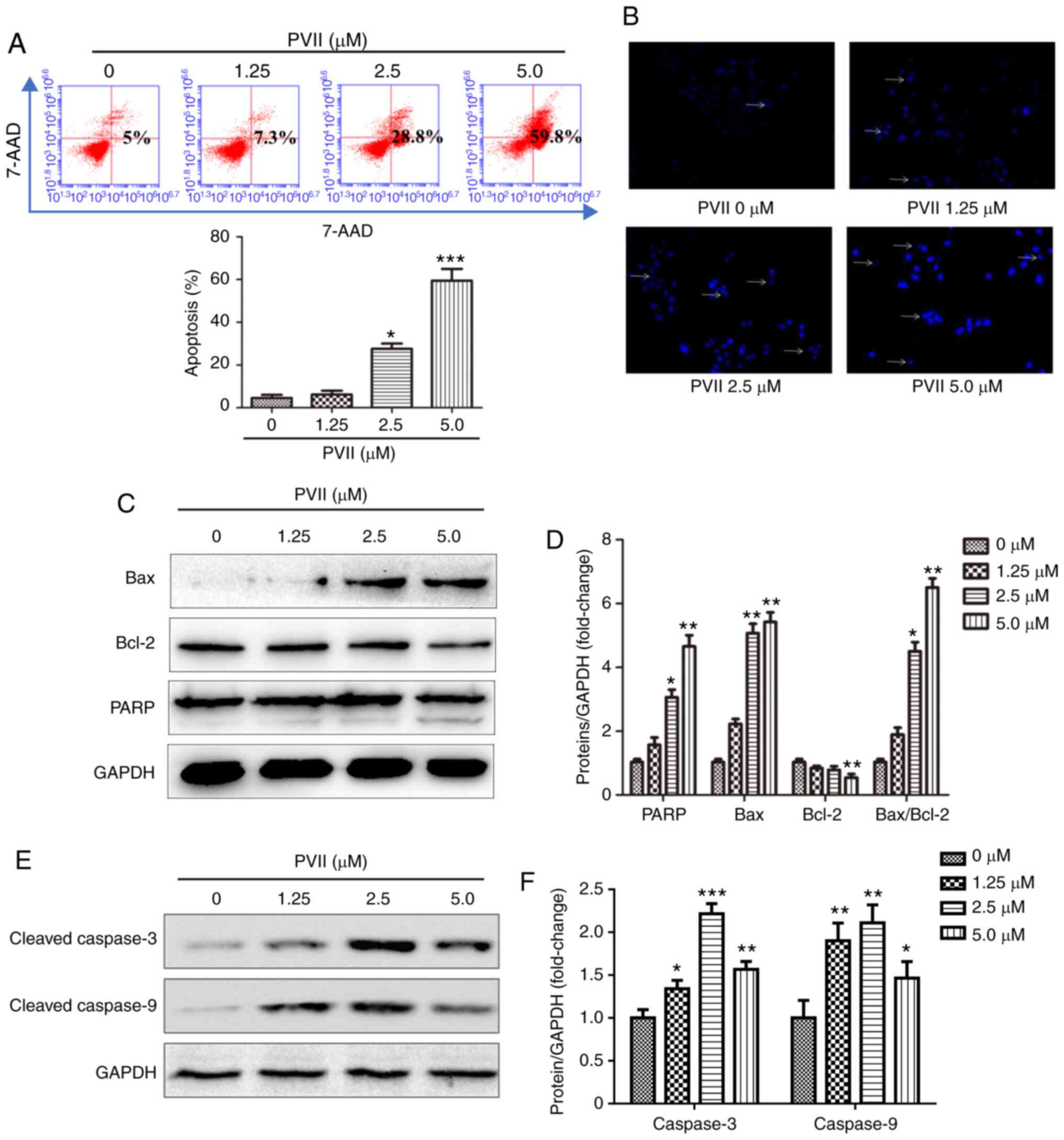
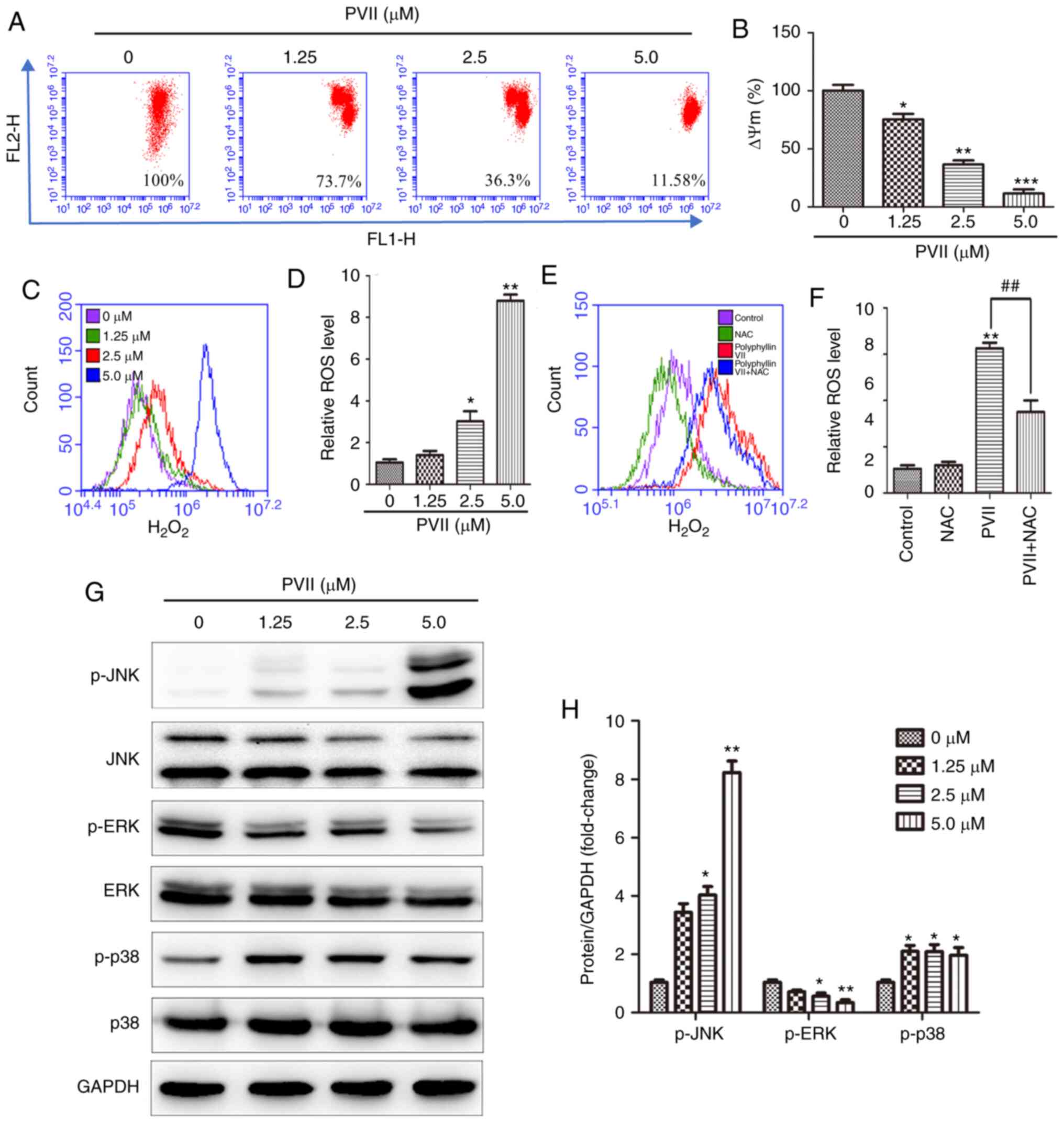
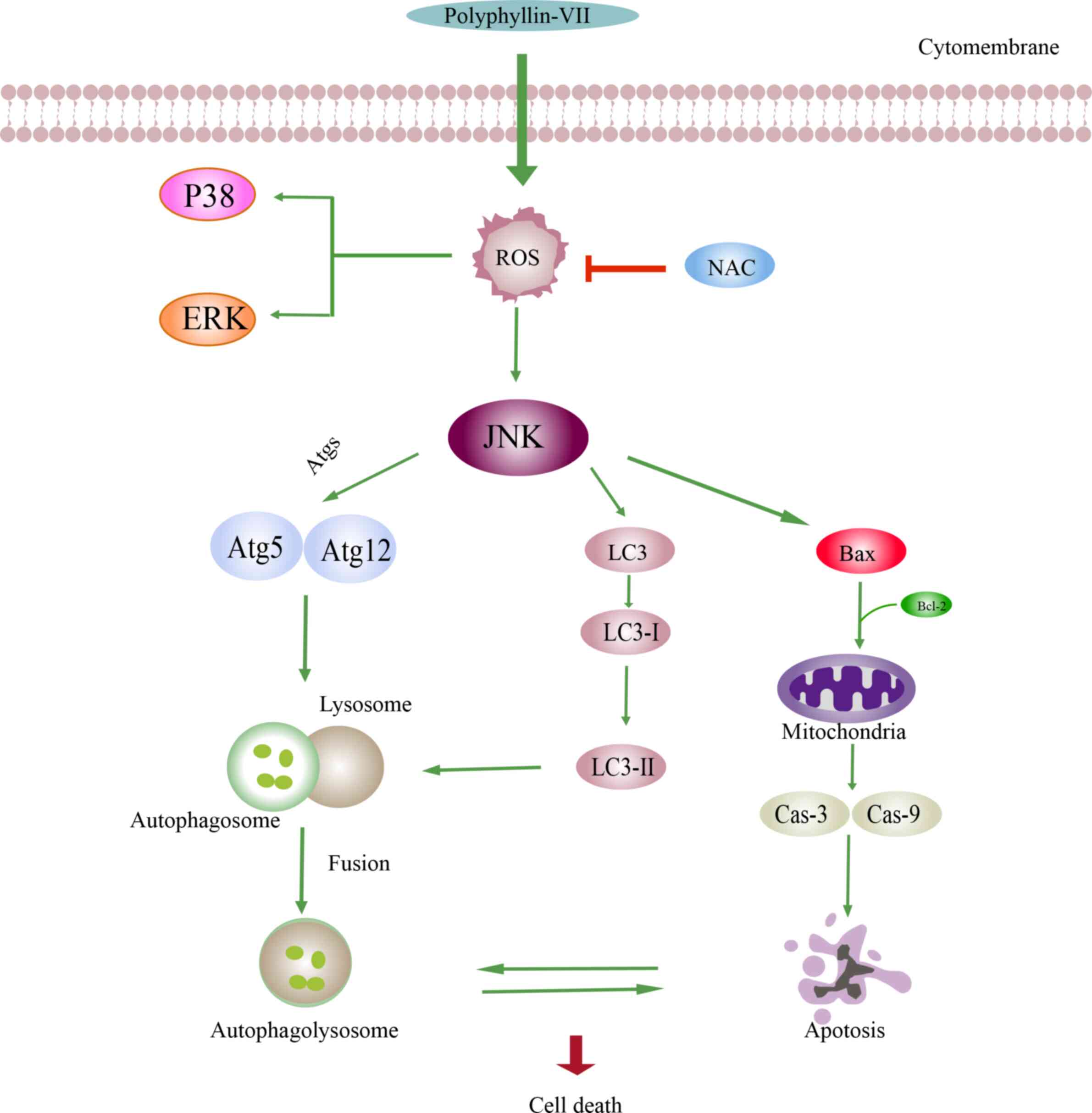
|
1
|
Whelan JS and Davis LE: Osteosarcoma,
chondrosarcoma, and chordoma. J Clin Oncol. 36:188–193. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Harrison DJ, Geller DS, Gill JD, Lewis VO
and Gorlick R: Current and future therapeutic approaches for
osteosarcoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 18:39–50. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Burgess DJ: Apoptosis: Refined and lethal.
Nat Rev Cancer. 13:792013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li Z, Dong H, Li M, Wu Y, Liu Y, Zhao Y,
Chen X and Ma M: Honokiol induces autophagy and apoptosis of
osteosarcoma through PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
17:2719–2723. 2018.
|
|
5
|
Li Y, Zhu H, Zeng X, Fan J, Qian X, Wang
S, Wang Z, Sun Y, Wang X, Wang W and Ju D: Suppression of autophagy
enhanced growth inhibition and apoptosis of interferon-β in human
glioma cells. Mol Neurobiol. 47:1000–1010. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wong RW and Rabie AB: Effect of psoralen
on bone formation. J Orthop Res. 29:158–164. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang XD, Wang Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Han R,
Wu JC, Liang ZQ, Gu ZL, Han F, Fukunaga K and Qin ZH: p53 mediates
mitochondria dysfunction-triggered autophagy activation and cell
death in rat striatum. Autophagy. 5:339–350. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hsieh MJ, Yang SF, Hsieh YS, Chen TY and
Chiou HL: Autophagy inhibition enhances apoptosis induced by
dioscin in huh7 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:1345122012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Orrenius S: Reactive oxygen species in
mitochondria-mediated cell death. Drug Metab Rev. 39:443–455. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang C, Yang L, Wang XB, Wang JS, Geng
YD, Yang CS and Kong LY: Calyxin Y induces hydrogen
peroxide-dependent autophagy and apoptosis via JNK activation in
human non-small cell lung cancer NCI-H460 cells. Cancer Lett.
340:51–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Trachootham D, Alexandre J and Huang P:
Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: A radical
therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 8:579–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Torres M and Forman HJ: Redox signaling
and the MAP kinase pathways. Biofactors. 17:287–296. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
McClung JM, Judge AR, Powers SK and Yan Z:
p38 MAPK links oxidative stress to autophagy-related gene
expression in cachectic muscle wasting. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
298:C542–C549. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kamata H, Honda S, Maeda S, Chang L,
Hirata H and Karin M: Reactive oxygen species promote
TNFalpha-induced death and sustained JNK activation by inhibiting
MAP kinase phosphatases. Cell. 120:649–661. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Trejo-Solis C, Jimenez-Farfan D,
Rodriguez-Enriquez S, Fernandez-Valverde F, Cruz-Salgado A,
Ruiz-Azuara L and Sotelo J: Copper compound induces autophagy and
apoptosis of glioma cells by reactive oxygen species and JNK
activation. BMC Cancer. 12:1562012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wong CH, Iskandar KB, Yadav SK, Hirpara
JL, Loh T and Pervaiz S: Simultaneous induction of non-canonical
autophagy and apoptosis in cancer cells by ROS-dependent ERK and
JNK activation. PLoS One. 5:e99962010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang W, Zhang D, Ma X, Liu Z, Li F and Wu
D: Paris saponin VII suppressed the growth of human cervical cancer
Hela cells. Eur J Med Res. 19:412014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Sun Y, Fan L, Zhang F, Meng J, Han
J, Guo X, Zhang D, Zhang R, Yue Z and Mei Q: Paris saponin VII
inhibits growth of colorectal cancer cells through Ras signaling
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 88:150–157. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang C, Jia X, Bao J, Chen S, Wang K,
Zhang Y, Li P, Wan JB, Su H, Wang Y, et al: Polyphyllin VII induces
apoptosis in HepG2 cells through ROS-mediated mitochondrial
dysfunction and MAPK pathways. BMC Complement Altern Med.
16:582016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen JC, Hsieh MJ, Chen CJ, Lin JT, Lo YS,
Chuang YC, Chien SY and Chen MK: Polyphyllin G induce apoptosis and
autophagy in human nasopharyngeal cancer cells by modulation of AKT
and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in vitro and in vivo.
Oncotarget. 7:70276–70289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen S, Jin Z, Dai L, Wu H, Wang J, Wang
L, Zhou Z, Yang L and Gao W: Aloperine induces apoptosis and
inhibits invasion in MG-63 and U2OS human osteosarcoma cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 97:45–52. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li AX, Sun M and Li X: Withaferin-A
induces apoptosis in osteosarcoma U2OS cell line via generation of
ROS and disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 21:1368–1374. 2017.
|
|
23
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X
and Wang X: Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during
apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 15:269–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu C, Gong K, Mao X and Li W: Tetrandrine
induces apoptosis by activating reactive oxygen species and
repressing Akt activity in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 129:1519–1531. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
He DX, Li GH, Gu XT, Zhang L, Mao AQ, Wei
J, Liu DQ, Shi GY and Ma X: A new agent developed by
biotransformation of Polyphyllin VII inhibits chemoresistance in
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 7:31814–31824. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang X, Qi H, Wang Q, Zhu Y, Wang X, Jin
M, Tan Q, Huang Q, Xu W, Li X, et al: FGFR3/fibroblast growth
factor receptor 3 inhibits autophagy through decreasing the
ATG12-ATG5 conjugate, leading to the delay of cartilage development
in achondroplasia. Autophagy. 11:1998–2013. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Fan X, Han S, Yan D, Gao Y, Wei Y, Liu X,
Liao Y, Guo H and Sun S: Foot-and-mouth disease virus infection
suppresses autophagy and NF-κB antiviral responses via degradation
of ATG5-ATG12 by 3Cpro. Cell Death Dis. 8:e25612017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Scherz-Shouval R, Shvets E, Fass E, Shorer
H, Gil L and Elazar Z: Reactive oxygen species are essential for
autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J.
26:1749–1760. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Czabotar PE, Lessene G, Strasser A and
Adams JM: Control of apoptosis by the BCL-2 protein family:
Implications for physiology and therapy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
15:49–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang C, Jia X, Wang K, Bao J, Li P, Chen
M, Wan JB, Su H, Mei Z and He C: Polyphyllin VII induces an
autophagic cell death by activation of the JNK pathway and
inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in HepG2 cells. PLoS One.
11:e01474052016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lin Z, Liu Y, Li F, Wu J, Zhang G, Wang Y,
Lu L and Liu Z: Anti-lung cancer effects of polyphyllin VI and VII
potentially correlate with apoptosis in vitro and in vivo.
Phytother Res. 29:1568–1576. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim AD, Kang KA, Kim HS, Kim DH, Choi YH,
Lee SJ, Kim HS and Hyun JW: A ginseng metabolite, compound K,
induces autophagy and apoptosis via generation of reactive oxygen
species and activation of JNK in human colon cancer cells. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e7502013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hsieh MJ, Tsai TL, Hsieh YS, Wang CJ and
Chiou HL: Dioscin-induced autophagy mitigates cell apoptosis
through modulation of PI3K/Akt and ERK and JNK signaling pathways
in human lung cancer cell lines. Arch Toxicol. 87:1927–1937. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ko CP, Lin CW, Chen MK, Yang SF, Chiou HL
and Hsieh MJ: Pterostilbene induce autophagy on human oral cancer
cells through modulation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein
kinase pathway. Oral Oncol. 51:593–601. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Kim A, Yim NH and Ma JY: Samsoeum, a
traditional herbal medicine, elicits apoptotic and autophagic cell
death by inhibiting Akt/mTOR and activating the JNK pathway in
cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 13:2332013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Morales J, Li L, Fattah FJ, Dong Y, Bey
EA, Patel M, Gao J and Boothman DA: Review of poly (ADP-ribose)
polymerase (PARP) mechanisms of action and rationale for targeting
in cancer and other diseases. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr.
24:15–28. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Luo Q, Yuan L, Miao C, Mu X, Xiao W,
Li J, Sun T and Ma E: JNK-dependent Atg4 upregulation mediates
asperphenamate derivative BBP-induced autophagy in MCF-7 cells.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 263:21–31. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Gong K, Chen C, Zhan Y, Chen Y, Huang Z
and Li W: Autophagy-related gene 7 (ATG7) and reactive oxygen
species/extracellular signal-regulated kinase regulate
tetrandrine-induced autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Biol Chem. 287:35576–35588. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hileman EO, Liu J, Albitar M, Keating MJ
and Huang P: Intrinsic oxidative stress in cancer cells: A
biochemical basis for therapeutic selectivity. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 53:209–219. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Donadelli M, Dando I, Zaniboni T, Costanzo
C, Dalla Pozza E, Scupoli MT, Scarpa A, Zappavigna S, Marra M,
Abbruzzese A, et al: Gemcitabine/cannabinoid combination triggers
autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells through a ROS-mediated
mechanism. Cell Death Dis. 2:e1522011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chang L and Karin M: Mammalian MAP kinase
signalling cascades. Nature. 410:37–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sato A, Okada M, Shibuya K, Watanabe E,
Seino S, Narita Y, Shibui S, Kayama T and Kitanaka C: Pivotal role
for ROS activation of p38 MAPK in the control of differentiation
and tumor-initiating capacity of glioma-initiating cells. Stem Cell
Res. 12:119–131. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Xu J, Qin X, Cai X, Yang L, Xing Y, Li J,
Zhang L, Tang Y, Liu J, Zhang X and Gao F: Mitochondrial JNK
activation triggers autophagy and apoptosis and aggravates
myocardial injury following ischemia/reperfusion. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1852:262–270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|