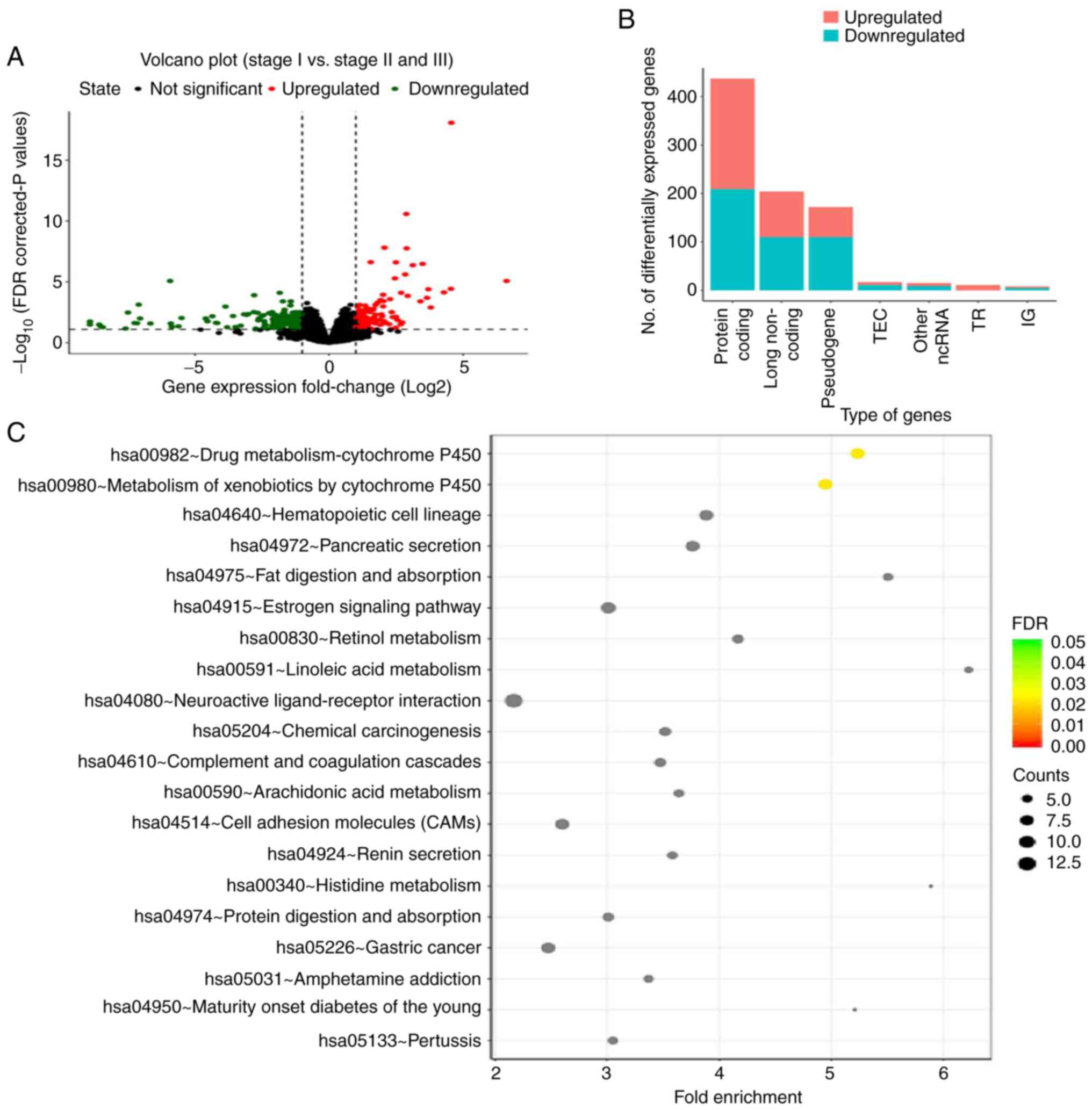
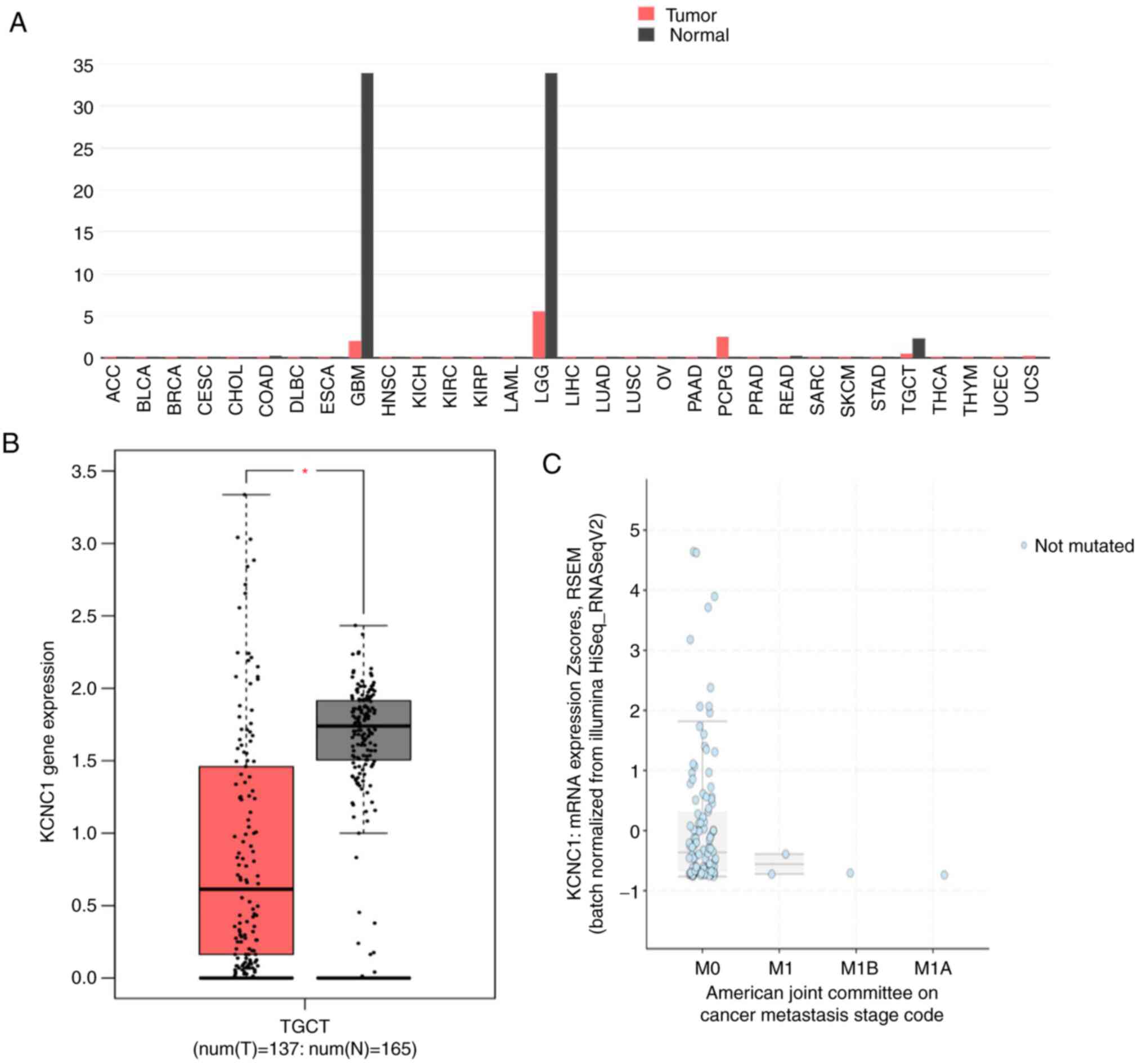
|
1
|
Gonzalez-Exposito R, Merino M and Aguayo
C: Molecular biology of testicular germ cell tumors. Clin Transl
Oncol. 18:550–556. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
di Pietro A, de Vries EG, Gietema JA,
Spierings DC and de Jong S: Testicular germ cell tumours: The
paradigm of chemo-sensitive solid tumours. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
37:2437–2456. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meyts ER, McGlynn KA, Okamoto K, Jewett MA
and Bokemeyer C: Testicular germ cell tumours. Lancet.
387:1762–1774. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chaganti RS and Houldsworth J: Genetics
and biology of adult human male germ cell tumors. Cancer Res.
60:1475–1482. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jørgensen N, Meyts ER, Graem N, Müller J,
Giwercman A and Skakkebaek NE: Expression of immunohistochemical
markers for testicular carcinoma in situ by normal human fetal germ
cells. Lab Invest. 72:223–231. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Richie JP: Re: Management of seminomatous
testicular cancer: A binational prospective population-based study
from the Swedish norwegian testicular cancer study group. J Urol.
186:2255–2256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chung PW, Gospodarowicz MK, Panzarella T,
Jewett MA, Sturgeon JF, Tew-George B, Bayley AJ, Catton CN,
Milosevic MF, Moore M and Warde PR: Stage II testicular seminoma:
Patterns of recurrence and outcome of treatment. Eur Urol.
45:754–759; discussion 759-60. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fankhauser CD, Curioni-Fontecedro A,
Allmann V, Beyer J, Tischler V, Sulser T, Moch H and Bode PK:
Frequent PD-L1 expression in testicular germ cell tumors. Br J
Cancer. 113:411–413. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yamada Y, Takayama KI, Fujimura T,
Ashikari D, Obinata D, Takahashi S, Ikeda K, Kakutani S, Urano T,
Fukuhara H, et al: A novel prognostic factor TRIM44 promotes cell
proliferation and migration, and inhibits apoptosis in testicular
germ cell tumor. Cancer Sci. 108:32–41. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Costello JF and Plass C: Methylation
matters. J Med Genet. 38:285–303. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Beta M, Chitipothu S, Khetan V, Biswas J
and Krishnakumar S: Hypermethylation of adenomatosis polyposis
coli-2 and its tumor suppressor role in retinoblastoma. Curr Eye
Res. 40:719–728. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ohtani-Fujita N, Dryja TP, Rapaport JM,
Fujita T, Matsumura S, Ozasa K, Watanabe Y, Hayashi K, Maeda K,
Kinoshita S, et al: Hypermethylation in the retinoblastoma gene is
associated with unilateral, sporadic retinoblastoma. Cancer Genet
Cytogenet. 98:43–49. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Perney TM, Marshall J, Martin KA,
Hockfield S and Kaczmarek LK: Expression of the mRNAs for the Kv3.1
potassium channel gene in the adult and developing rat brain. J
Neurophysiol. 68:756–766. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stegen B, Klumpp L, Misovic M, Edalat L,
Eckert M, Klumpp D, Ruth P and Huber SM: K(+) channel signaling in
irradiated tumor cells. Eur Biophys J. 45:585–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Edalat L, Stegen B, Klumpp L, Haehl E,
Schilbach K, Lukowski R, Kühnle M, Bernhardt G, Buschauer A, Zips
D, et al: BK K+ channel blockade inhibits radiation-induced
migration/brain infiltration of glioblastoma cells. Oncotarget.
7:14259–14278. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ouadid-Ahidouch H and Ahidouch A: K+
channel expression in human breast cancer cells: involvement in
cell cycle regulation and carcinogenesis. J Membr Biol. 221:1–6.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen BF, Gu S, Suen YK, Li L and Chan WY:
MicroRNA-199a-3p, DNMT3A, and aberrant DNA methylation in
testicular cancer. Epigenetics. 9:119–128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu X, Duan H, Zhou S, Liu Z, Wu D, Zhao
T, Xu S, Yang L and Li D: MicroRNA-199a-3p functions as tumor
suppressor by regulating glucose metabolism in testicular germ cell
tumors. Mol Med Rep. 14:2311–2320. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li R, Qu H, Wang S, Wei J, Zhang L, Ma R,
Lu J, Zhu J, Zhong WD and Jia Z: GDCRNATools: An R/Bioconductor
package for integrative analysis of lncRNA, miRNA and mRNA data in
GDC. Bioinformatics. 34:2515–2517. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hoadley KA, Yau C, Wolf DM, Cherniack AD,
Tamborero D, Ng S, Leiserson MD, Niu B, McLellan MD, Uzunangelov V,
et al: Multiplatform analysis of 12 cancer types reveals molecular
classification within and across tissues of origin. Cell.
158:929–944. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Silva TC, Coetzee SG, Gull N, Yao L,
Hazelett DJ, Noushmehr H, Lin DC and Berman BP: ELMER v.2: An
R/Bioconductor package to reconstruct gene regulatory networks from
DNA methylation and transcriptome profiles. Bioinformatics.
35:1974–1977. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:W98–W102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schulz M, Salamero-Boix A, Niesel K,
Alekseeva T and Sevenich L: Microenvironmental regulation of tumor
progression and therapeutic response in brain metastasis. Front
Immunol. 10:17132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
De Palma M, Biziato D and Petrova TV:
Microenvironmental regulation of tumour angiogenesis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 17:457–474. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ehnman M and Larsson O: Microenvironmental
targets in sarcoma. Front Oncol. 5:2482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rudy B and McBain CJ: Kv3 channels:
Voltage-Gated K+ channels designed for high-frequency repetitive
firing. Trends Neurosci. 24:517–526. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lang F and Stournaras C: Ion channels in
cancer: Future perspectives and clinical potential. Philos Trans R
Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 369:201301082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|