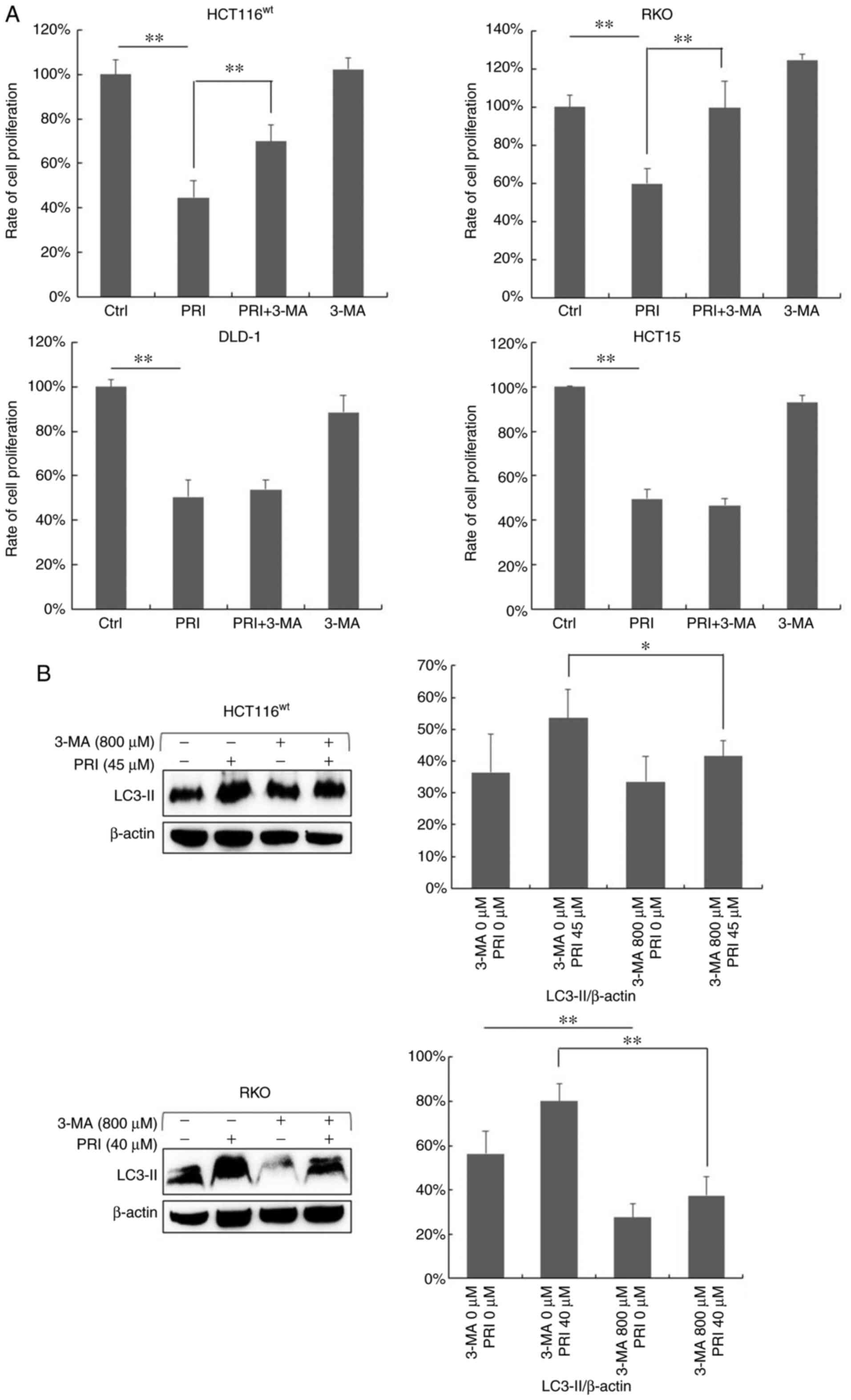
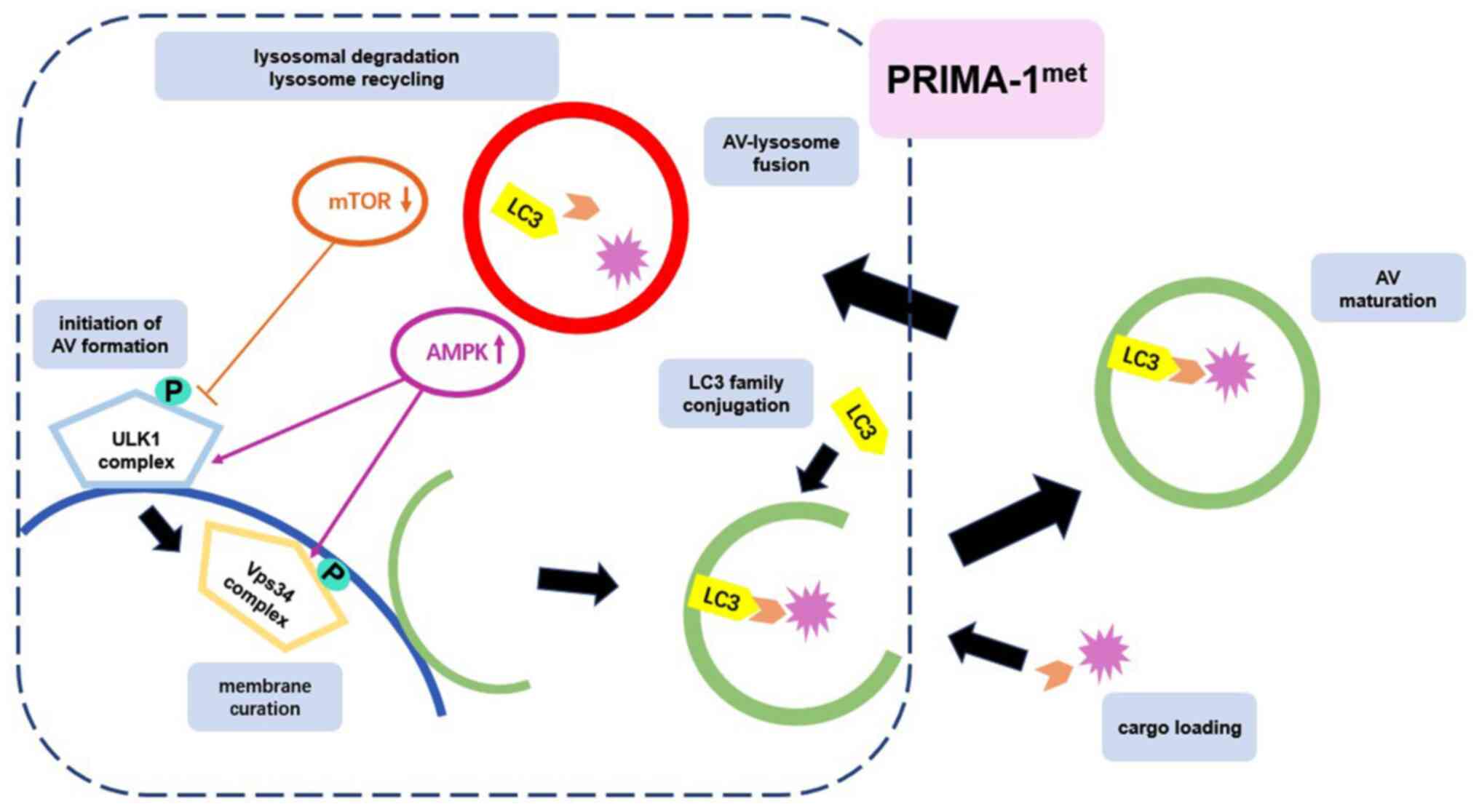
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kyaw M and Sung JJ: Young-onset colorectal
cancer in the Asia-Pacific region. Med J Aust. 205:450–451. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brenner H, Kloor M and Pox CP: Colorectal
cancer. Lancet. 383:1490–1502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ryan KM, Phillips AC and Vousden KH:
Regulation and function of the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 13:332–337. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bieging KT, Mello SS and Attardi LD:
Unravelling mechanisms of p53-mediated tumour suppression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:359–370. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takayama T, Miyanishi K, Hayashi T, Sato Y
and Niitsu Y: Colorectal cancer: Genetics of development and
metastasis. J Gastroenterol. 41:185–192. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li XL, Zhou J, Chen ZR and Chng WJ: P53
mutations in colorectal cancer-molecular pathogenesis and
pharmacological reactivation. World J Gastroenterol. 21:84–93.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lambert JM, Moshfegh A, Hainaut P, Wiman
KG and Bykov VJ: Mutant p53 reactivation by PRIMA-1MET induces
multiple signaling pathways converging on apoptosis. Oncogene.
29:1329–1338. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yoshikawa N, Kajiyama H, Nakamura K,
Utsumi F, Niimi K, Mitsui H, Sekiya R, Suzuki S, Shibata K, Callen
D and Kikkawa F: PRIMA-1MET induces apoptosis through accumulation
of intracellular reactive oxygen species irrespective of p53 status
and chemo-sensitivity in epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Oncol
Rep. 35:2543–2552. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu T, Zou Y, Xu G, Potter JA, Taylor GL,
Duan Q, Yang Q, Xiong H, Qiu H, Ye D, et al: PRIMA-1Met suppresses
colorectal cancer independent of p53 by targeting MEK. Oncotarget.
7:83017–83030. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sobhani M, Abdi J, Manujendra SN, Chen C
and Chang H: PRIMA-1Met induces apoptosis in Waldenstrom's
Macroglobulinemia cells independent of p53. Cancer Biol Ther.
16:799–806. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tessoulin B, Descamps G, Moreau P, Maïga
S, Lodé L, Godon C, Marionneau-Lambot S, Oullier T, Le Gouill S,
Amiot M and Pellat-Deceunynck C: PRIMA-1Met induces myeloma cell
death independent of p53 by impairing the GSH/ROS balance. Blood.
124:1626–1636. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li XL, Zhou J, Chan ZL, Chooi JY, Chen ZR
and Chng WJ: PRIMA-1met (APR-246) inhibits growth of colorectal
cancer cells with different p53 status through distinct mechanisms.
Oncotarget. 6:36689–36699. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
White E, Mehnert JM and Chan CS:
Autophagy, metabolism, and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:5037–5046.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K,
Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H and Levine B: Induction of autophagy and
inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature. 402:672–676. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Aita VM, Liang XH, Murty VV, Pincus DL, Yu
W, Cayanis E, Kalachikov S, Gilliam TC and Levine B: Cloning and
genomic organization of beclin 1, a candidate tumor suppressor gene
on chromosome 17q21. Genomics. 59:59–65. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Karantza-Wadsworth V, Patel S, Kravchuk O,
Chen G, Mathew R, Jin S and White E: Autophagy mitigates metabolic
stress and genome damage in mammary tumorigenesis. Genes Dev.
21:1621–1635. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang KK, Ramnarayanan K, Zhu F,
Srivastava S, Xu C, Tan ALK, Lee M, Tay S, Das K, Xing M, et al:
Genomic and epigenomic profiling of high-risk intestinal metaplasia
reveals molecular determinants of progression to gastric cancer.
Cancer Cell. 33:137–150.e5. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Amaravadi RK, Kimmelman AC and Debnath J:
Targeting autophagy in cancer: Recent advances and future
directions. Cancer Discov. 9:1167–1181. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hardie DG: The AMP-activated protein
kinase pathway-new players upstream and downstream. J Cell Sci.
117((Pt 23)): 5479–5487. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kumar S, Gu Y, Abudu YP, Bruun JA, Jain A,
Farzam F, Mudd M, Anonsen JH, Rusten TE, Kasof G, et al:
Phosphorylation of Syntaxin 17 by TBK1 controls autophagy
initiation. Dev Cell. 49:130–144.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP and Harper
JW: Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature.
466:68–76. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou F, Yang Y and Xing D: Bcl-2 and
Bcl-xL play important roles in the crosstalk between autophagy and
apoptosis. FEBS J. 278:403–413. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang J, Cui D, Gu S, Chen X, Bi Y, Xiong X
and Zhao Y: Autophagy regulates apoptosis by targeting NOXA for
degradation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1865:1105–1113.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|